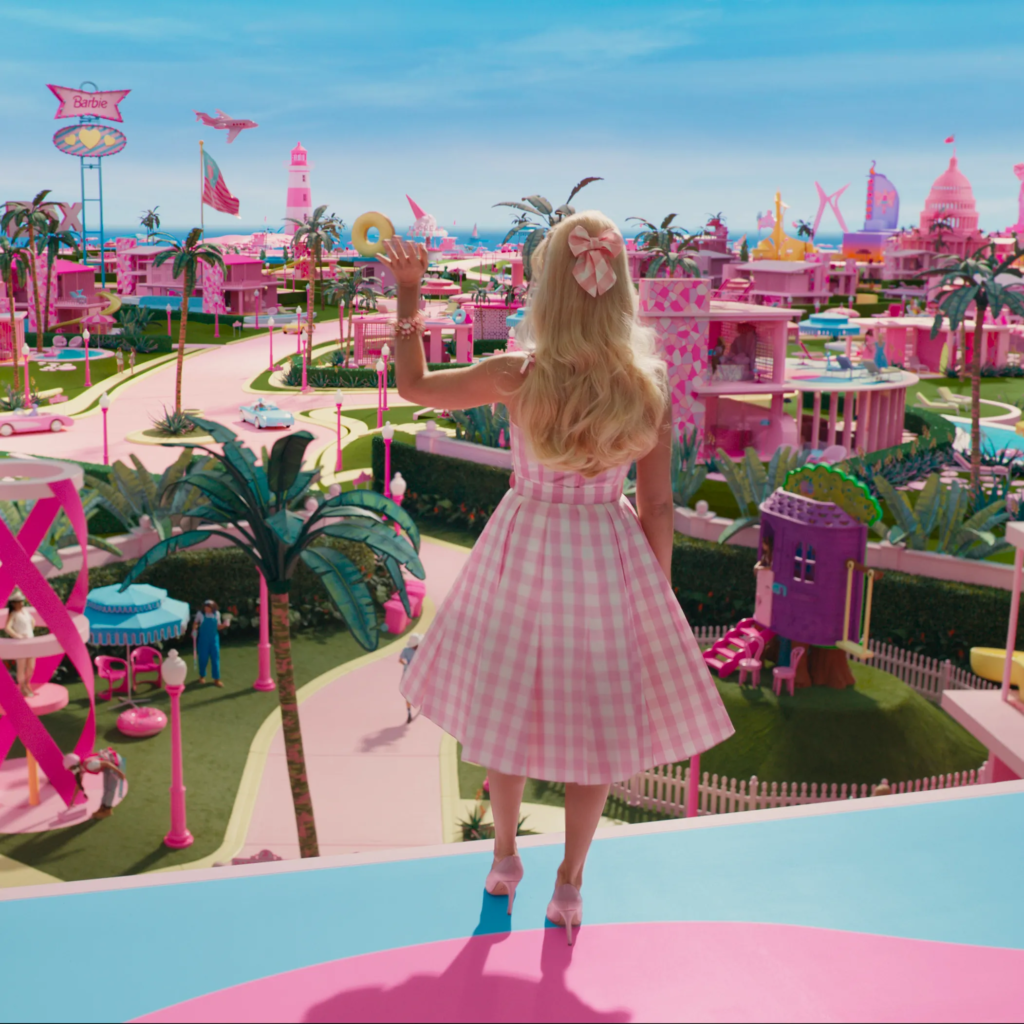
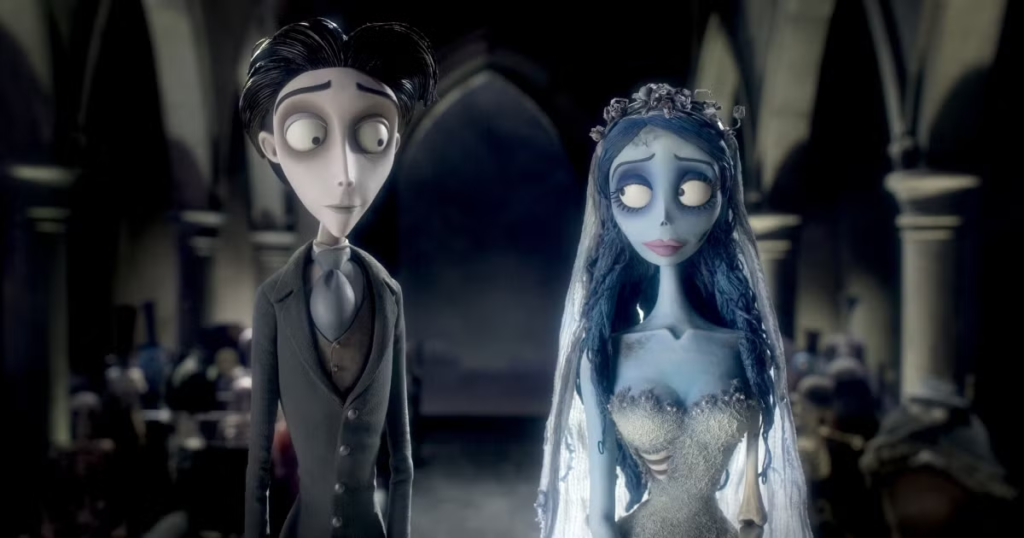
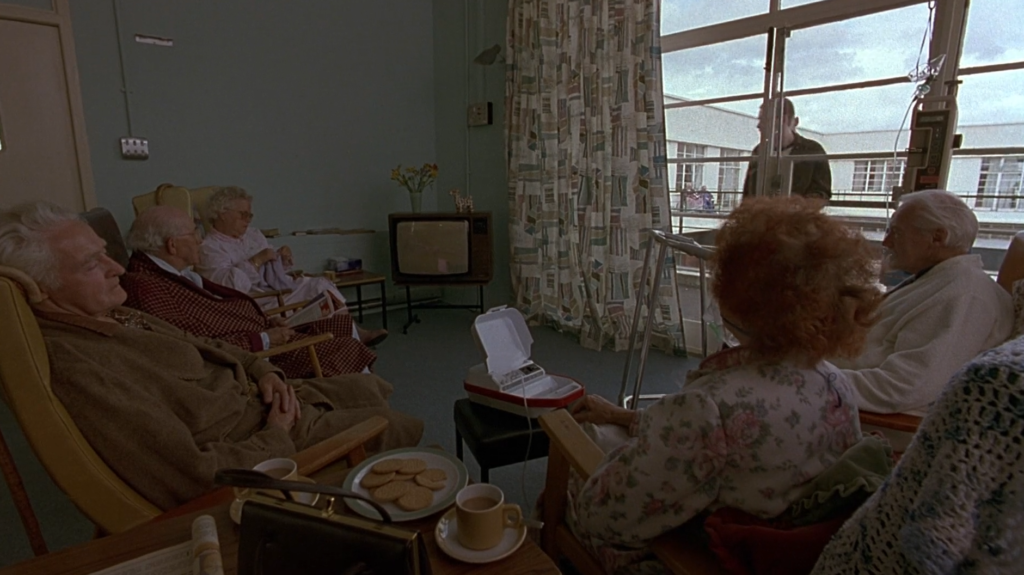
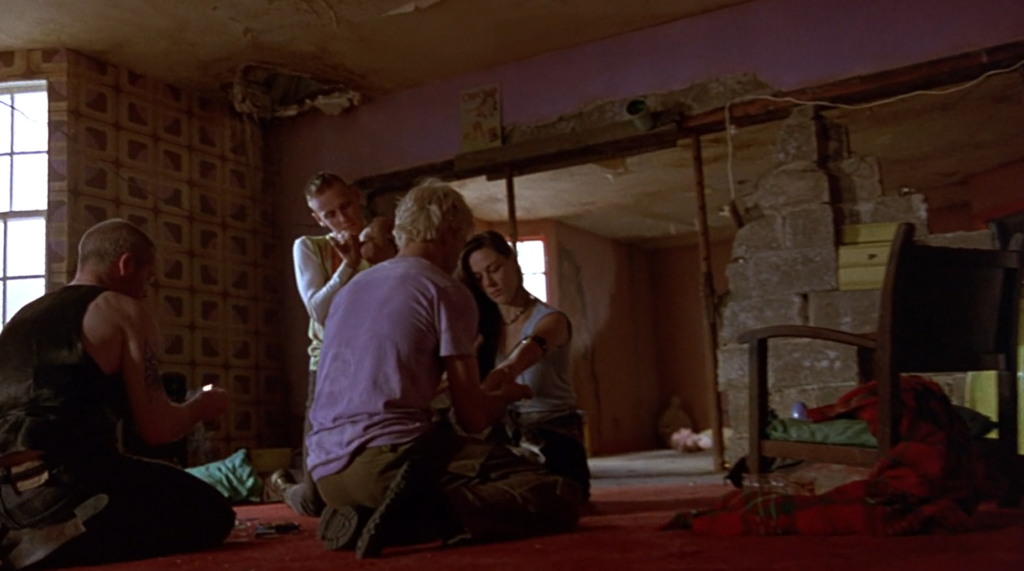
Aesthetics are the colours, shapes, and objects that can be categorised based on the emotion/feeling they evoke.
Realism
Verisimilitude – The appearance of being true or real.
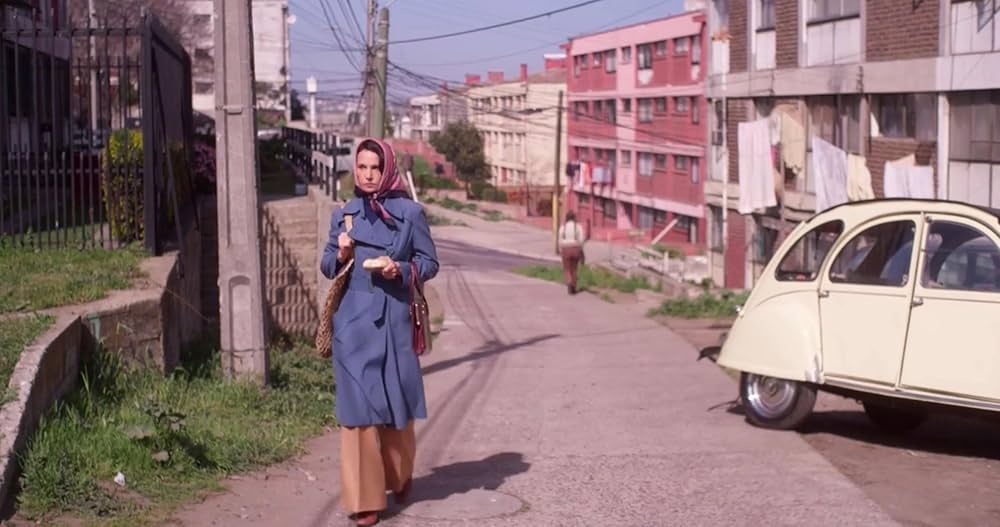

Social Realism – work that aims to draw attention to the real socio-political conditions of the working class as a means to critique the power structures behind these conditions.

Magic Realism – a literary or artistic genre in which realistic narrative and naturalistic technique are combined with surreal elements of dream or fantasy.

Hyperreality – an artificially created copy that is perceived as somehow more real than the real thing, or too real to be real.

Visual Style
Iconography – the use of recurring visual images and symbols in movies that convey specific themes, evoke emotions, and build a film’s narrative identity.
Intertextual Referencing – when a text implicitly or explicitly refers to another text, by using distinctive, common or recognisable elements of the referenced text.

Visual/Sound Motifs – a recurring story element that acts as a way to highlight a films thematic meaning.

Colour Grading – post-production process of altering the appearance of an image for presentation in different environments on different devices.

Auteur Trademarks – A directors “iconic” style of direction

Tone
Pathos – an emotional appeal to an audience.

Bathos – an effect of anti-climax created by an unintentional lapse in mood from the sublime to the trivial or ridiculous.

Suspense – a state or feeling of excited or anxious uncertainty about what may happen.

Comedy – type of drama or other art form the chief object of which, according to modern notions, is to amuse.
Dramatic Irony – a literary or film technique originally used in Greek tragedy, where the significance of a character’s words or actions is clear to the audience but unknown to the character.

Distancing Effect – breaking the fourth wall, through action, set, or sound

Postmodern Humour – Challenges accepted notions and expectations of genre, philosophy, and humanity.