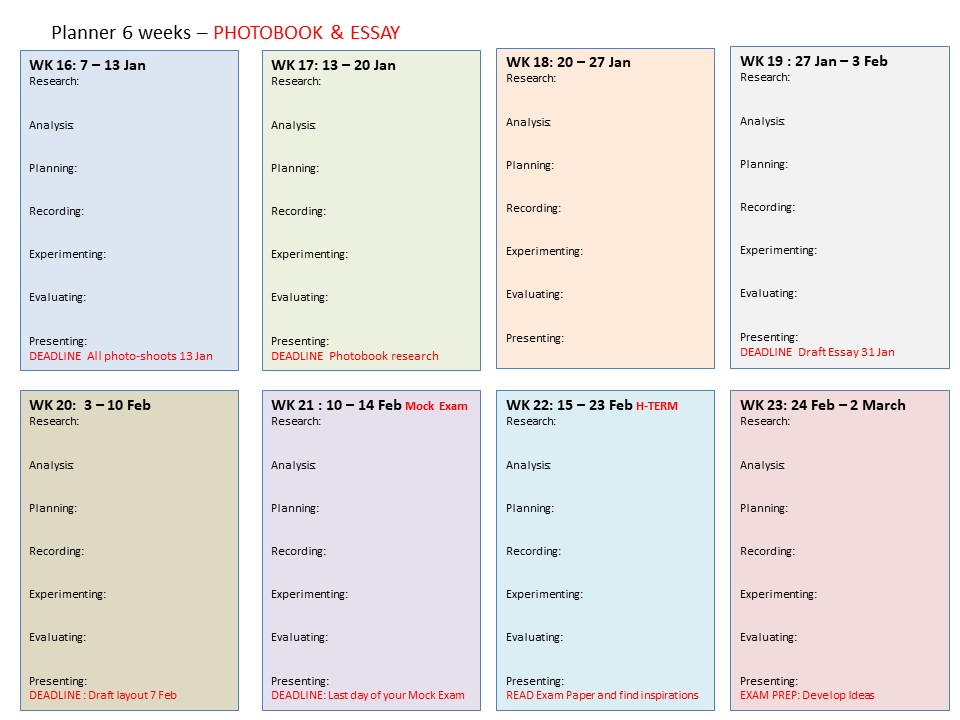
DEADLINE: DRAFT ESSAY 31 JAN 2020. Week 16 – 17 – 18 – 19
WE ONLY HAVE 4 WEEKS LEFT TO COMPLETE A DRAFT of your ESSAY
PLANNER – Download and save in your folder. Make sure you monitor and track your progress
6 weeks remaining – including MOCK EXAM!
ESSAY: We will be spending 1 lesson a week every Wednesday on writing and developing your essay. However, you will need to be working on it independently outside of lesson time.
Objective: Criteria from the Syllabus
- Be aware of some of the methods employed by critics and historians within the history of art and photography.
- Demonstrate a sound understanding of your chosen area of study with appropriate use of critical vocabulary. – use for image analysis
- Investigate a wide range of work and sources
- Develop a personal and critical inquiry.
Academic Sources:
- Research and identify 3-5 literary sources from a variety of media such as books, journal/magazines, internet, Youtube/video .
- Begin to read essay, texts and interviews with your chosen artists as well as commentary from critics, historians and others.
- It’s important that you show evidence of reading and draw upon different pints of view – not only your own.
- Take notes when you’re reading…key words, concepts, passages
- Write down page number, author, year, title, publisher, place of publication so you can list source in a bibliography
Quotation and Referencing:
- Use quotes to support or disprove your argument
- Use quotes to show evidence of reading
- Use Harvard System of Referencing…see Powerpoint: harvard system of referencing for further details on how to use it.
Essay Plan:
Make a plan that lists what you are going to write about in each paragraph – essay structure.
- Essay question:
- Opening quote
- Introduction (250-500 words): What is your area study? Which artists will you be analysing and why? How will you be responding to their work and essay question?
- Pg 1 (500 words): Historical/ theoretical context within art, photography and visual culture relevant to your area of study. Make links to art movements/ isms and some of the methods employed by critics and historian. Link to powerpoints about isms andmovements M:\Departments\Photography\Students\Resources\Personal Study
- Pg 2 (500 words): Analyse first artist/photographer in relation to your essay question. Present and evaluate your own images and responses.
- Pg 3 (500 words): Analyse second artist/photographer in relation to your essay question. Present and evaluate your own images and responses.
- Conclusion (250-500 words): Draw parallels, explore differences/ similarities between artists/photographers and that of your own work that you have produced
- Bibliography: List all relevant sources used
Essay question: Hypothesis
Think of a hypothesis and list possible essay questions
Here is a list of possible questions to investigate that may help you.
Opening quote: Choose a quote from either one of your photographers or critics. It has to be something that relates to your investigation
ESSAY STRUCTURE
See below for a possible essay structure. Further help can be found here essay structure or see link here The Royal Literay Fund
Introduction (250-500 words). Think about an opening that will draw your reader in e.g. you can use an opening quote that sets the scene. You should include in your introduction an outline of your intention of your study e.g. what and who are you going to investigate. How does this area/ work interest you? What are you trying to prove/challenge, argument/ counter-argument? What historical or theoretical context is the work situated within. Include 1 or 2 quotes for or against. What links are there with your previous studies? What have you explored so far in your Coursework or what are you going to photograph? How did or will your work develop. What camera skills, techniques or digital processes in Photoshop have or are you going to experiment with?
Paragraph 1 Structure (500 words) : Use subheading. This paragraph covers the first thing you said in your introduction that you would address. The first sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Other sentences develop the subject of the paragraph.
Content: you could look at the following…exemplify your hypothesis within a historical and theoretical context. Write about how your area of study and own work is linked to a specific art movement/ ism. Research and read key text and articles from critics, historians and artists associated with the movement/ism. Use quotes from sources to make a point, back it up with evidence or an example (a photograph), explain how the image supports the point made or how your interpretation of the work may disapprove. How does the photograph compare or contrast with others made by the same photographer, or to other images made in the same period or of the same genre by other artists. How does the photograph relate to visual representation in general, and in particularly to the history and theory of photography, arts and culture.
Include relevant examples, illustrations, details, quotations, and references showing evidence of reading, knowledge and understanding of history, theory and context!
See link to powerpoints: Pictorialism vs Realism and Modernism vs Postmodernism here: M:\Departments\Photography\Students\Occupation vs Liberation\Presentations
Paragraph 2 Structure (500 words) : Use subheading. In the first sentence or opening sentences, link the paragraph to the previous paragraph, then introduce the main idea of the new paragraph. Other sentences develop the paragraphs subject (use relevant examples, quotations, visuals to illustrate your analysis, thoughts etc)
Content: you could look at the following...Introduce your first photographer. Select key images, ideas or concepts and analyse in-depth using specific model of analysis (describe, interpret and evaluate) – refer to your hypothesis. Contextualise…what was going on in the world at the time; artistically, politically, socially, culturally. Other influences…artists, teachers, mentors etc. Personal situations or circumstances…describe key events in the artist’s life that may have influenced the work. Include examples of your own photographs, experiments or early responses and analyse, relate and link to the above. Set the scene for next paragraph.
Include relevant examples, illustrations, details, quotations, and references showing evidence of reading, knowledge and understanding of history, theory and context!
Paragraph 3 Structure (500 words) : Use subheading. In the first sentence or opening sentences, link the paragraph to the previous paragraph, then introduce the main idea of the new paragraph. Other sentences develop the paragraphs subject (use relevant examples, quotations, visuals to illustrate your analysis, thoughts etc)
Content: you could look at the following…Introduce key works, ideas or concepts from your second photographer and analyse in-depth – refer to your hypothesis…Use questions in Pg 2 or add…What information has been selected by the photographer and what do you find interesting in the photograph? What do we know about the photograph’s subject? Does the photograph have an emotional or physical impact? What did the photographer intend? How has the image been used? What are the links or connections to the other photographer in Pg 2? Include examples of your own photographs and experiments as your work develop in response to the above and analyse, compare, contrast etc. Set the scene for next paragraph.
Include relevant examples, illustrations, details, quotations, and references showing evidence of reading, knowledge and understanding of history, theory and context!
Conclusion (500 words) : Write a conclusion of your essay that also includes an evaluation of your final photographic responses and experiments.
List the key points from your investigation and analysis of the photographer(s) work – refer to your hypothesis. Can you prove or Disprove your theory – include final quote(s). Has anything been left unanswered? Do not make it a tribute! Do not introduce new material! Summarise what you have learned. How have you been influenced? Show how you have selected your final outcomes including an evaluation and how your work changed and developed alongside your investigation.
Bibliography: List all the sources that you used and only those that you have cited in your text. Where there are two or more works by one author in the same year distinguish them as 1988a, 1988b etc. Arrange literature in alphabetical order by author, or where no author is named, by the name of the museum or other organisation which produced the text. Apart from listing literature you must also list all other sources in alphabetical order e.g. websites, exhibitions, Youtube/TV/ Videos / DVD/ Music etc.