




Initial Rating – 9/10
What I enjoyed about Casablanca was it’s simplicity, set design, and character dynamics. Each character got a satisfying development across the story and it led to me feeling sympathetic for the problems being faced by our main trio. The design of Rick’s bar, as well as the exterior shots of Casablanca, were visually interesting and kept me engaged in the story unfolding. As for the editing style, I can’t say that it made the movie any more interesting to me but it worked well for the themes being portrayed in the movie.
Humphrey Bogart – Rick Blaine
Bogart had a successful Hollywood career prior to Casablanca, usually playing secondary villain characters until being cemented as a suave leading man by Casablanca. On contract with Warner Bros, and originally not cast as Rick (for Ronald Reagan)
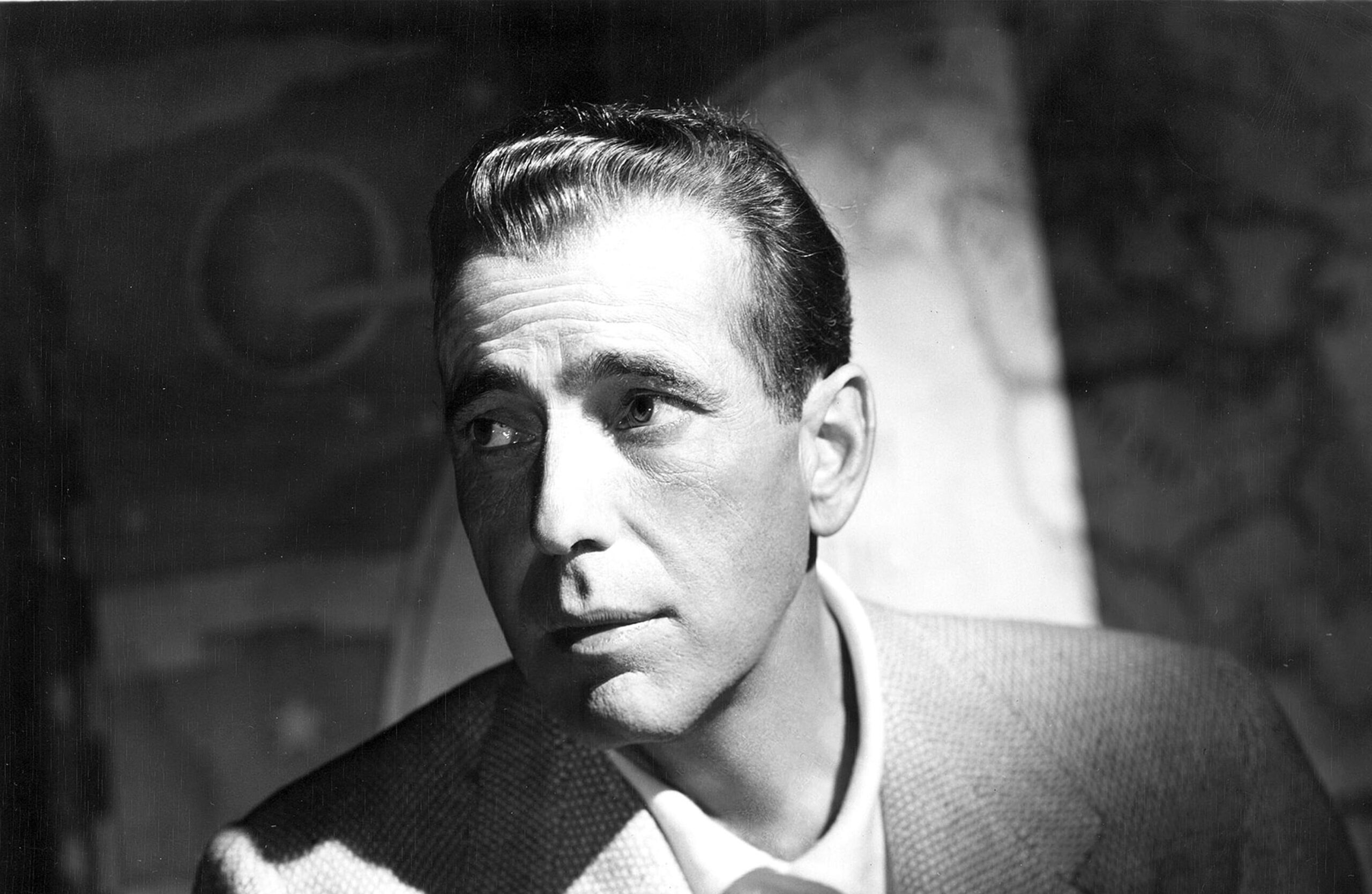

Ingrid Bergman – Ilsa Lund
As Ingrid was of Swedish origin, she waconsidered ‘exotic’ by American producers, and Curtiz wanted Ilsa to be played by a foreign actress, as he thought they would be able to sympathise with her character. She was active in Europe before Casablanca, being in films like 1936’s On the Sunny Side, or 1935’s Walpurgis Night.

Paul Henreid – Victor Laszlo
Paul was born in Austria to Austrian-American parents, and developed a love for acting early on. Paul was originally attracted to the role of Victor due to his hatred for the Nazi regime, as he was sectioned into concentration camps before reaching America.

Claude Rains – Captain Louis Renault
Rains was a British actor known for playing villains, like The Phantom Of The Opera and The Invisible Man

Conrad Veidt – Major Strasser
Conrad was from Germany but strongly opposed the Nazi regime, speaking out against their anti-sematic viewpoints. Most of his filmography features anti-nazi and anti-war films, apart from occasional villainous roles like in “The Cabinet Of Dr Caligari” and “The Man Who Laughs” (in which the character he plays became the inspiration for DC’s Joker)
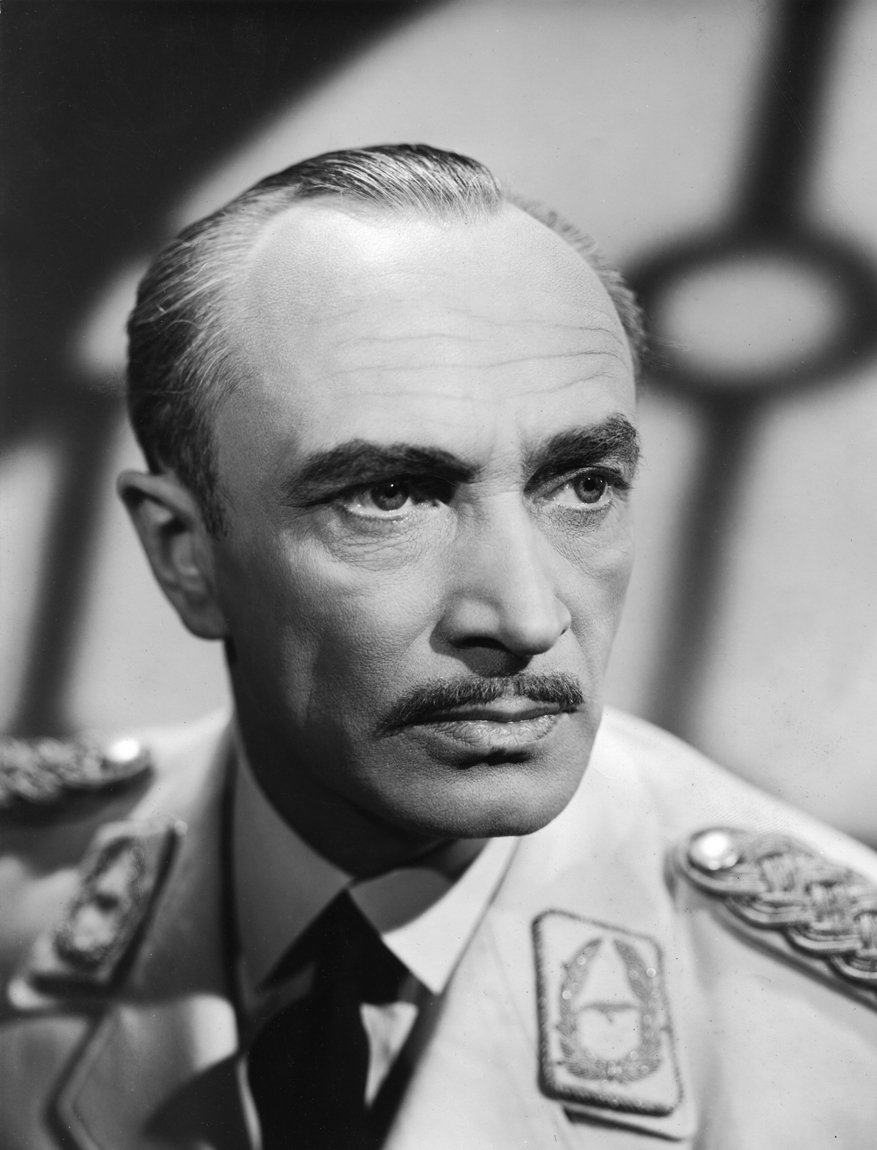

Sydney Greenstreet – Signor Ferrari
Greenstreet avoided appearing in any films until he was 61, where he worked with Humphrey Bogart in “The Maltese Falcon” only a year before Casablanca.

Peter Lorre – Ugarte
Lorre was a Hungarian actor, who was known for playing “timidly devious” characters. He worked with Warner Bros for years on different crime films.

S.Z. Sakall – Carl
Sakall is a Hungarian actor who worked on stage throughout the 10s-20s. He moved to Hollywood after the Nazi’s pushed him out of Berlin. He spent his career playing supporting roles in film and musical.

Madeleine LeBeau – Yvonne
French actress who fled France with her Jewish husband after Axis takeover, once arriving in America she was given a contract by Warner Bros and started with Casablanca

Dooley Wilson – Sam
Wilson was a popular musician in the 20’s and 30’s, having toured across the world with his band before starring in Casablanca.

Joy Page – Annina Brandel
Though her stepfather was the head of Warner Bros, he did not want Page to be in Casablanca. Reluctantly she was cast at age 17, and never made any movies with Warner Bros again

John Qualen – Berger
Originating in theatre troupes in America and Canada, Qualen went on to make over 100 movies across his career, with his biggest role being in 1940’s “The Grapes Of Wrath”

Mise En Scene in Casablanca
Although Casablanca is set in Morocco, it was shot on a soundstage in Burbank, California; specifically in Warner Brothers Studios. It was chosen to be shot on specially designed soundstages instead of on location in Morocco due to both the expense of international production and the ongoing war in Morocco at the time. Each set was built for the movie, meant to mimic actual Moroccan architecture to create verisimilitude for the settings.
Editing in Casablanca
Casablanca utilises the invisible style of storytelling to engage us in the character’s personal relations. The very claustrophobic and intimate shots of Rick and Ilsa we see when they are talking in Rick’s bar clue us in to the dynamic that they share, and allows us to connect with the emotional tone of the scene.
Sound in Casablanca
Max Steiner composed the orchestral score for most of the film, which provided an epic and patriotic feel to particularly emotional scenes. Though it is synonymous with the film, “As Time Goes By” wasn’t written for Casablanca, it was written for a Broadway musical by Herman Hupfeld.
Aesthetics in Casablanca
Casablanca’s set and costume is designed to specifically create verisimilitude for Casablanca, trying to precisely mimic the architecture and sensibilities of an urban Moroccan town.
Hal Wallis, as producer for Casablanca, put together the production team and script for the movie.
Themes and Issues
Isolationism – a policy of remaining apart from the affairs or interests of other groups, especially the political affairs of other countries. Rick starts the movie as an isolationist, but ends as a sentimentalist and a patriot.
What was America’s view on WWII? 88% of Americans opposed the idea of declaring war against the Axis powers in Europe, and only 35% of Americans believed their government should risk war to help the British.
Representation in Casablanca
Women: Minor female characters, only used as love interests or “damsels in distress” if not background characters, gender roles reinforced
Men: Leading force of the story, all characters with authority are male, gender roles reinforced
Authority Figures: Police, private investigators, all white males
People Of Colour: Only a few POC characters, most notably Sam, the piano player
Americans: Rick and Sam, presented as positive and in demand characters
Europeans: Most European characters as shown to be struggling immigrants caught between war-torn countries
34 different nationalities are represented in Casablanca, both in front of and behind the camera.
Political and Social Contexts in Casablanca
ALLIES – Great Britain, The United States, and The USSR
AXIS – Germany, Italy, and Japan
France was occupied quite early in WWII, causing some rogue soldiers to become the “free French” (allies). Vichi France is a territory occupied by the German forces in France, run by a pseudo-German government (has control over Casablanca)
WWII starts in 1939, but The US doesn’t join the war until the December 7th Pearl Harbour bombing by Japan in 1941, prompting their entry to the war.
Operation Torch
Allied invasion of French North Africa during WWII. Torch was a compromise operation that met the british objective of securing victory in North Africa while allowing American armed forces the opportunity to begin their fight against Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy on a limited scale. “It captured the zeitgeist”
On November 26th, 1942, Casablanca was premiered in New York City
Casablanca Conference
Was held in Casablanca, from Jan 14-24 1943. Used to plan the Allied European strategy for the next phase of WWII. Main discussion was between US President Franklin B Roosevelt, and British PM Winston Churchill.
Americans learn about the war through Newspaper, Radio, and Film.
(1900-1930)
Film makers and producers moved to Hollywood to avoid Thomas Edison’s lawyers in New Jersey, and because of it’s usually sunny weather and diverse landscapes
Some of the big stars, directors and pictures from the Silent Era of Hollywood were Charlie Chaplin, Greta Garbo, Buster Keaton, John Gilbert, Nosferatu, and The Cabinet Of Dr Caligari
The early Hollywood studio system was like a factory or production line, as they integrated an assembly line method of creating a movie, by having specific jobs done in order to efficiently produce their films
The first “talking picture” was The Jazz Singer, which released on the 6th of October, 1927
The end of the silent era caused problems for some performers working in the film industry as many actors didn’t have the voice for talkies
The Great Depression, World War I, the Wall Street Crash, and the Dust Bowl were happening in America (and around the world) at this time in cinema history
The Hollywood Studio System
(1930-1947)
•1) What were the Big 5 studios & what type of movies was each studio famous for? Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, Paramount, 20th Century Fox, RKO, Warner Brothers
•2) Explain what vertical integration and block-booking was? Vertical Integration was when a production company owned all parts of movie production and distribution, and block-booking
•3) Why and when did the original studio system collapse? It was challenged under the antitrust laws in a 1948 Supreme Court ruling which sought to separate production from the distribution and exhibition and ended such practices
•4) What was happening in America(and around the world) at this time? The Great Depression had just started and WWII was right in the middle of the era, so people were worried at about war and financial struggles during the Studio System period
•5) What genres were popular and why did people go to the movies in this period?
gangster films, musicals, historical biopics, social-realism films, lighthearted screwball comedies, and westerns were all popular at the time, and people went to the cinema as a form of escapism from the grim reality of the post-depression society they lived in
Classic Hollywood Style
What is meant by the invisible style of storytelling? Subtle cuts and non-distracting set and costume design contribute towards an immersive storyline and character development
What is continuity editing? When shots are presented chronologically to provide a cohesive storyline for a movie
Aesthetics are the colours, shapes, and objects that can be categorised based on the emotion/feeling they evoke.
Realism
Verisimilitude – The appearance of being true or real.

Social Realism – work that aims to draw attention to the real socio-political conditions of the working class as a means to critique the power structures behind these conditions.

Magic Realism – a literary or artistic genre in which realistic narrative and naturalistic technique are combined with surreal elements of dream or fantasy.

Hyperreality – an artificially created copy that is perceived as somehow more real than the real thing, or too real to be real.

Visual Style
Iconography – the use of recurring visual images and symbols in movies that convey specific themes, evoke emotions, and build a film’s narrative identity.
Intertextual Referencing – when a text implicitly or explicitly refers to another text, by using distinctive, common or recognisable elements of the referenced text.

Visual/Sound Motifs – a recurring story element that acts as a way to highlight a films thematic meaning.

Colour Grading – post-production process of altering the appearance of an image for presentation in different environments on different devices.

Auteur Trademarks – A directors “iconic” style of direction

Tone
Pathos – an emotional appeal to an audience.

Bathos – an effect of anti-climax created by an unintentional lapse in mood from the sublime to the trivial or ridiculous.

Suspense – a state or feeling of excited or anxious uncertainty about what may happen.

Comedy – type of drama or other art form the chief object of which, according to modern notions, is to amuse.
Dramatic Irony – a literary or film technique originally used in Greek tragedy, where the significance of a character’s words or actions is clear to the audience but unknown to the character.

Distancing Effect – breaking the fourth wall, through action, set, or sound

Postmodern Humour – Challenges accepted notions and expectations of genre, philosophy, and humanity.

Impressive Phrases:
“This “reframing” of the central character” has a potentially cathartic effect on the spectator“
“Arthur, who was earlier depicted as pathetic and sad, is now depicted as powerful and heroic.“
Diegetic: something occurring within the context of the story and able to be heard by the characters.
Cathartic Effect: the release of strong emotions through a particular activity or experience
Reframing: change in camera angle without a cut and can include changing the focus of the scene
Connote: to imply as a consequence or condition. Synonyms include imply, suggest, indicate, signify, etc etc
Paragraph Structure: Point / Example / Explain / Link
Throughout Joker, cinematography is used effectively to create a sense of chaos within the film’s diegetic world. This is particularly evident in the scene towards the end of the film where Arthur is shown in a low- angle, close-up looking out of the police car window and reacting with glee at the riots taking place around him. Here, the camera is used to position the spectator as not only connecting with Arthur, but now looking up to him. This suggests to the spectator that the tables have turned and Arthur, who was earlier depicted as pathetic and sad, is now depicted as powerful and heroic. This “reframing” of the central character” has a potentially cathartic effect on the spectator who has, up until this point, been encouraged to sympathise with Arthur’s point of view as a victim of circumstance. The deliberate and stylised use of this slow-motion reaction shot, enables the spectator to get a sense of poetic justice being served: Arthur is now on his way to prison.
Young People:
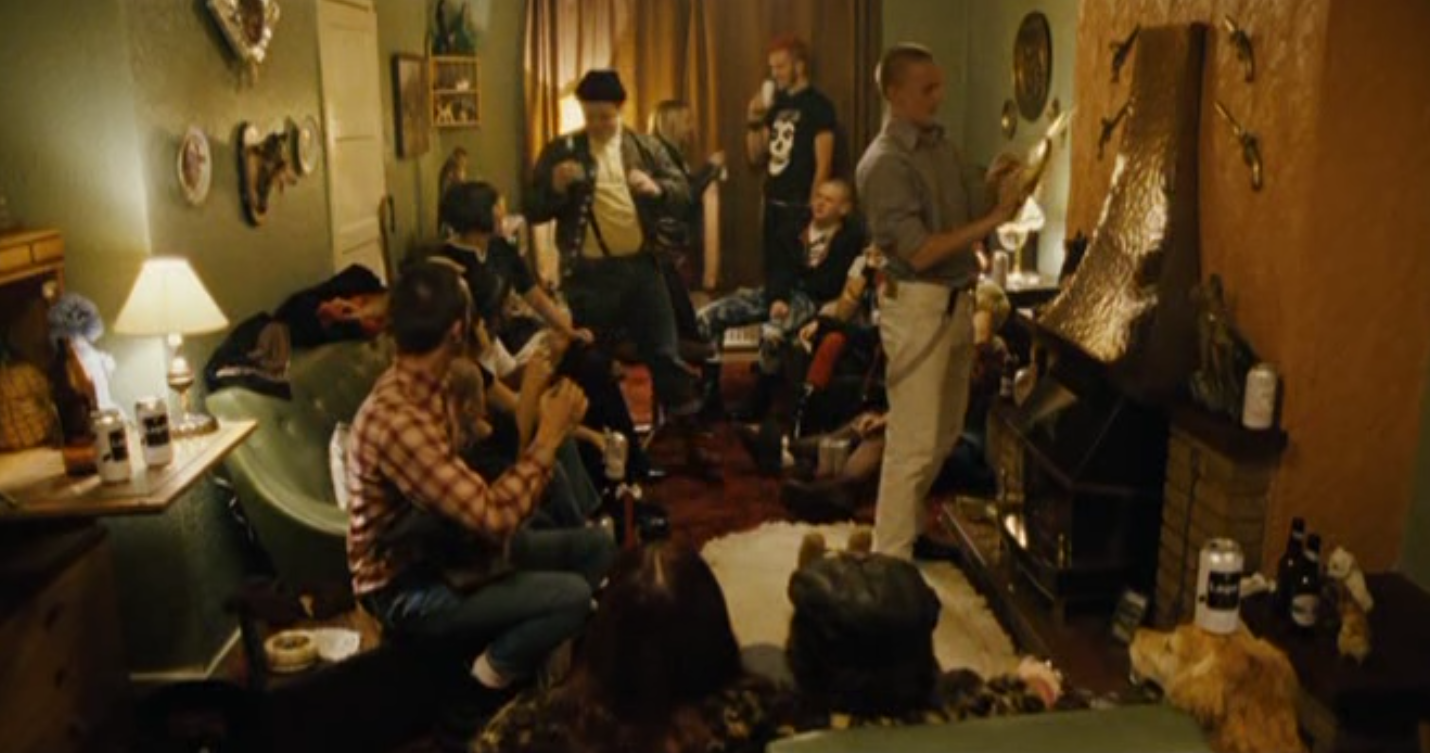
Young people are shown in This Is England to be reckless and irresponsible. At various points throughout the movie, we’re shown the younger characters in the movie making irresponsible or wrong choices, not caring for the consequence of their actions. Examples of this portrayal are how Woody and his gang go to an abandoned housing complex to destroy the building for fun, or how Gadget goes to Combo’s gang purely out of spite, instead of because of his belief in their politics.
Older People:
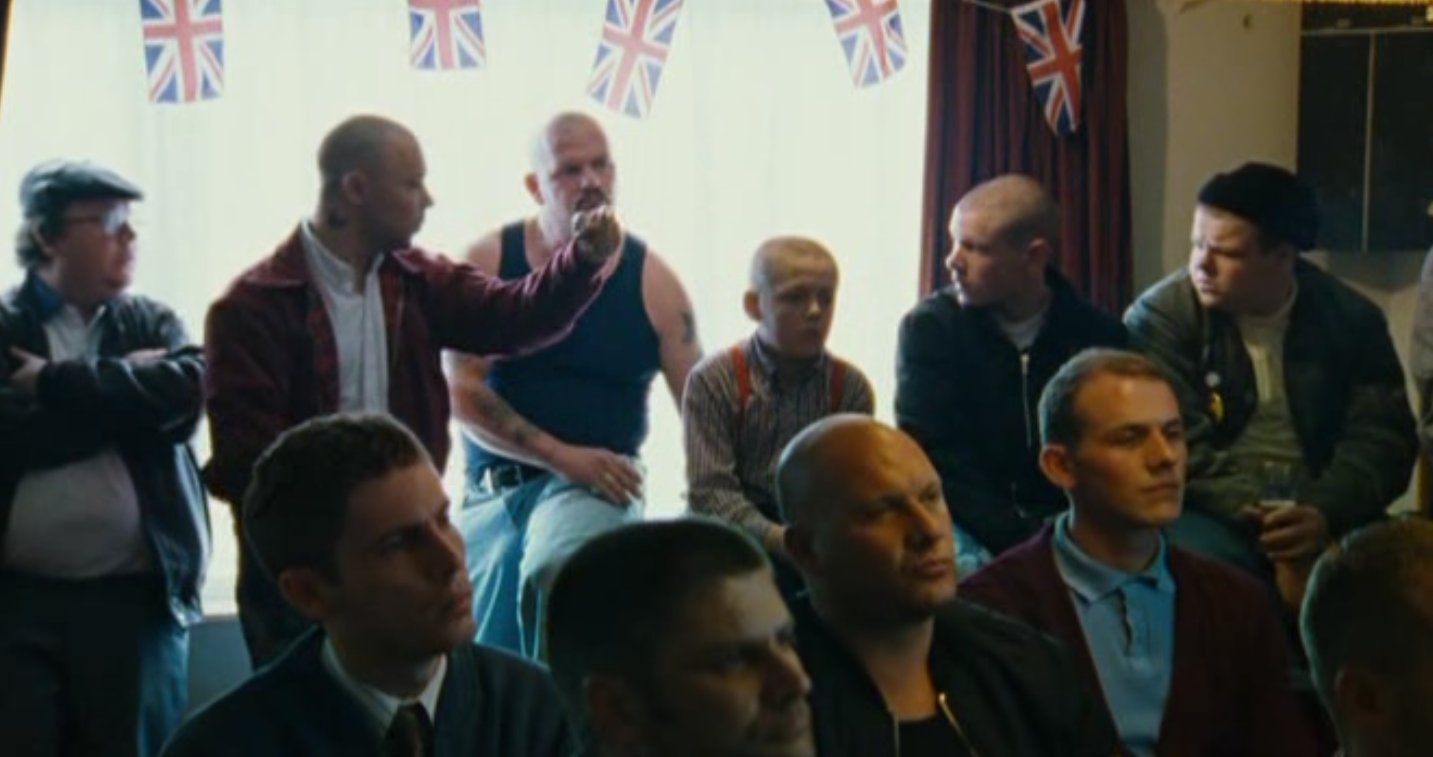

One of the few times we see characters in This Is England that are older than their early 20’s is when Combo and his gang attend the nationalist rally. This shows that the older generation at the time would’ve cared about the nationalist policies and agreed generally with the anti-middle eastern policies they carried. This racially insensitive stance paints the older generation as being bitter.
Class:
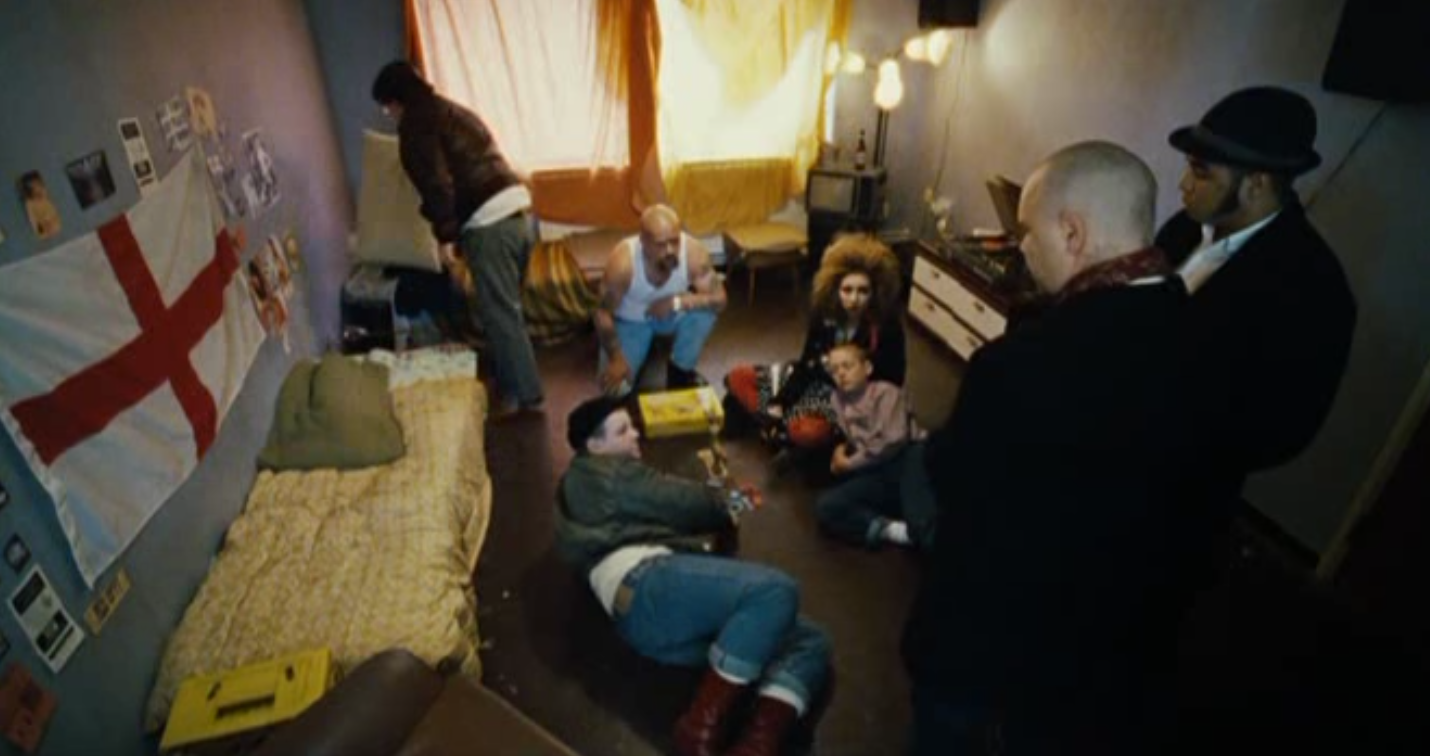

Most of the characters in This Is England are from a lower middle working class background, and the indoor settings they are shown in give us an idea that these lower classes generally have worse living conditions. For example, Shaun lacks real furniture in his room, needing to use a chair as a bedside table, and the paint on his walls is peeling. We can further infer that the living conditions is worse through the actions of each character. Most of the lower class characters shown in the movie show a lack of intelligence, and this portrayal paints the lower classes as being generally less educated than higher ones.
English People:
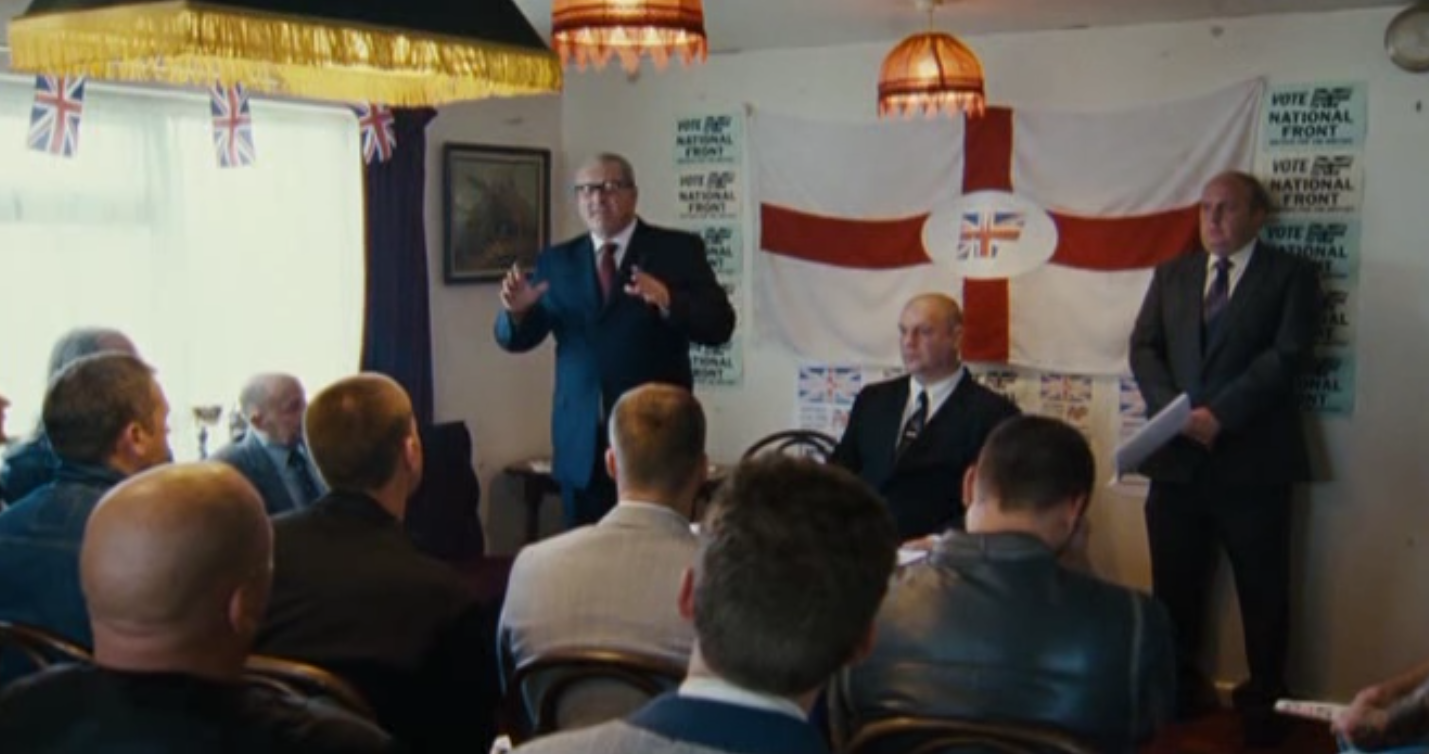

Much like older people, English people are portrayed as being driven by entitlement, through the nationalist party. The only times we hear England being mentioned in the movie is in tandem with the viewpoints of the nationalist party, showing English people as agreeing with nationalist views.
Asian/Black People:
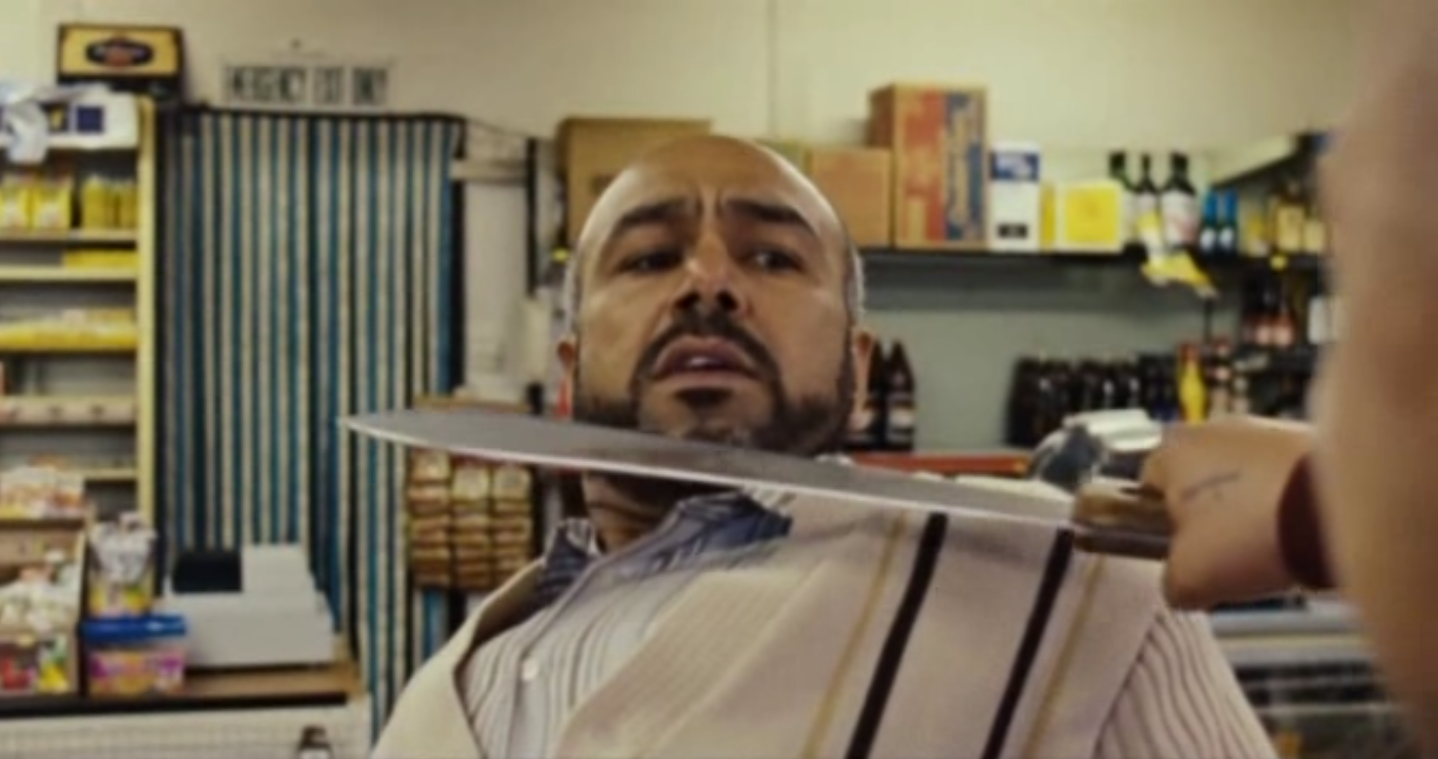

Every racial minority shown in This Is England becomes a victim to Combo and his gang, and these racial attacks portray Asian and black people as being victims in a 1980’s British society, as the common viewpoint of the time was that they were threats to “usual” society.
Men/Masculinity:
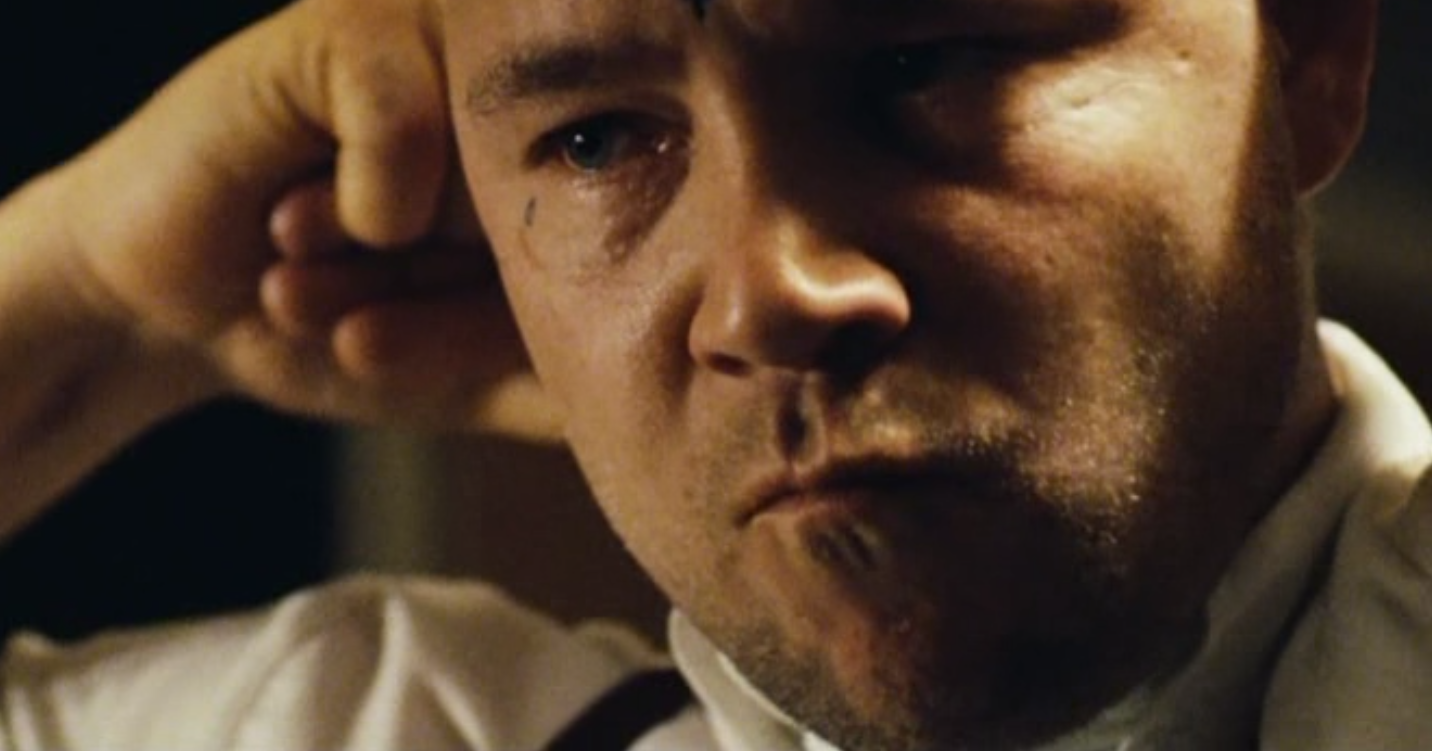

This Is England features toxic masculinity quite strongly, having the first issue of the movie be that Shaun gets bullied for having feminine trousers. Men are portrayed as being excessively aggressive throughout the movie, mainly through Combo. Combo’s irrational and crazed attacks through the latter half of the movie tell us as an audience that masculinity is being portrayed negatively, and as something that leads to most of the “evils” shown in the movie.
Women:
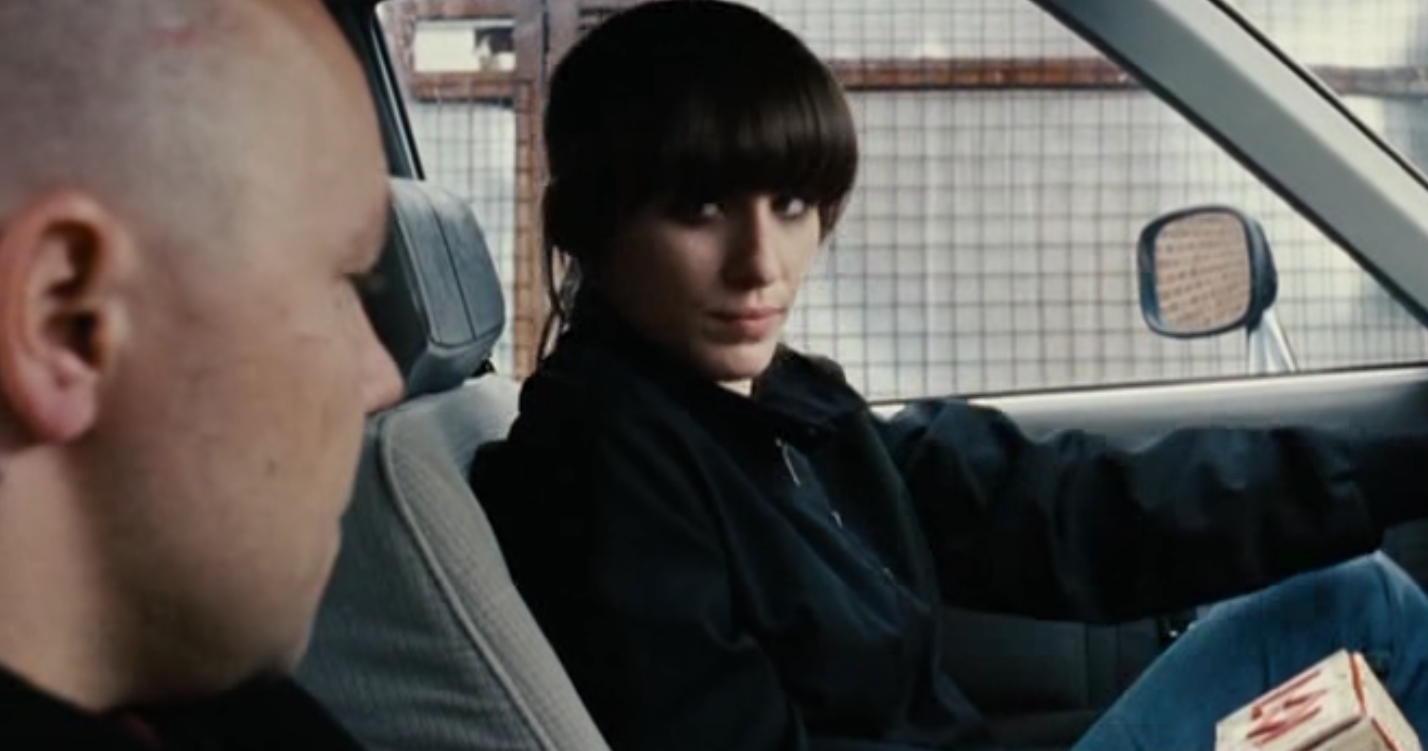

Women take a more submissive role in This Is England, with their plotlines having no agency in the main story of the movie. Although women aren’t directly shown to have agency in the story, Loll acts to portray women as equally as masculine as the main cast of the movie, through her character design and actions towards Combo. Her fearless denial of his love shows that she is a character that can stand up for herself and her skinhead character design helps to roughen up her character, helping subvert typical gender roles for women.
Place:
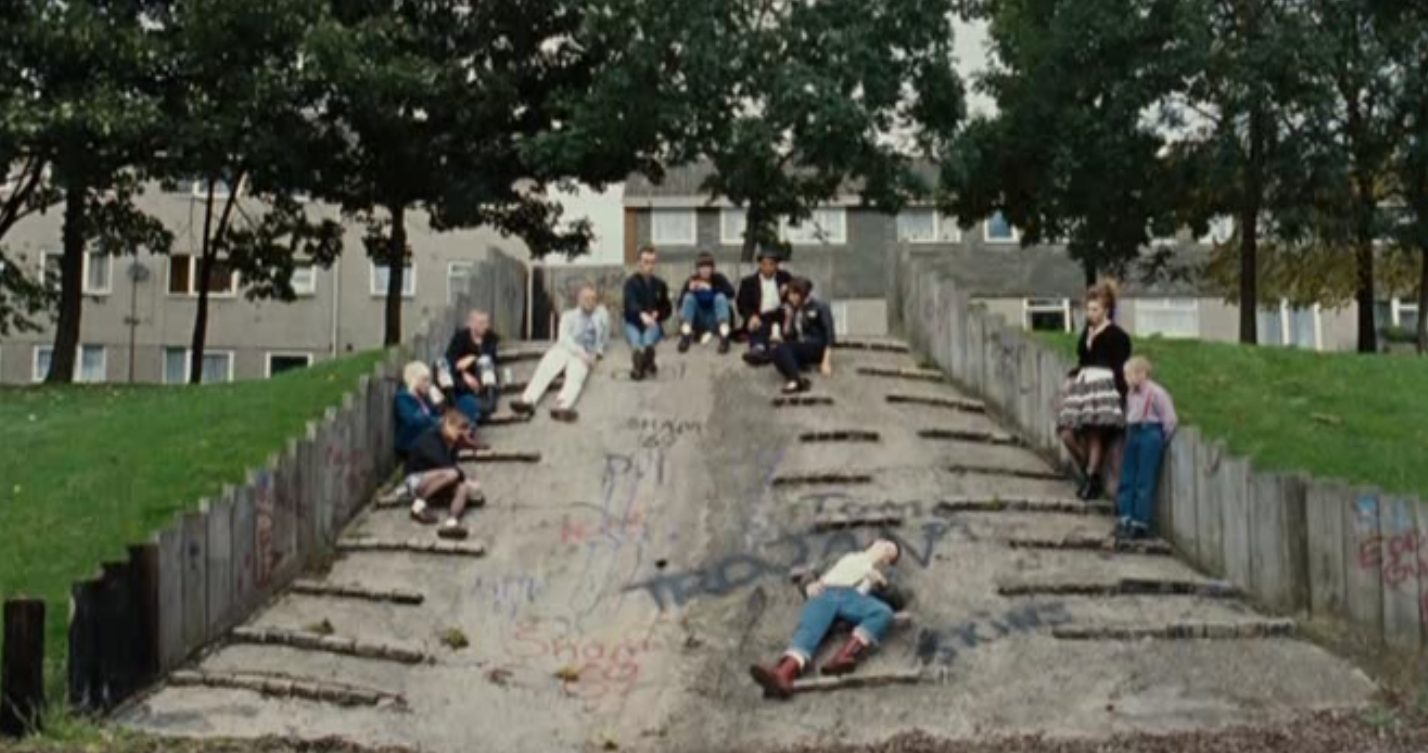

The Midlands are shown to be grimy and urban in This Is England, with a lot of the external set featuring graffiti or broken down/unmaintained housing. This, combined with the aforementioned internal set design, tells us that The Midlands wasn’t a particularly nice place to live in the 1980’s, as it was unkept and ran by the younger (less responsible) generation.
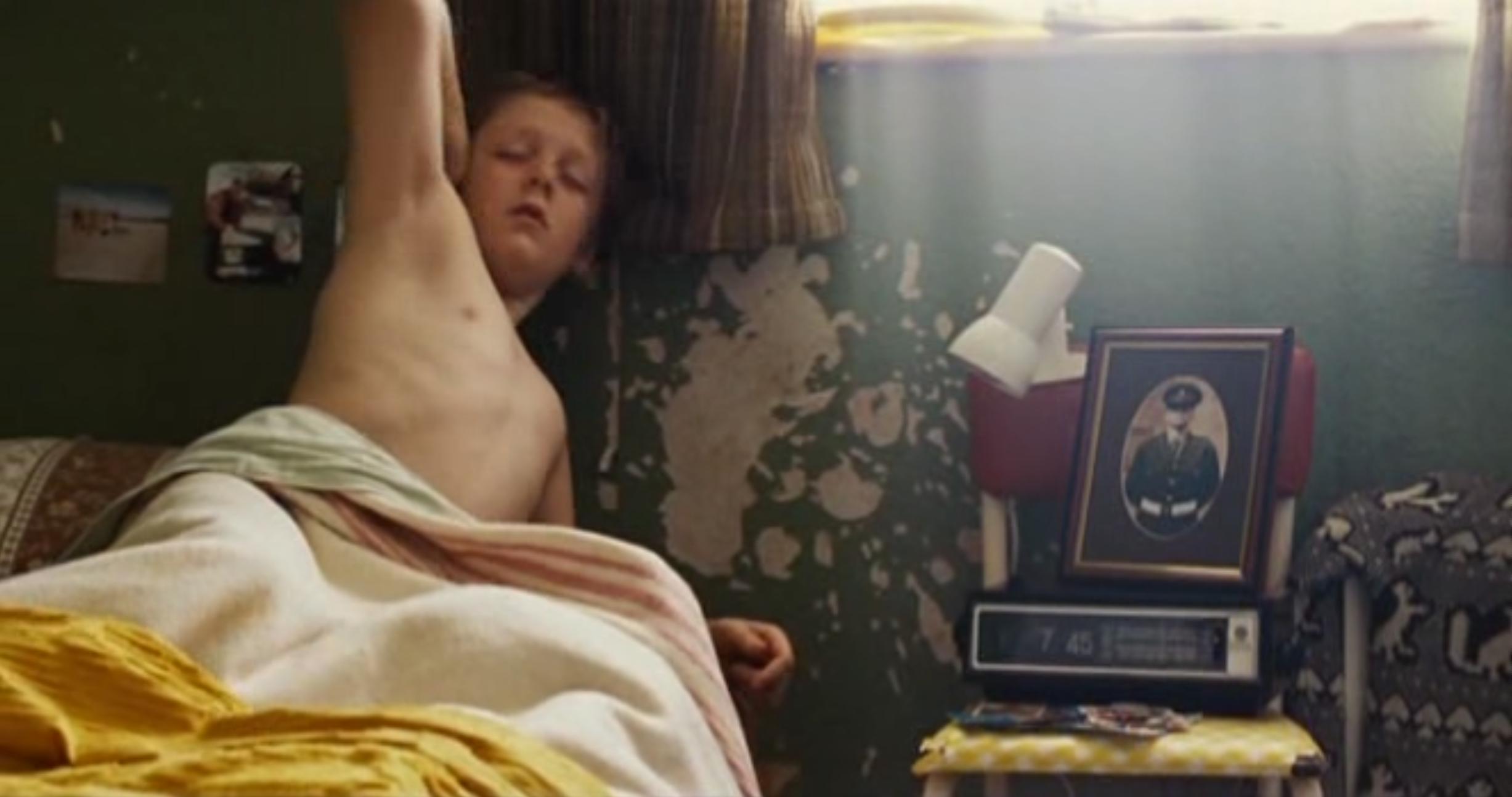
Mise-En-Scene: At 04:06, we see Shaun waking up and getting ready for school. In this shot we see that the paint on his wall is peeling, and that his “bed-side table” is a chair that he’s stacked items on top of. As this is one of the first shots we see of Shaun, we’re instantly made to believe that Shaun is less fortunate when it comes to money, as his mother can’t afford to properly furnish and decorate his room.

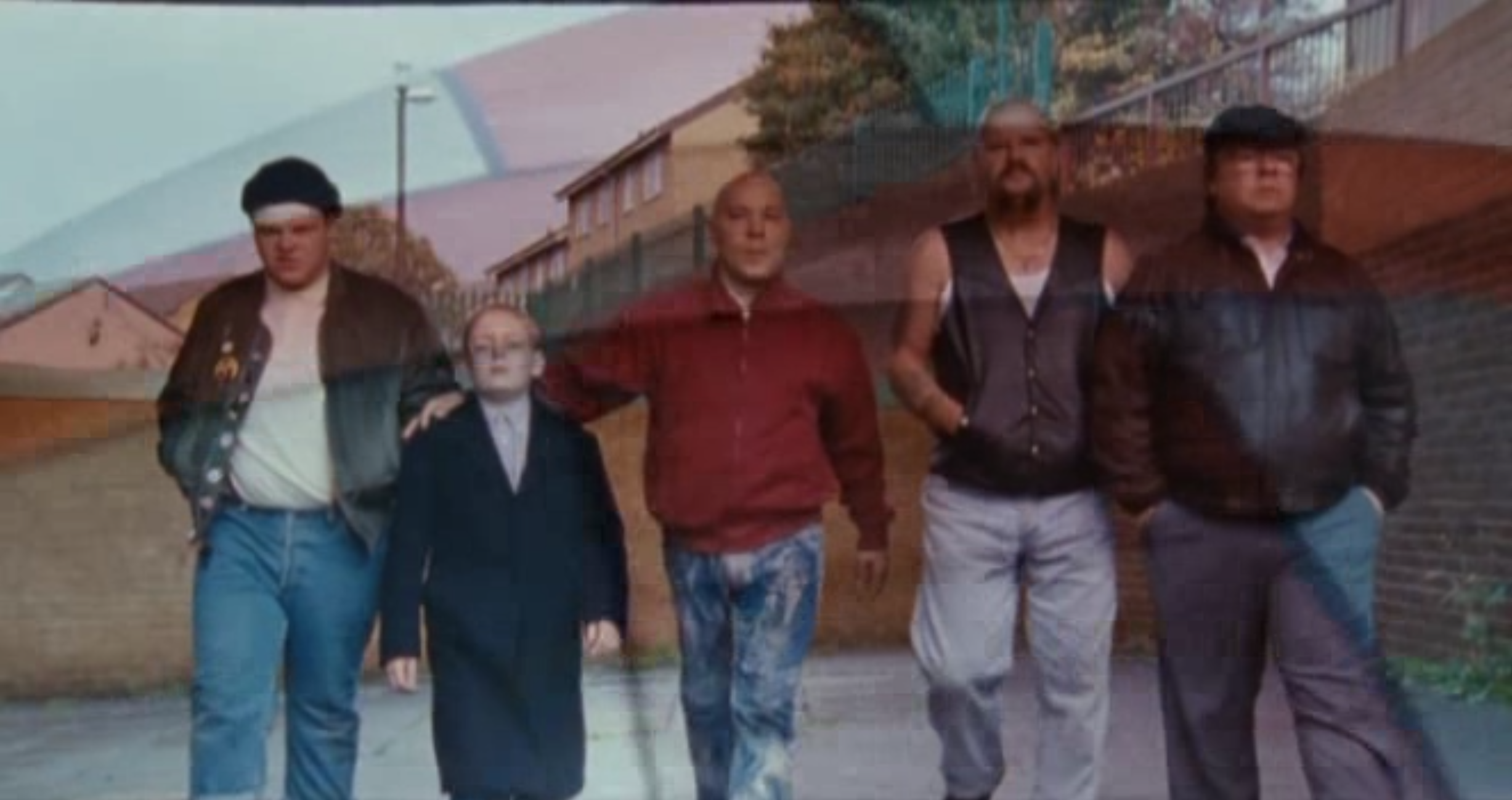
Editing: At 58:50, we see Shaun, Combo, Gadget, Banjo, and Meggy walking together in slo-mo, with the English flag imposed over them. This shot mimics a scene prior, where Shaun is shown walking in the same figuration with his old group, and this shot with the added context of the English flag shows Shaun’s transition to nationalism, through Combo’s mentoring.

Cinematography: At 01:02:50, we see Shaun getting apprehended by the shop owner, ending in the store getting raided by Combo and his gang. During this scene, the camera pans between characters frequently, making the documentary style that the film aims for feel much more realistic, and due to the amount of pans we do, it adds to the franticness of the scene, and throws the audience off when paired with the scenes racist undertones.
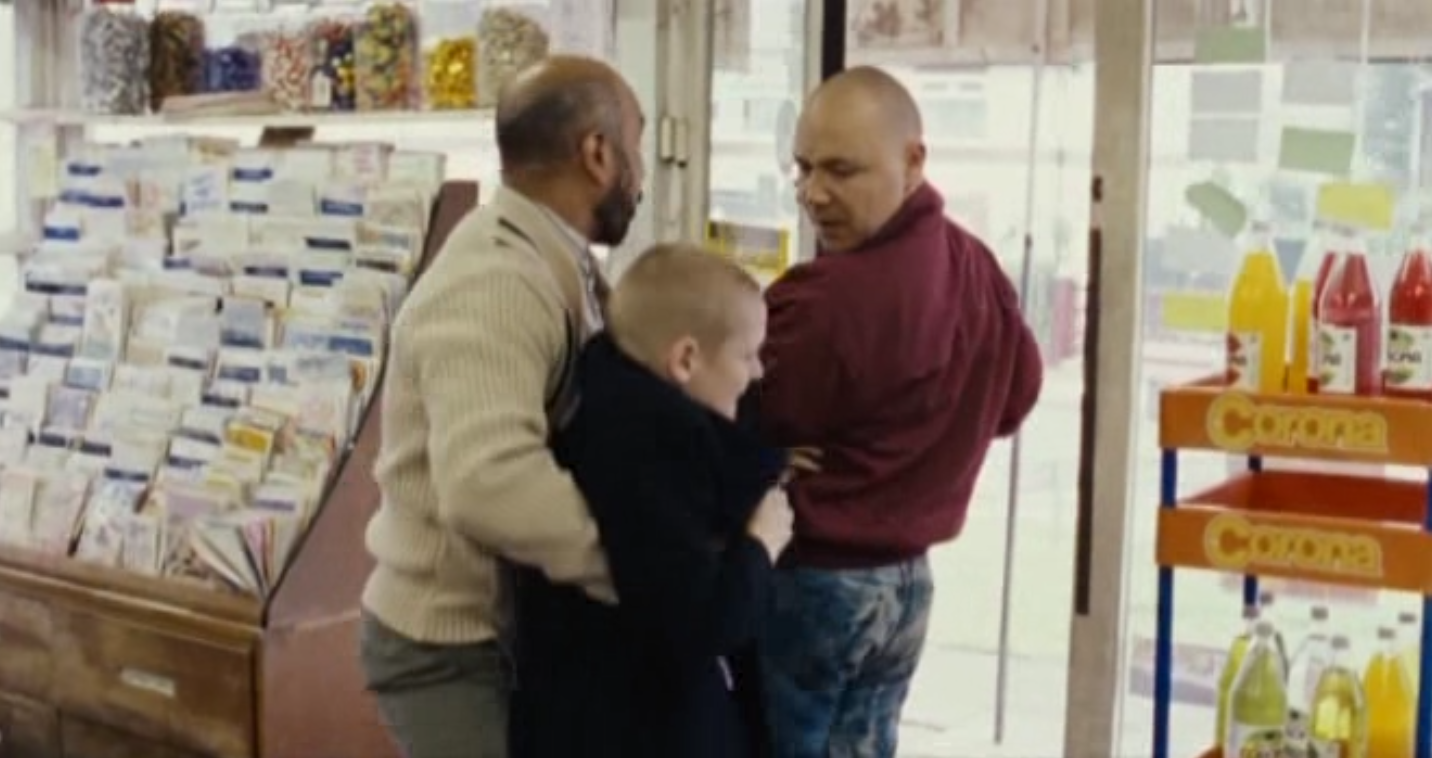

Sound: From 00:00, the movie starts with the song “54-46 Was My Number” by Toots And The Maytals, and this ska track paired with the 1980’s broadcast television footage on screen tells the audience about both the topic and time period this movie is set in. Through the song, we can infer that we will be dealing with the 1980’s Skinhead revival, as Ska was one of the genres skinhead culture was based around.

–
All aspects of film form including narrative contribute to the representations of cultures and societies (gender, ethnicity and age) including the ideological nature of those representations
–
Performance
Age, ethnicity, wardrobe, facial expression, body language, and gestures are all examples of representation through performance.
–
Stereotype
A stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group’s personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes are often overgeneralized, inaccurate, and resistant to new information. A stereotype does not necessarily need to be a negative assumption. They may be positive, neutral, or negative.
–
Countertype
A representation that actively seeks to subvert and challenge negative stereotypes usually of a person, group or place.
–
Sarah Connor Examples
–
Countertype
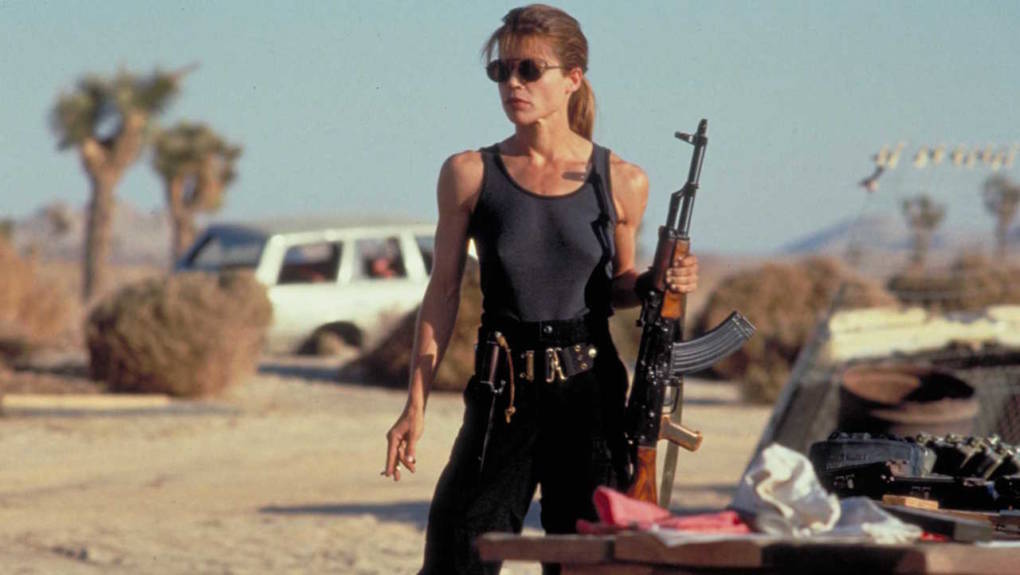

Although Sarah Connor was shown as a submissive female character in the first movie, in the second she is shown a lot more masculine, donning more utilitarian costuming and displaying tight muscles and shorter hair. These all hint towards Sarah fitting a much stronger character type in the second movie, one commonly assumed to be fit with men.
–
Stereotype

In the first movie, Sarah is shown to be a lot more ditzy and feminine, wearing light colours and having large styled hair, whilst working in a service job, we get the idea that this is the “damsel in distress” type character
–
Representations In Trainspotting
–
Danny Boyle
2. WHO IS BEING REPRESENTED ? (Identify specific social groups)
Heroin addicts, Scottish people
3. WHAT SOCIAL GROUPS ARE OMITTED FROM THE REPRESENTATIONS?
POC, women
4. WHAT MESSAGES ABOUT PARTICULAR SOCIAL GROUPS ARE BEING CONVEYED?
People who do drugs are generally less intelligent than clean people
5. WHICH CHARACTERS OR SOCIAL GROUPS HAVE POWER WITHIN THE REPRESENTATIONS?
White men have power, and older people are given the most
6. DO THE CHARACTERS ADHERE TO OR CHALLENGE STEREOTYPES?
Begby adheres to the stereotype of Scottish men being very aggressive and angry
7. ARE THE CHARACTERS TYPICAL OF FILMS IN THAT GENRE?
They don’t fit the typical character types of dark comedies like itself, but the ensemble matches casting of similarly “British” films
8. WHAT DO REPRESENTATIONS TELL AUDIENCES ABOUT SOCIETY AT THE TIME THE FILM WAS MADE AND/OR SET?
As this film is set in Edinburgh, Scotland, the main theme being about drug addiction tells us that Scotland has an issue with drugs
9. HOW ARE ELEMENTS OF FILM FORM (MISE EN SCENE/PERFORMANCE/SOUND/EDITING/CINEMATOGRAPHY) BEING USED TO CONSTRUCT THE REPRESENTATIONS?
The grimy setting of “Mother Superiors” den conveys the idea that drug addicts usually dont pay much attention to taking care of their surroundings, and end up living in nasty conditions
Critical Score: 6/10
This Is England does a great job of capturing a slice of British life in the 1980’s, and while it boasts impressive documentary style cinematography, the shoddy acting and narrative pacing/continuity knocks the movie down significantly. The first 30 minutes act as a highlight for me, as the movie loses steam once Combo is introduced.
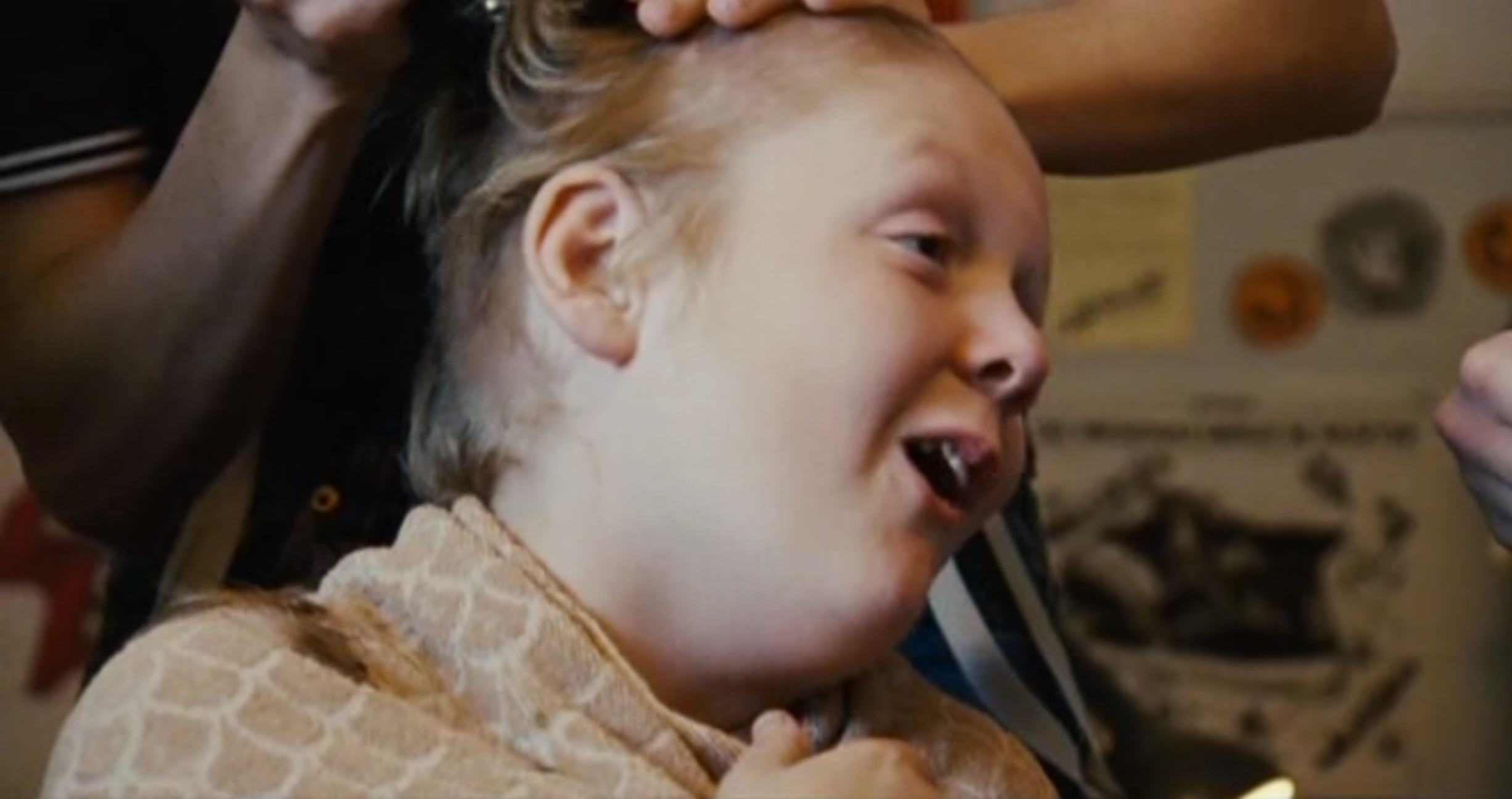
Favourite Scene: Shaun’s haircut
This scene is my favourite as it shows the close relationship that has developed between Shaun and Woody. This lays the foundation for Shaun’s “betrayal” very effectively, by showing Woody as a pseudo-father figure to Shaun, playing on all the things we know about Shaun and his personal life in this part of the movie.

Critical Score: 5.5/10
This film does a good job at capturing audiences attention through its subtly introduced depiction of being under the influence of drugs, and the rather fantastical aspects of this depiction really engaged me through otherwise boring scenes (Spuds job interview, Renton visiting the mother superior whilst on probation, etc). My only gripe with the film is that I felt as if Renton was poorly written, and as he is the main character, this disconnected me from sympathising with his situation, which is the driving force of the film.
Favourite Scene: Spud’s Interview
I’ve chosen Spud’s interview as my favourite scene in Trainspotting as I love it’s use of Mise-En-Scene, shot distances, and Ewen Bremner’s performance to illustrate the effects of drugs on the characters in the movie. In this scene, Spud is at a job interview for a leisure centre, and has just taken drugs to calm his nerves. This scene is set in an office, that is extremely long, so that Spud and the interviewers are on separate sides of the room. This subtle set design mimics the effect that the drugs Spud took will have had on his perception, as the unnatural room size matched with the erratic zooming in and out of the different camera shots used in Spud’s speech create a sense of discomfort and slipping control commonly associated with the side effects of drugs. Ewan Bremner’s performance in this scene is stellar, creating a truly memorable and comedic display of character for Spud, and solidifying his personality in this early stage in the movie.
