| What do you know about | What meanings or understandings do you have of their ideas? How can you apply their ideas to the CSPs? | |
| Noam Chomsky | The 5 filters of mass media – Structures of ownership, role of advertising, links with “The Establishment”, Diversionary tactics and Uniting against a “Common Enemy” | Newspapers such as “Daily Mail” or “The i” ‘use’ these filters for profit – the motive of media – i.e. The Daily Mail will make powerful people look good in their newspapers. |
| James Curran | “Media enables viewers to plug into different views and different perspectives” “The professional media sector occupies a space wholly independent on the state and the market”. Wrote a book about how the media landscape has fallen under the control of a handful of global media conglomerates whose main goals are profit and reflects on contemporary concerns relating to digital media. | The Daily Mail and The i are both owned by the Daily Mail General Trust despite the newspapers having differing views (The i is more left wing/neutral and the Daily Mail is more right wing) This shows that the DMGT are gaining profit from both left wing and right wing audiences. |
| Habermas | The public sphere | With the rise of newspapers it introduced widely available information that wasnt available before. Which people could either agree or disagree with, and this created an arena of public debate. |
Category Archives: Uncategorized
Filters
| What do you know about? | What meaning or understanding do you have to their ideas, how can you apply to CSP? | |
| Noam Chomsky | -Five filters of the mass media machine -Structure of ownership, the role of advertising, links with the establishment, divisionary tactics, uniting against a comment enemy. | -Chomsky explains how propaganda and systemic biases function in corporate mass media. The model seeks to explain how populations are manipulated and how consent for economic, social, and political policies, both foreign and domestic, is “manufactured” in the public mind due to this propaganda. -Using the 5 filters; >1: Mass media conglomerates owning multiple newspaper brands via vertical or horizontal integration >2: Advertisement supposedly selling us a product in reality we are the product, adverts buy our attention. 3>: Media distributors are in debt with those in power so majority write for them. >4: Those that go against will be discredited or pushed to the margins. >5: |
| James Curren | Distribution and media regulation. | |
| Habermas | Created the theory of the public sphere. | -The theory that the public sphere which was public debates and discussions about many diversing ideaologies turned into a priavte sphere where people believe false news or everything tyhey read failing to understand |
| David Gauntlet | fluidity of identity: constructed identity- changed and altered throughout experienced collective- specific groups such as ethnicity. negotiated identity- fluidity- an identity that has the potential to be changed and shaped frequently in many directions. | |
| Lasswell | Passive consumption model, (who, says what, through what channel, to whom, with what effect) Adapted by Shannon and Weaver adapted adding, noise, feedback, communication. | To apply it to the passive people to get more attention from viewers who won’t think about what they’re buying. Who: Hearth CFO Men’s health. Says what: see media pack Channel: online, print, socials. To whom: active men who persue a healthy lifestyle. Why: To sell magazines |
| Lazarfield | filtered through influential opinion leaders who interpret a message and first and then relay them back to the mass audiences. Step Flow Model. | |
| Uses and Gratification | -information / education -empathy and identity -social interaction -entertainment -escapism | |
| Staurt hall | -active consumption -“Reconstruction Work: Images of Postwar Black Settlement”, – | For Hall, culture was not something to simply appreciate or study, but a “critical site of social action and intervention, where power relations are both established and potentially unsettled” Page 94 95, dominant: the men want to be fit and active and to gain muscle and agree these foods are the best to bulk — nothing has a representation until the media represents it to try and create a fixed meaning to which the audience can argue against; for example people being perceived as trouble makers from repeated stereotypes of them represented in the media to which using Hall’s receptive theory we can go the three ways, eg.. negotiated |
| George Gerbner | television programming and how these changes affect viewers’ perceptions of society. mean world syndrome to describe the fact that people who watch large amounts of television are more likely to perceive the world as a dangerous and frightening place.[8] | Mainstreaming: the excessive consumption of media products the more you will conform to the medias ideologies,,, eg. mens health- no other than Christianism presented, mostly men, mostly white, mostly middle aged, abled body people. Shirkley: disagrees by saying modern day has the end of the audience theory- society have become more active and fragmented as apposed to passive consumption of what the media puts out. |
revison
| what do you know about | what meaning or understandings do you have of their ideas? How can you apply their ideas to the CSPs | |
| Noam Chomsky | He published a book called ‘the manufacture of consent’. He came up with the theory called ‘propaganda theory’ | Chomsky’s theory can be applied to the newspaper for rules and regulation. Their a 5 filters of mass media,1: Structures of ownership is a part of bigger conglomerates with an endgame profit. part 2: To earn money by profiting of the product. 3: |
| James curren | Published a book about the liberal free press and he writes about diversity of ownership, participation, representation and consumption . The three key questions about the relationship between media and society “how much power do the media have” “what is the relationship between media and power in society” “who really controls the media” | |
| Jean Seaton | ||
| Jurgen Habermas | Habermas came up with the public sphere. In its ideal form, the public sphere is the arena where citizens come together, exchange opinions regarding public affairs, discuss and deliberate ideas | |
| Semiotics | sign code convention dominant signifier anchorage | Pierce Bathes |
| Representation | ||
| Audience | is a key topic, lots of different people and terms to know, like: Stuart hall Laswell Lazarfeld | |
| Feminist critical thinking | ||
| postcolonialism | ||
| narrative theories | ||
| genre | ||
| key terms for industry and business | ||
| PSB public service broadcasting | ||
| C.S. pierce | symbolic signs indexical signs iconic signs | |
command words
Describe: To say or write what someone or something is like without explaining why.
Compare: Finding a difference between two things through similarities and differences.
Evaluate: Describe the benefits and or drawbacks of ideas with an explanation of why with the backup of evidence.
Analyse: Explain in close detail to achieve an accurate representation of something.
Knowledge: Vague outline of an idea or concept.
Understanding: To be able to apply knowledge to different situations as you have deeper knowledge about the idea or concept.
COMMAND WORDS
Command words:
Describe: To say or write what someone or something is like without explaining why.
Compare: Finding a difference between two things through similarities and differences.
Evaluate: Describe the benefits and or drawbacks of ideas with an explanation of why with the backup of evidence.
Analyse: Explain in close detail to achieve an accurate representation of something.
Knowledge: Vague outline of an idea or concept.
Understanding: To be able to apply knowledge to different situations as you have deeper knowledge about the idea or concept.
revision table


command words
describe – remembering specific elements
compare – talking about the similarities and differences between two things
evaluate – to judge and share own opinions/ real evidence
analyse – in depth look at an idea with accurate explanation
knowledge – vague outline of an idea or concept / can touch on it
understanding – to explain clearly and deeply about an idea or concept / can evaluate it
| what do you know about | What meanings or understandings do you have of their ideas? In another way how can you apply those ideas to your CSPS? | |
| Noam Chomsky | the five filters of media | ownership- having control over a platform and what comes out of it is down to you. Advertising- sharing media with everyone for personal gain for example bossed life advertising is fun and bright to attract audiences to buy the product. official source-having the correct data statistics and facts to back up what you’re saying like the daily mail and the I |
| James curran | power in media industries | Curran has released a book called power without responsibility which suggests that people with power within the media industry use that to their advantage to use and take advantage of people in an unfair and unjust way. this is made possible due to the lack of responsibility being held against them for these actions which is why they abuse their power in this way. ghost town Margret thatcher abusing her power in a racial way |
| Habermas | public sphere the difference between communicative rationality and rationalization on one hand and strategic/instrumental rationality and rationalization on the other. | media is consumed passivly. If someone well known says something people will believe it and/or follow through with it like the government. The public are like sheep and will follow what anyone recognisable says. |
| david gauntlett | fluidity of identity collective identity constructive identity negotiated identity | everyone has the freedom to identify as what they want. He thinks “media doesn’t create identities” but reflects them. in terms of men’s health it suggests a negotiated identity as on the front cover vin diesel is stood boldly in the front then inside the magazine we see a softer sensitive side to him. |
| Laswell | Communication model. Who (sender) What (message) channel (medium) to whom (receiver) with what effect | Harold Laswell was a media theorist who studied the idea of communication. An example can be a dior mascara advertisment. Dior being the sender as the company producing this advert. What would be the anchorage giving a definition about the mascara. Medium is the type of media it is presented on, in this case it would be a magazine to anyone who reads the magazine but as its mascara we presume its in a woman’s magazine therefore targeted at woman with the effect of selling this product. I understand that the model shows the easy manipulation of those vulnerable and how easy it is to rope people in to buying thigs as the believes they’ll have a certain outcome out of it but in reality will not. |
| Lazerfeld | two step media theory information and influence. The theory was introduced in 1944 but elaborated in 1955 | Lazarfeld said was that if a well populated/known opinionated leader were to say something to the mass media a wider population would listen to it and possibly believe it and follow through with certain plans or statements. For example Margret Thatcher didn’t like dark skinned people being in England and wanted them gone and so she stated this to the general public and white British citizens sided with her which is shown in the specials and blinded by the light. Also with elections in order to know who to vote for political candidates put forward their ideas for the country which the public listen to. If the public like what they hear they will vote for that person. |
| uses and gratifications | a Mass Communication theory that focuses on the needs, motives and gratifications of media users. -escapism -understanding yourself -strengthen family/friendships -enjoyment -self confidence -knowledge about the world | the idea of media using peoples data to present them with things they may need. For example ESCAPISM- advertisements for a holiday to escape reality. Advertisers use these to understand their audience better, Like Facebook when we accept cookies we allow them to use our data which’ll then be used to give us adverts the they know well enjoy which ropes audiences in to look at a product which pays the advertisers or even potentially buy the product which will them show a high demand for the product and be shared to more users on media platforms like Facebook such as Instagram or twitter. |
| Stuart Hall | Hall’s work covers issues of hegemony and cultural studies. He regards language-use as operating within a framework of power, institutions and politics/economics. | everyone sees different things in different ways. Dominant negotiation oppositional |
| George Gerbner | Cultivation theory / behavioural psychology extended Laswell’s communication model consisting with a verbal aspect where someone observes an event and gives feedback about the situation, and a schematic model where someone perceives an event and sends messages to the sender | verbal feedback helps better a person when taken on board. Face to face rather than through a screen is considered top be verbal and the aftermath of constructive criticism shows how people take on board feedback. mainstreaming- the more mainstream TV/other media forms we watch the more dominant our ideas become and accepting dominant ideas are more likely due to a form of brainwashing. |
Clay Shirky argued audience behaviour has progressed from the passive consumption of media texts to a much more interactive experience with the products and each other. Therefore he disagrees with George Gerbner.
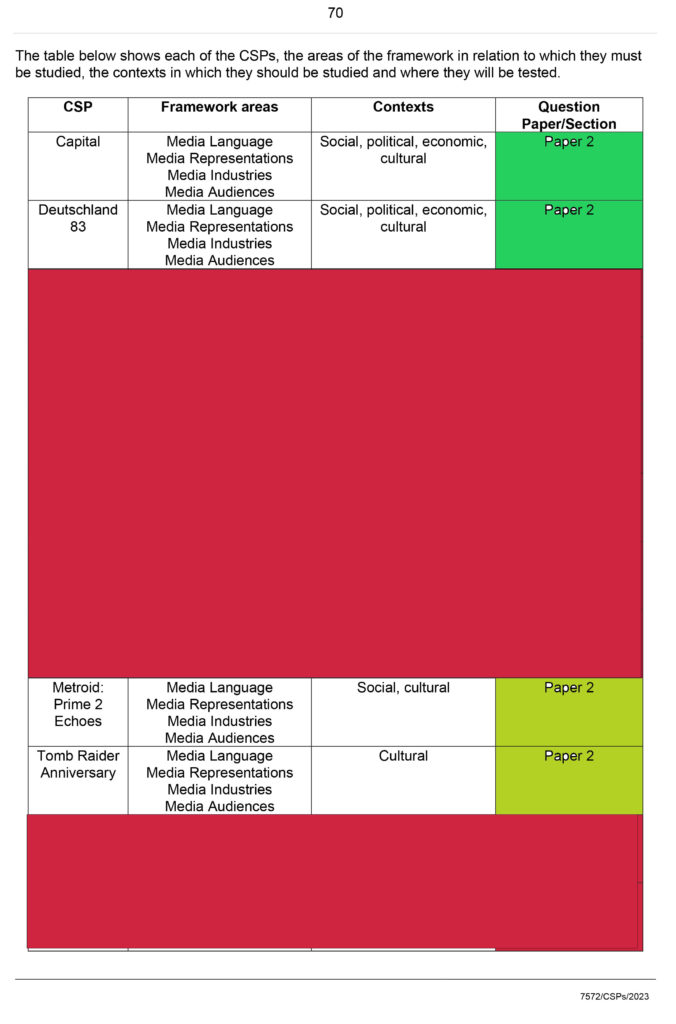
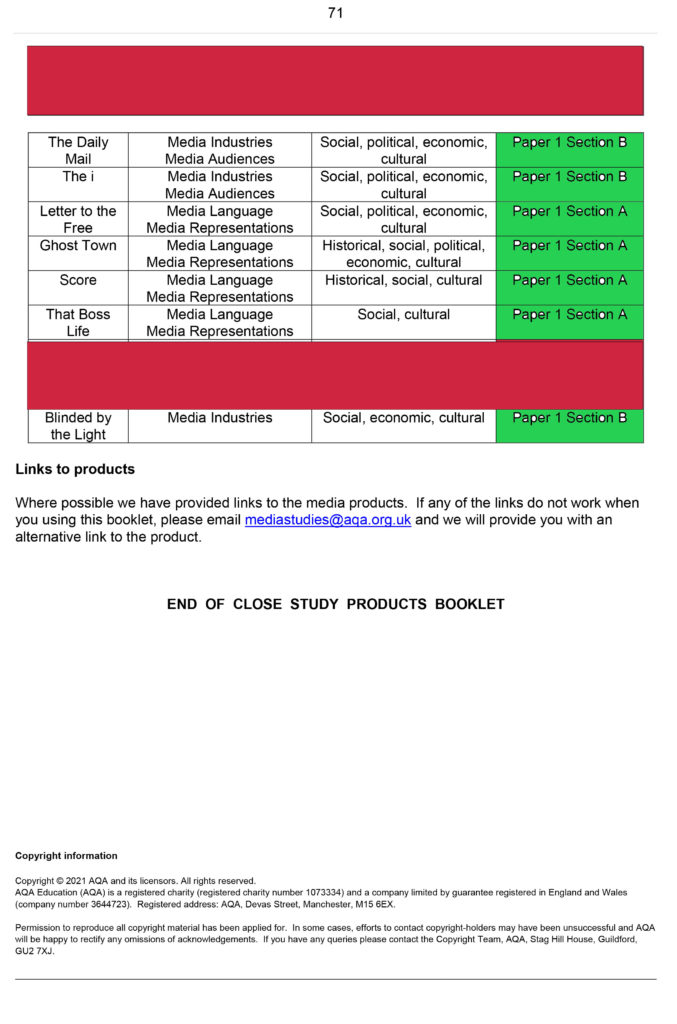
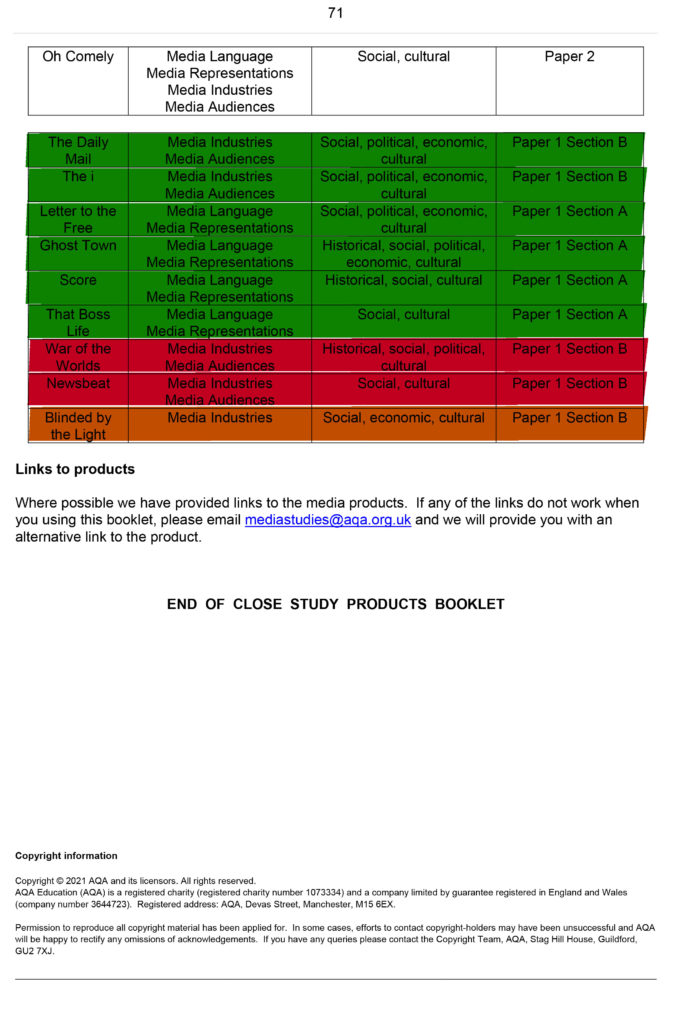
CSP
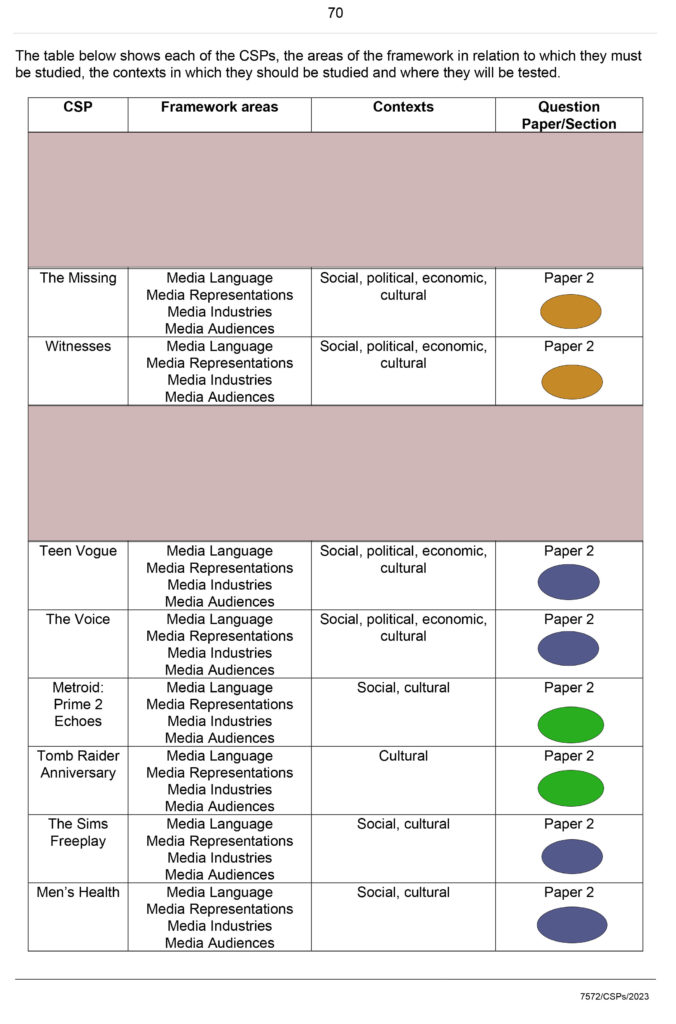

(CSP recap)
csp Revision
2023-Alevel-Media-Studies-Close-Study-Products-v1.5-1

Command words
- Describe: Depict something based on its key features
- Compare: To base something and relate it to another item and evaluate different key features from each, can be similar or similar
- Evaluate: To assess the whole idea, decide and discuss overall the idea
- Analyse: Discuss all features and ideas and generate a thesis or idea from it
- Knowledge:
- Understanding:
revision


BLUE MEANS HAVENT DONE
COMMAND WORDS
describe- give an account of specific features
compare- give a account and distinguish the difference and similarities … juxtapose
evaluate- forming an opinion, discussion and judgment of a thing as a whole.
analyse- examine something, find minor details.
knowledge-
understanding-