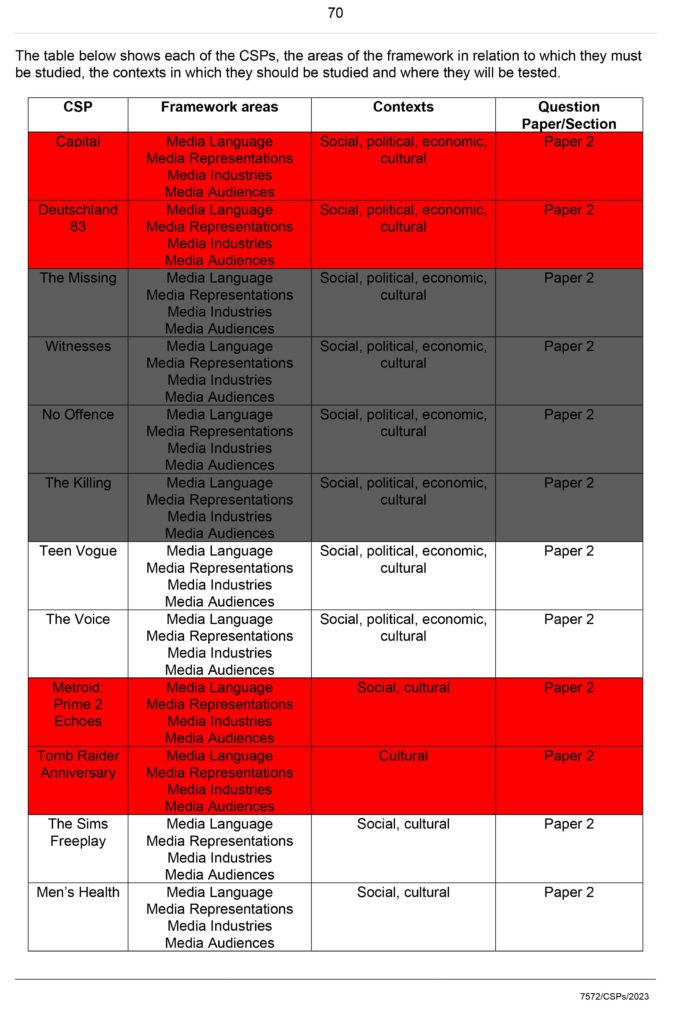
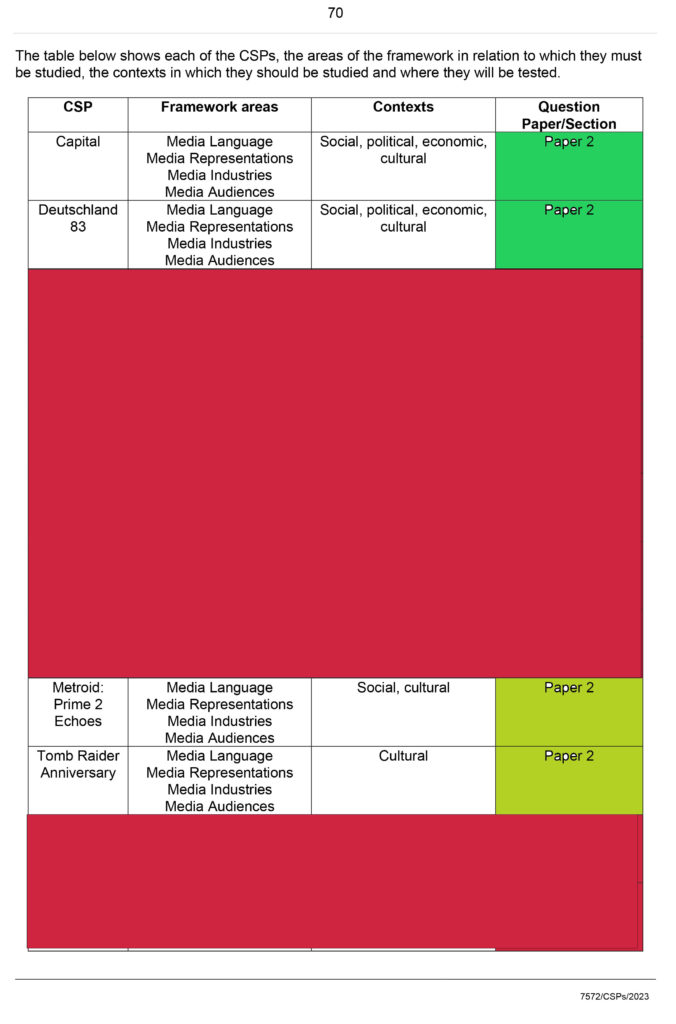
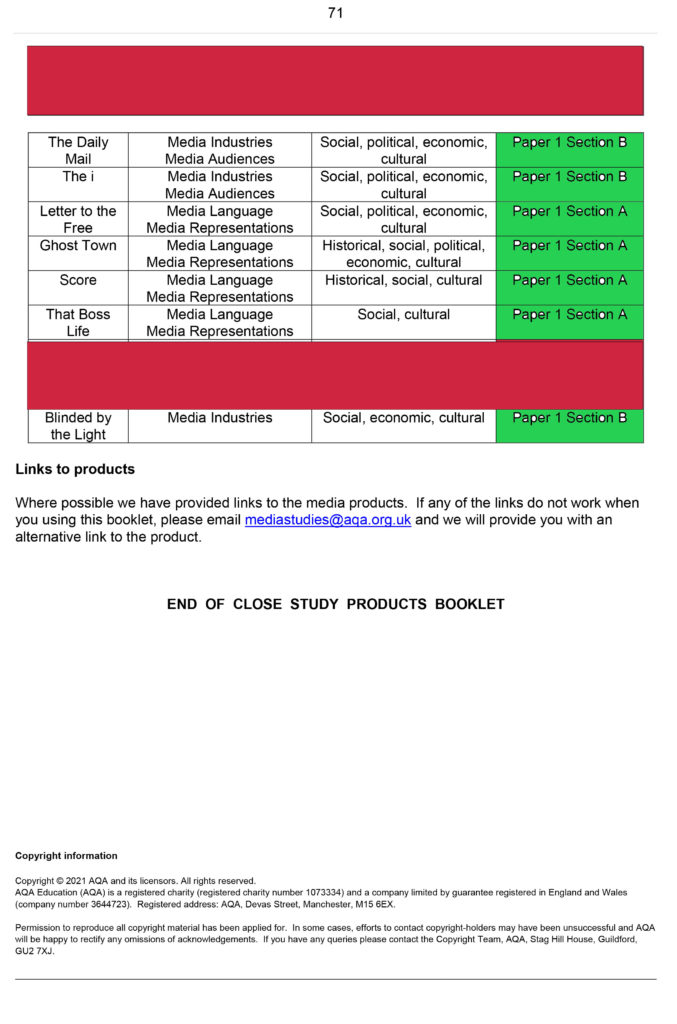
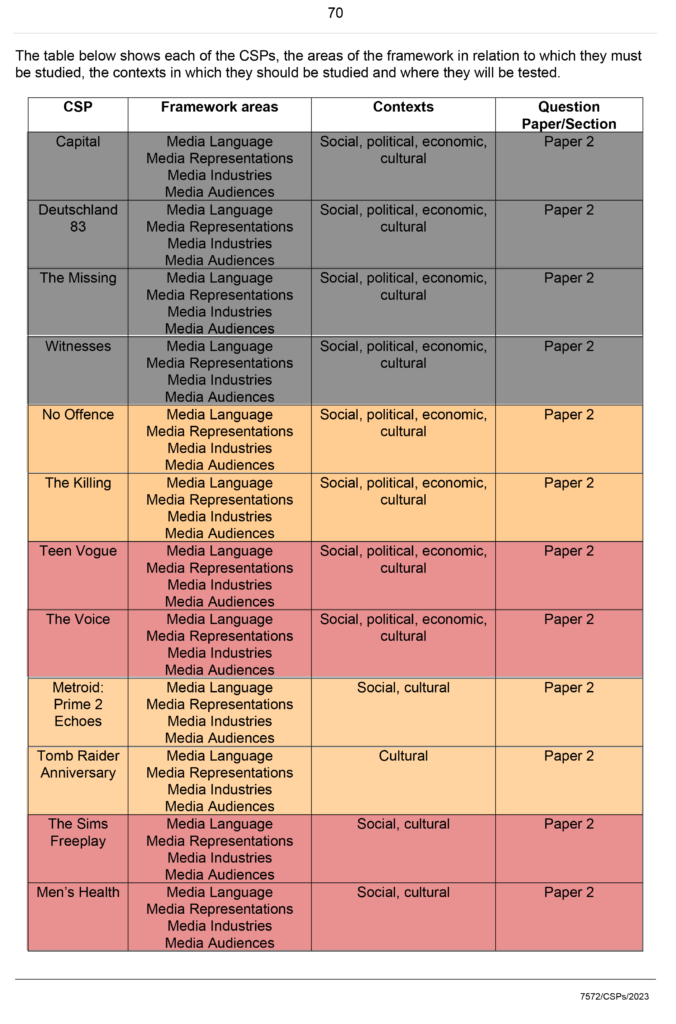
| What do you know? | What meaning or understanding do you have of their ideas-apply to CSP. |
| Noam Chomsky | Noam Chomsky is an American linguist, philosopher and political activist. He explains that media products target audiences by constructing an ideological view of the world through marketing. Explaining how propaganda and systematic biases function in corporate media.
He theorised the 5 Filters of Mass Media
These are:
1. The role of advertising
2. Diversion (Flak)
3. Structures of ownership
4. Finding a common enemy
5. Links with the establishment.
He believed that media goes hand in hand with the government. | This explains how populations can/are manipulated through the use of propaganda. He uses the term “manufacturing consent” which describes the presentation of the dominant ideology creating an obedient and willing audience. This results in narrowing the public sphere with the audience engaging passively instead of actively. He also highlights the media’s ability to link a common enemy in order to distract the public from the real problem. |
| Jurgen Habermas | Best known for transformation of the public sphere.
– Public Vs Private
Discussion vs Directorial
– Libertarian vs Authoritarian
– Free vs Slave
– He expresses his idea that “once the media is subject to regulation,” the public will lose their ability to share opinion in a public domain.
| -For Habermas, the misuse of publicity undermines the public sphere.
-The public sphere remains a site for the production of public opinion
-Habermas is key for the role of media in promoting a better, more inclusive society (eg in politics, morals, ethics).
Particularly useful for news, information |
| Semiotics | -Roland Barthes’ theory of semiotics – (Denotation, connotation, myth)
– C.S Pierce (icon, index, symbol – arbitrary)
-De Saussure (signifier, signified) | -Roland Barthes’ theory of semiotics – study of individual signs. Then how the structure of relationships between signs create meaning.
This links with Gramsci’s notion of HEGEMONY
|
| Representation | – Radical and reactionary representations.
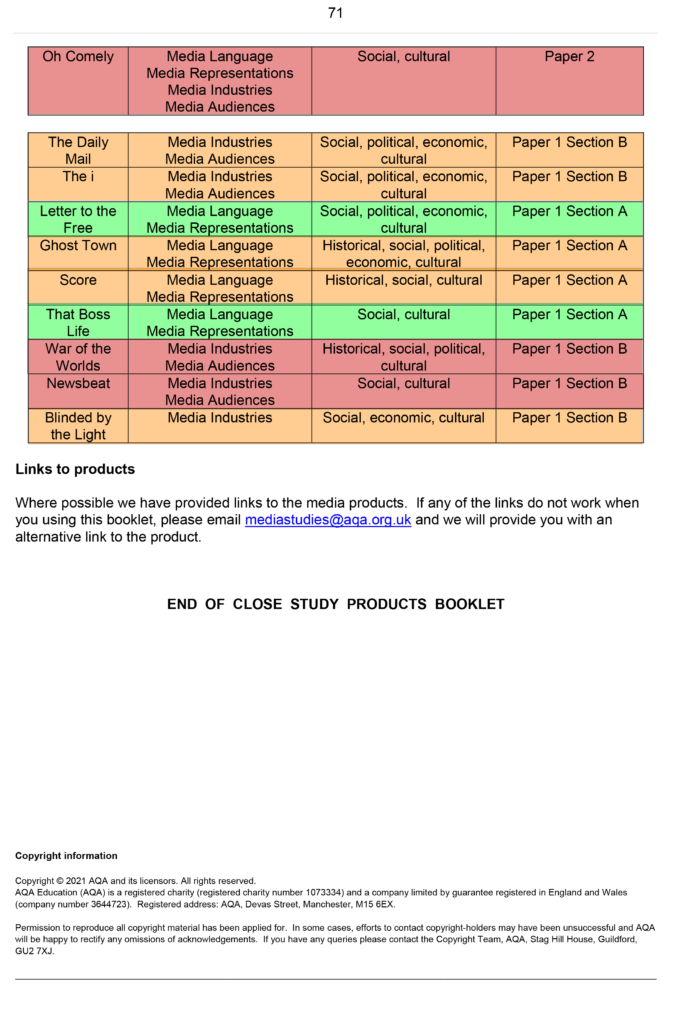
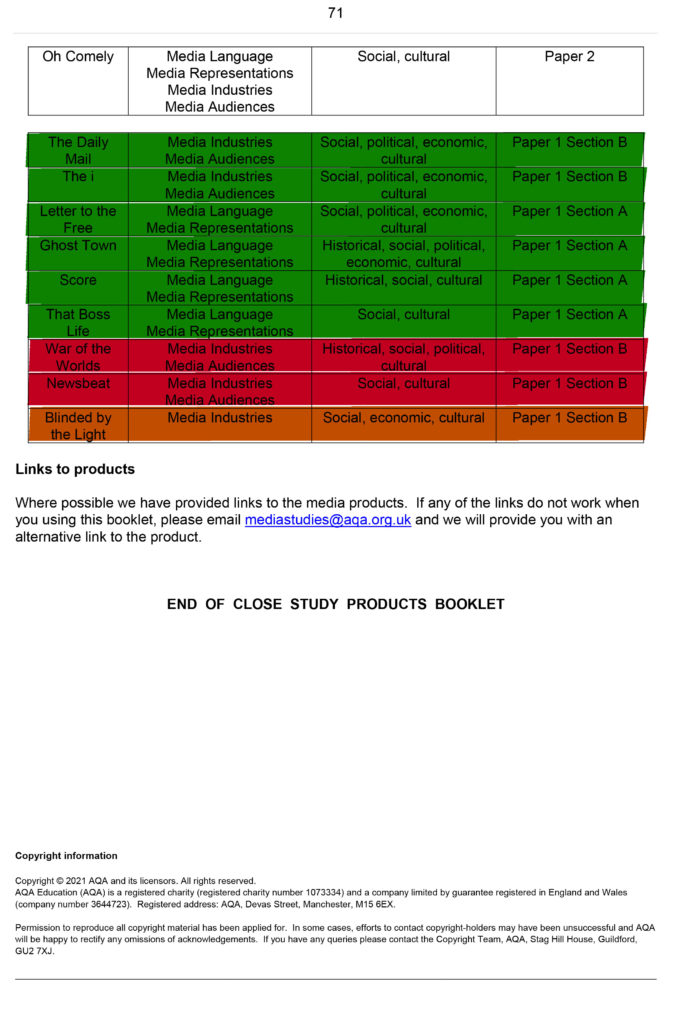
– Use of Stereotypes and counter types | CSP’s reactionary (Daily Mail, The i , Tomb Raider, Score) and radical texts (Maybelline, Common, Blinded by the Light, Ghost Town)
|
| Audience | Lasswell – Hyperdormic needle theory. (Passive/ Active)
Lazarfeld- Two- step flow of communication (Passive/Active)
Gerbner- cultivation theory
Stuart Hall- theory of preferred reading
Active / passive / | Audience is underpins other approaches eg analysis (semiotics, representation) and ownership (Chomsky, Habermas etc) |
| Feminist Critical Thinking | Toril Moi’s (1987) distinctions of feminine, female and feminist:
Feminist = a political position
Female = a matter of biology
Feminine = a set of culturally defined characteristics
Judith Butler: talks about how we normally view gender in a binary fashion. She believes that gender is performative and a social construct.
Laura Mulvey’s theory of the male gaze: encourages the sexual politics of the gaze and suggests a sexualised way of looking that empowers men and objectifies women.
Feminist Frequency, a website that hosts videos and commentary analysing portrayals of women in popular culture. | Critically engages with the concept of the patriarchy.
It is a key position or perspective to read culture (e.g media texts)
Tomb raider relates to Mulvey’s theory of the male gaze. The dominant signifier is wearing little clothing that accentuates her body figure which is a reactionary stereotype of female characters. |
| Postcolonialism | Bringing race into the picture in the 1980s, Paul Gilroy
highlighted how black youth cultures represented
cultural solutions to collectively experienced problems
of racism and poverty.
After WWII, Britain faced a mass labour shortage which lead to the migration of half a million people from the Caribbean (the Windrush generation 1950s-70s) searching for jobs
However, they faced severe discrimination which made it difficult for them to find employment and housing.
During the 1970s and 80s, the children of the Wind Rush Generation were reaching adulthood, but found it difficult to find employment due to having faced the same prejudice their parents did – the difference was that they were willing to resist this racism
– Frantz Fanon
The Black Atlantic
-Edward Said, (Orientalism)
-Jacques Lacan
The ‘Other’
| Postcolonialism very important in terms of looking at society from a white, male perspective (ie dominant patriarchy perspective)
Orientalism: The stereotyping of the east. The assertion of western power over the east. a general patronizing Western attitude towards Middle Eastern, Asian, and North African society.
The Other: He came up with the ideology that we never really know who we truly are, our identity is impossible to fully see ourselves. Relates to postcolonialism as it talks about the west viewing the east as ‘the other’
The black Atlantic: Gilroy resists that simple understanding of Black cultures from around the Atlantic as being marginal or derived from dominant national cultures which has ended up in specific sub cultures like African-American or Anglo-African that have a closer relation to American or British culture-at-large than to each other. |
| David Gauntlett | He talks about the fluidity of identities:
1.Fluid identity
2.Negotiated identity
3.Constructed identity
4.Collective identity
“Audiences realise they can change their identities”– David refers to Anthony Giddens’ theory who suggests “late- modernity” – where our identities are transitioning from the rigid stereotypes and starting to construct our own.
Audiences are in control of the media – adapting and assimilating ideas about themselves through the various representation that the media presents.” – illustrating how audiences are collectively adapting cultural norms and adapting themselves to fit in to society.
“Contemporary media practices mean that heteronormatitvity does not completely dominate”– showing how heterosexuality is not in complete control over society and that we are becoming a more inclusive community. | That our identities can depend on who we are with or what we are doing.
The magazine Men’s Health can relate to David Gauntlett’s theory of fluidity of identity. Specifically the use of a celebrity which promotes Gauntlett’s constructed identity. This helps to influence the audience to listen to the magazine in hopes that they will have some resemblance of Vin Diesel. |
| Lasswell | Lasswell’s Hypodermic model based on passive consumption which is significant to advertising. He based this on Propaganda Technique in the World War “subtle poison, which industrious men injected into the veins of a staggering people until the smashing powers… knocked them into submission”.
1. Who? –>
2. Says what? –>
3. Channel? –>
4. To Whom –>
5. With what effect? –> | The idea of telling someone to do something and they do it.
Brainwashing through the act of propaganda.
Men’s Health:
1. Hearst Communications.
2. Transforming successful men and helping them to take control over their physical and emotional side.
3. Print Magazine./ Online
4. Men.
5. That they will become the alpha male. They will have everything the want in life e.g their dream body, lots of wealth, love life, work life, social life. |
| Lazarfeld | Created the Two- step flow of communication model in 1948 | The flow of information and influence from the mass media to their audiences involves two steps: from the media to certain individuals (i.e., the opinion leaders) and from them to the public.
He identified that message are passed through opinion leaders (celebrities, influencers) who interpret the message first and then relay it to the audience, in hopes that the audience would have grown due to fan culture.
Rather than looking at the ‘passive’ audience he looks at the ‘active’ audience (audiences control how they think about what they consume). |
| Uses and Gratifications |
This reflects the decision process the audience go through and the different categories that media products fall under for the consumer. Falling under Maslow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs.
1. Understanding Self
2. Enjoyment
3. Escapism
4. Knowledge about the world
5. Self confidence/ Self esteem
6. Strengthen connections with family and/or friends
Theory by Jay G. Blumler and Elihu Katz based on Lasswell’s research. | These are divided into PERSONAL NEEDS
escapism
entertainment
knowledge and understanding
SOCIAL NEEDS
knowledge of the world
being together with friends and family
Mass Communication theory that focuses on the needs, motives and gratifications of media users. The Theory suggests that audiences are playing a more active role. |
| Narrative Theories | – Todorov
(Equilibrium, Disruption,
New equilibrium)
– Freytag
(Exposition, Climax, Denouement)
– Propp
(Hero, Helper, Princess, Villain,
Victim, Dispatcher,
Father, False Hero)
– Aristotle
(Catharsis, Peripetia,
Anagnorisis)
– Levi-Strauss
(Binary Oppositions) Chatman
(Kernels = Key moments in the plot/ narrative structure.
Satellites = Embellishments, developments, aesthetic that add “fluff”. Not essential to the storyline but enhance how it is consumed.)
– Barthes – Enigma code.
(Proairetic code = Action, movement
Hermenuetic code = Dialogue, character, reflection) | T – Narratives are broken down into a three-part structure and single character transformations are pursued.
P- Stock characters are used to structure stories, suggesting that the majority of stories use familiar character types to provide familiar narrative structures. These characters are not always separate individuals.
A- 3 Unities : Time, Place, Action. The idea that a narrative should be consistent and should encompass the same place, time frame and plot/action.
L- Narrative is simply a structure of key (oppositional) themes, creating a dominant message. Good v bad, young v old.
B- He came up with the ideology that narratives are often made up of action and thinking or talking about action.
|
| Genre | –Steve Neale
(Theory of repetition in Genre.) | |
| Key terms for Industry and Business | | |
| PSB public service broadcasting | | |
| James Curran | | |
| Shannon and Weaver | | |
| Stuart Hall | Theory of Preferred reading and ENCODING and DECODING model of communication
Hall compares two models of communication: The first, the traditional model, is criticized for its linearity – sender/message/receiver | The encoding and decoding model of communication refers to how media messages are produced, disseminated and interpreted. He believes that the audience actively take part in how they decode a message relying on their own social contexts.
His theory states that media tries to create a fixed opinion (dominant ideology) from hegemony in order to control and dominate the public. Audiences can accept and reject these influences. Accepting the influences by majority can lead to stereotypes. |
| George Gerbner | Cultivation theory
RECEPTION THEORY (developed by George Gerbner based around research on TV viewing) suggests that exposure to reinforced messages will influence our ideas, attitudes and beliefs.
Perception is based on what they repeatedly see. | People who consume media in large amounts are more susceptible to believing everything the media messages convey, believing they are valid and real. This is because they perceive society as pertaining to the values within those texts.
2 key terms World Mean Index – the more we watch TV (or other media forms) the more we think the world is mean and nasty.
Mainstreaming – the more mainstream TV (and other media forms) we consume the more mainstream we become ie more compliant, accepting of dominant messages.
This process is called enculturation, assimilation (or brainwashing?) |