- Chronological-the order in which the events occurred, from first to last
- Sequential– series of scenes that form a distinct narrative unit
- Circular structure– story ends the same as how it began
- Time based– is to watch it unfold over time according to the temporal logic of the medium as it is played back.
- Narrative arc– the story a film follows along including a dramatic arc somewhere to draw attention from the audience
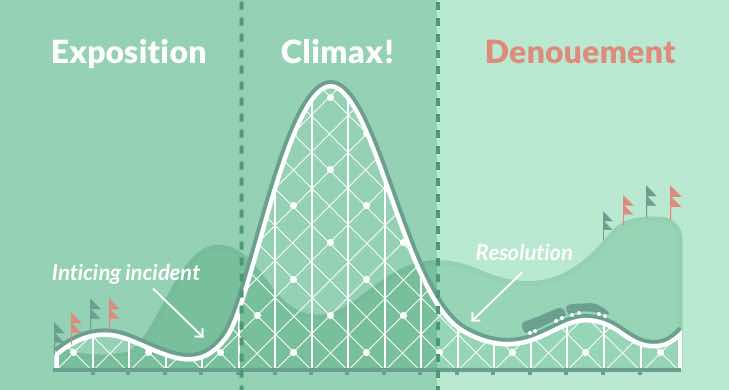
- Freytag’s Pyramid– the structure outlining events in a story
- exposition- a comprehensive description of an event, story or idea.
- inciting incident,
- rising action,
- climax- everything that the plot leads up to
- falling action– what happens after the climax and the plot/action calms down
- resolution
- denouement
- Beginning / middle / end– the idea that every storyline is split into three components
- Equilibrium
- Disruption
- New equilibrium
- Peripeteia– change in fortune
- Anagnoresis– dramatic revelation
- Catharsis– the idea that we are freed by consuming something
- The 3 Unities: Action, Time, Place
- flashback / flash forward
- Foreshadowing– the idea of hinting towards events further on in the storyline
- Ellipsis– a jump/missing out certain events in films.
- Pathos
- Empathy
- diegetic / non-diegetic
- slow motion
Physical Internal Structures:
Technical equipment (lighting, sound), actors, set, camera crew, software, writers, props, special effects, director, editors and costume designers
Theoretical Internal Structures:
Storyline, performance, generating emotions, events, characters, themes, genre, antagonist/ protagonist, linear/circular, start middle and end, time based, chronological, sequential and freytag pyramid.
Synopsis– A girl goes missing on a night out, her family and friends are all worried about her and file a missing police report. We are shown the trauma they go through. 2 years later her dead body is found, her ‘ghost’ haunts her family and friends. They then discover the body was not her. A group of her friends form together to be detectives and figure out that the ‘ghost’ was actually her asking them for help. They go on a quest to find her and end up finding her however she is very mentally damaged.
Todorov– presents a three part structure (beginning,middle,end)
Equilibrium
Disruption
New equilibrium
- the stage of equilibrium
- the conflict that disrupts this initial equilibrium
- the way / ways in which the disruption looks to find new equilibrium
- the denouement and/or resolution that brings about a new equilibrium