Semiotics:
Dominant signfier – Vin Diesal
Dominant ideology – body image
Selective Representation – big, dominant, muscular (predominantly) white men
Iconic sign: The bold text tells you what you can find inside this magazine issue. It all relates to losing weight fast
Icon – picture of Vin Diesel
indexical signs: sweat = worked out
symbolic sign: The magazine’s colour theme is mostly blue which is seen as a stereotypical colour for men, influencing them to buy the magazine. Big bold texts all about losing weight “demolishing junk food cravings” and “Blast body fat”. The dominant signifier, Vin Diesel, is positioned in the middle showing off his muscles.
By choosing to represent big, dominant, muscular (predominantly) white men, Men’s Health has a reactionary representation. It adheres to the male gaze, and stereotypes people have. Vin Diesel is a pretty good representation of what society thinks men should look like… not what men actually look like. additionally, Vin Diesal’s ‘cool man’ persona (calm, in control, cool, strong) also plays into stereotypes of the way that men should act.
Use of capital letters – exclamation points – colours – dialogue “true grit” – all appeal to men
The use of the traditional boy colour, blue, further reinforces this.
Lasswell’s model applied to Men’s Health:
sender: Men’s Health is one of the largest health magazines on the market – directed at men – made by men for men
says what: wants to push healthy eating and gym workouts. It is aimed at men who want to gain muscle and lose fat.
what channel: through print – and also through the website (online)
to whom: Educated men with families, who spend big on travel, style, sports/gym, personal grooming, and live an active + adventurous life.
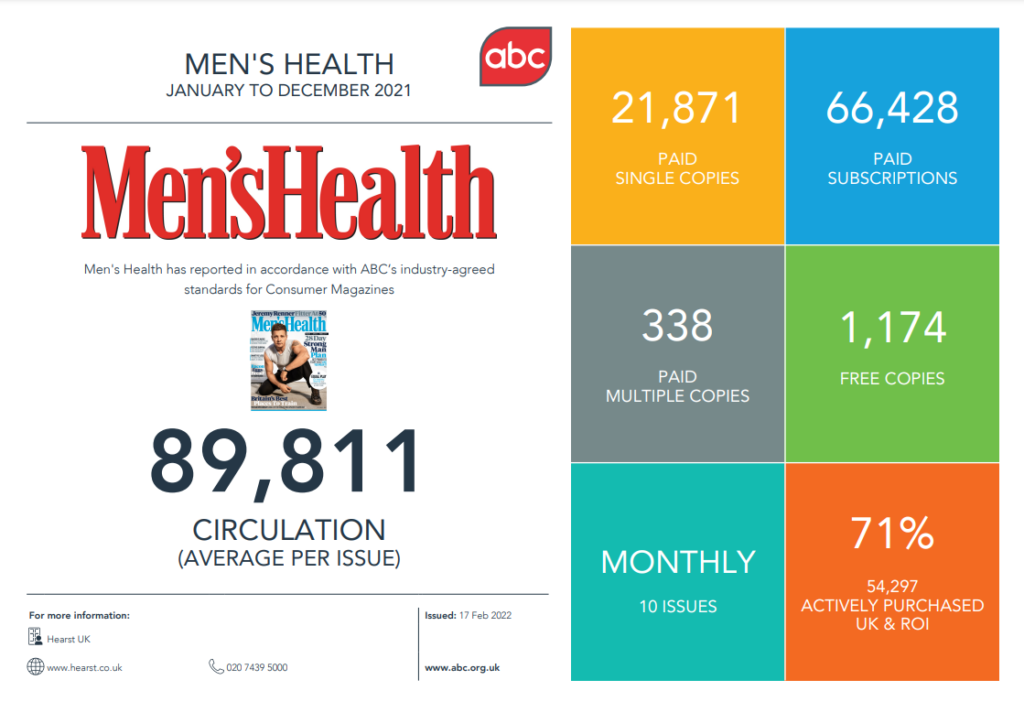
what effect: 9m print audience. 16.5 mill social followers.
89,000 average buys per issue
(66,000 paid subscriptions)
Two-step flow of communication
Vin Diesel is an opinion leader, who people actively follow. People will be more likely to buy certain products etc. if they know that an opinion leader such as Vin Diesel supports it.
Uses and Gratifications
Self-esteem – page 13 is aimed at improving readers’ self-esteem through getting back in shape and improving fashion style.
Men’s health is owned by Hearst (founded in 1887) who owns 40 different companies, making them a conglomerate.
Stuart hall
– Hall provides a framework for decoding messages:
1: Accept the dominant message
2: negotiate the dominant message
3: reject the dominant message
George Gerbner’s Cultivation Theory states that people who consume media often are more susceptible to the messages in said media
Two-step flow of communication
Vin Diesel is an opinion leader, who people actively follow. People will be more likely to buy certain products etc. if they know that an opinion leader such as Vin Diesel supports it.
Uses and Gratifications
Self-esteem – page 13 is aimed at improving readers’ self-esteem through getting back in shape and improving fashion style.
Essay draft
Men’s Health does not challenge the social and cultural contexts in which it was created. Instead, it takes a reactionary stance. This is telling when you look at the dominant signifier on the front page, Vin Diesel, who is standing in a dominant stance, which emphasises his size and muscle. Through choosing Vin Diesel as the face of their magazine, Men’s Health is subtly suggesting to its audience that he is the standard for what a man should look like and that all men should strive to be as strong, dominant, and muscular as him. The use of photoshop and Vin’s oiled-up muscles further accentuates this unrealistic body standard which is being set for men. One way they have altered the image is by clearly increasing the contrast, in an effort to further define his already-defined muscles. This is similar to the Score advert which also features this idea of a ‘perfect man’ who men strive to be like. This is a very common theme in media, which consistently uses ‘cool men’ such as James Bond, Don Draper, and Ryan Gosling as the standard for masculinity. These men are usually strong, confident, desirable, promiscuous, and cold, they never show their true emotions, and always act in a composed manner. These men usually tend to appeal more to the male gaze than the female gaze, as men are conditioned to believe that this is how they should look and act. Vin Diesel is another example of a ‘cool man’ with his large muscles and laid-back masculine persona. David Gauntlett refers to this as constructed identity. There are other examples of the ‘cool man’ on other pages of the magazine. For instance, on page 2-3 of the magazine, there is a double-page spread of an advert where a ‘cool man’ stands with a girl on his arm. His shirt is ripped to show off his muscles, and he is extremely tall, masculine, and handsome. Later in the magazine, Vin Diesel is shown in the editor’s letter, with the text “Diesel’s slant is one to aspire to” which again tells audiences that they should be like him. George Gerbner’s Cultivation Theory states that people who consume media often are more susceptible to the messages in said media, so Men’s Health showing Vin Diesel multiple times throughout the magazine and stating that he is “one to aspire to” sends the message to audiences that Vin Diesel is the standard for all men. The reason why Men’s Health seems to focus more on appealing to the male gaze rather than the female gaze is that the large majority of their audience are men, and more specifically, educated men with families, who spend big on travel, style, sports, and personal grooming. `These men also tend to live an active, adventurous life, with the majority playing sports. Further proof that the magazine is aimed at men, is the lack of sexualisation of Vin Diesel on the front cover. This is a common theme for all Men’s Health adverts, which put an emphasis on the men’s muscles rather than their sexual regions, with just 40% doing this. Compare this to Women’s Health, where 90% of front covers have an emphasis on their sexual regions. This suggests that both Men’s and Women’s Health have been created to adhere to the Male Gaze.