
Sound Editing and Sound Mixing
A sound mixer is the leader of the production sound crew. They are responsible for recording the high-quality audio on set. Their job is to set up wires, affixing lapel mics, operating the sole boom mic and also mixing on a mobile controller.
Then, the job of a sound editor is to make sure all the sounds that come together in post-production are in sync and run smoothly. This includes stuff like the three primary elements: dialogue, music and other sound effects. They are sometimes known as track layers.
A good sound editor enhances the quality and continuity of the audio, and can really carry the storyline being played out on the screen by raising the tension or the comedic value.
What is a sound effect?
A sound effect is artificially created or enhanced sounds that can be played throughout the film to emphasize artistic or other content of films. For example the creator of the iconic lightsaber sound from Star Wars is Ben Burtt.
Examples of non-diegetic and diegetic sound
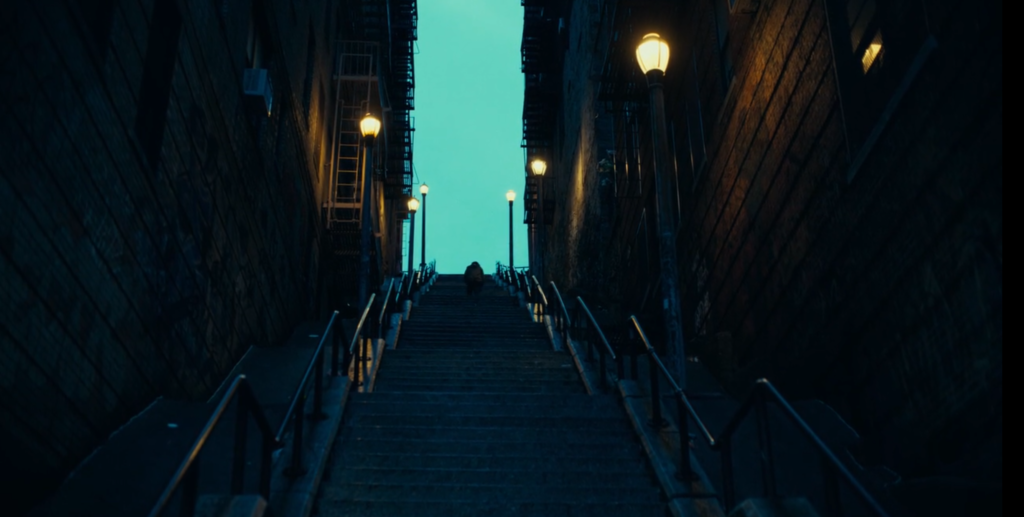

In this scene there is non-diegetic sound. While Arthur walks up the stairs there is a melancholy sounding song in the background.
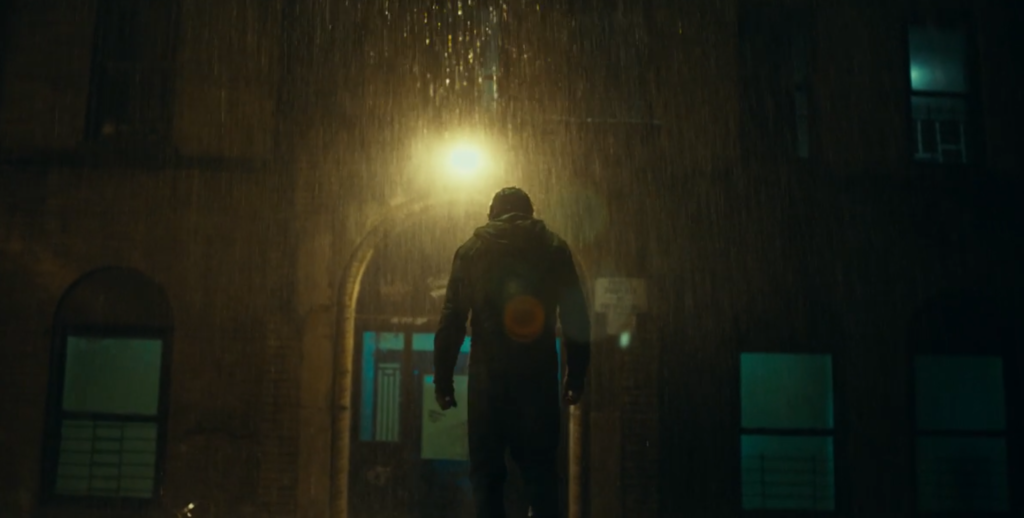

In this scene the sound is diegetic because you can hear the sound of the rain and the Joker can also hear the same, therefore it exists in the world.
Synchronous and Asynchronous Sound
Synchronous sound is sound that is matched with the action and movements being seen. Such as the sound of a water flow near a bank of water, punching sounds during a fight scene, and also character dialogue.
Whereas Asynchronous sound is sound that is not matched with a visible source of the sound on screen. This type of sound can be used when the director wants to create tension (as the audience can hear the sound but not see it). For example when a character on screen is walking down a hallway and they hear a dog barking, yet there is no sign of a dog in the frame.
“A needle drop” in film refers to when a pre-existing song that is usually quite popular is used in the underscore for a certain scene. An example is “Where is My Mind?” in Fight Club.
The Foley Artist
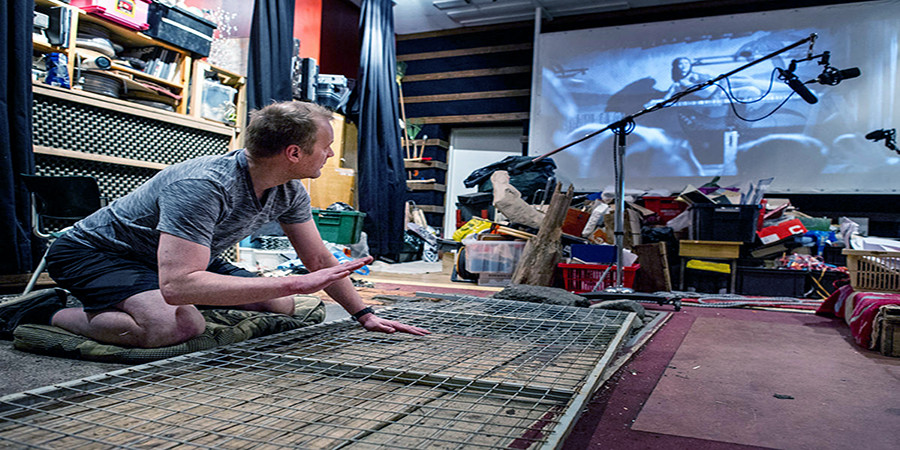

This is a form of creating sound effects using an arsenal of props. They record in a sound-proof studio to produce a clearer sound, and they then layer it on top of images.
Leitmotif
This is a “short, recurring musical phrase” that is immediately associated with something. For example: setting– the Harry Potter theme, character– the Imperial March for Darth Vader, emotion- The Shire Theme in Lord of the Rings (when the characters are thinking of the Hobbiton), evolutions of character- the infamous Up theme (evolution from young life, to then an older life)
Sound bridges
A sound bridge is a type of sound editing that occurs when sound carries over a visual transition in a film.
Two examples of this is the L-Cut and the J-Cut:
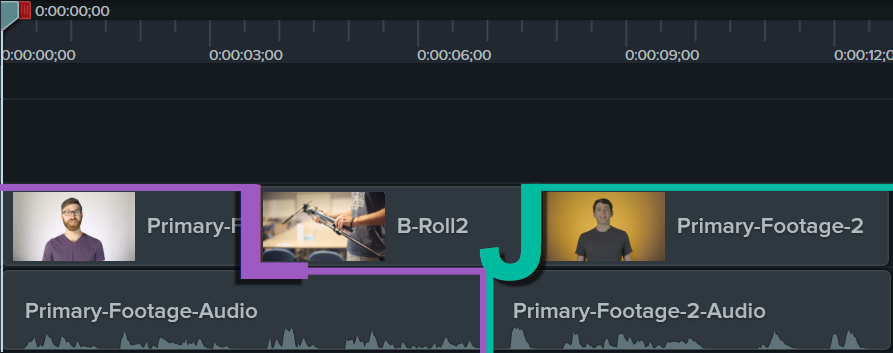
Voice over / Narration
A voice over is a sound device where you can hear the voice of a character and/or narrator speaking but you cannot see them talking while being shown on screen. Narration can be first person, or “voice of god” style. In some cases, this narration and voice over can be unreliable, leading to interesting plot devices.
An example of this in films is The Shawshank Redemption, Taxi Driver and American Psycho.
Score and Underscore
The score of a film is the music specifically made and composed for a certain film. It is designed to match with the story of the film and has to make sense. This defers to a soundtrack which is music from other places chosen to appear in the film.
An underscore is when the music is played “underneath” sequences to enhance the mood of the scene or to dramatize something. Usually it is blended in with dialogue or other sound effects.
Sound Perspective
This refers to the apparent distance of a sound source, so when sound is being heard from a different perspective than what the “main” character can hear. It can be the sound in the foreground, and is a different sound than the one that is dominant.
My favourite soundtrack is from the Harry Potter movies because it is nostalgic and I think it fits really well into the universe of the movies- they all have a fantasy aspect to them and are all instantly recognisable, which is a sign of how iconic it is. In particular, I’m referring to “Hedwig’s Theme” which appears in all eight of the movies. The composer of this theme is John Williams.