- Free: The act of being ones self with the rights of free will, speech and actions, without being forced to obey ones commands. ‘Able to act or be done as one wishes; not under the control of another.’
- Slave: A person that has been forced out of their own freedom rights to contribute to ones rules and commands, through the ownership of a person. ‘A person who is the legal property of another and is forced to obey them.’
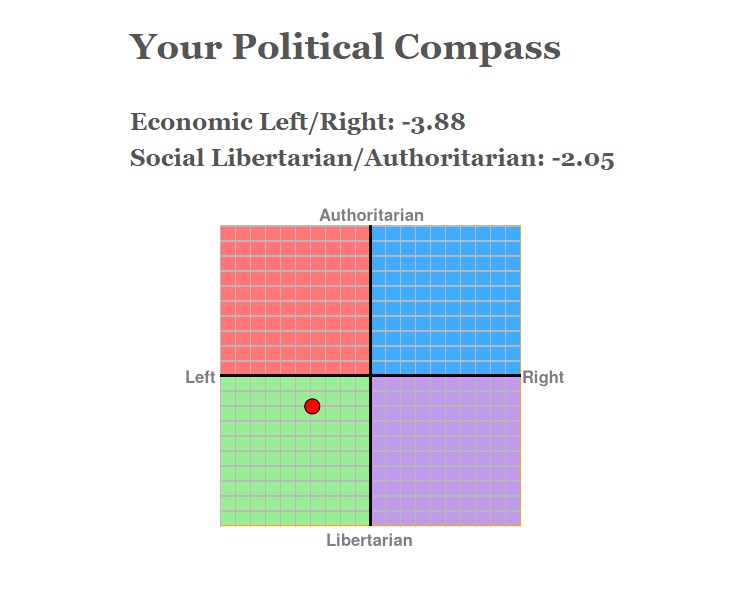
- Authoritarian: The strict rules and laws put into force by those of hierarchy and power to eliminate personal freedom of those with less freedom of speech. ‘Favouring or enforcing strict obedience to authority at the expense of personal freedom.’
- Libertarian: The act of being free from controlled ownership such as the government, and be able to choice what one would like to. ‘Libertarians seek to maximise autonomy and political freedom, and minimise the state’s violation of individual liberties; emphasising free association, freedom of choice, individualism and voluntary association.’
- Hedonism: The theory that pleasure and pain give us the motivation to act towards something. Binary opposition , if you have pleasure, you have pain. ‘Hedonism‘ comes from the ancient Greek for ‘pleasure’. Psychological or motivational hedonism claims that only pleasure or pain motivates us. Ethical or evaluative hedonism claims that only pleasure has worth or value and only pain or displeasure has disvalue or the opposite of worth.’
- Permissive Society: A society in which some social norms become increasingly liberal, especially with regard to sexual freedom. This usually accompanies a change in what is considered deviant. This was a society within the rise of the teenager.
The Frankfurt School
- The founders of the theory of pleasure and happiness being turned into objects and the sense that happiness does not come from being rich and famous. Happiness comes from how you see yourself / within.
- The scholars theorized that this experience made people intellectually inactive and politically passive.
- The idea that the public need to be wary of the media and the message the media gives out. This can cause us to become confused, trapped and intimidated.
| Key Questions: | Focus | Specifics |
| Why regulate the media? | – Truth – Child Protection (Of the vulnerable) – Political Bias – Privacy (Slander / Reputation damage / Libel / Defamation – Human Morals and Ethics – Relative / Subjective (Good behaviour) – Specific or particular political opinions – Ownership (avoid monopolies / increase choice / diversity) – Health and safety | – Depp vs Heard – Rooney vs Vardy – Elon Musk purchasing Twitter – Activision case of sexual assault |
| Who regulates what (media)? | – Government – Specialist bodies (Ofcom – broadcasting) – Key Individuals (Celebrities and influencers) – Internal Companies/structural regulations (Code of ethics/practice/Self regulation) – BBDC (Cinema) – PEGI (Games) – PRS (Music) – IPSO (Newspapers & Magazines) – ITU (Radio) | – ‘R’ for radio friendly – ‘E’ for explicit content – Vevo |
| How will regulation be put in place? | – Rating System – Copyright | – Instagram – PEGI Rating |
| What gets regulated? | – Newspapers – Films – Video Games – Radio – Television (TV) – Music – Animations – The News – Books – Magazines – Internet | – Pixar – Marvel – The Sun – Safari |