Even though both sound designers and mixers play very important roles within the world of film, there are some differences between the two, such as:
sound designer – sound designers have the role of recording or finding the audios and sounds used in a specific sequence or scene (e.g. dialogue, background noise, sound effects). sound designers often create their own sounds which often get used as “fillers” in scenes where there might not even be any dialogue.
Diegetic & non-diegetic sounds
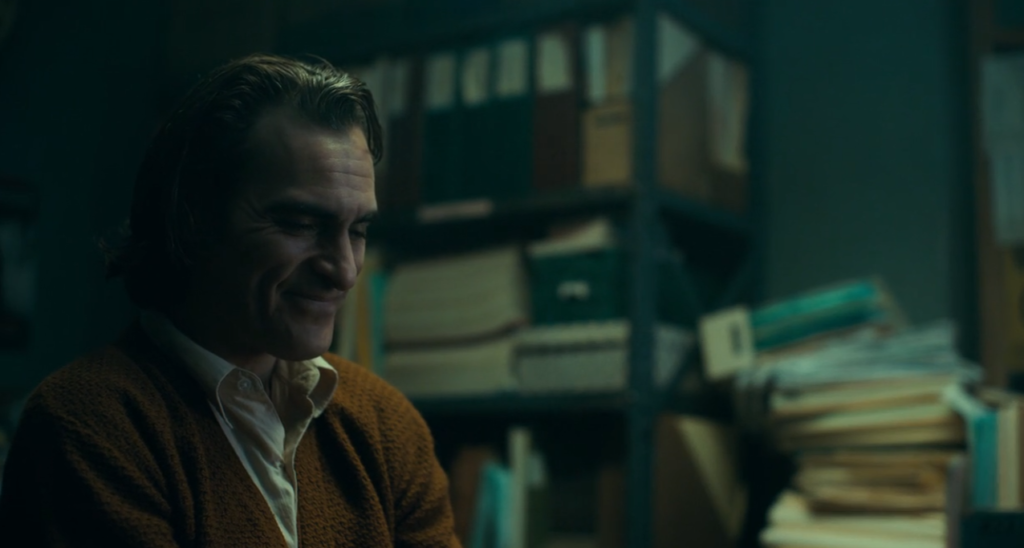

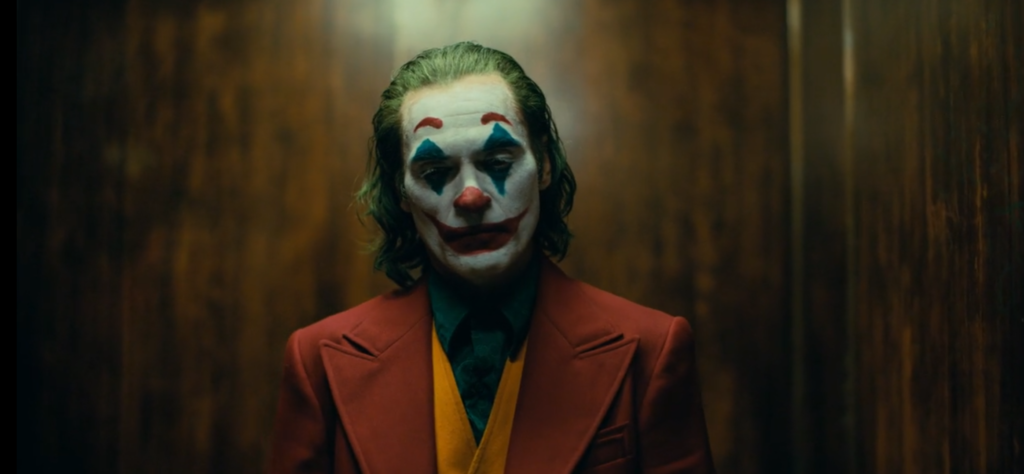
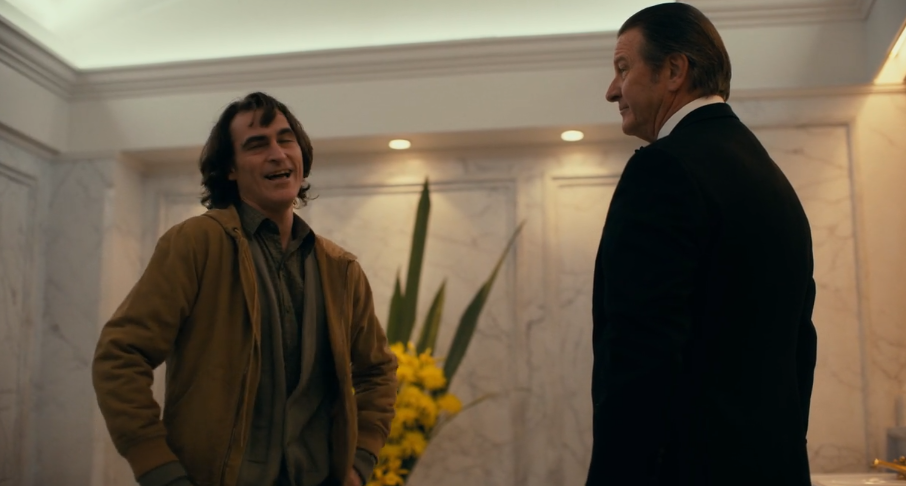
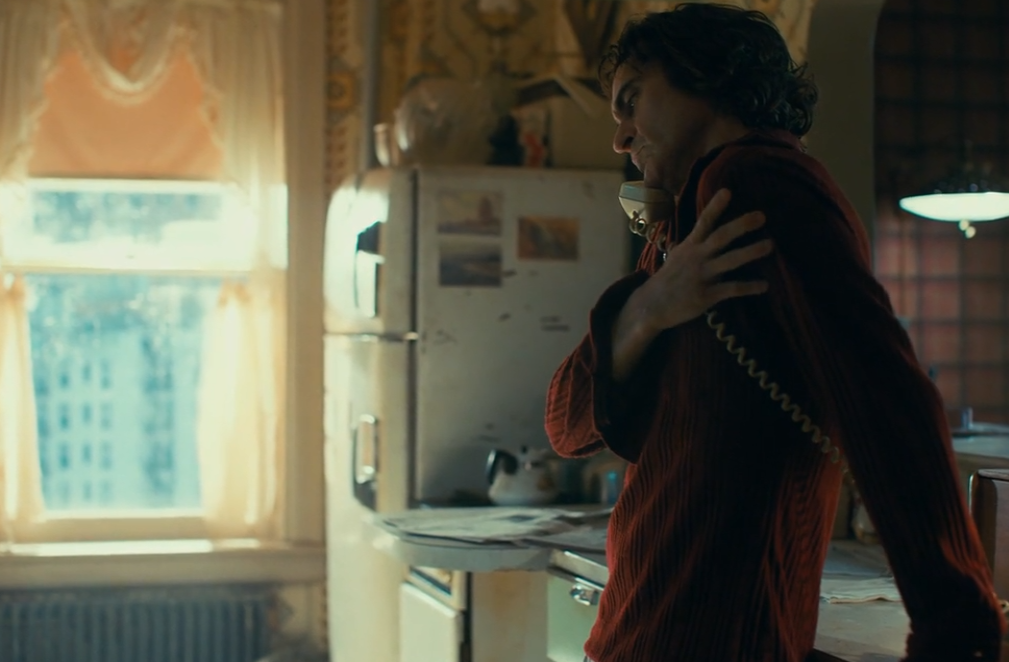
Non-diegetic: This scene in joker begins with no sound at all other than the subtle dialogue between Arthur and his social worker however, as the dialogue gets more “heated” and tense, tense music starts playing over the top. As the scene goes on, the music gets louder and louder creating tension and anticipation making the audience curious and intrigued.
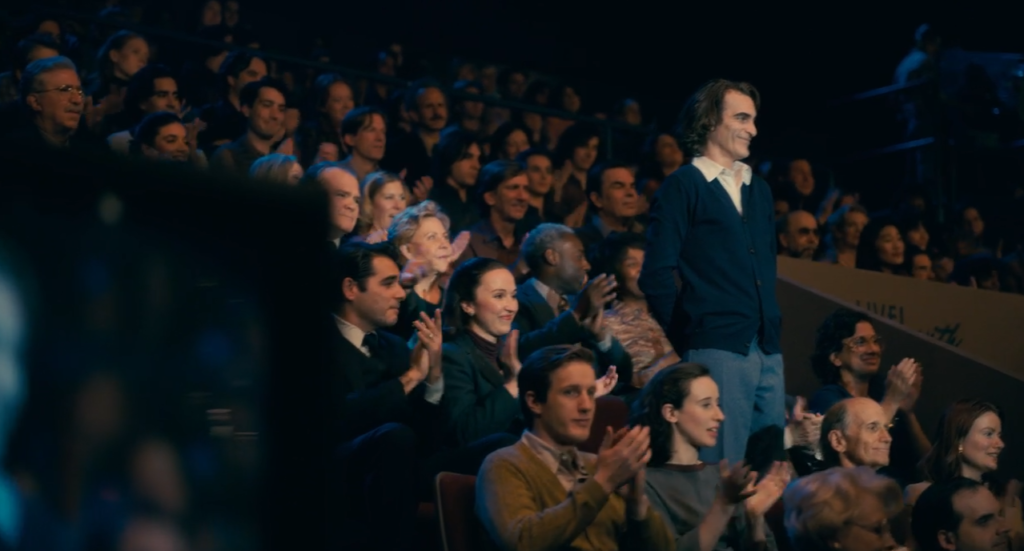

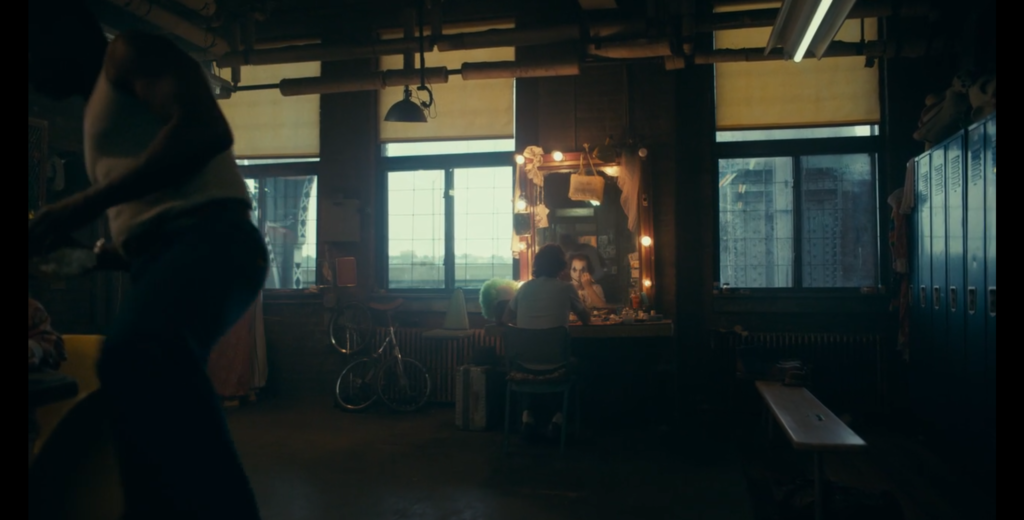
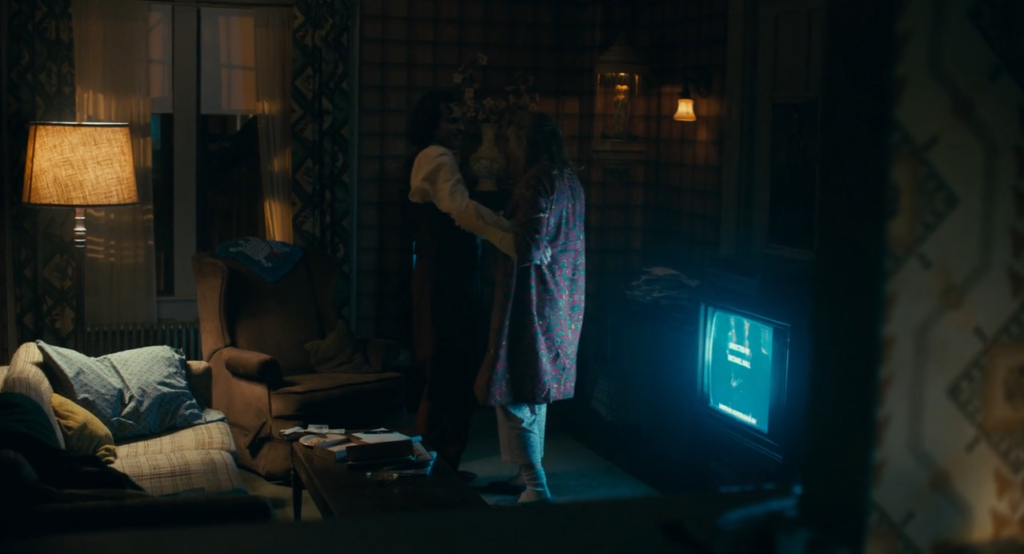
Diegetic: This scene in Joker had the diegetic sound of applause happening in real time with the actions in the movie making it authentic and makes it seem as if we (the audience) are there living it with him.
synchronous – sound which is matched with the actions and movements being viewed.
asynchronous – sounds which are not matched with what the audience is seeing, usually used to create tension as the4 viewer can hear the sound but not see the source.
sound mixers – sound mixers are in charge of figuring out the timing of when those sounds get used in the sequence or scene. They have the skill of mixing sound elements together in order to make the final sound track sound like a whole.
sound effects – artificially created of enhanced sounds which are used in artistic ways to emphasise an action, mood or feeling.
Foley artist – creating a clean sound replicating what is on screen which then gets added in post-production.
leitmotif – “short, recurring musical phrase” associated with a particular character, setting, emotion and development of a character. “leitmotifs are guides” they condition the audience emotionally for the interventions, arrival or actions of a particular character.
sound J & L cuts – sound bridges which creates a smooth visual transition between scenes.
voice over/ narration – often informs the audience with all the information they need about a certain character or event, this can sometimes also be presented as “unreliable narration” meaning the viewer does not get all the information straight away.
musical score – pieces of music specifically created for a film/specific scene.
underscore – music playing “under” the dialogue between characters, usually quite quiet.
needle drop – popular pre-exciting pieces of music (out of the world of the film) which helps set the tone of the scene, this can go with what is happening in the scene or juxtapose it which usually creates a “jarring” of off-putting mood.
sound perspective – the apparent distance of a sound source, this can be supported by its volume, timber and pitch.