narrative- Narrative film: A fictional or fictionalized story. As opposed to documentaries (non-narrative films). Classical Hollywood narrative: A specific storytelling structure developed in early American cinema that has become the norm for narrative film.
naratology- NARRATOLOGY EXAMINES THE WAYS that narrative structures our perception of both cultural artifacts and the world around us. The study of narrative is particularly important since our ordering of time and space in narrative forms constitutes one of the primary ways we construct meaning in general.
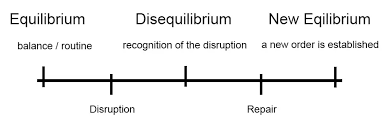
Todorov- Todorov posited that all narratives contain equilibrium, disequilibrium, recognition, resolution, and new equilibrium. “Logical and artistic necessity” mandates these formal similarities. Narrative, Todorov suggests, is a language that humans are conditioned to speak.
levi-strauss- Levi Strauss, a French anthropologist in the 1900s, proposed a theory of ‘binary opposites’ which entails that the majority of narratives in media forms such as books and film contain opposing main characters. These binary opposites help to thicken the plot and further the narrative; and introduce contrast.

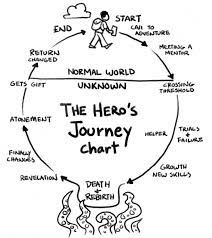
campell heros journey- Monomyth: The Hero’s Journey. Joseph Campbell’s Monomyth, developed in Hero With A Thousand Faces, describes the common heroic narrative in which a heroic protagonist sets out, has transformative adventures, and returns home. It is a useful formula for comparing literary traditions across time and culture.
barthes narrative codes- Those five narrativecodes are; hermeneutic code, proairetic code, cultural code, connotative code, and symbolic code. This study applies qualitative research design to analyze the source of data.