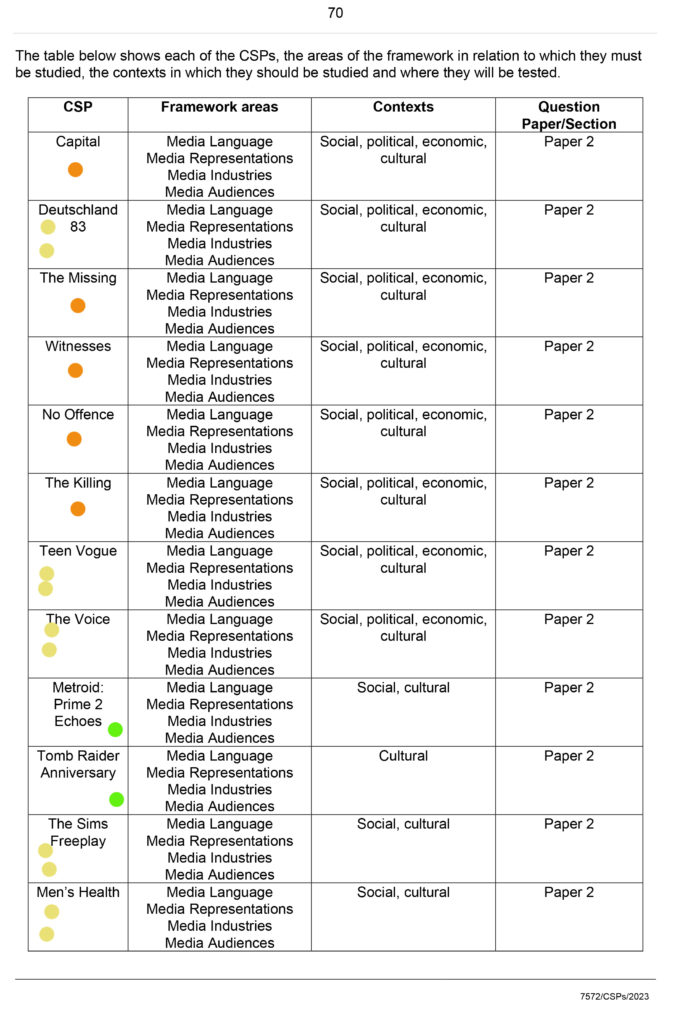
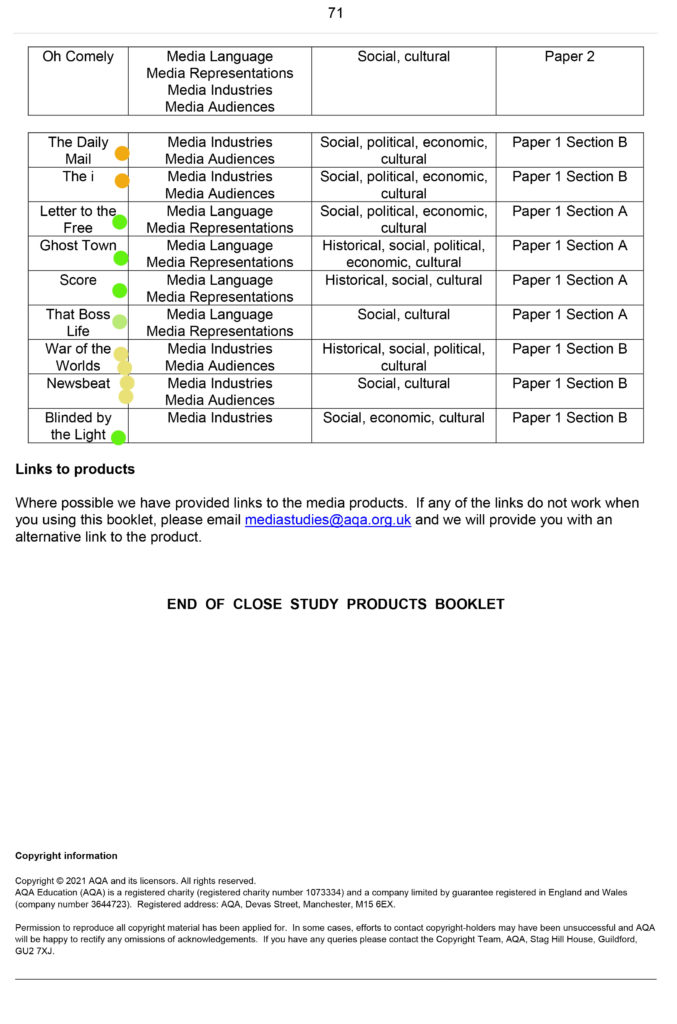
Command Words:
- Describe – Give a detailed account of words.
- Compare- Estimate, measure, evaluate or note the similarity or differences between. Determined similarities and differences between something and the outcome.
- Evaluate- : To determine or fix the value of. To determine the significance, worth, or condition of usually by careful appraisal and study.
- Analyse-Examine something in detail, typically in order to explain and interpret it.
- Knowledge-
- Understanding-
| What Do You Know | Understanding | |
| Noam Chomsky | – five filters- The common enemy, Flak machine, The media Elite, role of Advertising, Ownership. Official sources. – Manufacturing consent -Mass media -Structures of ownership | – Media utilises the common enemy to ignore the real problems. – |
| Jürgen Habermas | – the public sphere | – The public sphere refers too” society engaged in critical public debate”. -The public sphere is an area in social life where individuals can come together to freely discuss and identify societal problems, and through that discussion influence political action. A “Public” is “of or concerning the people as a whole. |
| Semiotics | – The study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation. | -semiotics theory is that signs do not convey a meaning that is inherent to the object being represented. –Iconic signs – icons are signs where meaning is based on similarity of appearance. –Indexical signs – have a cause-and-effect relationship between the sign and the meaning of the sign. –Symbolic signs – these signs have an arbitrary or conventional link. |
| feminist critical thinking | – Feminist = a political position -Female = a matter of biology -Feminine = a set of culturally defined characteristics -Judith Butler -Laura Mulvey | Judith Butler- “an identity instituted through a stylized repetition of acts”. -Male gaze |
| postcolonialism | -Postcolonialism is about where does our identity come from? How is our identity formed? How do we understand our own identity and how is our identity represented in the local, national and global media? | |
| David Gauntlet | – fluidity of identity – negotiated identity – constructed identity – collective identity. The increase of a pick and mix culture in society is where individuals see options from which they can pick and choose the ones that are a best fit for them. This results in society shifting into a postmodern era whereby economic theory and individualisation rule over our decisions we make. | -He assumed there was a generational divide in attitudes towards gender roles. -post traditional society. |
| Lasswell | – who-sender -says what-message -channel-medium to whom-receiver -with what effect. passage consumption – through propaganda then people believe it -notion of brainwashing -believing what people say. -active and passive | Lasswell’s model of communication (also known as Lasswell’s communication model) describes an act of communication by defining who said it, what was said, in what channel it was said, to whom it was said, and with what effect it was said |
| Lazarfeld | The concept of the ‘two-step flow of communication’ suggests that the flow of information and influence from the mass media to their audiences involves two steps: from the media to certain individuals (i.e., the opinion leaders) and from them to the public. | |
| George Gerber | Cultivation Theory suggests- – Television influences its audience to the extent that their world view and perceptions of the world. ( start reflecting what they repeatedly see meaning TV is considered to contribute independently to the way people perceive social reality. ) – will have an effect on the audience’s attitudes and values. -Long term exposure to violent media makes the audience less likely to be shocked by violence. mean world syndrome- violence is easy to translate, accepting mainstreamed dominant ideology’s. The world is used to violence, all country’s translate things such as humour but violence is the same in all country’s. | Cultivation theory suggests that repeated exposure to television over time can subtly ‘cultivates’ viewers’ perceptions of reality. George Gerbner and Larry Gross theorised that TV is a medium of the socialisation of most people into standardised roles and behaviours. The criticism of this theory is that screen violence is not the same as real violence. Many people have been exposed to screen murder and violence, but there is no evidence at all that this has lead audiences to be less shocked by real killings and violence. media consumption mainstreaming wants the world to believe the same ideologies Shirky believes Gerbners theory is not applicable to modern forms of media. the media has changed and audiences are more active and believes you can no longer talk about users of media products as an audience |
