Sound Designer
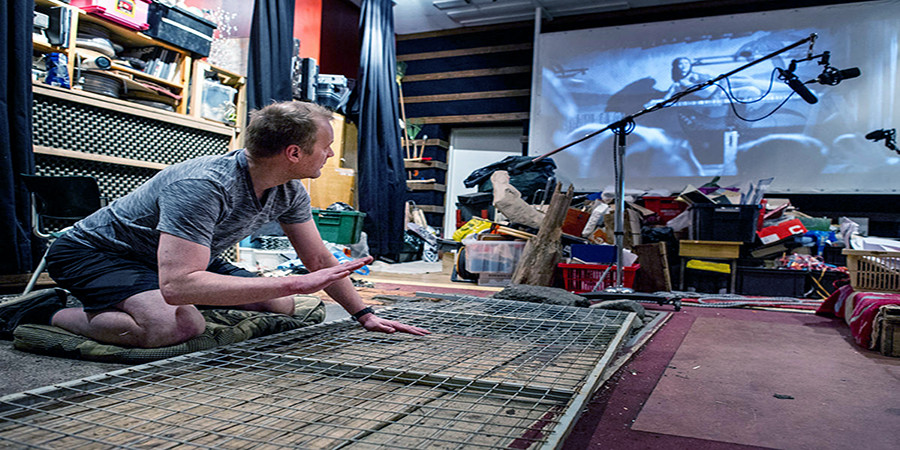
Sound designers find, create (foley) and edit sound to be used in the film. This includes sound effects, diegetic noise, score, etc.
Sound Mixer
Edits and balances the dialogue, sound effects and the other sounds.
Diegetic sound in Joker
An example of diegetic sound in Joker is the people laughing in the comedy club when Arthur is watching the comedian
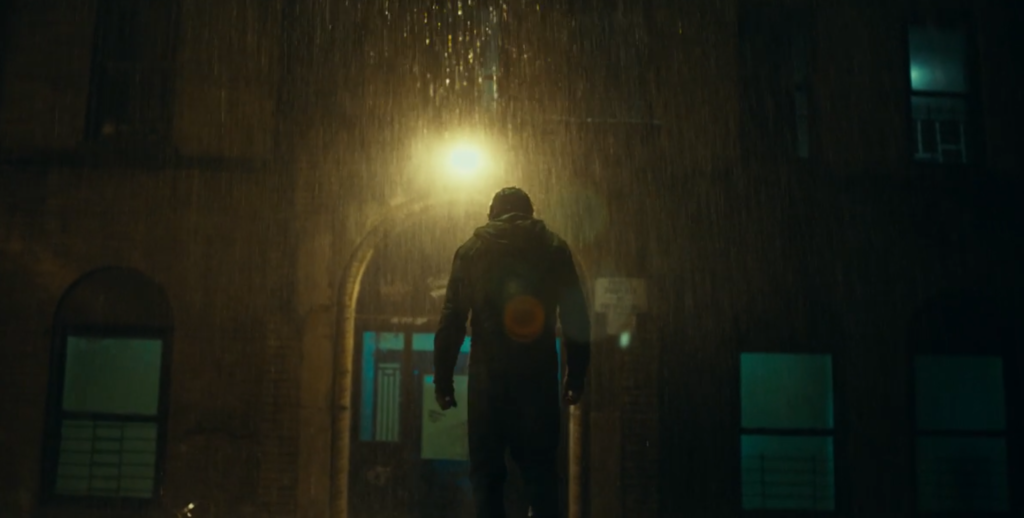
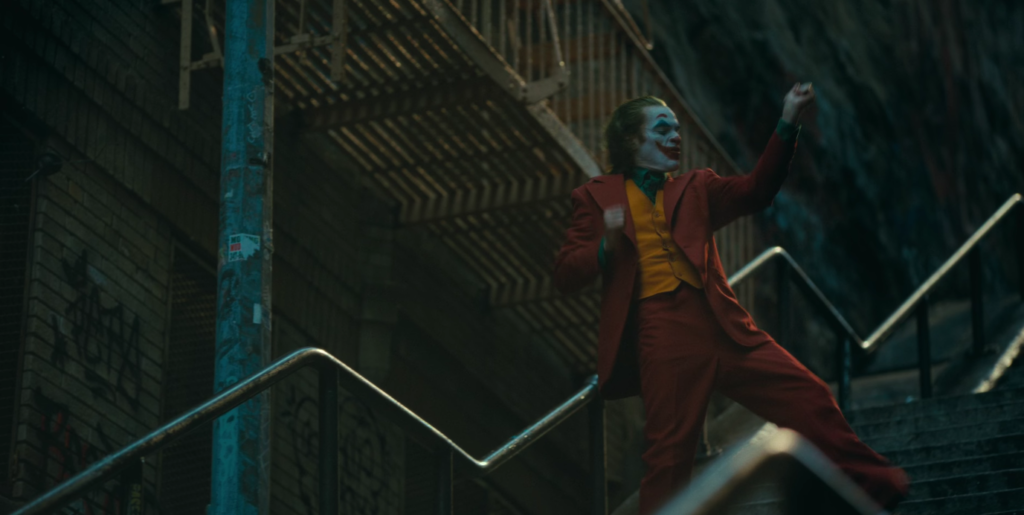
Non-Diegetic sound in Joker
An example of non-diegetic sound in Joker is the creepy orchestral score during Arthurs weird interpretive dance after killing the people on the train
A needledrop is when a licenced song is played in a movie, and it is used to create tension, comedy, and/or emotion for the audience, or set the tone e.g “That’s Life” in Joker, “Cry Little Sister” in The Lost Boys or “Stuck In The Middle With You” in Reservoir Dogs
Sound Effect:
Sound effects are artificially created/edited sounds that are used in film to emphasise an action or create mood and feeling
Foley artists would create sounds like glass breaking, footsteps, walking in sand or snow, impact sounds etc. by creating and using objects to make the sound effects.
A leitmotif is a short, recurring musical phrase associated with a character, like the theme from Jaws, a setting, like in Lord Of The Rings, emotion, like in Stand By Me, or a character’s evolution, like Darth Vader in Star Wars.
L Cuts and J Cuts are “sound bridges” that make the transition from one scene to another smoother
Voice Over is a sound technique where the audience hears the voice of a character or a narrator speaking over shots where the character or narrator isn’t speaking or on screen. Examples of films that use this are Fear And Loathing in Las Vegas, The Crow and Stand By Me. Voice over can also be utilised with an “unreliable narrator”, where the audience is given the information from the biased perspective of the narrator.
Score/Underscore
The score of a film is music composed specifically for use in the film to enhance emotion and themes of what is happening on screen. The Underscore is score that is played under sequences, usually mixed with dialogue and/or sound effects.
Synchronous sound is sound matched with actions being viewed, Asynchronous sound is not matched with what is happening on screen, which can be used to create tension by giving the audience a noise that they can’t match with a source, or giving the audience sound that a character in the film can’t hear.
Sound Perspective refers to the apparent distance of a sound source emulated through volume, pitch and timbre. In Spielberg’s film Munich, sound perspective is used through emphasising sounds to bring attention to important points of the scene, such as the target’s daughter’s footsteps being the dominant sound when she runs back into the building the assassins were going to bomb or silence being broken by the noise of a phone box’s metal dial to create danger and tension.
A soundtrack is music used in and/or made for the film
My favourite film soundtrack is The Crow (1994), as it utilises a lot of bands that I really enjoy to create the grungy, industrial, dark and gloomy setting the film produces. It works so well as it sounds good in the context of the film and is a good soundtrack by itself. There are so many scenes in the film that are elevated by the music, like the iconic scene where Eric puts on his makeup set to The Cure’s Burn, or the scene where he fights the room full of gangsters when After The Flesh by My Life With The Thrill Kill Kult plays.