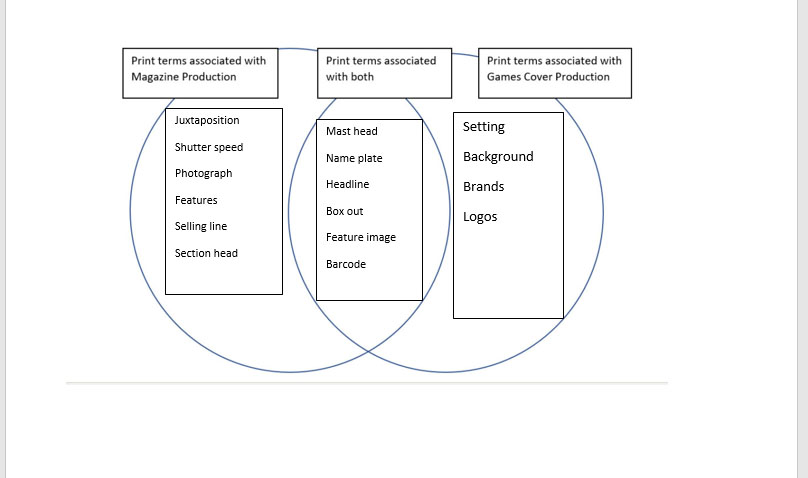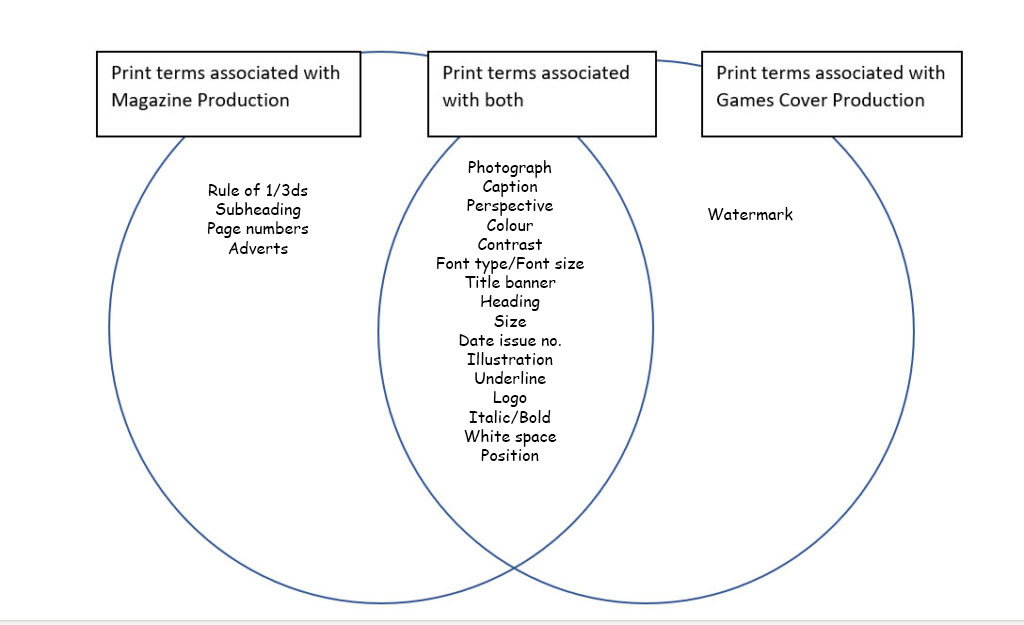
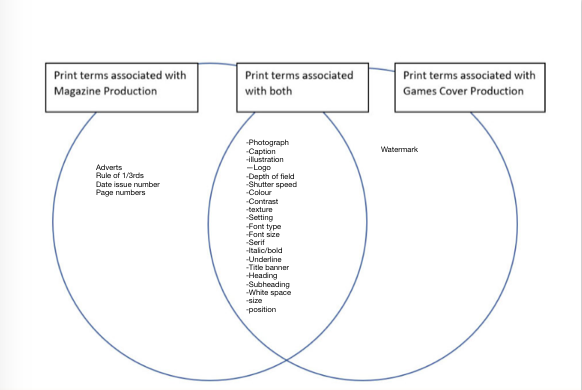
Venn Diagram


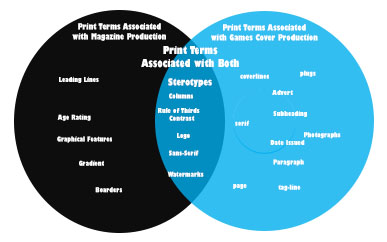
Positive and negative stereotypes – a good or bad accepted idea of something.
Counter-types – something opposing the stereotypes.
Misrepresentation – the misleading or false belief.
Selective representation – only representing certain things.
Dominant ideology – the most widely believed idea.
Constructed reality – the idea that society is created by humans and human interaction.
Hegemony – leadership by one person/group.
Audience positioning – the techniques used by the creator to get the audience to understand the idea.
Fluidity of identity – the idea that your identity changes.
Constructed identity – the identity you build, such as on Instagram.
Negotiated identity – agreeing that certain people have certain roles in a relationship and that these roles can not change.
Collective identity – the identity of a group.
I suggest you look at this post of mine about Media Language to make sure that you understand what it means ie it is much more than spoke or written communication and is specific to each media form.
Make sure you analysis is focused on MEDIA LANGUAGE and REPRESENTATION. Try to make some insightful points rather than stating the obvious, for example, discuss the use of semiotics, the notion of preferred reading and the concept of self-identity in Modernity (Giddens – see below).
Therefore make sure you are confident in this area and to test your knowledge can you present a comparison between this CSP and one other CSP that we have looked at so far. Again think about how you wish to organise your ideas and feedback your presentation. Or as part of your revision you could complete this mini mock?
If this topic comes up in the exam you can expect your question to be based around discussion of the Maybelline advert mainly on representation of gender, age, ethnicity and lifestyle with opportunities for direct comparison with other advertising CSPs.
Read this extract from a book called Modernity and Self Identity: Self and Society in the Late Modern Age, written by Anthony Giddens.

here is an edited version:
“The reflexive project of the self, which consists of the sustaining of consistent, yet continuously revised, biographical narratives, takes place in the context of multiple choice as filtered through abstract systems. In modern social life, the notion of lifestyle takes on a particular significance. The more tradition loses it hold, and the more daily life is reconstituted . . . the more individuals are forced to negotiate lifestyle choices among a diversity of options. Of course there are standardising influences . . . Yet because of the ‘openess’ of social life today, the pluralisation of contexts of action and the diversity of ‘authorities’, lifestyle choice is increasingly important in the constitution of self-identity and daily activity.”
Can you translate some of his ideas? For example, what is reflexivity? If you need more help you can read this post from my own blog: Representation, Identity & Self
Once you have thought about this, think about the concept of a ‘non binary identity’. Follow this link to find out more. What does this mean to you? How do you feel about it? What about the concept of CIS? Or Intersex? Do these concepts help you to understand the idea behind the Maybelline marketing campaign?Again discuss this with your group of friends, make notes and be prepared to feedback to the rest of the class.
Ayesha Tan Jones is a non-binary artist and musician who goes by the stage name ‘YaYaBones’
So how is the traditional male representation adjusting to this new world from the perspective of Advertising & Marketing?
Positive and negative stereotypes = general expectation of something or someone, including looks, personalities and behavior
Counter-types = a positive stereotype
Misrepresentation = giving a false or misleading representation with the intention to lie
Selective representation = parts of an image are selectively chosen to show
Dominant ideology = agreeing with what we believe
Constructed reality = how we represent ourselves/ things in a way we want it to be seen or things or the idea of that we’ve been influenced by other factors
Hegemony = dominance of authority
Audience positioning = techniques that are used to control how we perceive and understand things ideology of the media
Fluidity of identity = flexibility of gender
Constructed identity = how something is formed – is it real? has it been constructed?
Negotiated identity = changing someones beliefs through the concept of cultural beliefs and media
Collective identity =
.