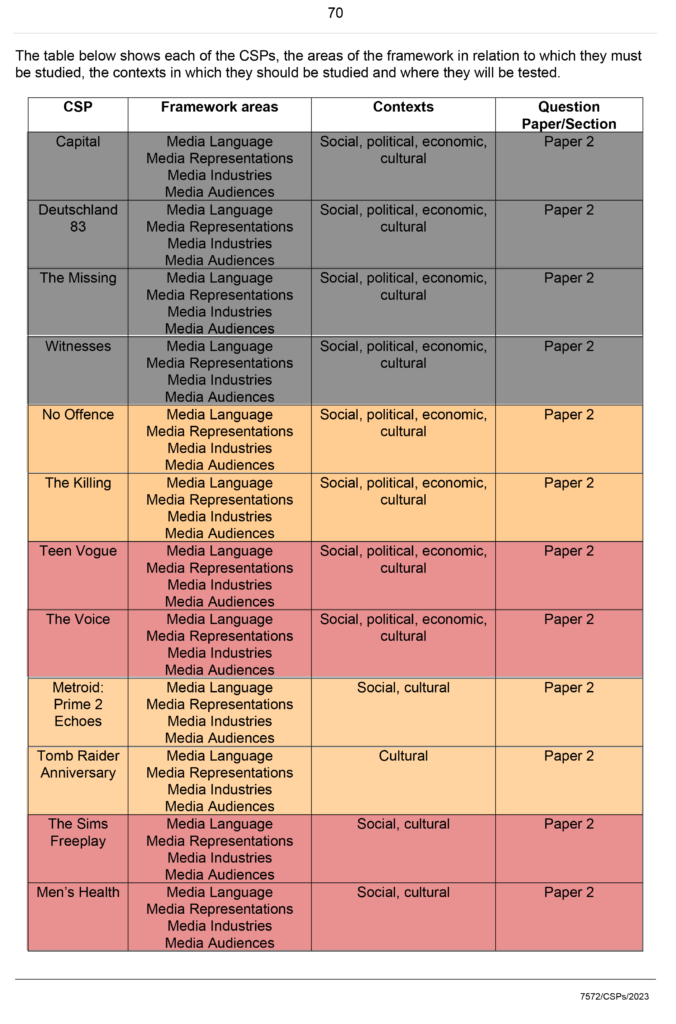
CSP Pg 70 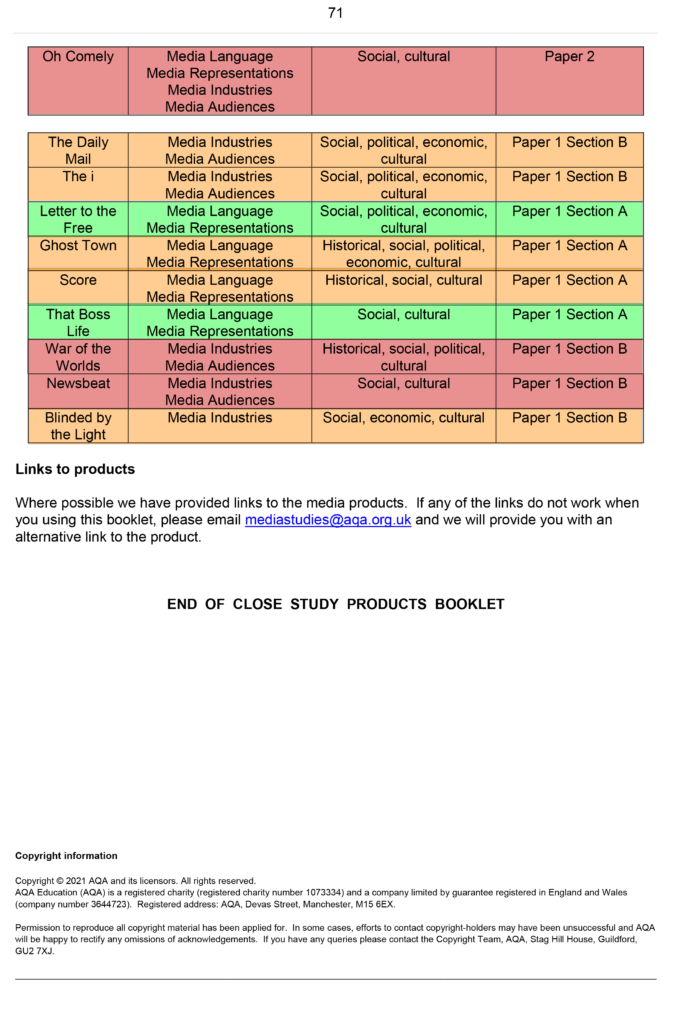
CSP Pg 71
Command Words:
- Describe – A detailed paragraph on what you can see with an explanation.
- Compare – Point out the differences and similarities or negative and positives between two different things.
- Evaluate – Overall opinion and conclusion.
- Analyse – Separate / detailed focus on different points.
- Knowledge – Facts, information, and skills acquired through experience or education
- Understanding – The ability to understand something; comprehension.
| Theorists | What do you know? | What meaning or understanding do you have of their ideas? How can you apply their ideas to your CSP’s? |
| Noam Chomsky | – The 5 filters of mass media: 1) Structures of ownership, 2) The role of advertising, 3) Links with ‘The Establishment’, 4) Diversionary tactics, 5) Uniting against the ‘common enemy’. – Produced the book named ‘Manufacturing Consent’ with Edward S. Herman in 1988. | – He claims that the media is hand in hand with the government such as ‘The Daily Mail’ is more right ring where as ‘The I’ is more left wing. – ‘The Daily Mail’ and ‘the I’ are not necessarily allowed to put specific somethings that make the government or hierarchy’s look bad. |
| Jurgen Habermas | – His first book was focused on the public sphere, known as ‘The Structural Transformation of the Public Sphere’. – Public Sphere is an area in social life where individuals can come together to freely discuss and identify societal problems, and through that discussion influence political action. | – Habermas states that a variety of factors resulted in the eventual decay of the public sphere, including the growth of a commercial mass media, which turned the critical public into a passive consumer public. – Factors have affected the way people share their ideas and social issues willingly and freely. |
| Semiotics | – 3 important individuals: 1) Ferdinand de Saussure = Signifier (Any material thing that signifies (e.g words on a page)), Signified (The concept that a signifier refers to), 2) C S Pierce = Icon (Signs that represent the signified (e.g a picture)), Index (Signs where the signifier is caused by the signified), Symbol (Signs that is understood as representing an object, idea or relationship), 3) Roland Barthes = Signification (Levels of meaning), Denotation (A literal meaning of a sign.), Connotation (A secondary meaning for a sign.), Myth (Stories that are shared and widely believed by the media.), Ideology (Signs that support powerful structures), Radical (Something that goes against something that’s expected.), Reactionary (Something that agrees with typical ideas.) | – Signs and symbols that represent an overall meaning. – The study of signs – CSP’s: Metroid, Bioshock, Tomb Raider |
| Feminist Critical Thinking | – Feminist = a political position Female = a matter of biology Feminine = a set of culturally defined characteristics – Judith Butler describes gender as “an identity instituted through a stylized repetition of acts”. – First / Second and Third wave of feminism – Male Gaze (Laura Mulvey) – suggests a sexualised way of looking that empowers men and objectifies women. – Jean Kilbourne – Judiths ideology of gender performance | – CSP: Bombshell (The Bombshell movie is a true story based on the accounts of the women at Fox News who set out to expose CEO Roger Ailes for sexual harassment.), Metroid, Tomb Raider, Maybelline and Score. – An idea that women are represented in a sexual and objective manner in society, as well as the unique way of thinking about how men think and act towards women. |
| Postcolonialism | Hegemonic: Dominant, ruling-class, power-holders. ● Hegemonic culture: The dominant culture. ● Cultural hegemony: Power, rule, or domination maintained by ideological and cultural means. ● Ideology: Worldview – beliefs, assumptions and values. – Postcolonialism specifically looks at identity and representation through the lens of Empire and Colonialism. – Jacques Lacan = He expresses that we can never discover ourselves as we cannot see ourselves from the outside, from a 3rd person perspective. – Paul Gilroy | – CSP’s: Letter to the Free, 13th Netflix documentary and Ghost Town. – The study of cultural, political and economic legacy of colonialism and imperialism, focusing on the impact of human control and exploitation of colonized people and their lands. – The study of the impact of those in control … |
| David Gauntlet (Representation) | – Fluidity of identity (The ability to change how to see/view the world, yourself and actions.) – Constructed identity (An identity formed by personal and others perceptions interests.) – Negotiated identity (Agreements/discussion on a persons identity with another persons.) – Collective identity (An identification which is shared between groups and individuals.) – He mentions we live in a post … society. – | – David Gauntlet expresses how every individual has their own way of representing themselves whether that is around people or by themselves. |
| Harold Lasswell (Industry) | – Created the model of communication which describes an act of communication by defining who said it, what was said, in what channel it was said, to whom it was said, and with what effect it was said. – The 5 components of the model: 1) (Who) Sender 2) (Says what) Message 3) (Channel) Medium 4) (To whom) Receiver 5) (With what effect) Feedback. – Created the one-step flow of the hypodermic needle model or magic bullet theory, which explains. – Produced the 1927 book, Propaganda Technique in the World War. – (One step-flow of Hypothermic Needle) Media explores information in such a way that it injects in the mind of audiences as bullets. – Active and Passive Consumption | – Men’s Health with Model: – 1) Who said it: Hearst UK / Hearst Communications. – 2) Says what: – 3) Channel: Magazines / Print and digital copies of the magazines / Online through social media. – 4) To whom: To men and those interested in a healthy lifestyle. – 5) With what effect: To get men to start to think about their physical, mental and emotional well being. To buy into their product / company. |
| Paul Lazarsfeld | – Created the two-step flow of communication model. – Two-step flow communication model most people form their opinions under the influence of opinion leaders, who in turn are influenced by the mass media. – Two-step flow model, ideas flow from mass media to opinion leaders, and from them to a wider population such as the public. (the flow of information and influence from the mass media to their audiences involves two steps: from the media to the opinion leaders and from them to the public.) | – People form their ideas from influencers and those with a high reputation. – In the Men’s Health magazine, on page 6-7, Gerard Butler a famous actor and film producer models for a Hugo Boss advert. As he is a popular celebrity, people may feel influenced to buy it as people may think Butler wears the aftershave. |
| Uses and Gratifications (Audience) | – Uses and gratifications theory focuses on a Mass Communication theory that focuses on the needs, motives and gratifications of media users. | – Focuses on the needs of the audience. Examples, of these are enjoyment, escapism, fantasy, social interaction. – In Men’s Health magazine, page 10-11 as this represents escapism, enjoyment, and also self- esteem. (Social + personal needs). |
| Stuart Hall (Representation) | – Hall’s work covers issues of hegemony and cultural studies, taking a post-Gramscian stance. – Developed Hall’s Theory of encoding and decoding. – Created ‘The Encoding/decoding model of communication’ which is a theoretical approach of how media messages are produced, disseminated, and interpreted. – Stuart proposed that audience members can play an active role in decoding messages as they rely on their own social contexts, and might be capable of changing messages themselves through collective action. – Explores that audiences are active. | In Men’s Health page 2-3. Dominant = If wear perfume you get models. Negotiated = Its an advert and i can see both sides. Opposition = Sexist and inappropriately touching |
| George Gerbner | – Created the Cultivation Theory which explains people who are regularly exposed to media for long periods of time are more likely to perceive the world’s social realities as they are presented by the media they consume, which in turn affects their attitudes and behaviours. – The theory’s key proposition is that “the more time people spend ‘living’ in the television world, the more likely they are to believe social reality aligns with reality portrayed on television.” | |
