











Hesmondhalgh what is the differnece between culture industries and other industries`?
Cultural industries- For example, tarmacking a road is something that is essential. it is a necessity in life, however other industries such as media, is more for entertainment purposes.
Other industries is limited to what it can do where as in cultural industries are more able to adapt or be adapted, you can do many things with it to entertain or satisfy your intended audience.
media industries are a risky business according to Hesmondhalghs theory. You don’t know how people are going to react. however, in other industries such as Greggs if you sell a particular amount of goods one day you can likely predict what you can sell the next day based off the previous data.
Both industries rely on money to survive
transnational media- Media that is accessible to multiple nations, not just limited to one.e.g. Netflix
commercial media- privately owned, audiences don’t pay. (adverts) e.g. itv
structure- patterns of ownership
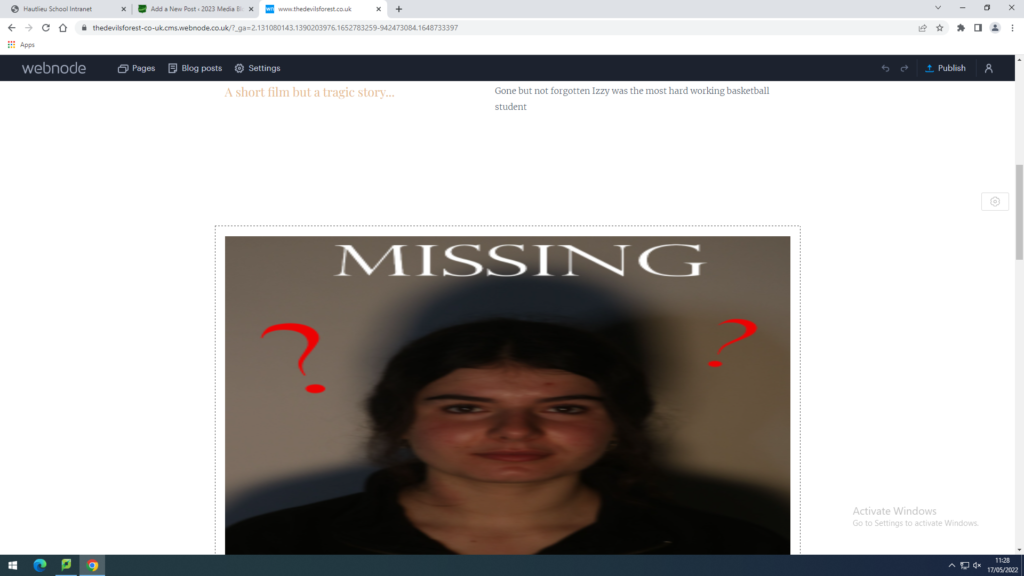
No Offence
regulation of ownership(no monopolies)
Types of ownership [State/public ownership-BBC, commercial/private ownership-ITV, community-Hautlieu Radio]
Channel 4- mixed model/owned by government with adverts
Hesmondhalgh
‘Media is a risky business’
what is it?
Public broadcasting involves radio, television and other electronic media outlets whose primary mission is public service. In many countries of the world, funding comes from governments, especially via annual fees charged on receivers.
BBC:
it is critical of the government
An ‘arms length’ away from government
Horizontal Integration = When a conglomerate acquires media companies of the same media type.
Vertical Integration = Ownerships that allow a media company to produce and distribute products.
the key theorists:
media ownership
Characteristics of the public sphere
livingstone and lunt
( media work in school)
Key theorist: Stuart Hall
stuart hall:
Lasswell created a model explaining the ‘linear model of communication.’ This explains how people are ‘spoon fed’ information.
Larzarfeld created a simpler liner model (Two step flow model) explaining that messages from the media aren’t directly given to the audience, but is filtered by ‘opinion leaders/influencers,’ who influence audiences/masses to like something based on what they say.
Quantitative- Social Grades
Qualitative- type of people they are (explorer/mainstreamer/aspirer)
David Gauntlet
David Gauntlett – identity theory. What is the theory? “Identity is complicated; everyone’s got one.” Gauntlett believes that while everyone is an individual, people tend to exist within larger groups who are similar to them. He thinks the media do not create identities, but just reflect them instead.
judith butler:
JUDITH BUTLER questions the belief that certain gendered behaviors are natural, illustrating the ways that one’s learned performance of gendered behavior (what we commonly associate with femininity and masculinity) is an act of sorts, a performance, one that is imposed upon us by normative heterosexuality.
language of moving image:
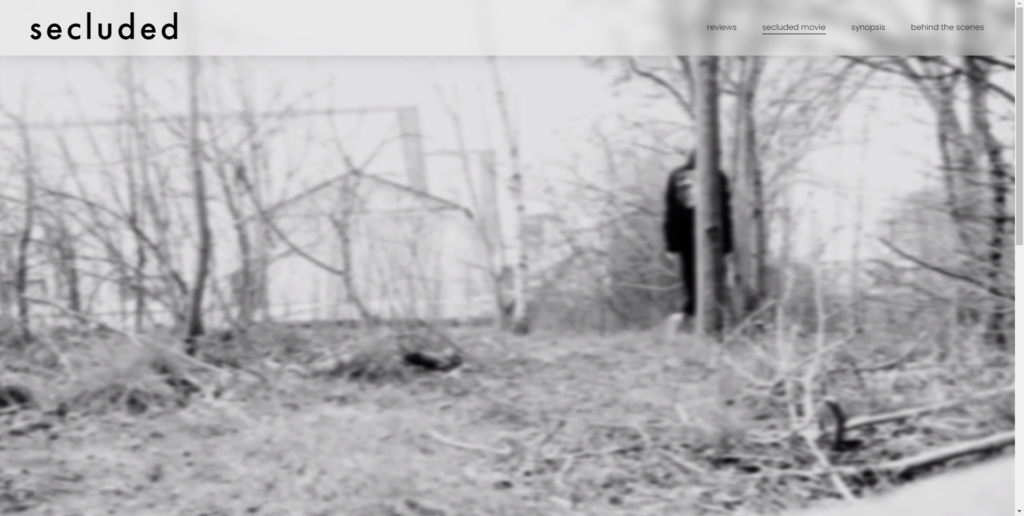
i am going to create a film sequence in the form of a trailer about someone who is running from something that they cant see and is going to follow them as they try escape the thing that they cannot see. i am going to be doing a series of films of the person in different shots as they are running or escaping this thing.


The Aim of this post is to provide an introduction to the topic of REGULATION
STARTER
https://www.businessinsider.com/elon-musk-twitter-purchase-political-reaction-2022-4
ACTIVITY 1
Get students to express their own ideas in relation to Musk’s take-over bid for Twitter. Ask students to simply state their own case for regulation, censorship and control – or lack of it. Get students to sit in a horseshoe that indicates: FOR v AGAINST CENSORHSIP, REGULATION AND CONTROL. This will indicate either a LIBERTARIAN or AUTHORITARIAN PERSPECTIVE. This is a key conceptual approach that can be revisited by completing the Political Bias activity on the next page.
Hopefully the discussion will focus on the need to speak-up. Make a clear link between the benefits and drawbacks of saying what you think. Underline the role of the (mass) media in SELECTING, GATE-KEEPING & AMPLIFYING particular conversations and ideas.

David Hesmondhalgh
Production
Key points for making Blinded By The Light:
DistributionBlinded By The Light was picked up by New Line Cinema at the 2019 Sundance Film Festival after a bidding war with various other major film distributors. The film had been well received by audiences at the film festival.
Reception and box office
Promotion and marketing
Blinded By The Light was backed by a major international marketing campaign:


my film is about a teenager who’s been set up for murder and the lengths him and his friends have to go to to release him of his charges. the story starts off when a group of friends get jumped by a rival gang, right infront of cctv, without anyone being badly hurt they leave the scene, 2 days later they are watching the news at the teenagers house and see that the teenager is wanted for the murder of a man in their rival gang. The teenager pleads guilty in court due to him being at the scene very close to the time of death, whilst his friends In the end, they manage to release him from prison and the death penalty, and put the true murderer where he belongs. The movie will take place in a rough town in England, where the group face many challenges, fights and deaths in order to save their friend.my movie will be called _______.
has the idea that all characters are the same.
Often there is a villain who has done something to a victim. This means that we need a hero, who (often) accompanied by a helper is sent out (by a dispatcher) to fight the villain. The dispatcher or similar donor (such as a father figure) prepares the hero in his ‘quest‘ and gives the hero some magical object. The hero generally meets the princess as part of his quest / journey which usually provides a happy ending. During the narrative we (and the princess) may be presented
they do not necessarily have all characters listed, but all of the characters in the film will be listed.