



KEY TERMINOLOGY
Linear = arranged in or extending a straight or nearly straight line
chronological = following the order in which they occurred
sequential = forming or following in a logical order or sequence
circular structure = an object that references itself. making sure the function that is being passed in, filters out repeated or circular data.
Time based = over a period of time
narrative arc = is an extended or continuing storyline in episodic storytelling media such as television, comic books, comic strips, board games, video games, and films with each episode following a dramatic arc.
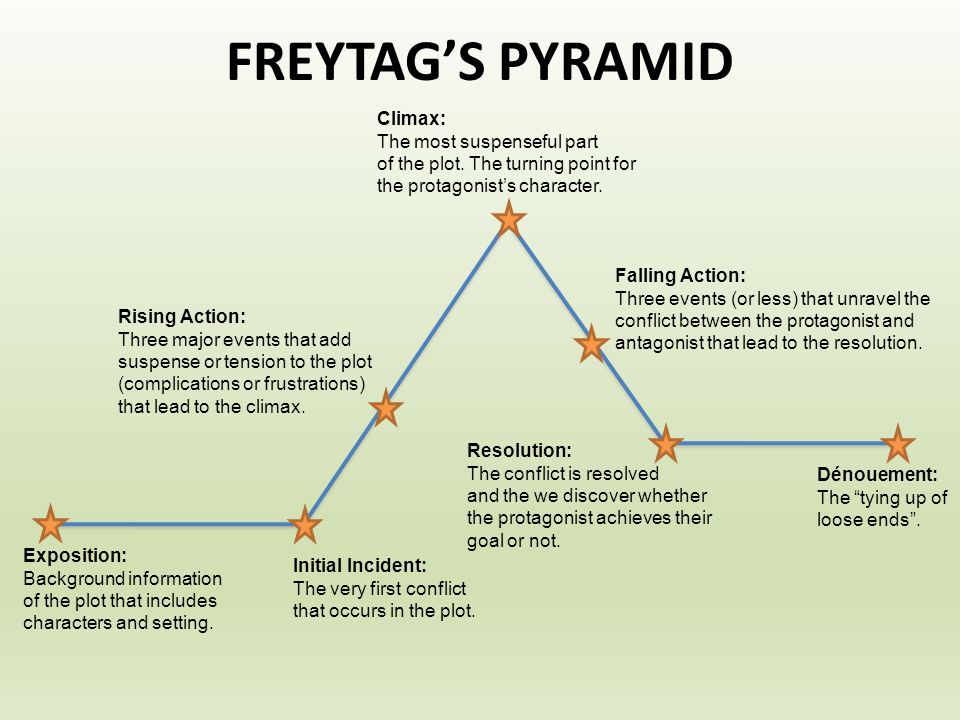
Freytag’s pyramid = Devised by 19th century German playwright Gustav Freytag, Freytag’s Pyramid is a paradigm of dramatic structure outlining the seven key steps in successful storytelling: exposition, inciting incident, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution, and denouement
Exposition = Narrative exposition is the insertion of background information within a story or narrative. This information can be about the setting, characters’ backstories, prior plot events, historical context.
Inciting incident = The event that sets the main character or characters on the journey that will occupy them throughout the narrative.
Rising action = starts right after the period of exposition and ends at the climax. Beginning with the inciting incident, rising action is the bulk of the plot. It is composed of a series of events that build on the conflict and increase the tension, sending the story racing to a dramatic climax.
climax = The ending and leading up to the end of the narrative
Falling action = Falling action is what happens near the end of a story after the climax and resolution of the major conflict. falling action is what the characters are doing after the story’s most dramatic part has happened.
Resolution = the ending of the story, happens after the conflict
Denouement = the final part of a play, film, or narrative in which the strands of the plot are drawn together and matters are explained or resolved.
Beginning / middle / end =
what you need to make a movie:


TZTEVAN TODOROV
Traditionally, narrative structures followed a formula which was identified by the theorist Tzvetan Todorov.
Todorov studied classic fairy tales and stories.
He discovered that narratives moved forward in a chronological order with one action following after another. In other words, they have a clear beginning, middle and end.
Todorov also suggested that the characters in the narrative would be changed in some way through the course of the story and that this would be evident by the resolution.
This traditional story arc format is known as a linear narrative:
| Steps | What happens |
|---|---|
| 1 | The narrative starts with an equilibrium |
| 2 | An action or character disrupts the equilibrium |
| 3 | A quest to restore the equilibrium begins |
| 4 | The narrative continues to a climax |
| 5 | Resolution occurs and equilibrium is restored |
FREYTAGS PYRAMID
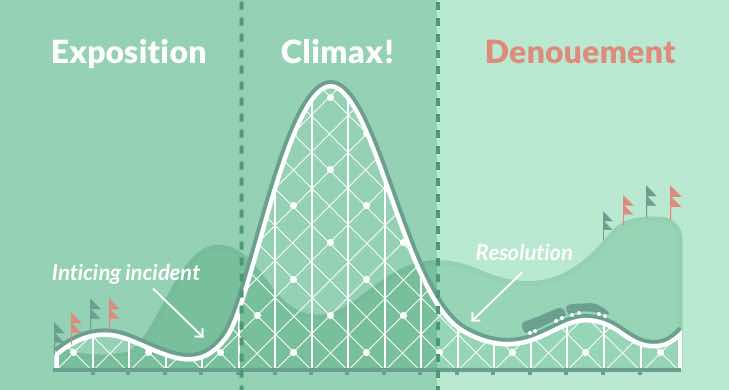
Novelist Gustav Freytag developed this narrative pyramid in the 19th century, as a description of a structure fiction writers had used for millennia. It’s quite famous, so you may have heard it mentioned in an old English class, or maybe more recently in one of our online fiction writing courses.
Freytag’s Pyramid describes the five key stages of a story, offering a conceptual framework for writing a story from start to finish. These stages are:
Here is the five-part structure of Freytag’s Pyramid in diagram form. Freytag’s Pyramid, it starts with the exposition. This part of the story primarily introduces the major fictional elements – the setting, characters, style, etc. In the exposition, the writer’s sole focus is on building the world in which the story’s conflict happens.
what you need to make a movie:
KEY TERMINOLOGY
Linear = arranged in or extending a straight or nearly straight line
chronological = following the order in which they occurred
sequential = forming or following in a logical order or sequence
circular structure = an object that references itself. making sure the function that is being passed in, filters out repeated or circular data.
Time based = over a period of time
narrative arc = is an extended or continuing storyline in episodic storytelling media such as television, comic books, comic strips, board games, video games, and films with each episode following a dramatic arc.
Freytag’s pyramid = Devised by 19th century German playwright Gustav Freytag, Freytag’s Pyramid is a paradigm of dramatic structure outlining the seven key steps in successful storytelling: exposition, inciting incident, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution, and denouement
Exposition = Narrative exposition is the insertion of background information within a story or narrative. This information can be about the setting, characters’ backstories, prior plot events, historical context.
Inciting incident = The event that sets the main character or characters on the journey that will occupy them throughout the narrative.
Rising action = starts right after the period of exposition and ends at the climax. Beginning with the inciting incident, rising action is the bulk of the plot. It is composed of a series of events that build on the conflict and increase the tension, sending the story racing to a dramatic climax.
climax = The ending and leading up to the end of the narrative
Falling action = Falling action is what happens near the end of a story after the climax and resolution of the major conflict. falling action is what the characters are doing after the story’s most dramatic part has happened.
Resolution = the ending of the story, happens after the conflict
Denouement = the final part of a play, film, or narrative in which the strands of the plot are drawn together and matters are explained or resolved.
Beginning / middle / end = The plot through out the films
Equilibrium = Everything is balanced at the beginning
Disruption = Changing something over and over again
Transgression = Often disequilibrium is caused by societal / moral / ethical
Peripeteia = a sudden reversal of fortune or change in circumstances, especially in reference to fictional narrative. “the peripeteias of the drama”
Anagnorisis = the point in a play, novel, etc., in which a principal character recognizes or discovers another character’s true identity or the true nature of their own circumstances.
Catharsis = is the purification and purgation of emotions through dramatic art, or it may be any extreme emotional state that results in renewal and restoration
The 3 Unities: Action, Time, Place = a tragedy should have one principal action. unity of time:
Flash-forward / Flash-back: a flash-forward takes a narrative forward in time, a flashback goes back in time, often to before the narrative began.
Foreshadowing = be a warning or indication of a future event.
Ellipsis = the omission from speech or writing of a word or words that are superfluous or able to be understood from contextual clues.
Pathos = to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel.
Empathy = is the capacity to understand or feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference
Diegetic / non-diegetic = In film, diegesis refers to the story world, and the events that occur within it. Thus, non-diegesis are things which occur outside the story-world
Slow motion = A slow movement to add to a tense scene
In media res = the practice of beginning an epic or other narrative by plunging into a crucial situation that is part of a related chain of events.
Metanarrative = in critical theory and particularly in postmodernism is a narrative about narratives of historical meaning, experience, or knowledge
Quest narratives = one of the oldest and surest ways of telling a story.




Peripeteia- a change in fortune e.g A very wealthy man has been making money for decades by taking big risks in the stock market. Suddenly, the stock market crashes and he is launched into poverty. In this example, peripeteia is a drastic change in circumstance, as a once wealthy man becomes poor.
Anagnorisis- moment of dramatic revelation. The moment when the protagonist realizes their own tragic flaw. e.g. the neighbour coming to the door, expecting to be shouted at but instead complimented.
Catharsis- purification or purgation of the emotions. e.g. the dad listening to Bruce Springsteen with the son.
Practical equipment-
Technical equipment – lighting, sound, microphones
actors
camera crew
writers, directors, editors, lighting directors
set designers
props
music
Conceptual
performance
emotion
time based
events
chronilogical
events
sequenntial
characters
theme
antagonist/protagonist
linear
beginning, middle, end
Freytag’s pyramid
Synopsis
A girl is walking on her phone as she receives texts from an unknown number. She hurries to get back to her car, however, the number begins to get closer to her until she is eventually captured.