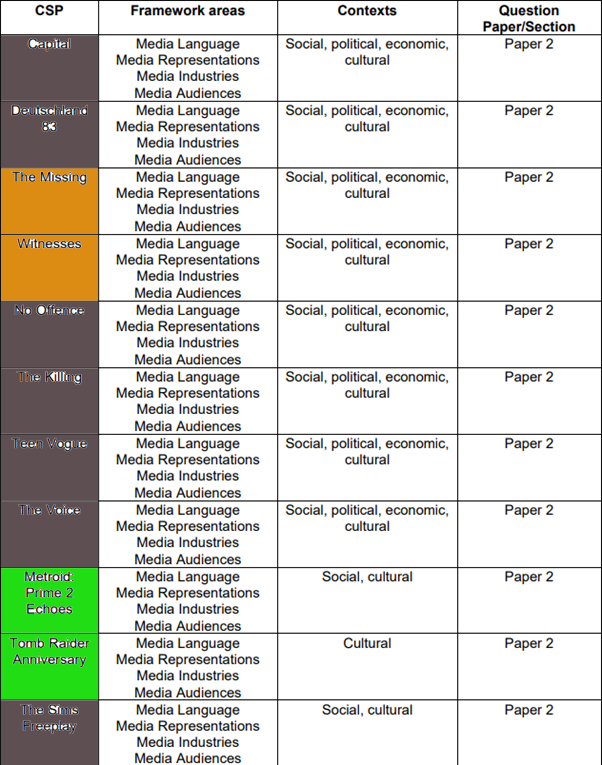
| NEW MEDIA | OLD MEDIA | COMMENT OR EXAMPLE |
| Active involvement | Passive involvement | |
| Two-way conversation | One-way conversation | |
| Open system | Closed system | |
| Transparent | Opaque | |
| One-on-one marketing | Mass marketing | |
| About Me | About You | |
| Brand and User-generated Content | Professional content | |
| Authentic content | Polished content | |
| FREE platform | Paid platform | |
| Metric: Engagement | Metric: Reach/ frequency | |
| Actors: Users / Influencers | Actors/ Celebrities | |
| Community decision-making | Economic decision-making | |
| Unstructured communication | Controlled communication | |
| Real time creation | Pre-produced/ scheduled | |
| Bottom-up strategy | Top-down strategy | |
| Informal language | Formal language |
share | active | creative | host | |
| example or comment | ||||
| story | re-connect | personalise | stream | |
| example or comment | ||||
| experience | store | scale | immerse | |
| example or comment | ||||
| interface | live | adapt | binge | |
| example or comment | ||||
| conversation | re-perform | circulate | endless | |
| example or comment |
The Voice newspaper was first published in 1982, “committed to celebrating black experience” and aiming to deliver “positive change” by “informing the black community on important issues”.
The impact of new technologies forced the production, distribution and circulation of The Voice to change drastically. Audiences started to consume media through online products and downloads instead of through physical copies of media products. This change in audience consumption forced The Voice to focus more on its digital output rather than physical output.
Val Mcalla, founder of The Voice, received £62,000 from Barclays Bank through the Loan Guarantee Scheme, which was part of a series of initiatives set up by Thatcher’s government to help unemployed people start their own businesses. This loan offered Mcalla an opportunity to raise the funds to start The Voice. Barclays was heavily criticised for it’s investments in South Africa where racial segregation was institutionalized in a system known as apartheid – a system of institutionalised racial segregation in South (West) Africa from 1948 to the early 1990s. This loan was a success for Mcalla and was paid off within 5 years.
The circulation of The Voice peaked in the early 1990s at 55,000 with young women being a substantial majority of its weekly buyers.
In 2004, The Gleaner Company (a Jamaican newspaper and media enterprise), took ownership of The Voice – paying over £3m. GV Media Group, a subsidiary of The Gleaner Company, still publishes the paper today.