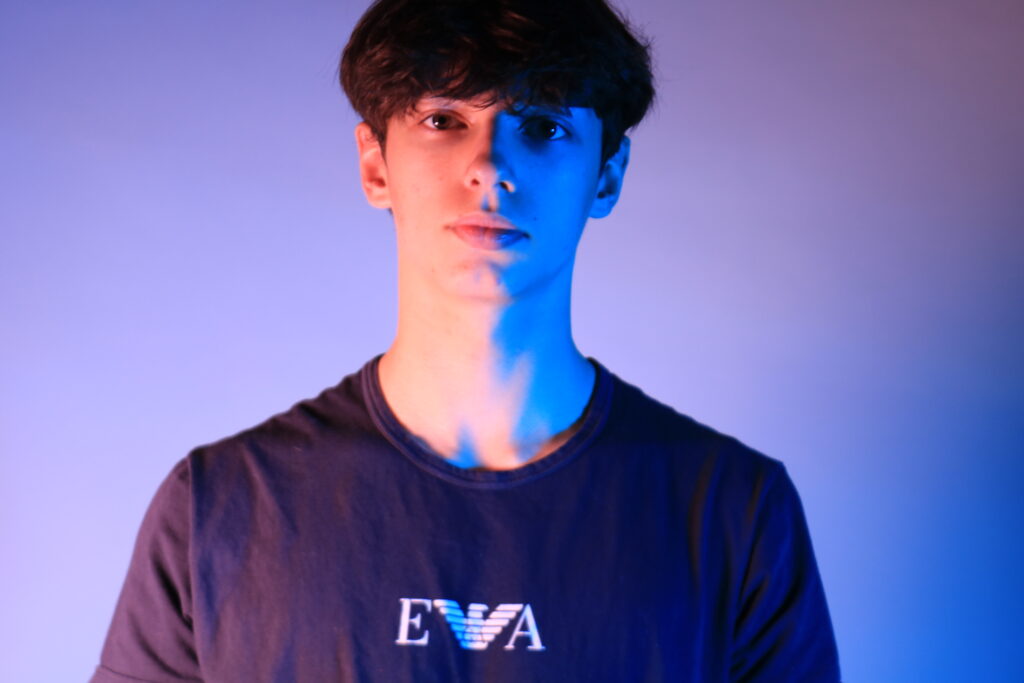
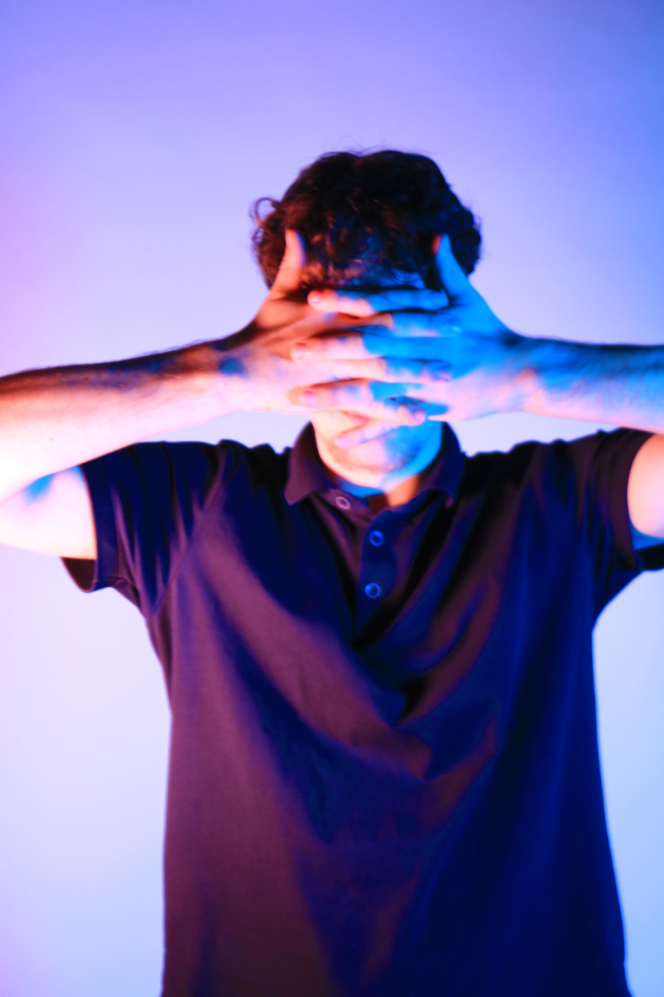
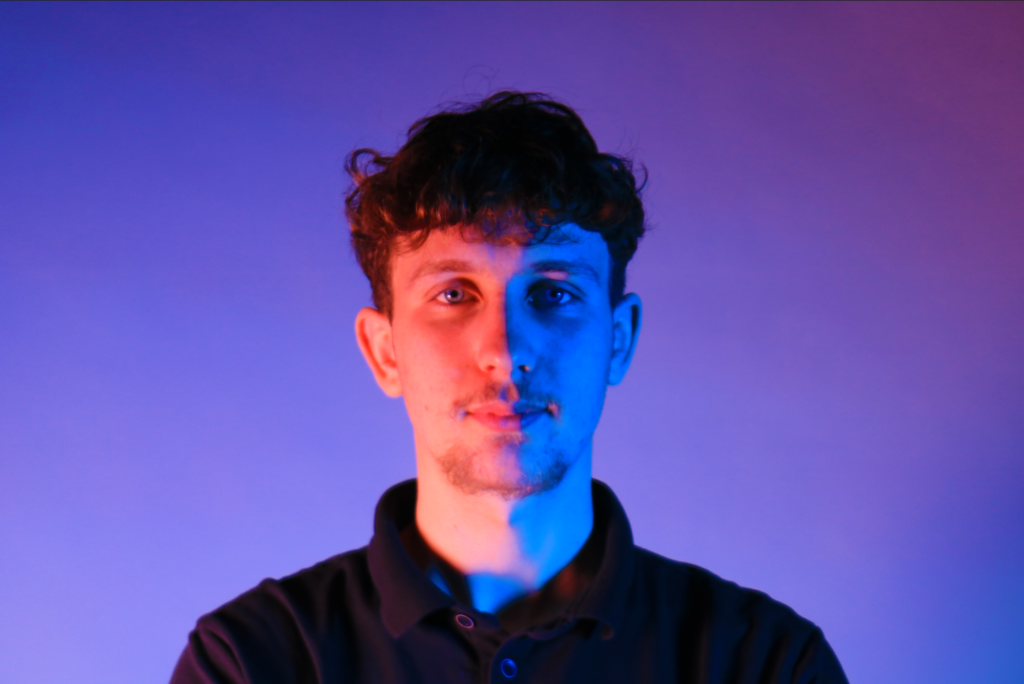
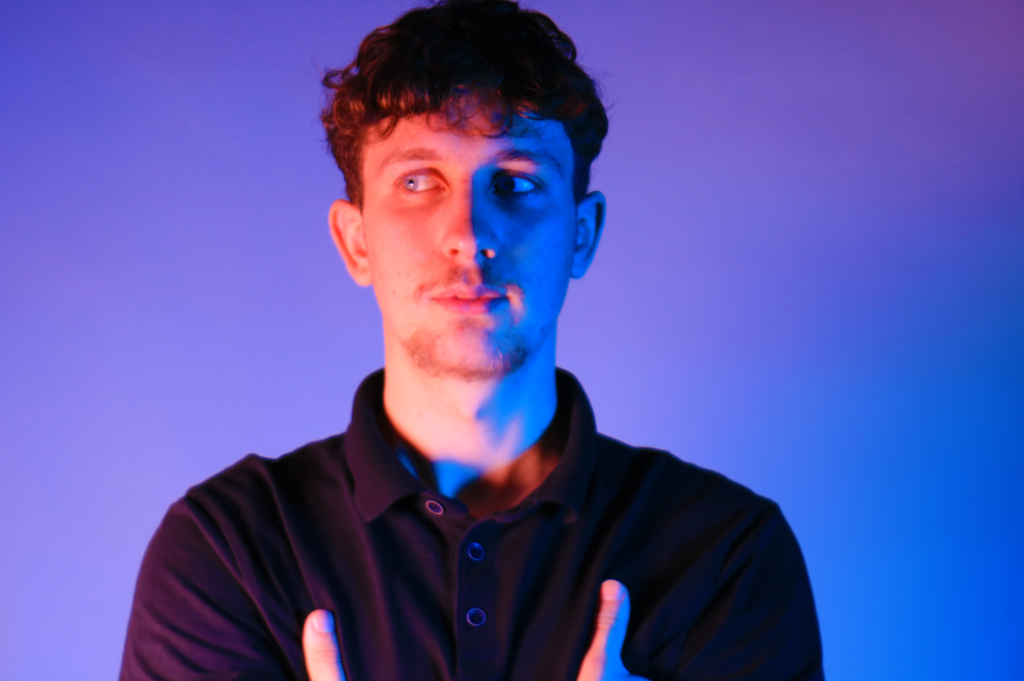
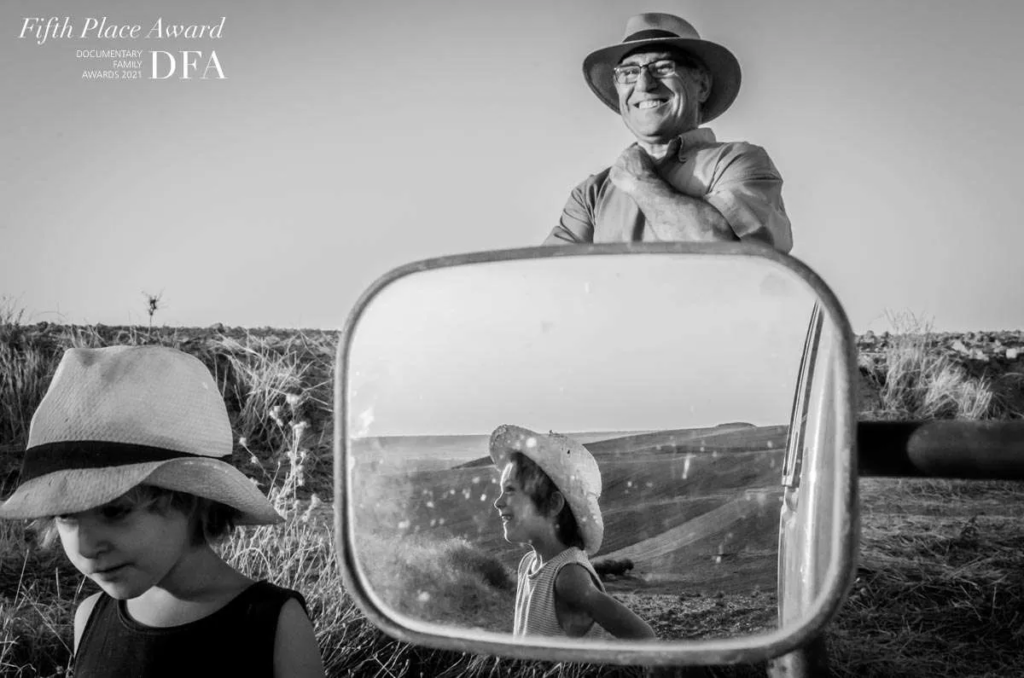
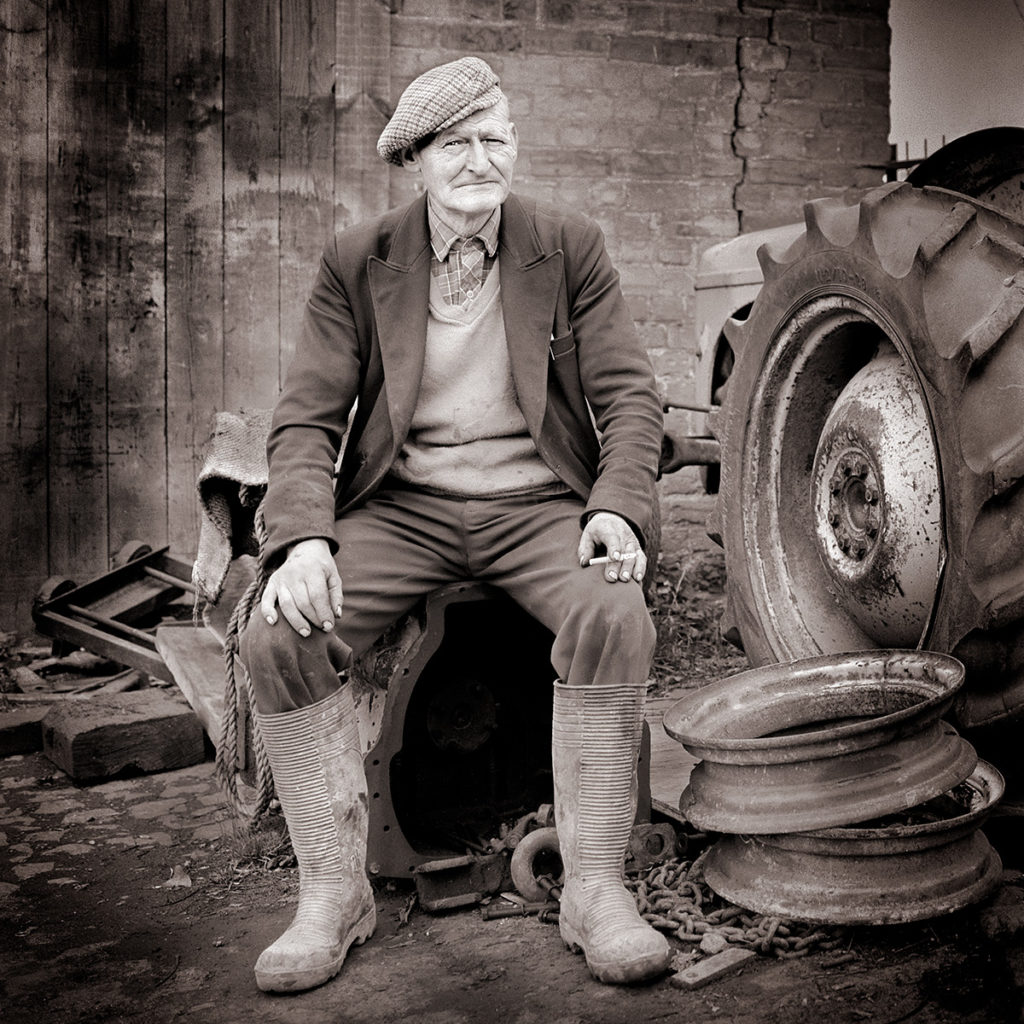
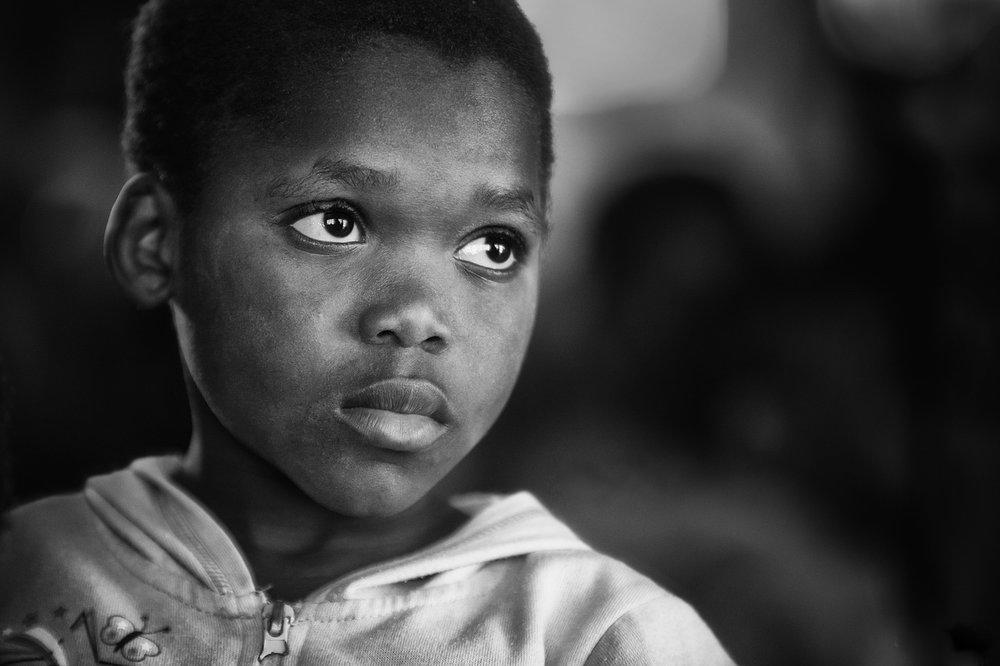
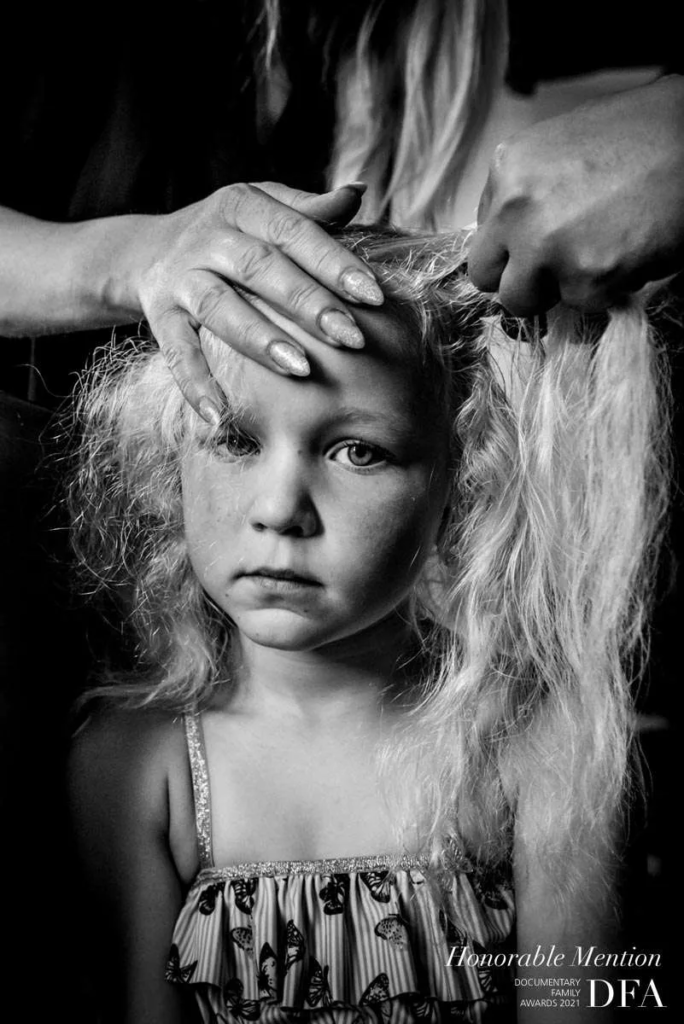
Identity in photography can be seen as the representation of an individual’s or group’s essence through visual imagery. It encompasses various aspects, such as gender identity, cultural identity, social identity, geographical identity, and political identity. Each of these identities can be expressed and explored through photographic work, allowing for a deeper understanding of the subjects and the contexts they inhabit.
Masculinity and Femininity
Femininity and masculinity in photography often manifest through the portrayal of subjects in ways that align with or challenge traditional gender norms. For example, images that depict women in nurturing roles may reinforce femininity, while those showcasing men in assertive or dominant positions may emphasize masculinity. However, contemporary photography increasingly seeks to subvert these stereotypes, presenting a more nuanced view of gender that reflects the complexities of identity.

The influence of place and belonging is significant in photography. An individual’s environment and upbringing shape their perspectives and experiences, which can be conveyed through their work. For instance, a photographer from a particular geographical region may capture the cultural identity of their community, highlighting local traditions and social dynamics. Conversely, the lack of or loss of identity can be explored through themes of alienation or disconnection in photography. Stereotypes and prejudices can also be challenged through visual narratives, prompting viewers to reconsider their perceptions and assumptions about different identities. Ultimately, photography serves as a powerful medium for exploring and expressing the multifaceted nature of identity.
Key Artists with References
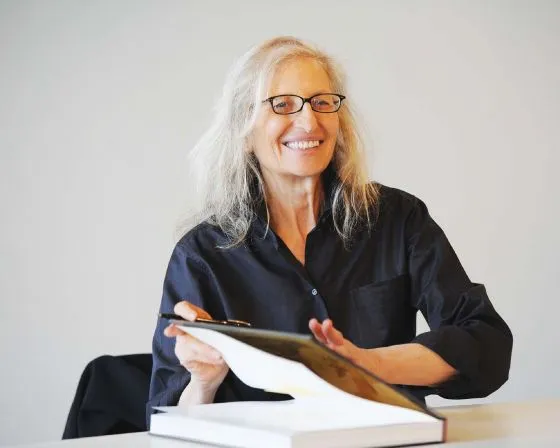
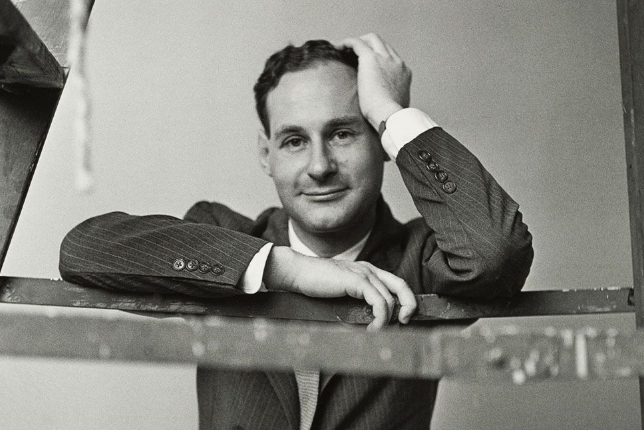
Cindy Sherman and Claude Cahun are two influential artists known for their explorations of identity, gender, and the self through photography.
Claude Cahun
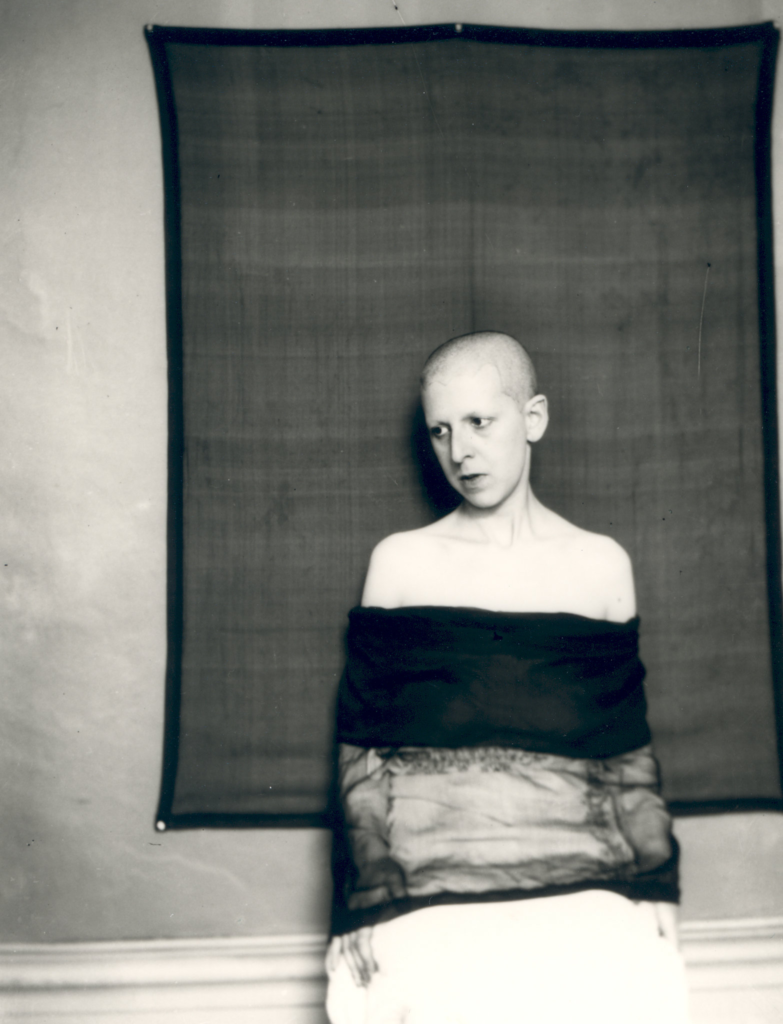
Claude Cahun, a pioneering figure in the early 20th century, also focused on identity and gender, but her approach was more avant-garde and surrealist. Cahun’s work often involved self-portraiture as well, but she used it to explore themes of androgyny and the fluidity of identity. In her photographs, she frequently manipulated her appearance, employing costumes, makeup, and props to challenge conventional gender norms. Cahun’s work emphasizes the performative aspects of identity, suggesting that it is not a fixed state but rather a series of roles that individuals play.
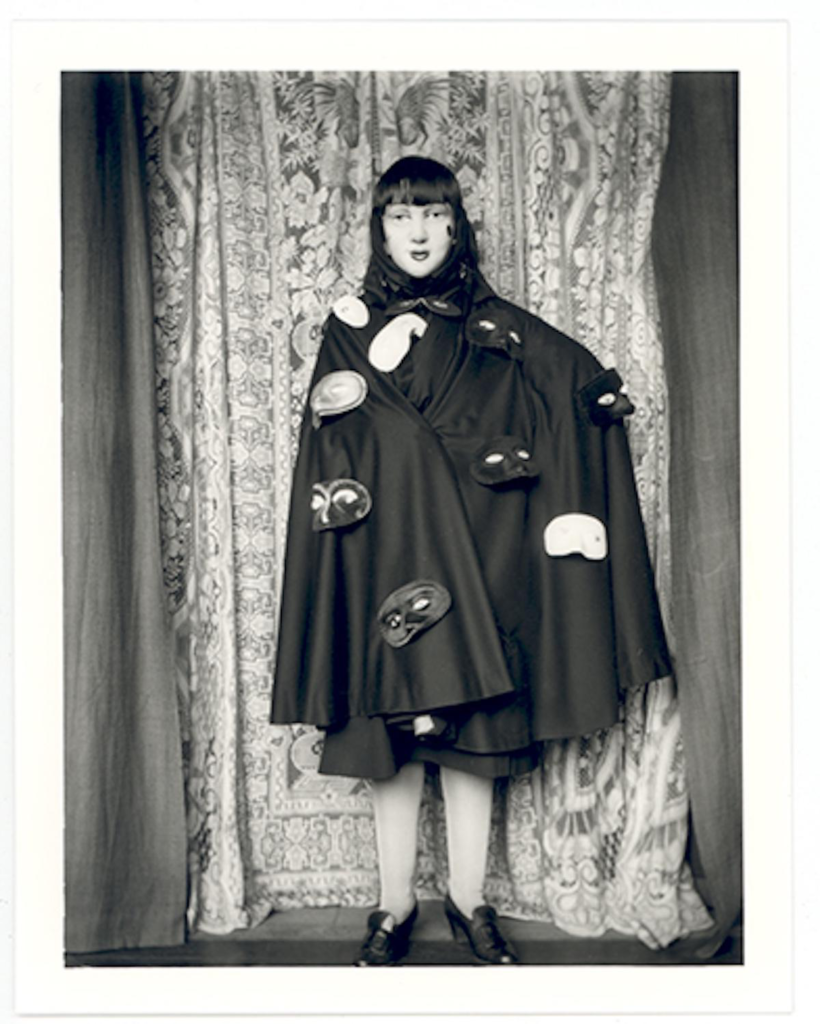
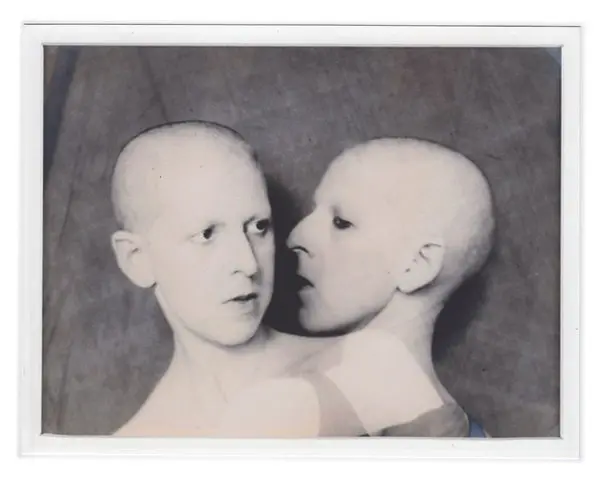




Cindy Sherman
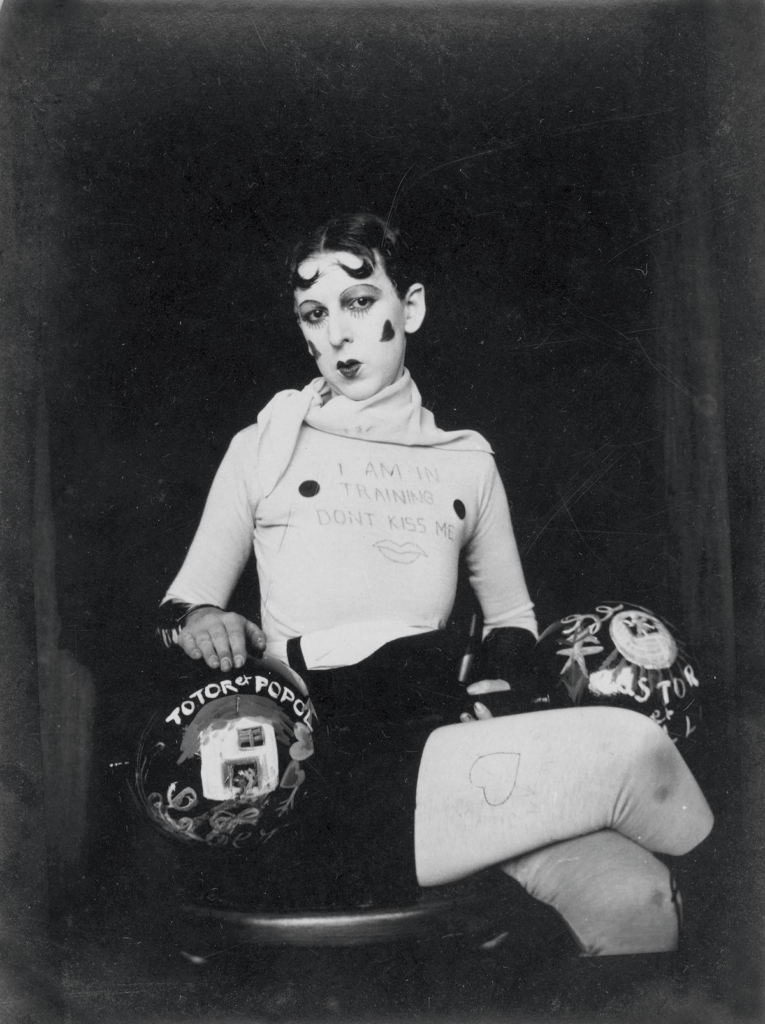
Cindy Sherman is renowned for her conceptual self-portraits, where she often adopts various personas and characters. Through her work, Sherman challenges traditional notions of femininity and the representation of women in media and art. By transforming herself into different roles—ranging from the glamorous to the grotesque—she critiques the stereotypes and societal expectations placed on women. Her series “Untitled Film Stills” is particularly notable, as it presents her as the protagonist in staged scenes that mimic film stills, allowing viewers to question the authenticity and construction of identity in visual culture.
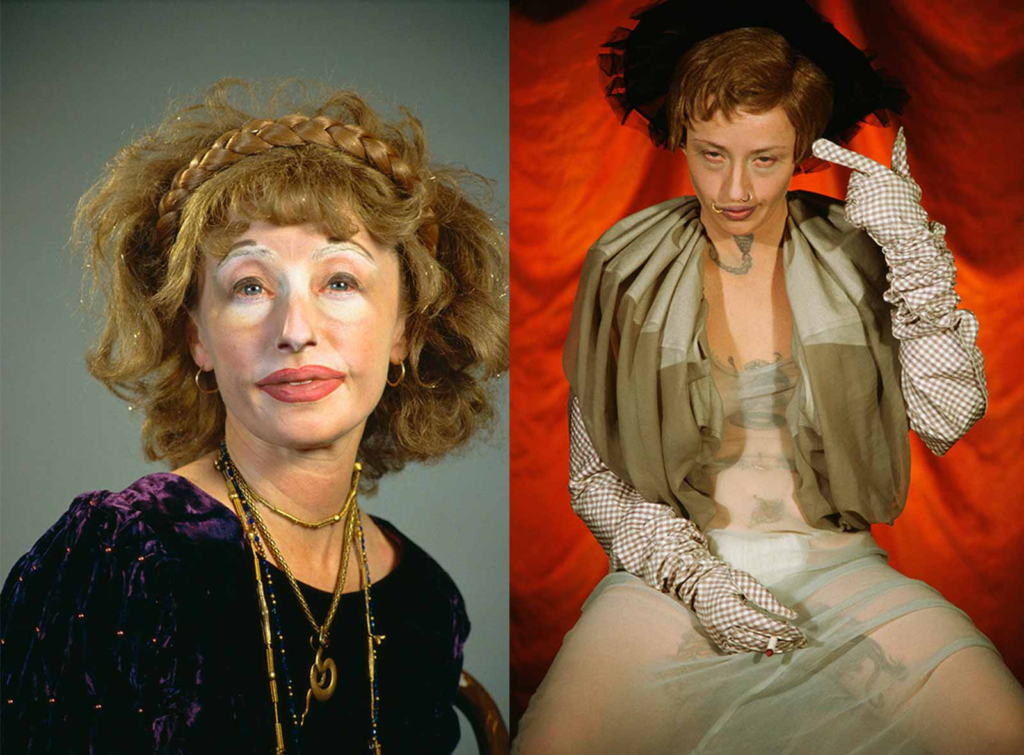




Both artists use photography to interrogate the construction of identity, but they do so in distinct ways. Sherman’s work often reflects a critique of popular culture and the roles women are expected to play, while Cahun’s work delves into the complexities of gender and self-representation. Together, they highlight how photography can serve as a powerful tool for exploring and deconstructing identity, encouraging viewers to reconsider their perceptions of gender, self, and the roles imposed by society.
Mood Board
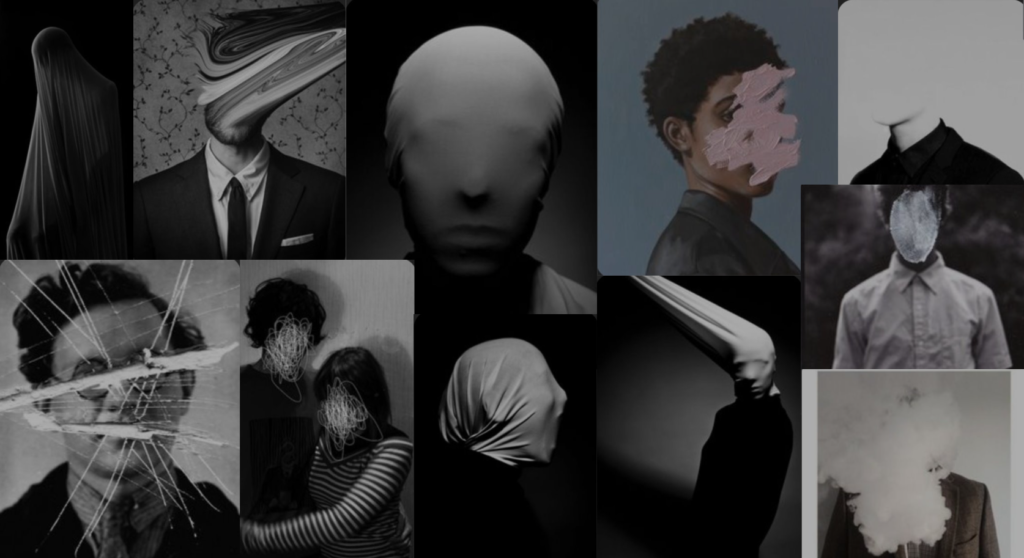

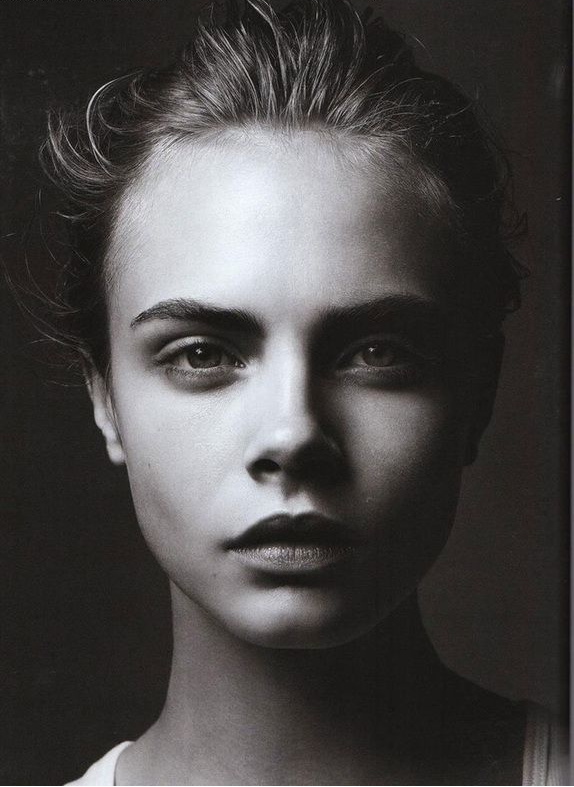
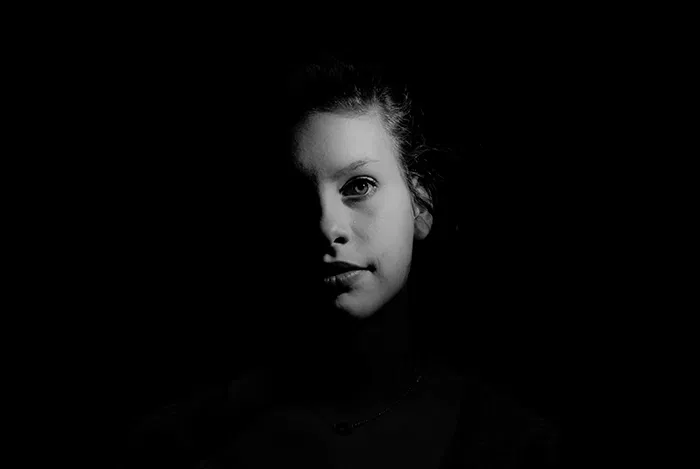
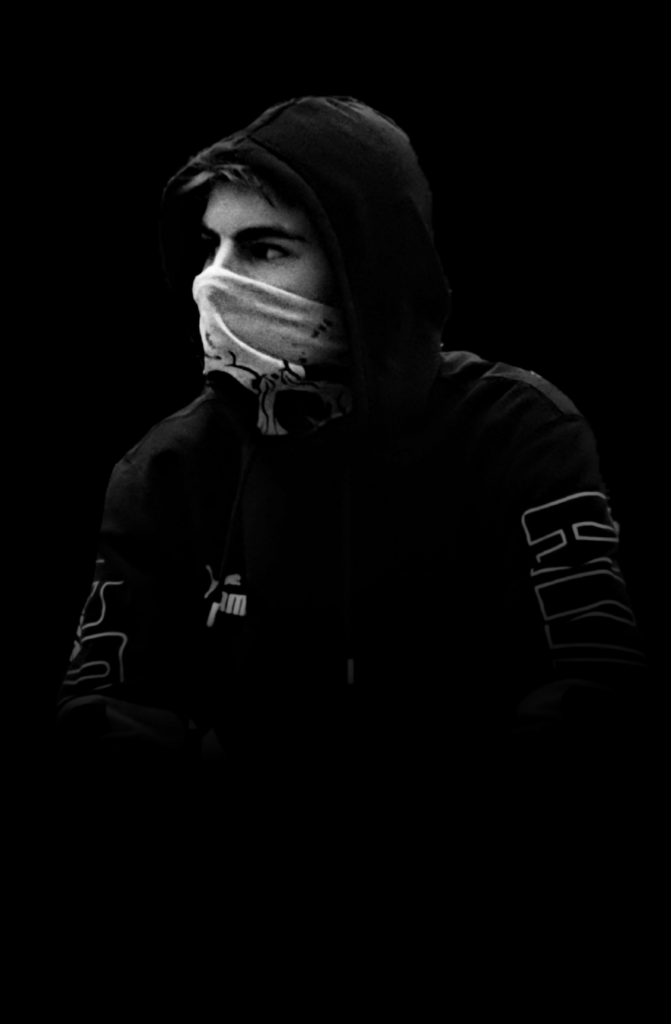
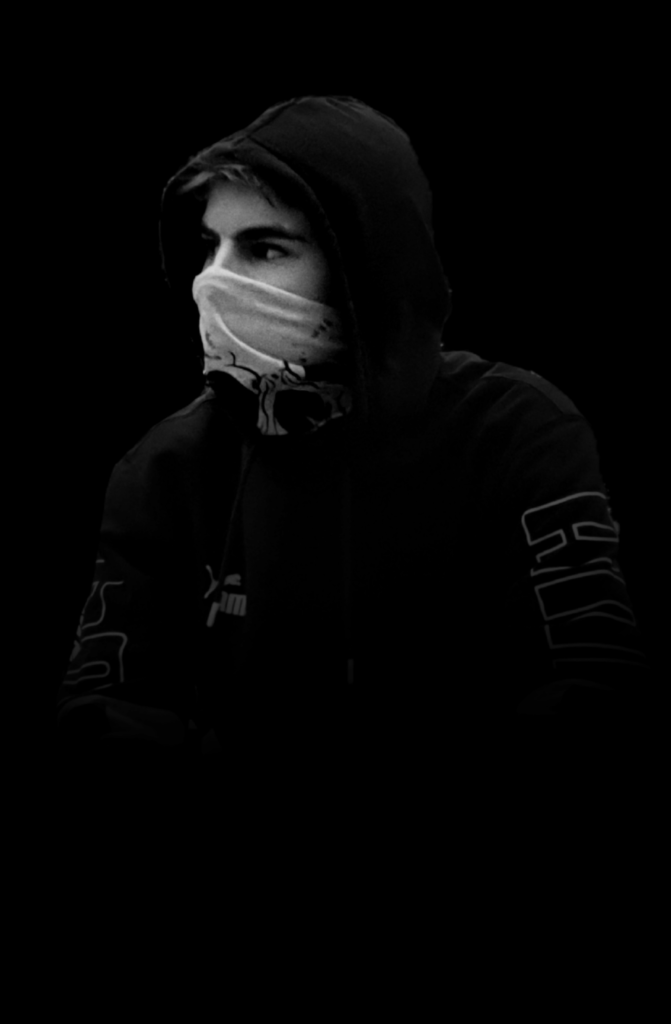
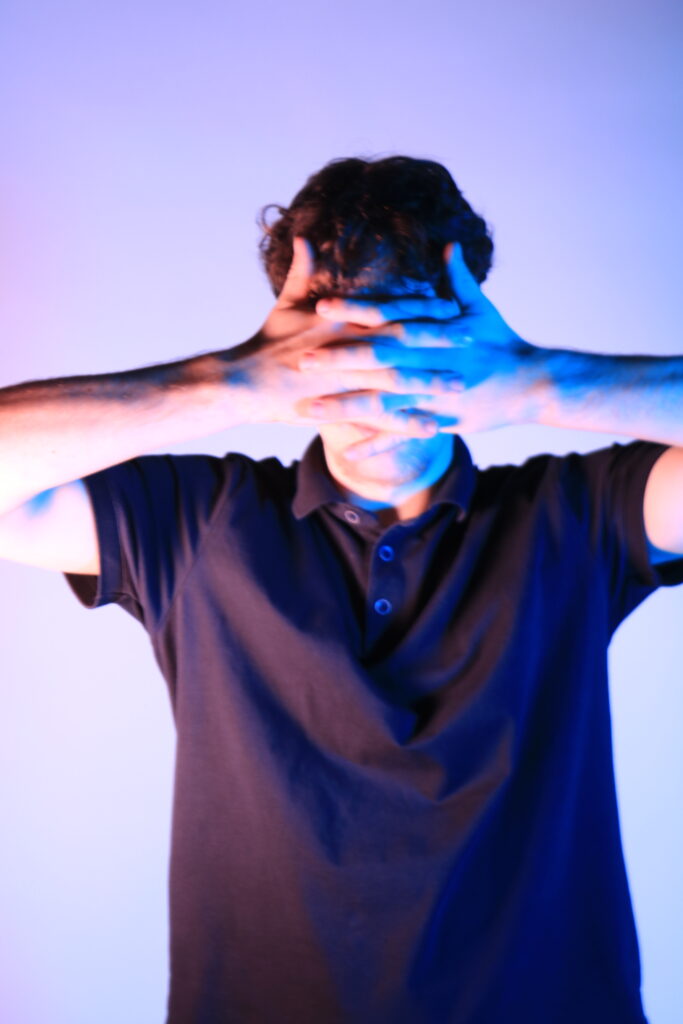
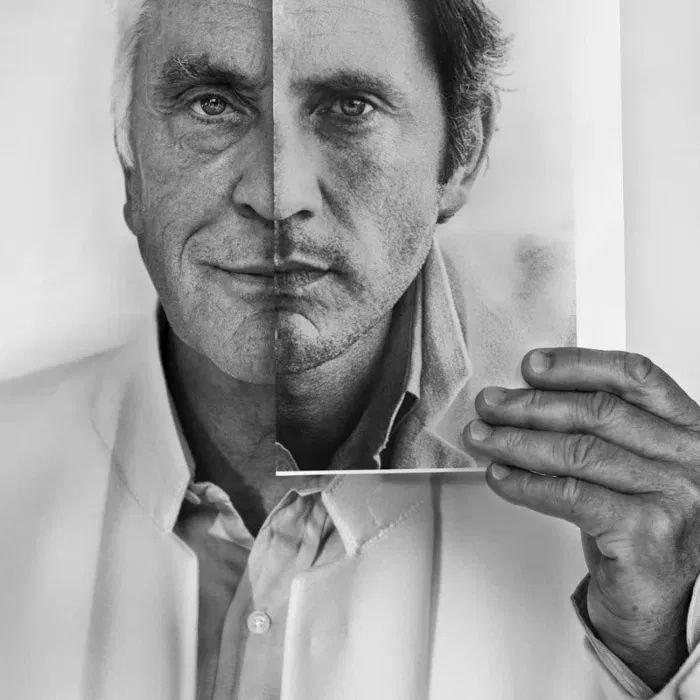
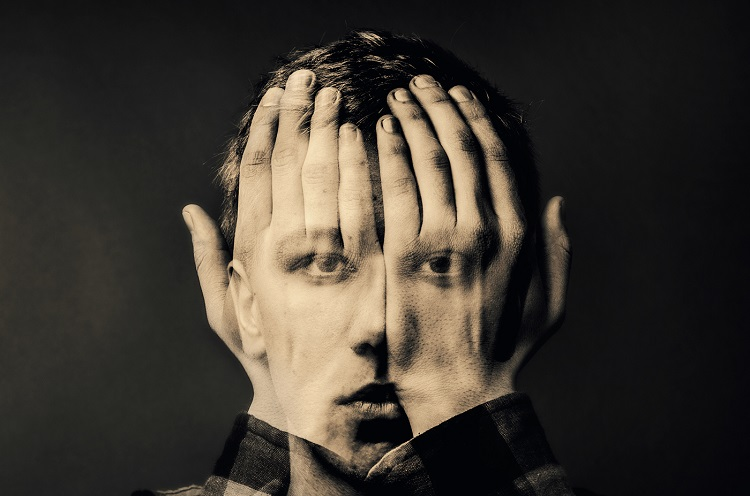
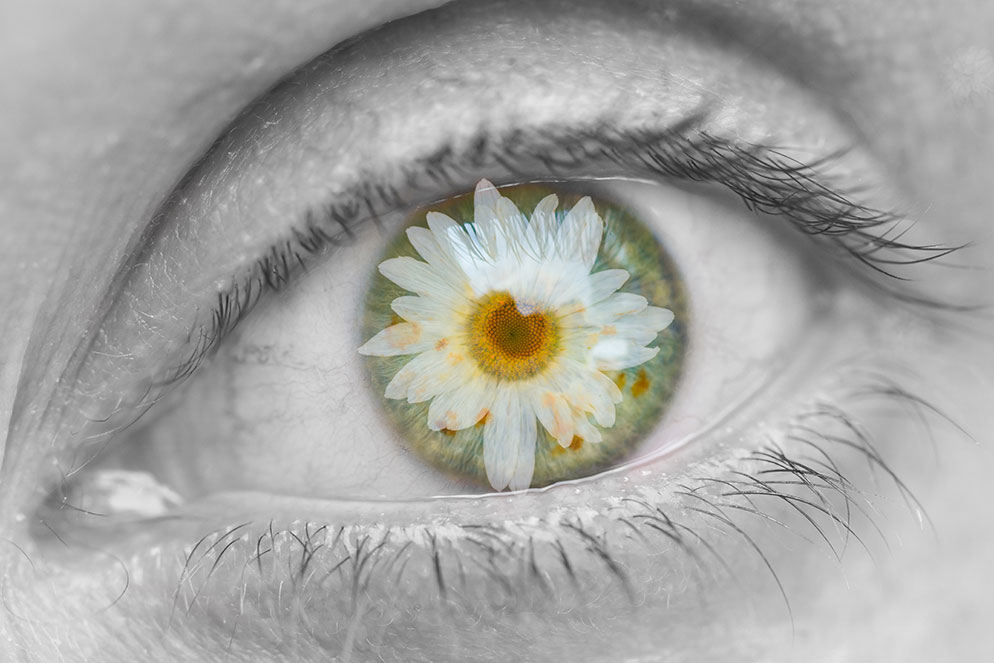
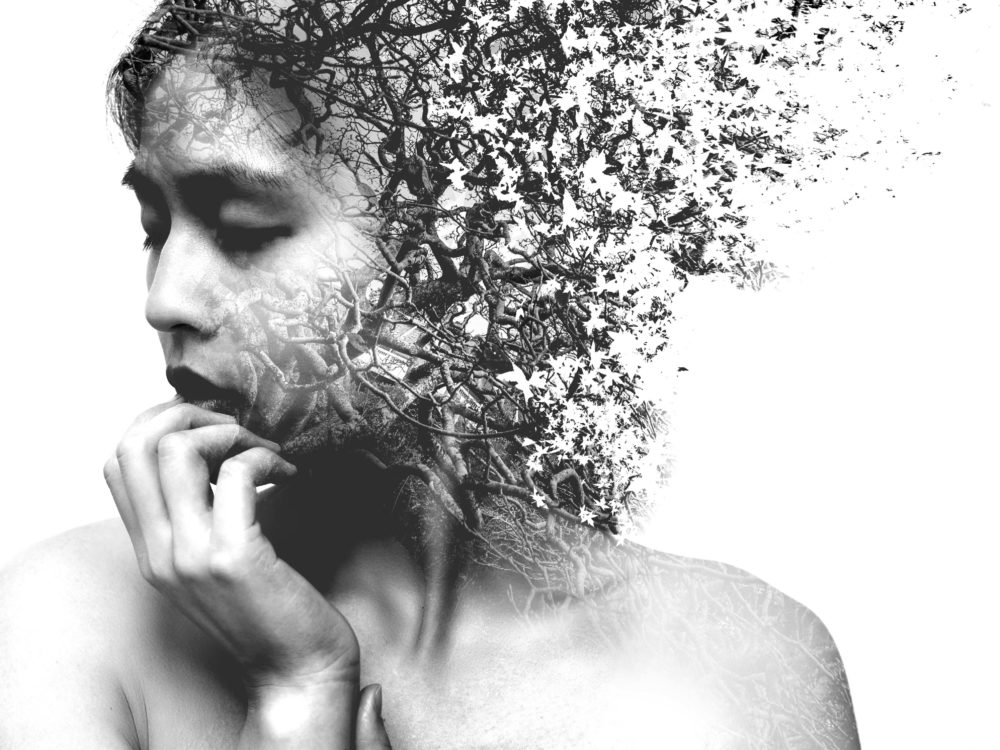
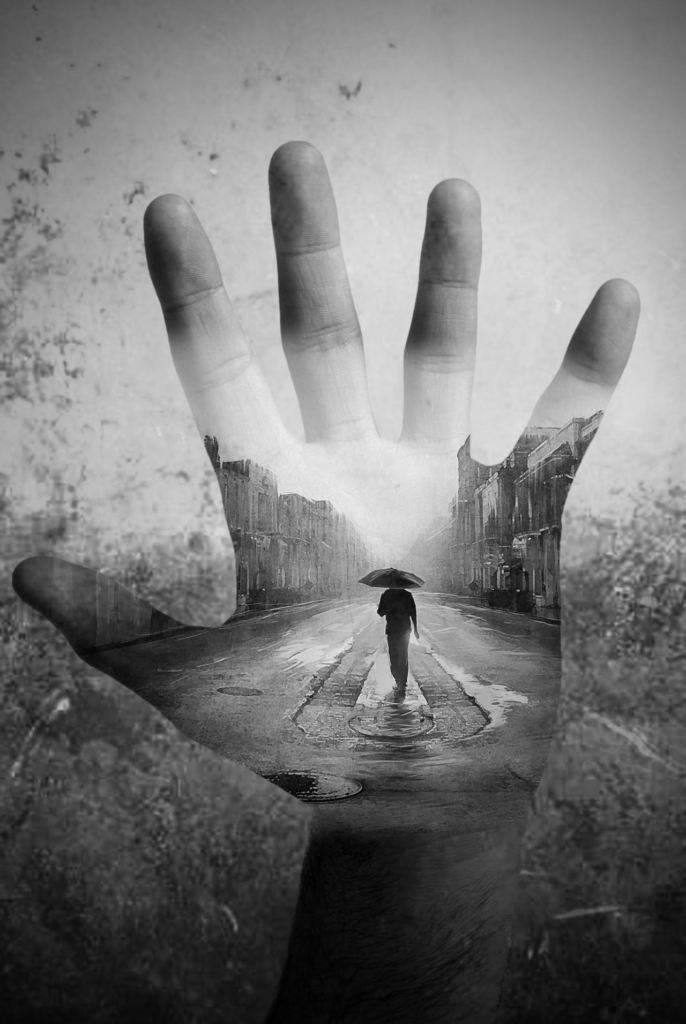
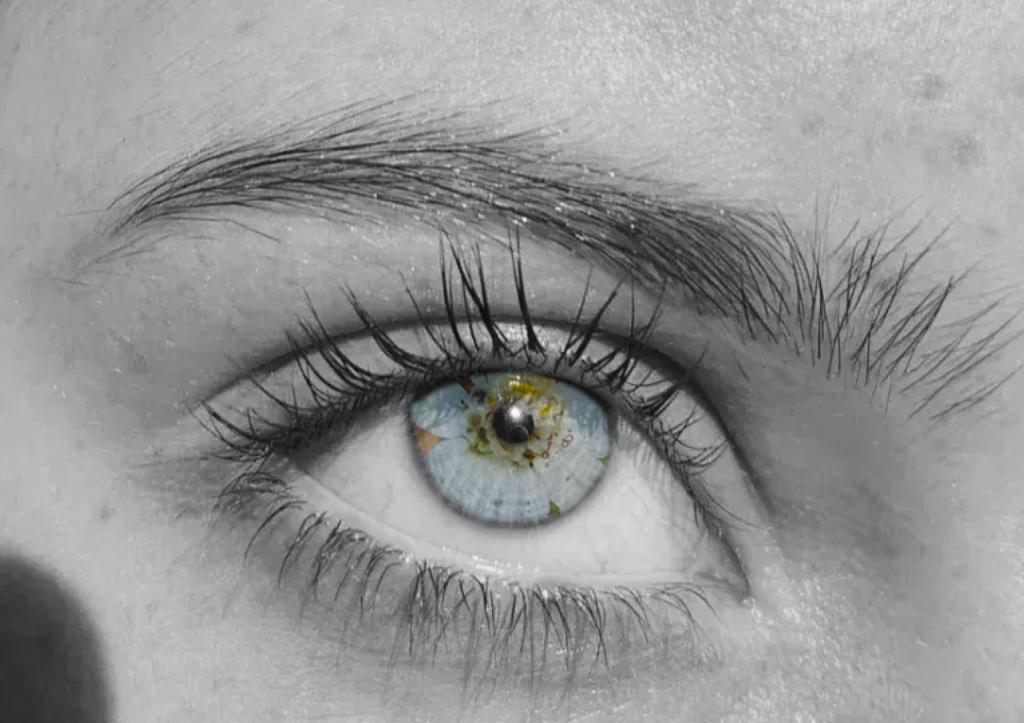
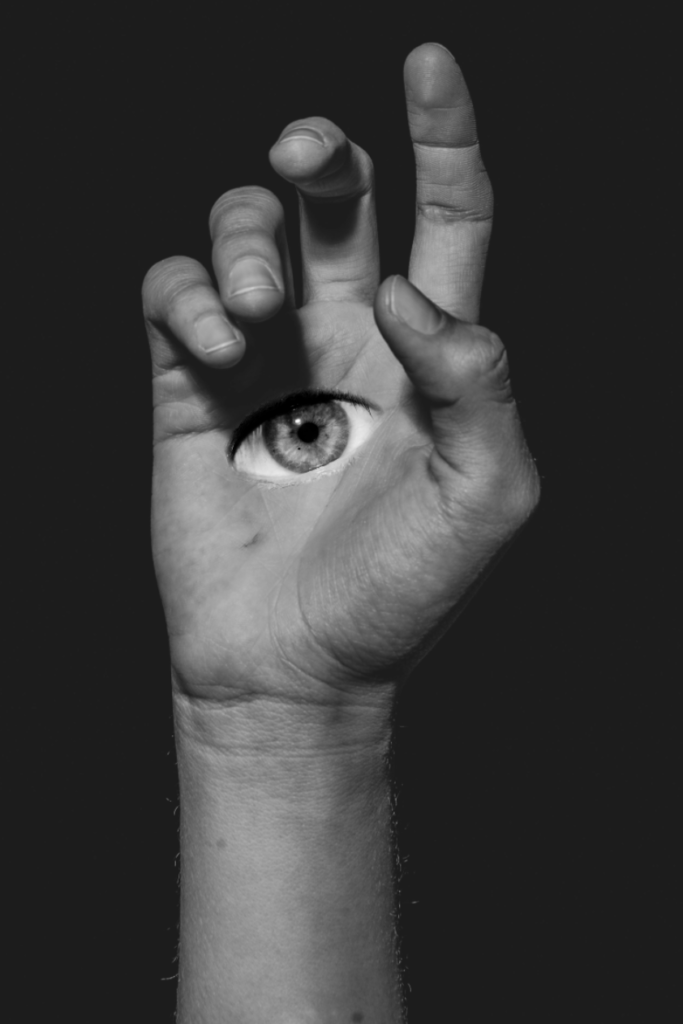
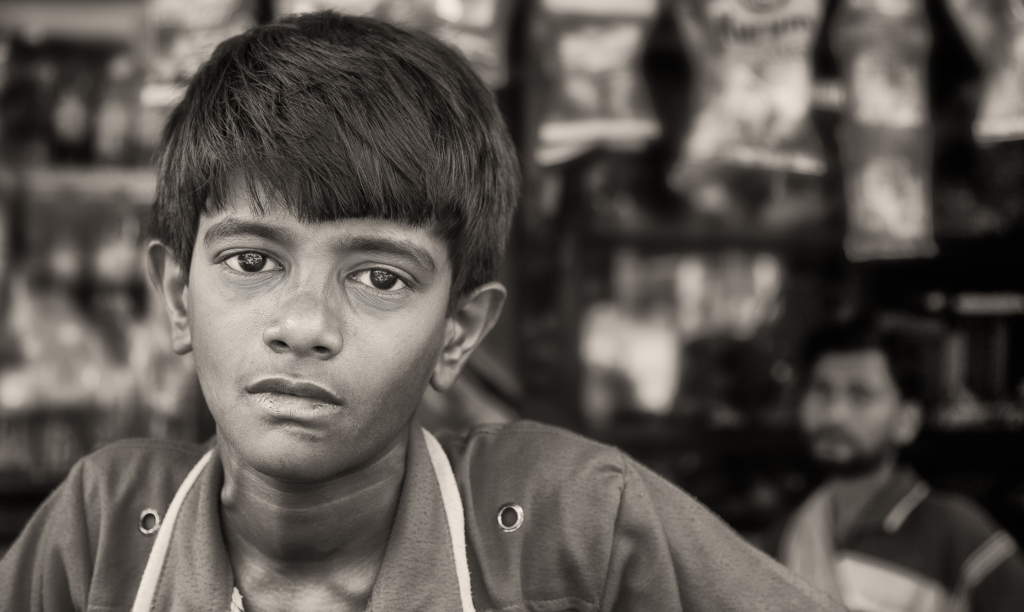
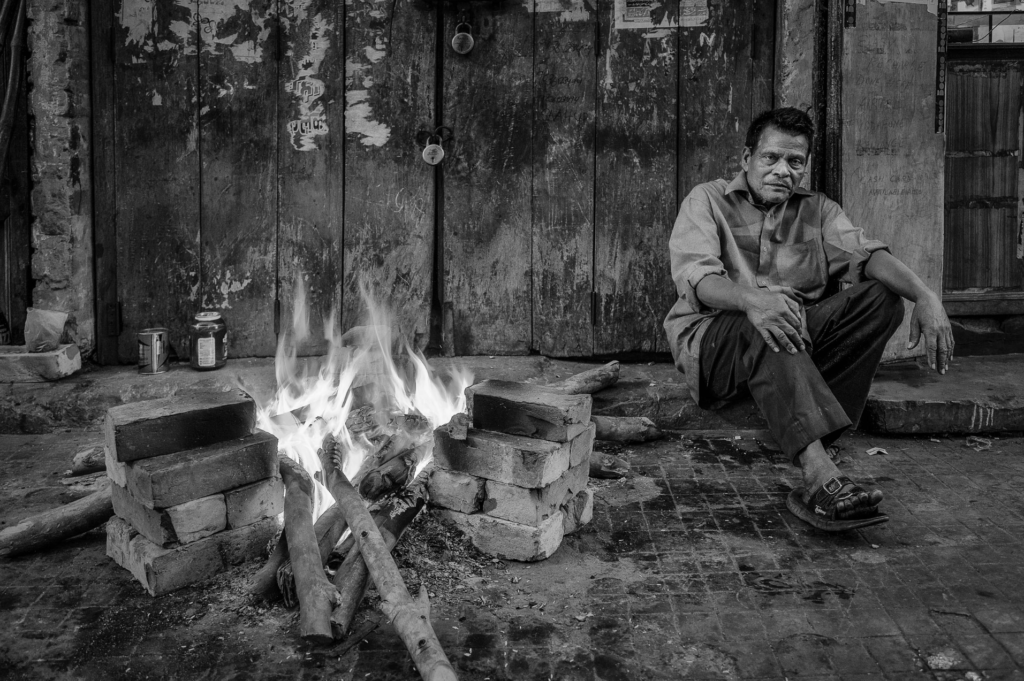
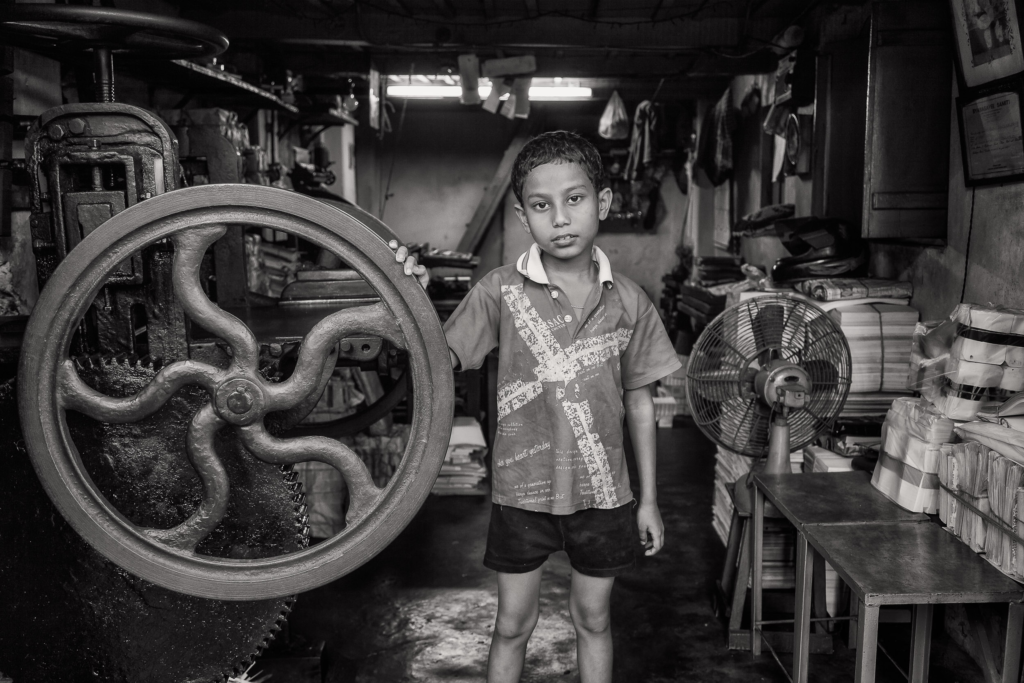
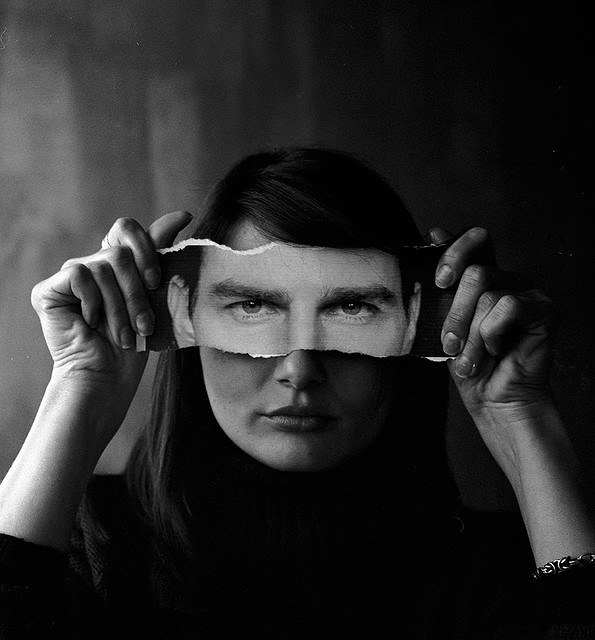
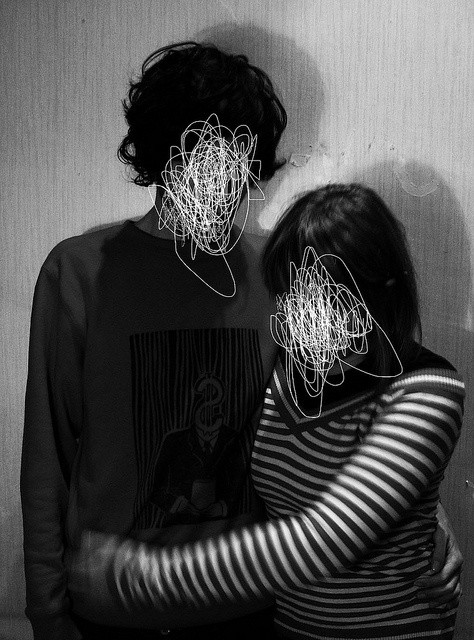
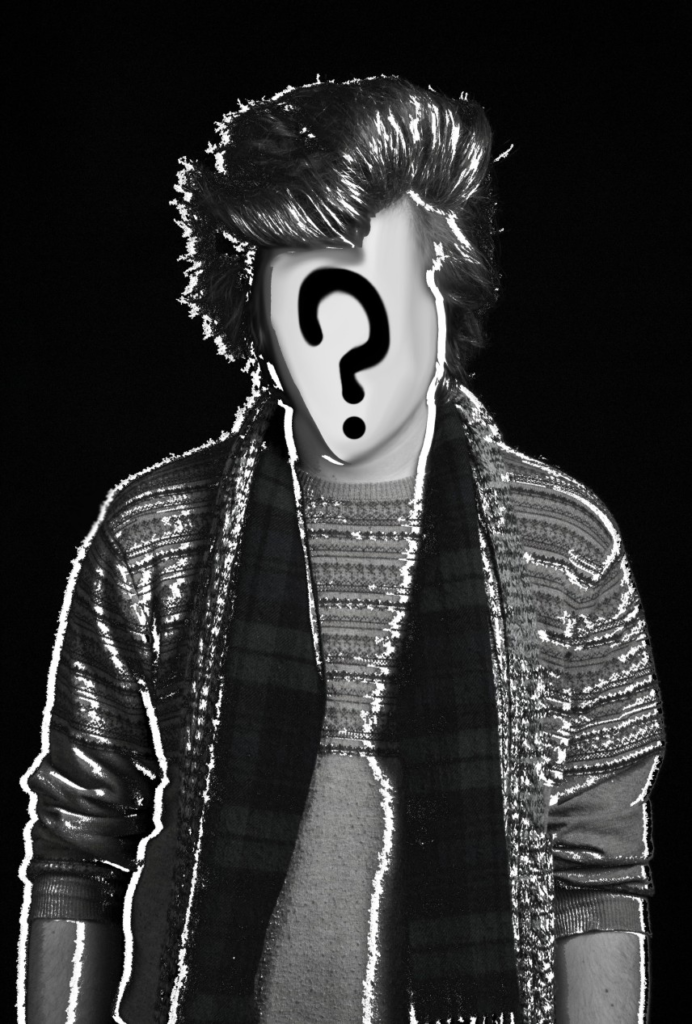
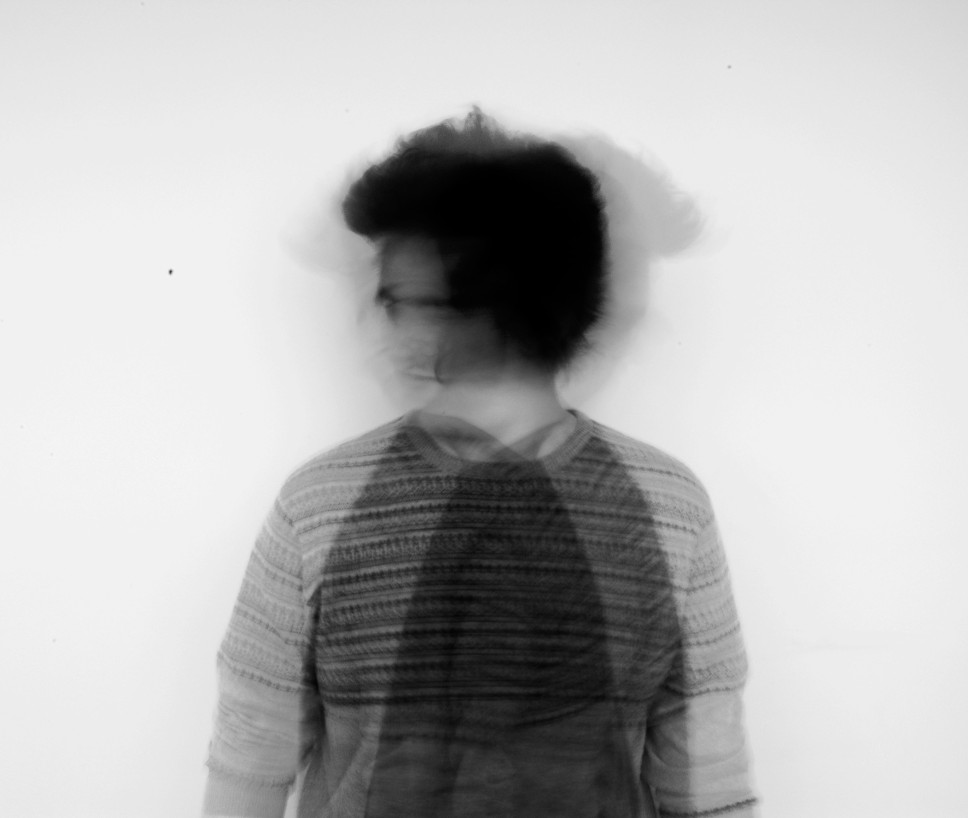
I conducted a lot of research into the theme of “Identity”, and came across these images. They are quite dark and monochromatic and when I asked for my teachers view of these images, he said they almost created the sense of “Loss of Identity”
Researching further into the theme “Loss of Identity” in photography, I found out that it can evoke a range of emotional and conceptual effects. It often creates a sense of disconnection, alienation, or introspection. When photographers explore this theme, they use techniques such as blurred images, fragmented compositions, or abstract representations to symbolize the struggle of individuals to maintain their sense of self in a rapidly changing world.
This theme can also provoke viewers to reflect on their own identities and the factors that contribute to their sense of self. It can lead to a deeper understanding of societal pressures, personal experiences, or cultural shifts that influence identity. Additionally, photographs focusing on loss of identity can foster empathy, as viewers may connect with the feelings of confusion or loss portrayed in the images. Overall, it opens up a dialogue about what it means to be oneself in various contexts.
Artists related to my Theme of Identity
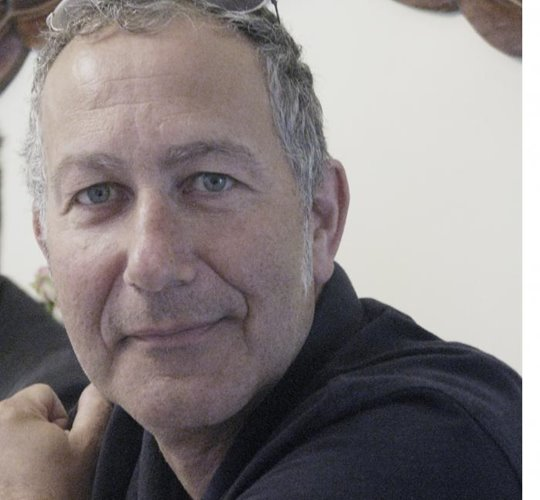
Andreas Poupoutsis
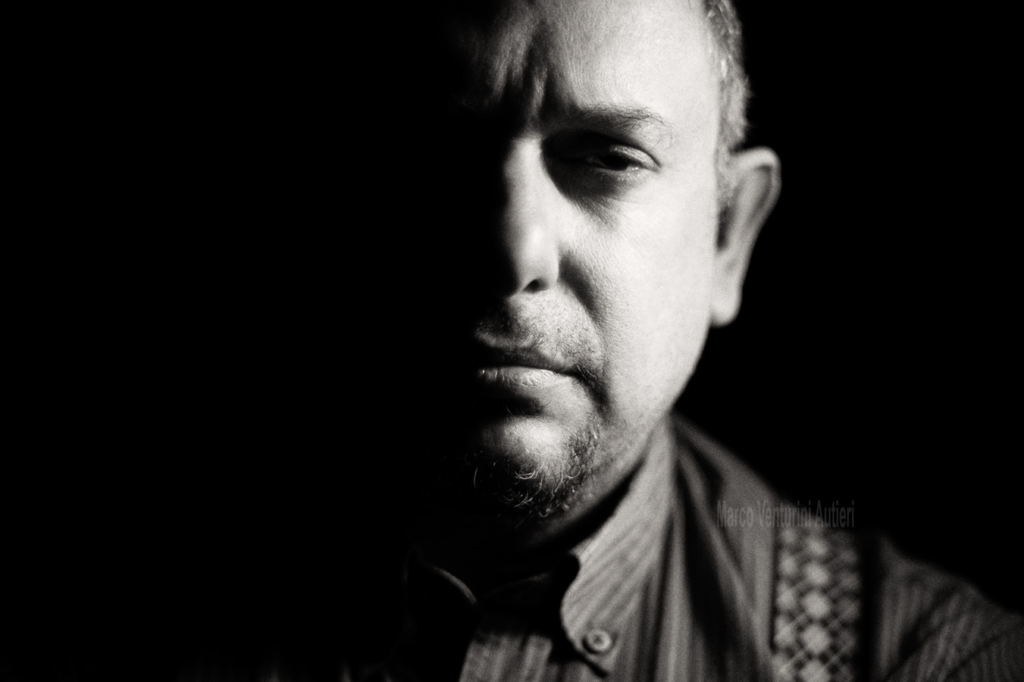
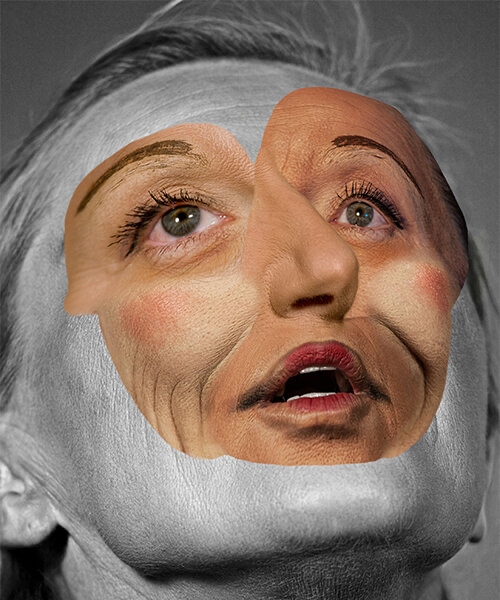
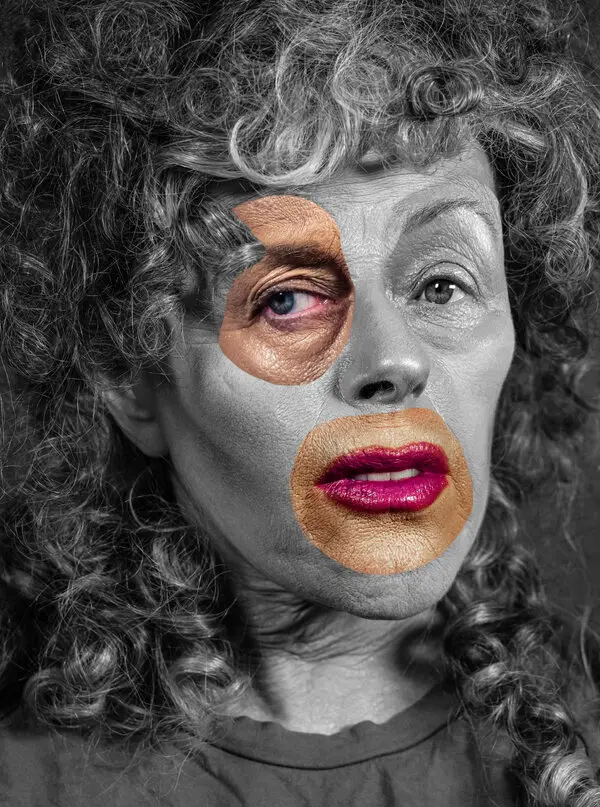
Andreas Poupoutsis is a contemporary photographer known for focusing on themes like identity and memory. His work often blends portraiture with conceptual photography, creating thought-provoking images that evoke emotions. He uses techniques like mixed media and digital manipulation, which add depth to his subjects. His photography reflects personal and collective experiences, encouraging viewers to think about their own identities and how they are shaped by their surroundings.
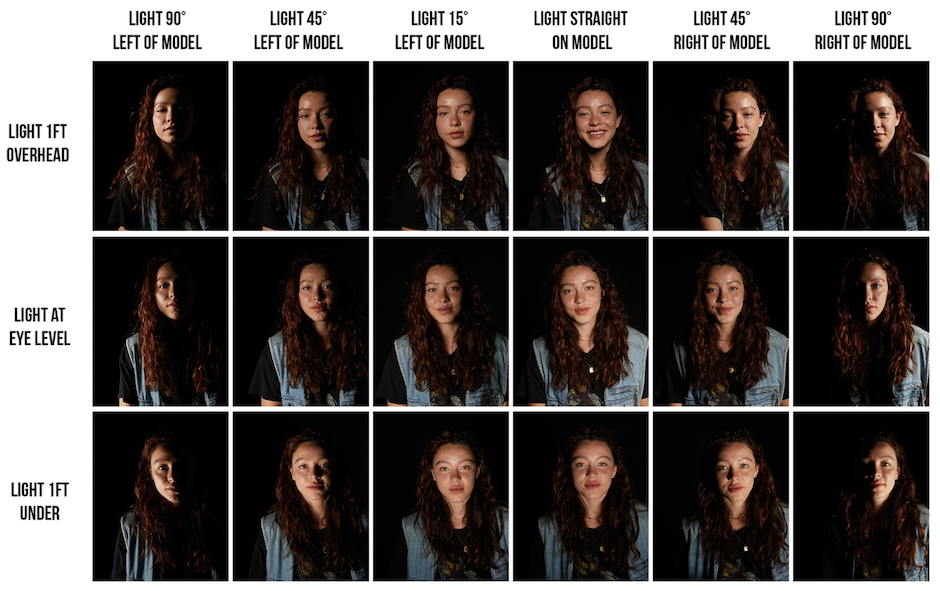
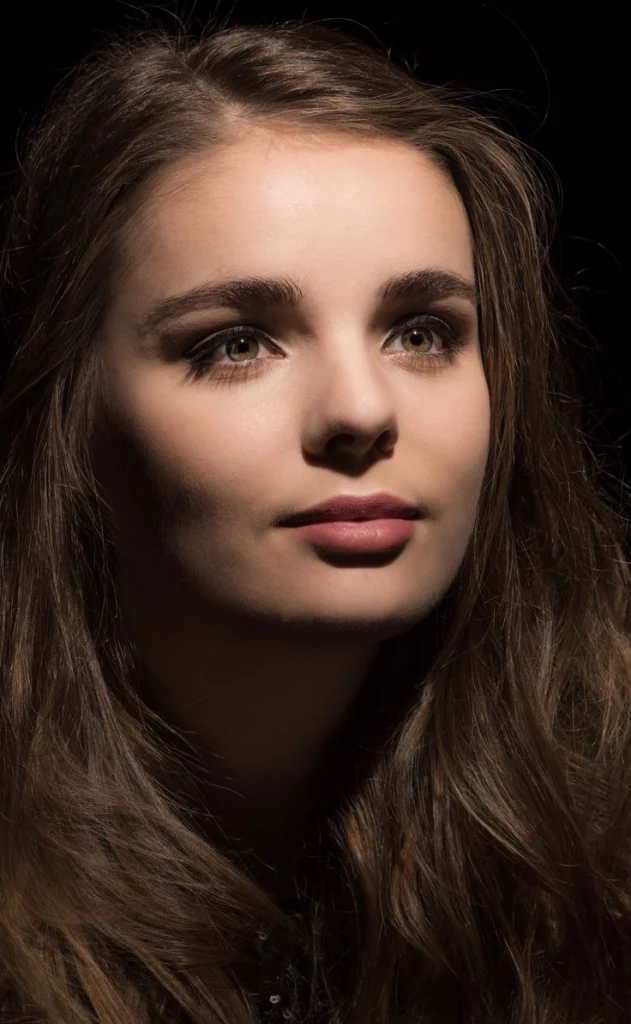
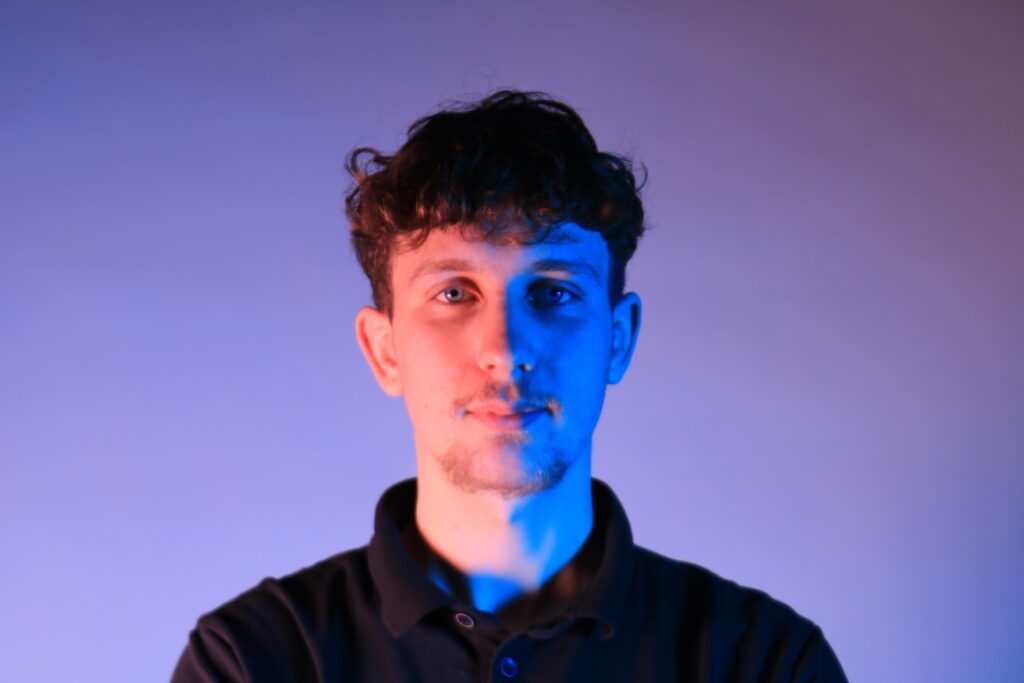
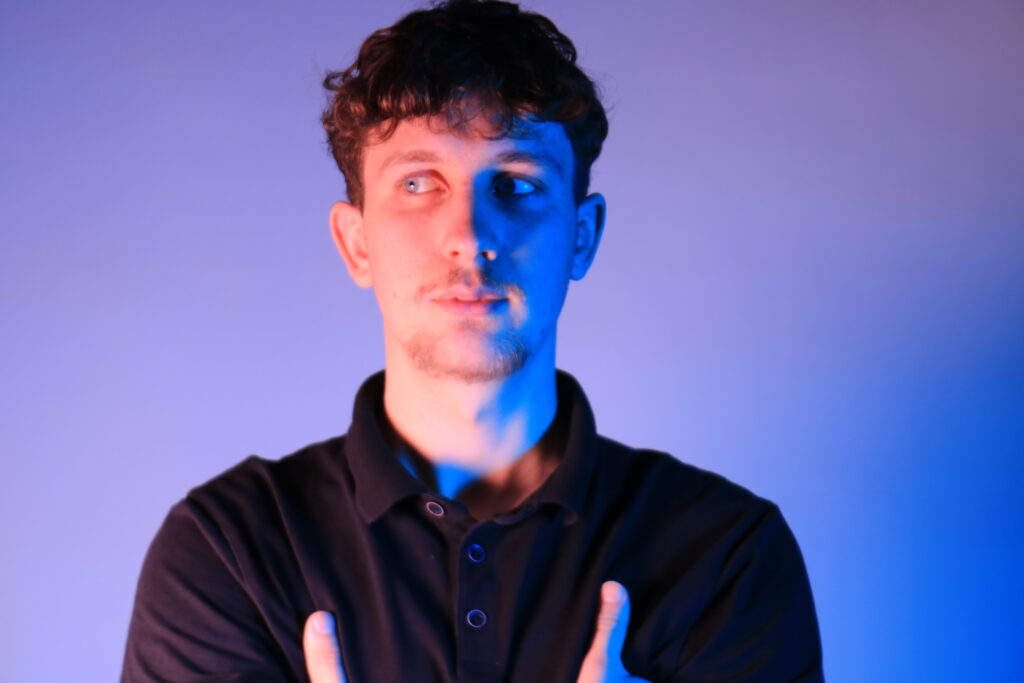
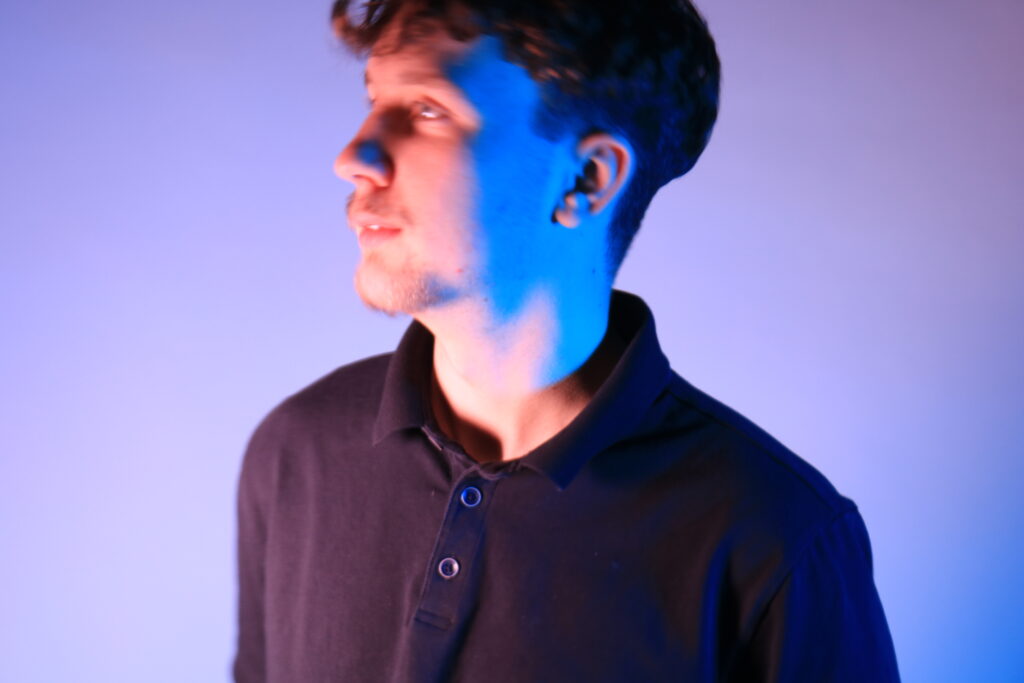
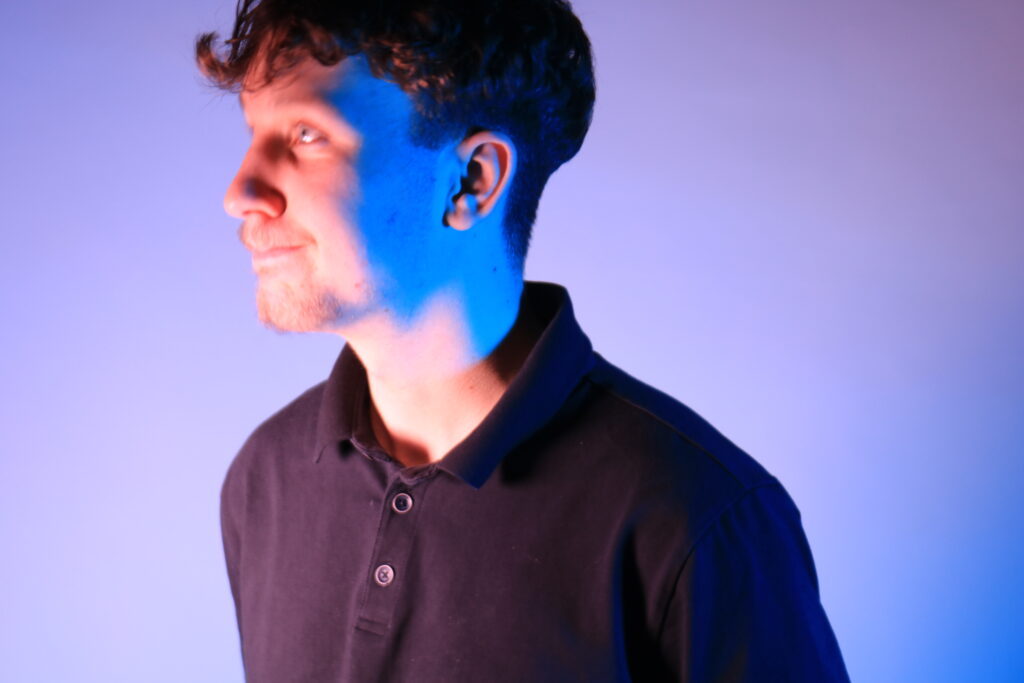
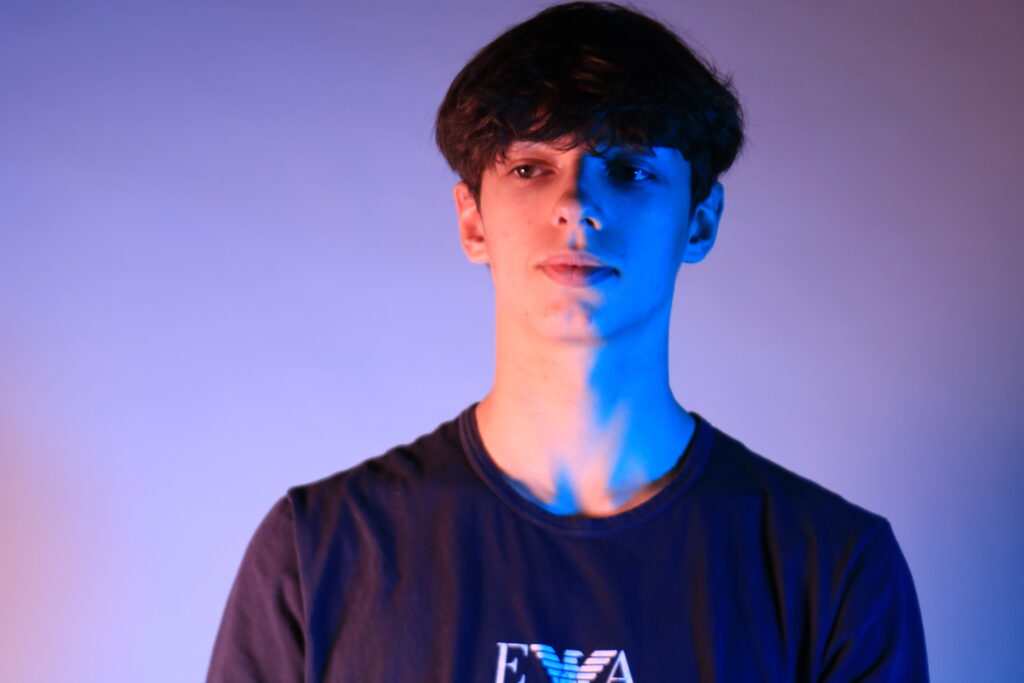
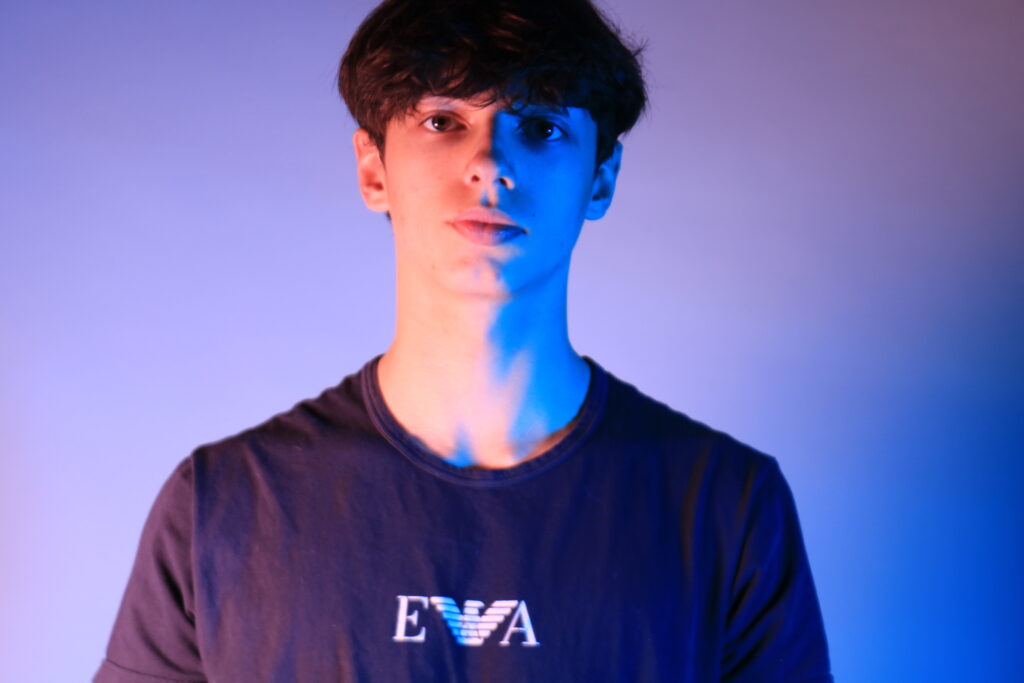
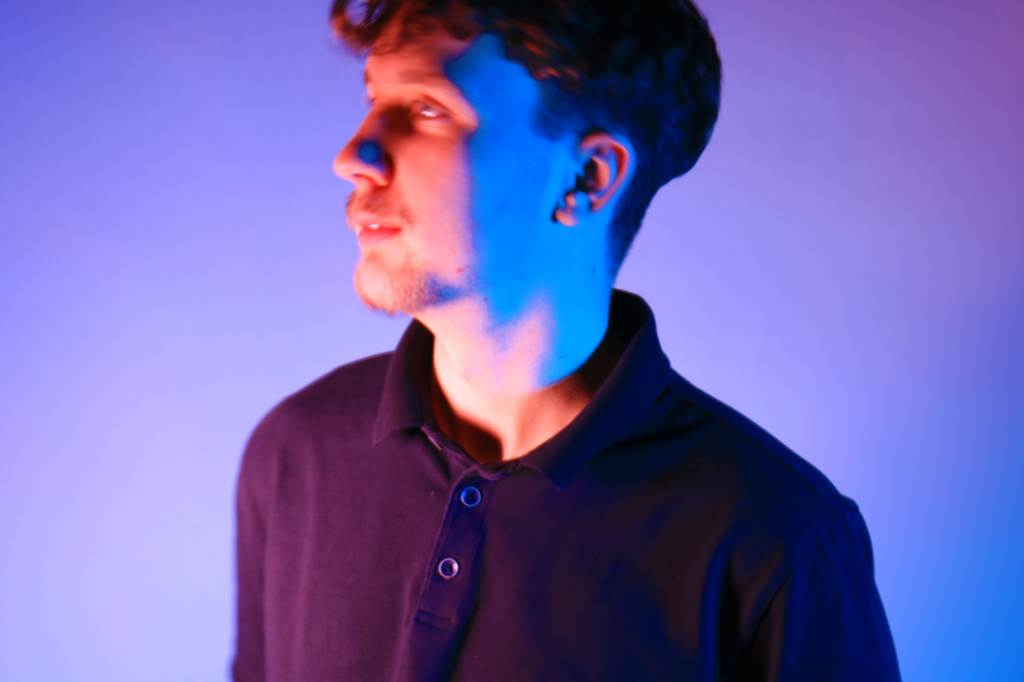
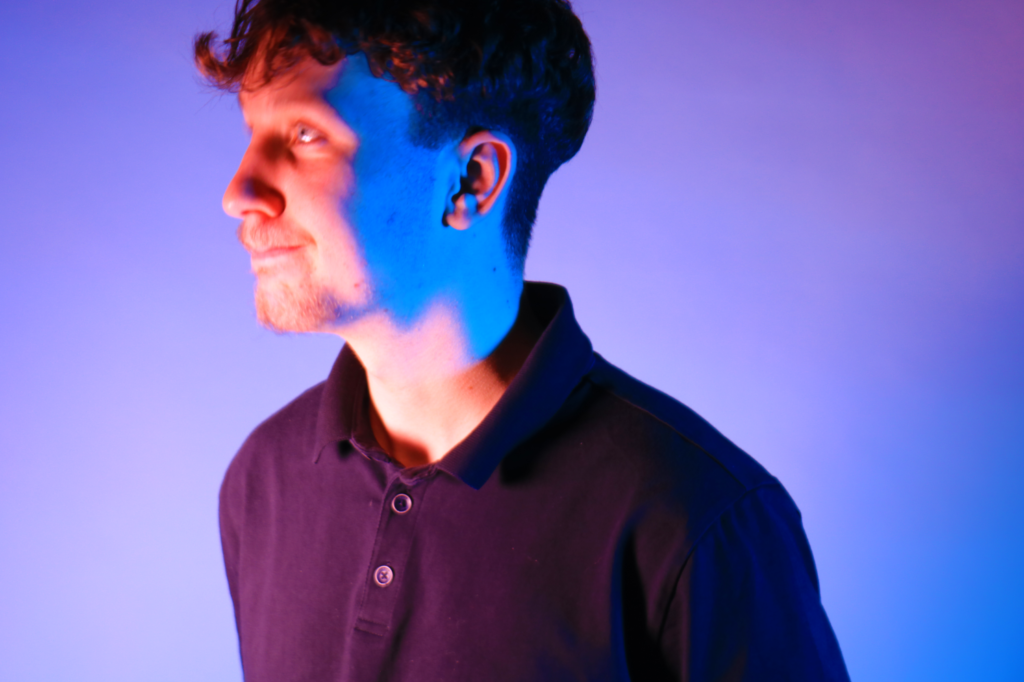
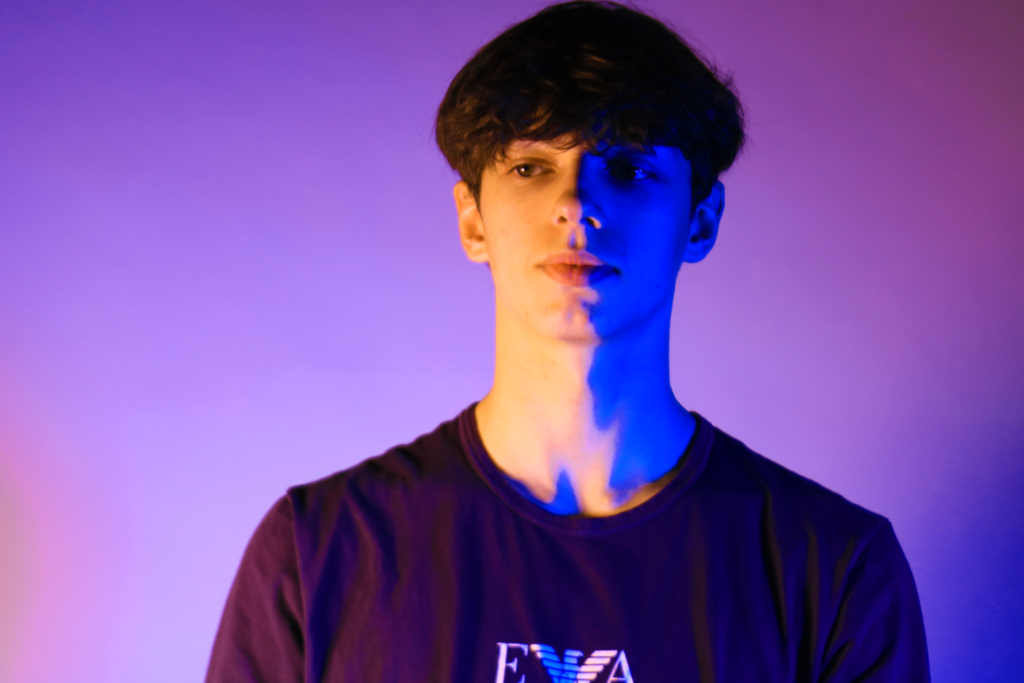
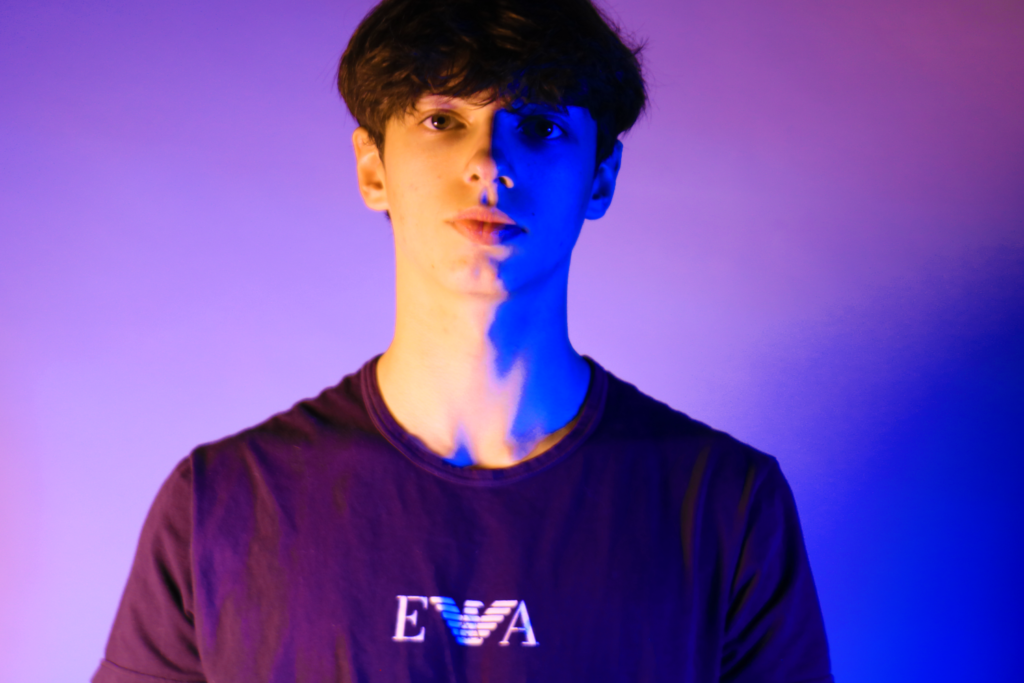
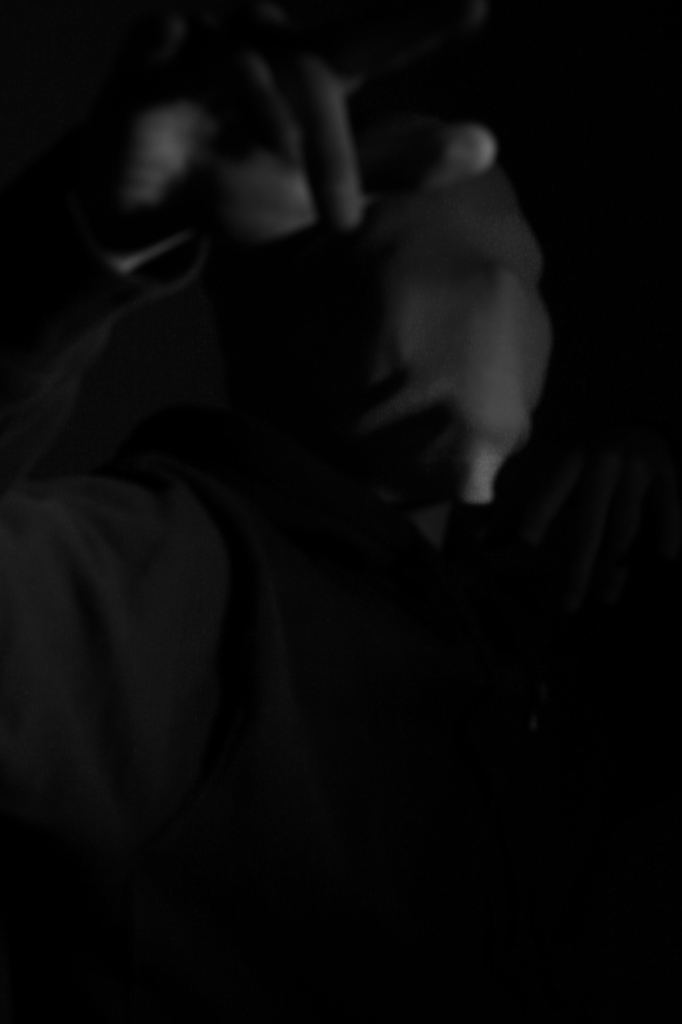
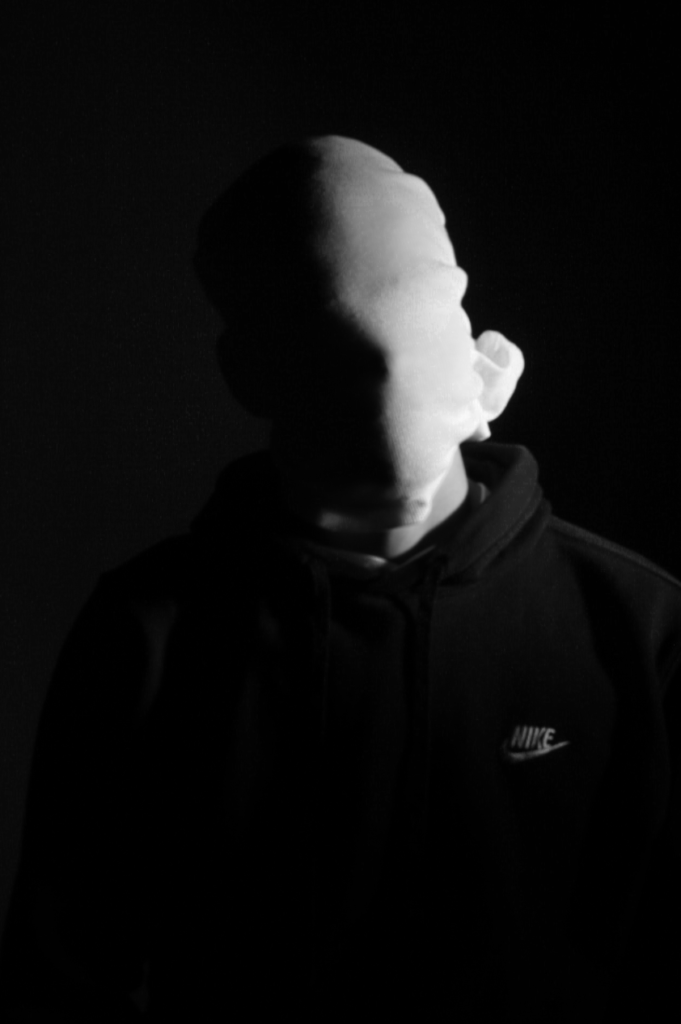
Poupoutsis takes his images from a close-up shot, to make the person in the image the whole focus. The person being the main focus is also created by the background being extremely dark: in the image on the middle it appears to be a vignette effect used, whereas the image on the left is fully black.
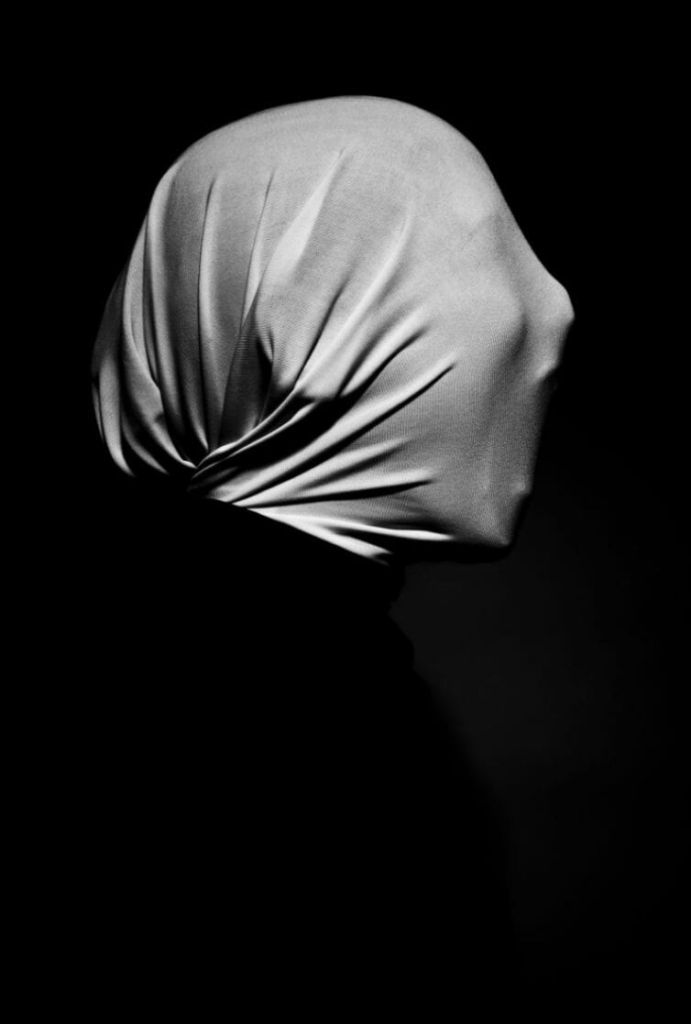
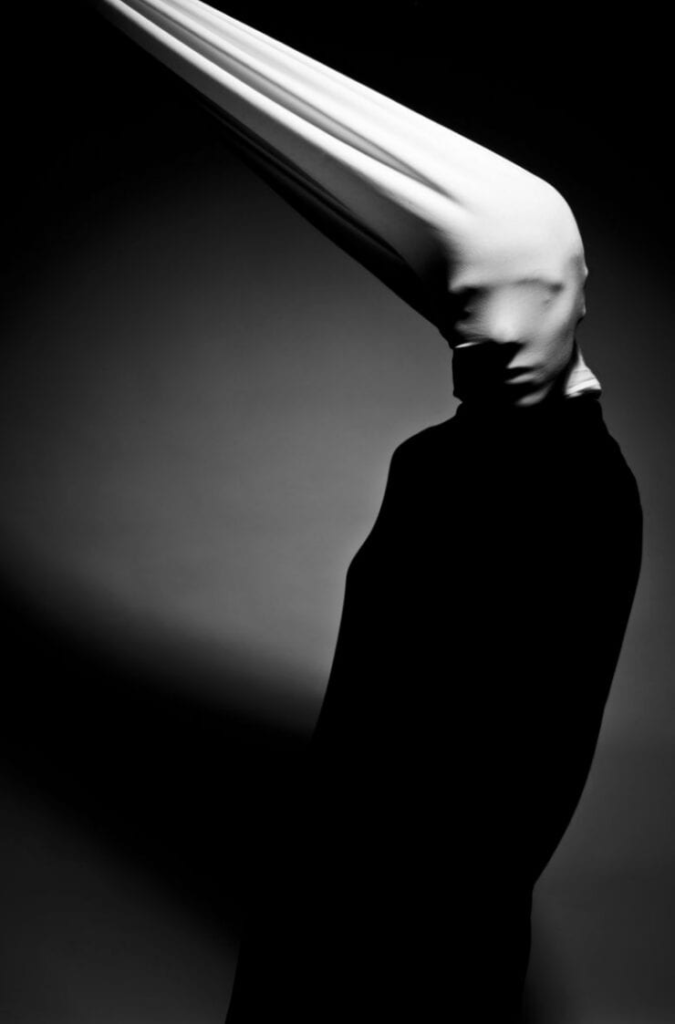
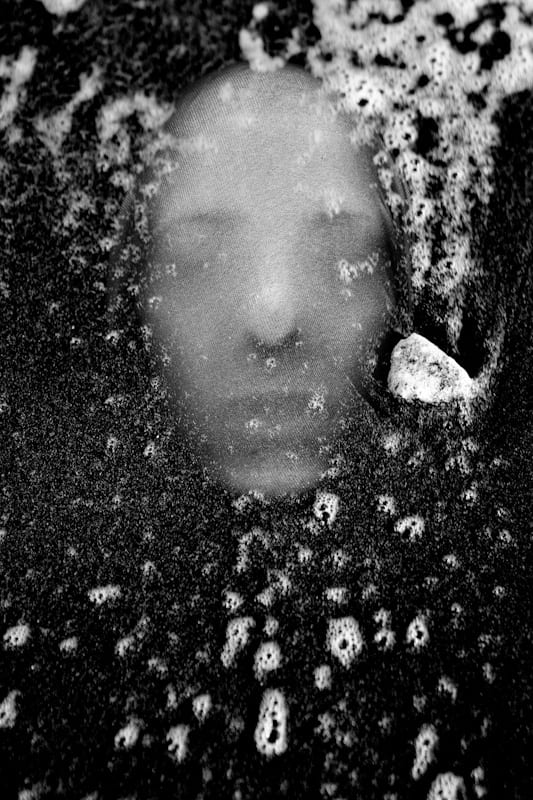



He talks a lot about his inspiration for his work and what he did to achieve these creative images.
” “Metamorphosis” would best describe my creative process. I am influenced by Cubism, shapes, shadows and textures. Creating beautiful and abstract images intrigues me. I am fascinated by people’s faces and especially by the transformation they go through in my photographs. We are complex and unique individuals with our own experiences, fears and losses and use our life experience to view the world. Being true to ourselves is one of the most challenging thing we can do. “
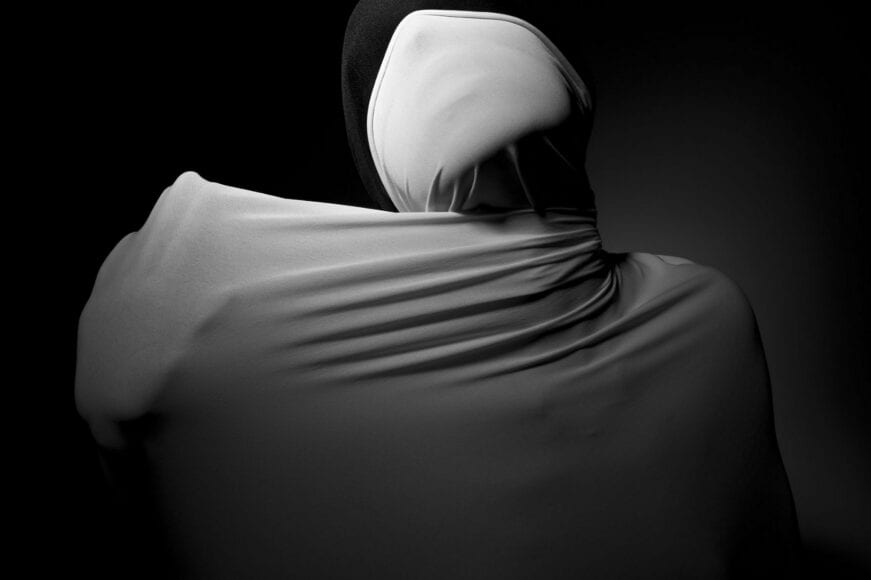
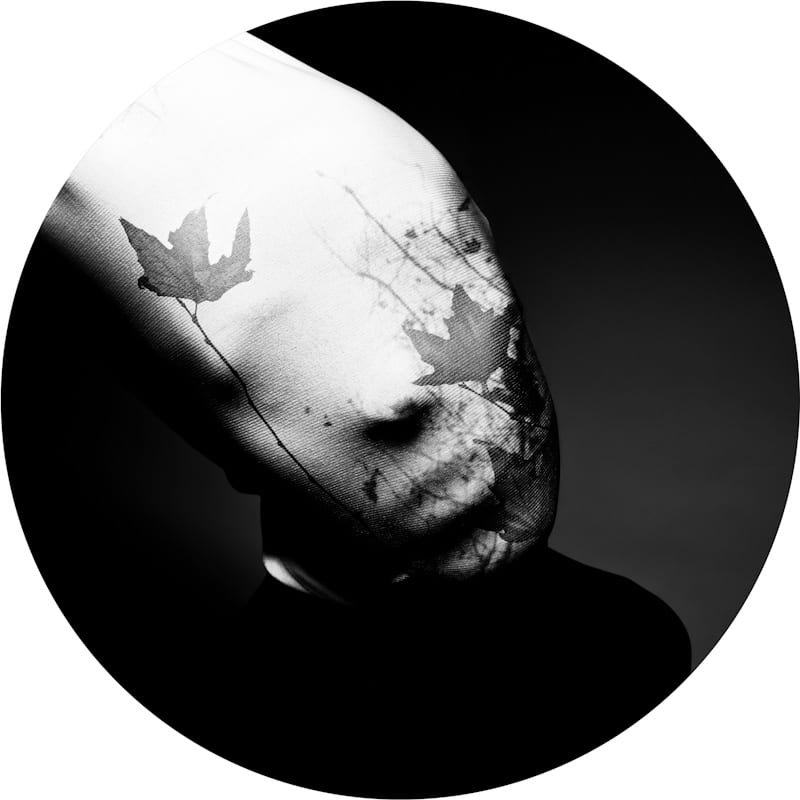


He further talks about his fascination with faces and how he prepares himself before his photoshoots to make sure everything is going according to plan.
“As for my fascination with faces, I have always been intrigued by abstract portraits, every face is unique in its own way and that sparks my imagination. At the same time I’m always looking for ways to transform that uniqueness and go deeper into analysing the identities of people.“
“My process is always different depending on the project. It all starts out with an idea which then turns into small sketches. I always have a diary in which I write down all my ideas. Pre-visualising the shoot is also very important and the search for the appropriate materials, textures, urban locations is needed. I prefer studio work because there I have total control of the light.“
Overall, Poupoutsis’s work highlights the power of visual storytelling in exploring human experiences.
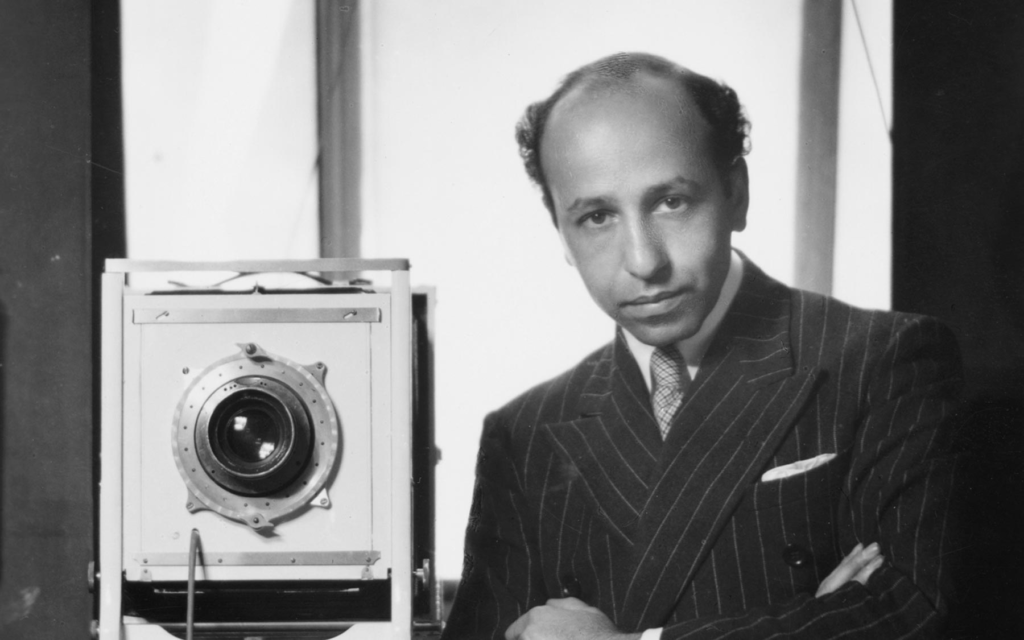
Michael Wills
Michael Wills is a notable photographer recognized for his contributions to the field, particularly in documentary and fine art photography. His work often focuses on capturing the essence of human experiences and social issues, using a narrative approach to tell stories through his images. Wills’s photography is characterized by its emotional depth and attention to detail, allowing viewers to connect with the subjects on a personal level. He has explored various themes, including identity, community, and the passage of time, making his work significant in contemporary photography.





My Photo-Shoot Response
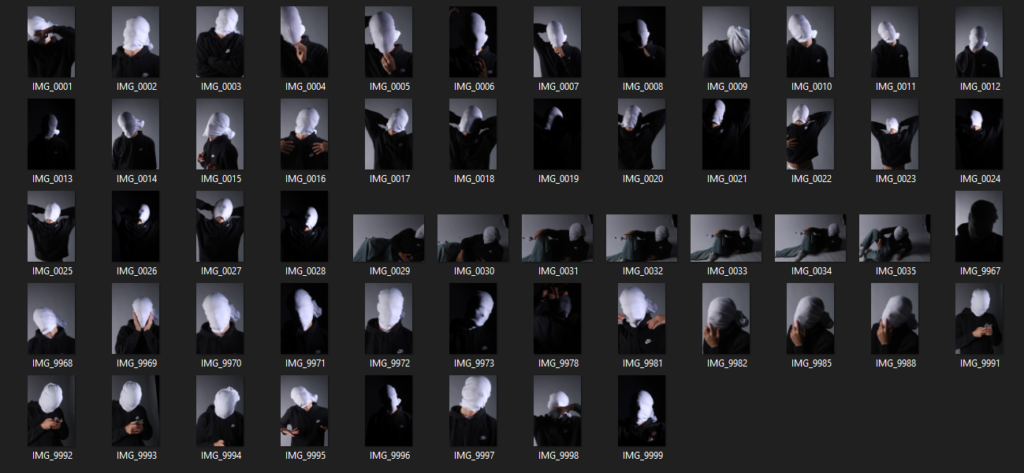
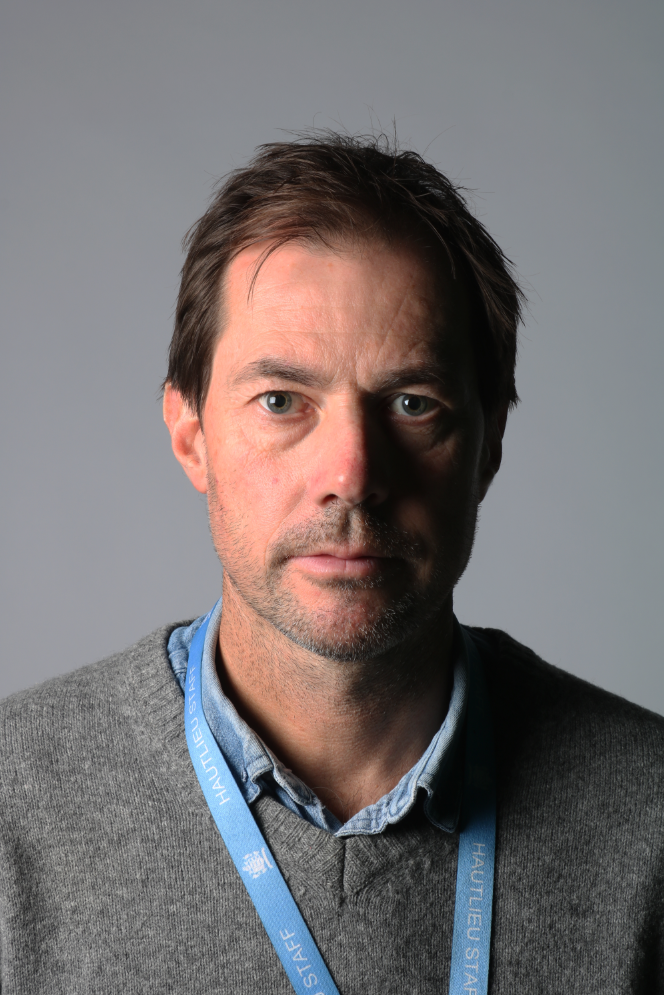
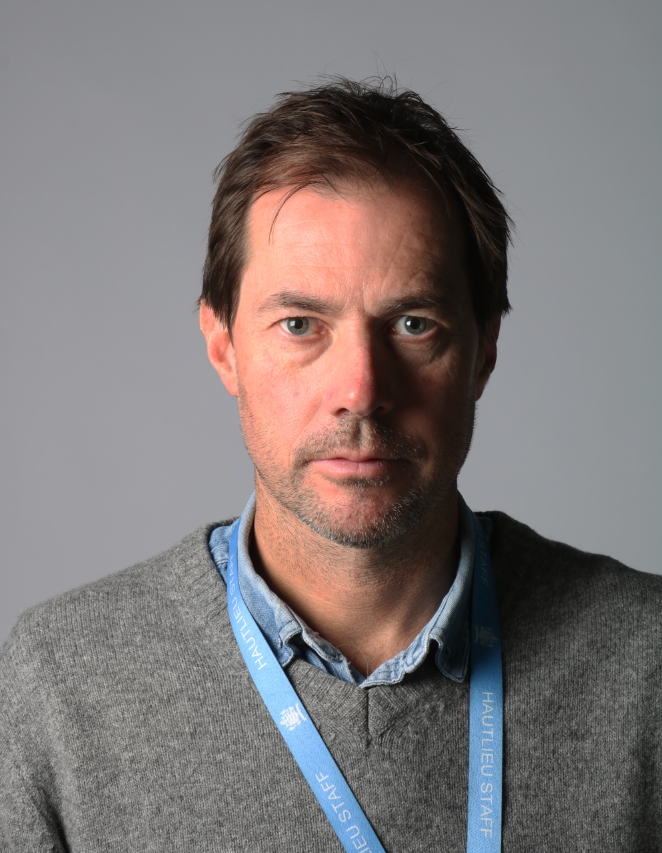
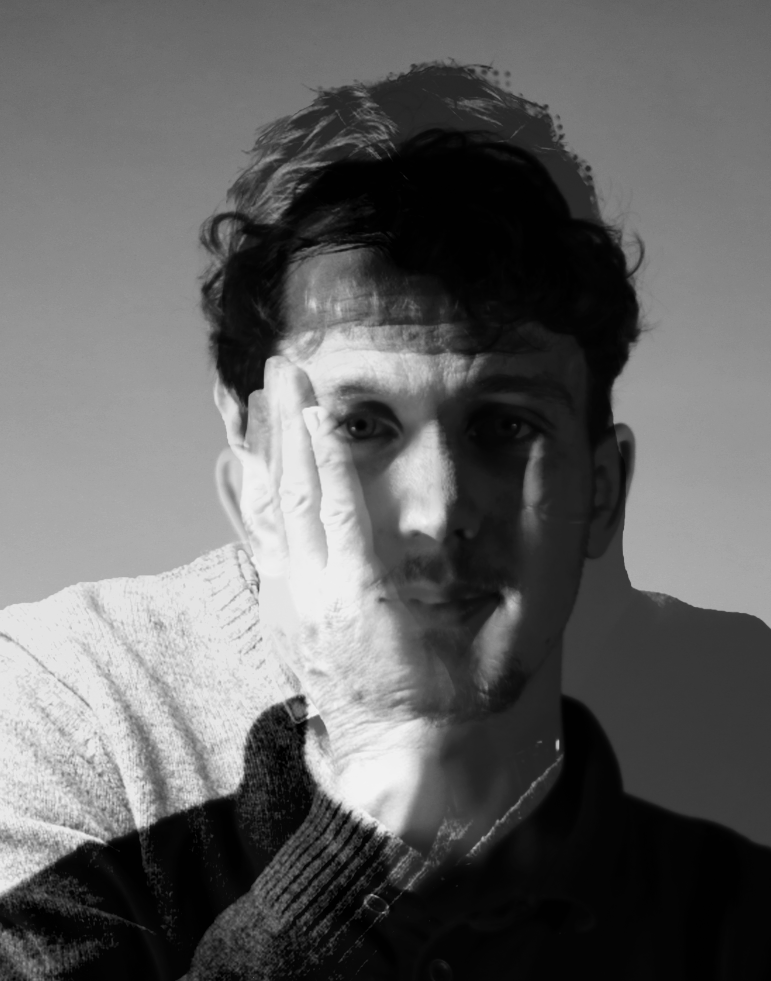
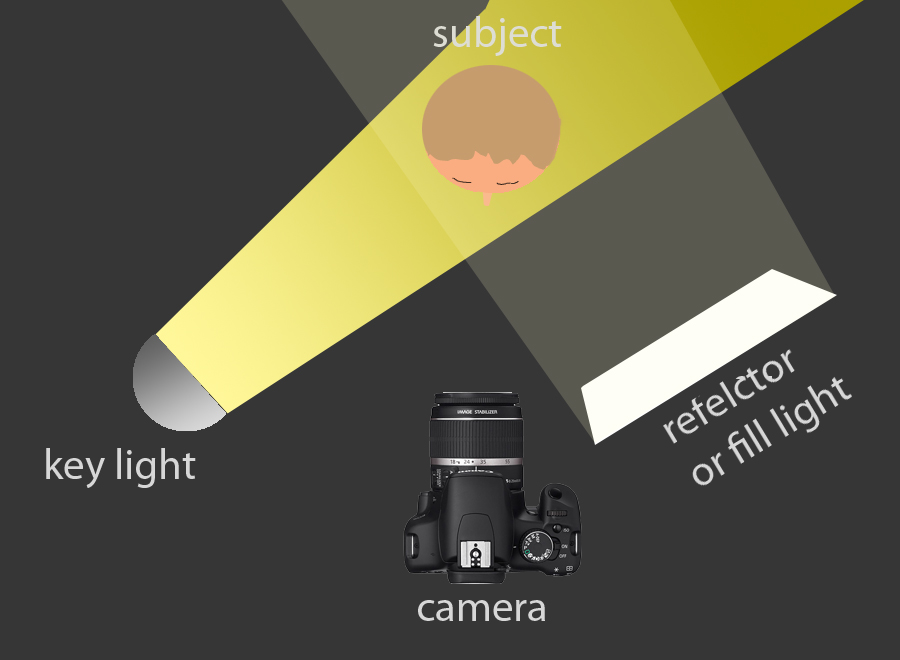
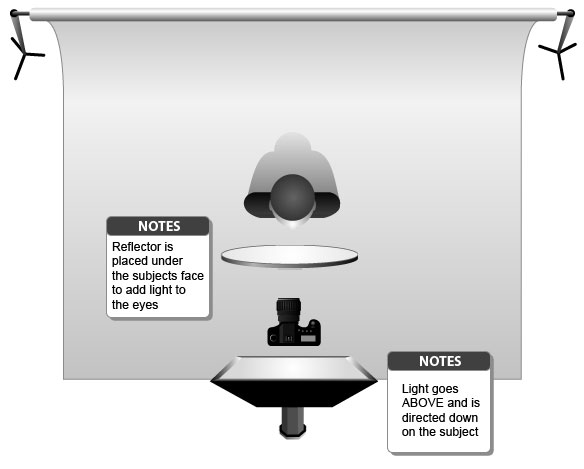
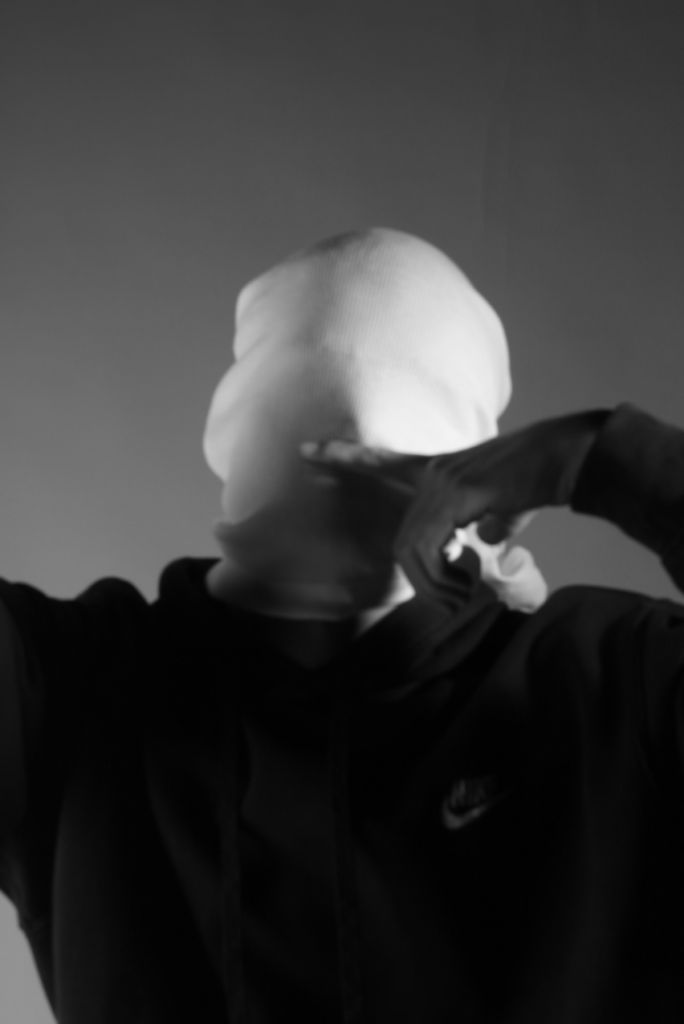
These are my Photoshoot Responses of Andreas Poupoutsis. I tried experimenting with the light and discovered quite a unique and interesting way to manipulate it. I first started adjusting the brightness of the flash and physically moving the light stand and proceeded to take the photos. I was taking Photos of my model and was repeatedly pressing the button for it, giving the flash less time to light up the room. This helped me focus the light only on my model and not the entire room.
I communicated with my model, explaining to them that their body can also convey their emotions, not just the face. This made my images stand out and feel more connected to them. For me at least.
Experimentation/Editing
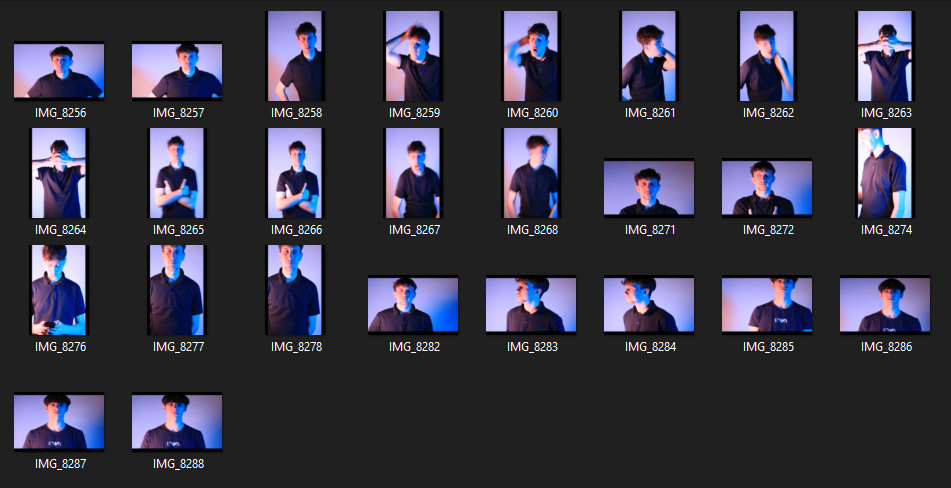
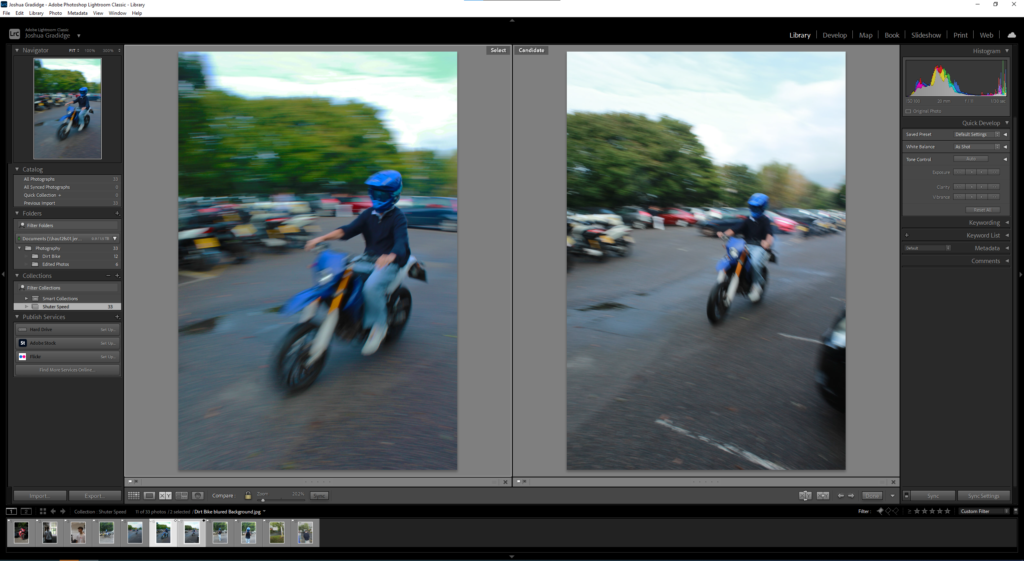
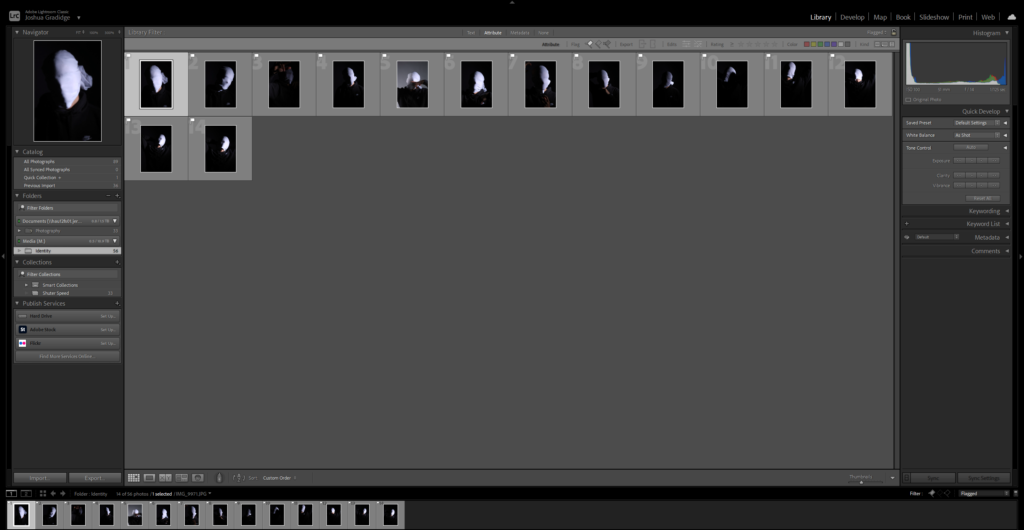
After uploading my Photos to my Hard drive, I used Adobe Lightroom Classic to browse through my photos and see which ones came out…Bad, Good or Great.
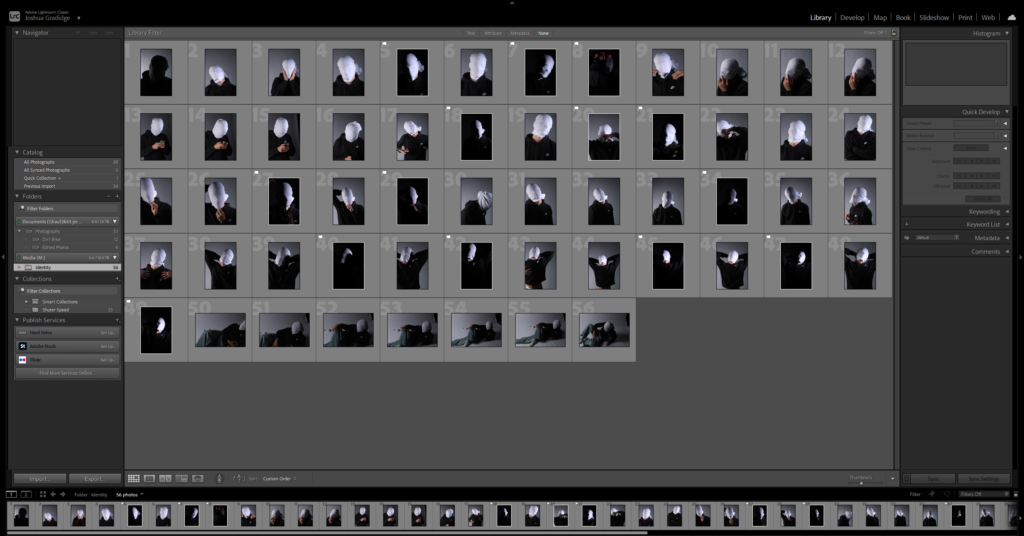
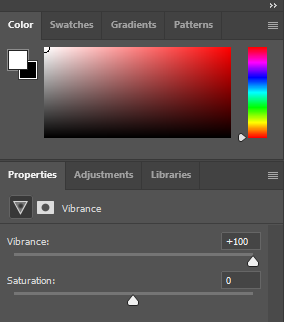
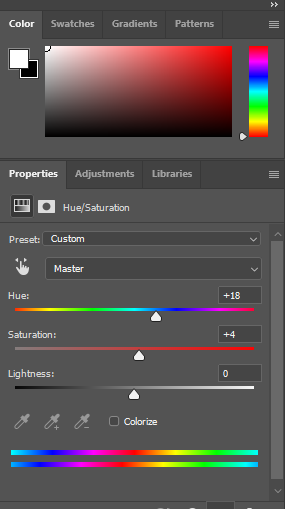
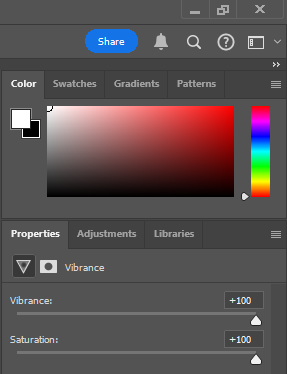
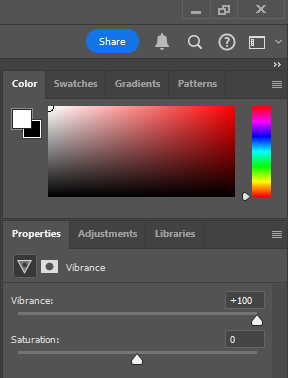
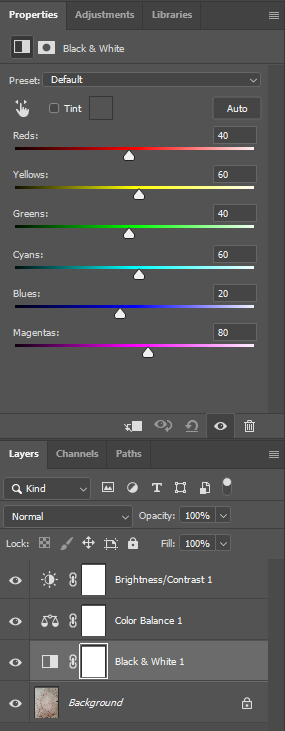
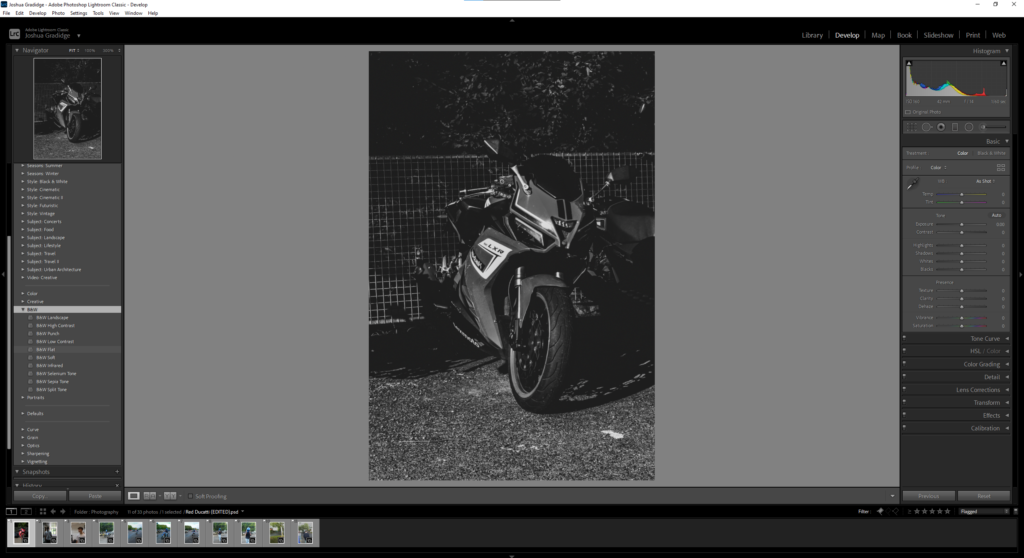
I flagged the Photographs which caught my attention and followed up by moving/editing them further into Adobe Photoshop. I decided to play around a bit with the settings in Photoshop to create these Monochrome based images. The settings that I used was…
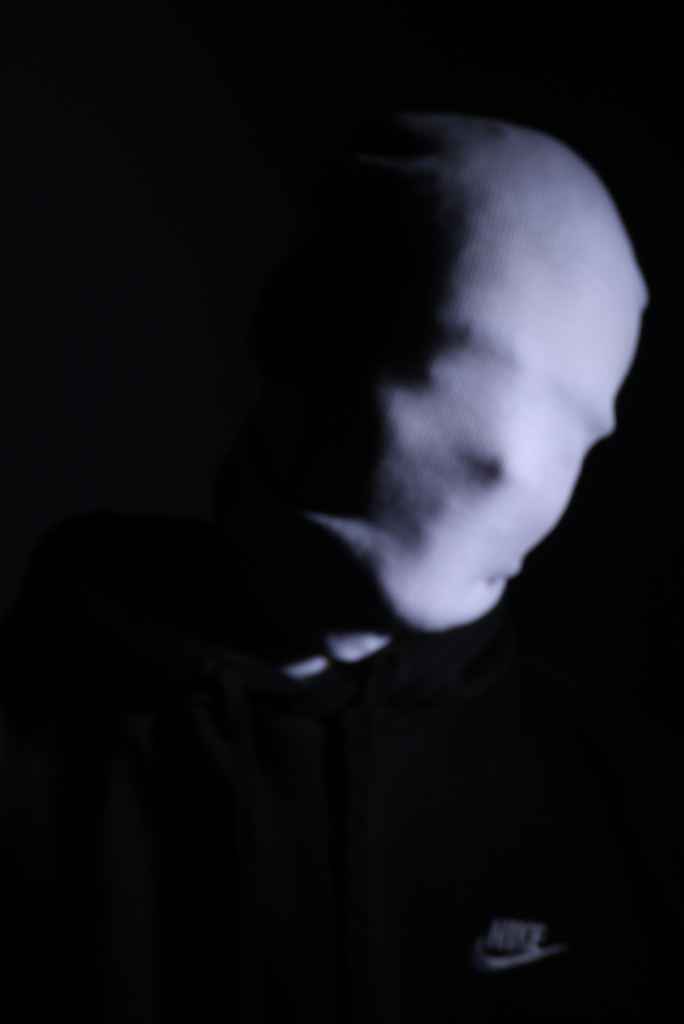
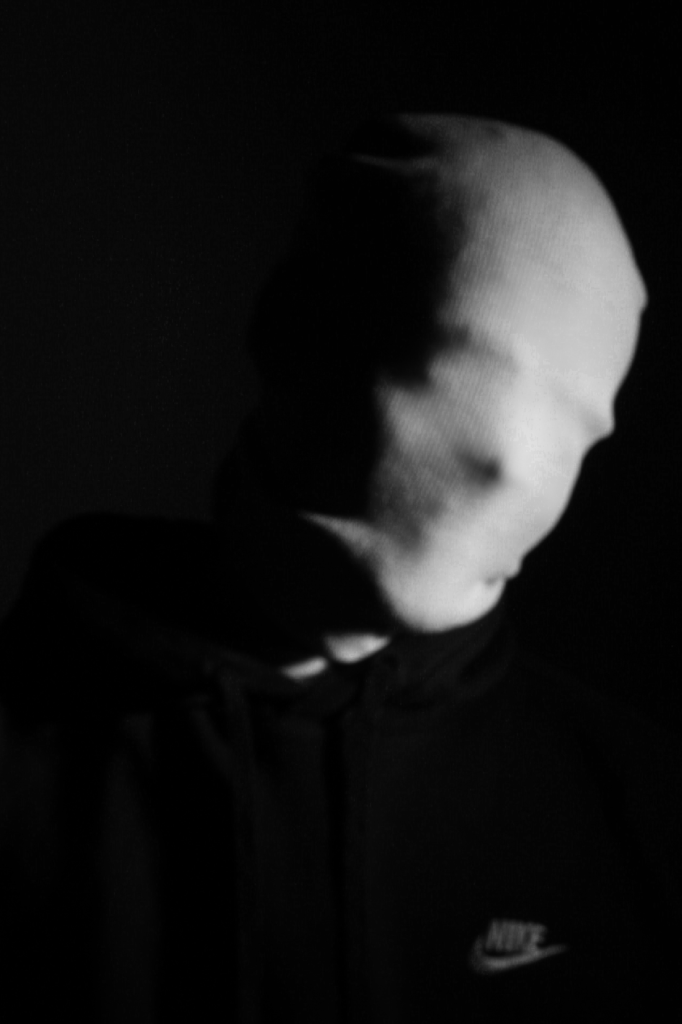
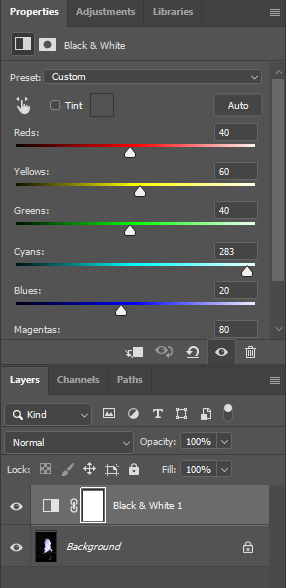


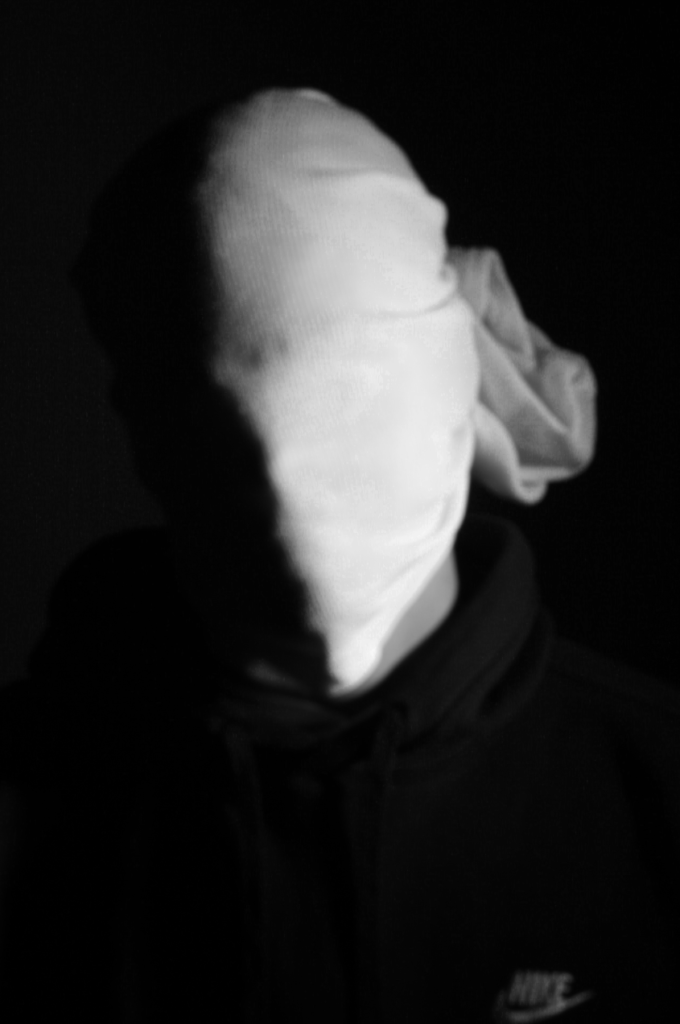
This is the Before and After of the Original Image with the Black and White Filter applied. All of my Images for the theme of Identity will all have the exact same Black and White filtered applied.
Slowly my photographs started looking like Andreas Poupoutsis. I could see similarities.



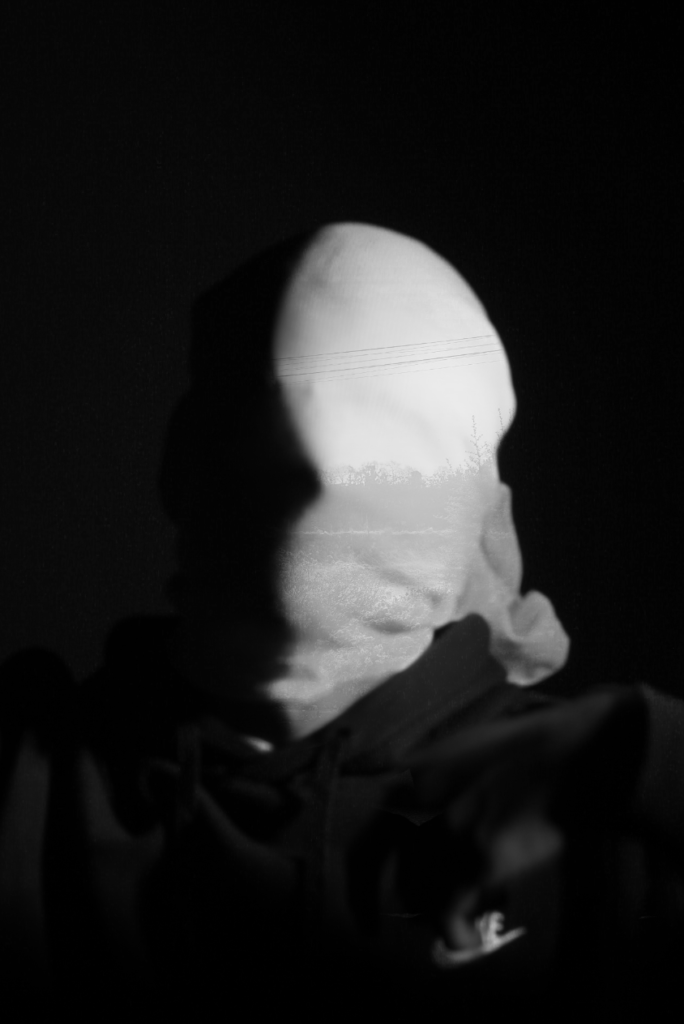
I experimented further by blending in different images such as a Landscape photograph that I took with my Identity Photos. Below is the image used to blend into my Photograph and the settings that I used to do this.
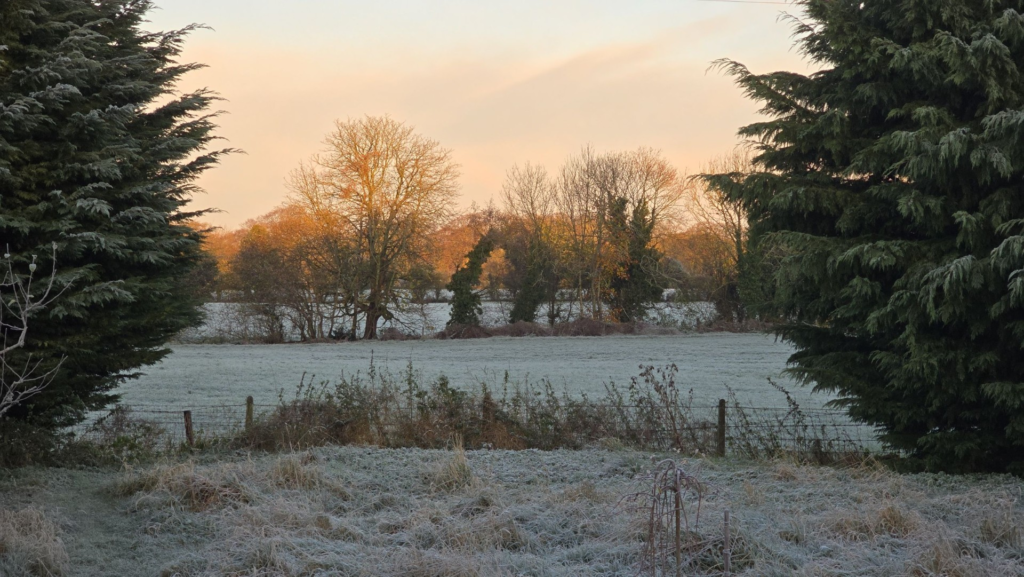
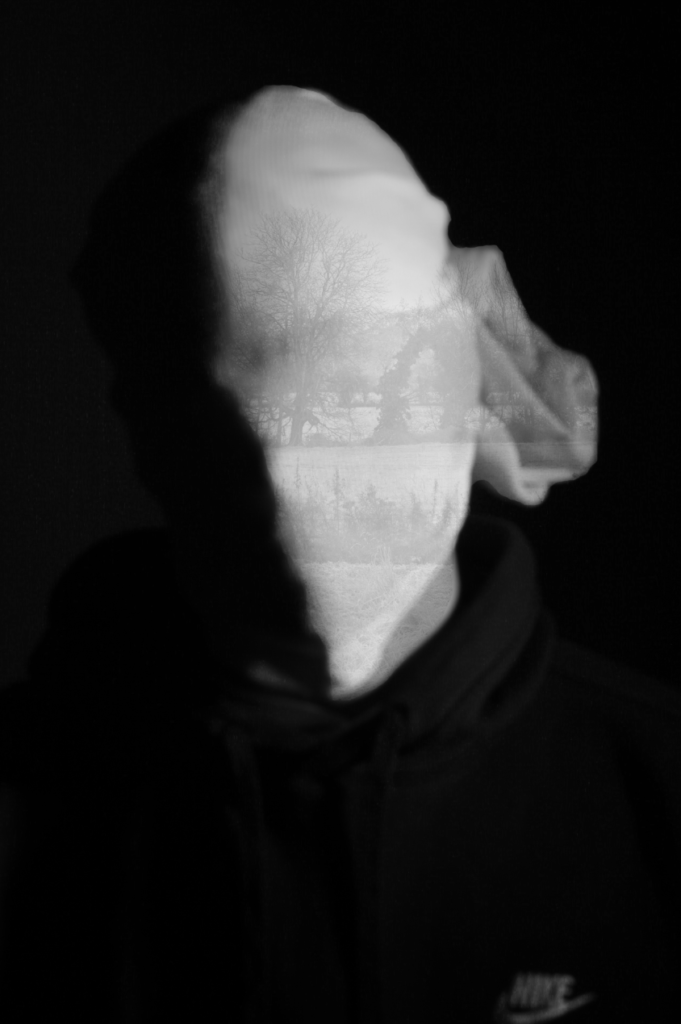
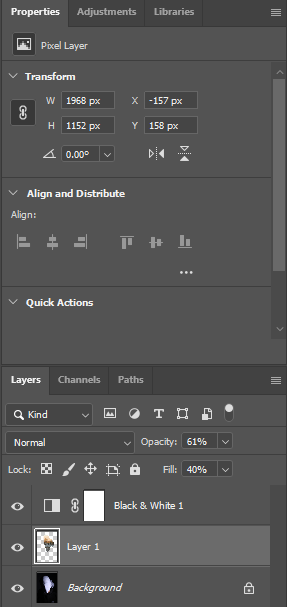



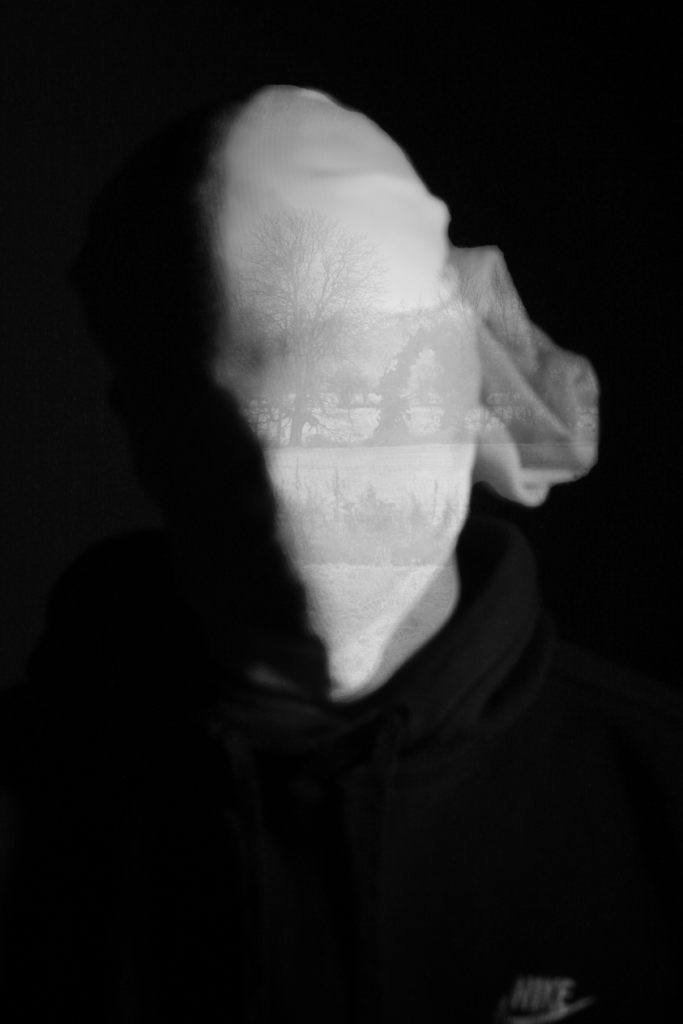
This is the Before and After of the Original Image with the blended image applied. I will be implementing this into some other Images.
Its a work in progress but I am slowly getting there.



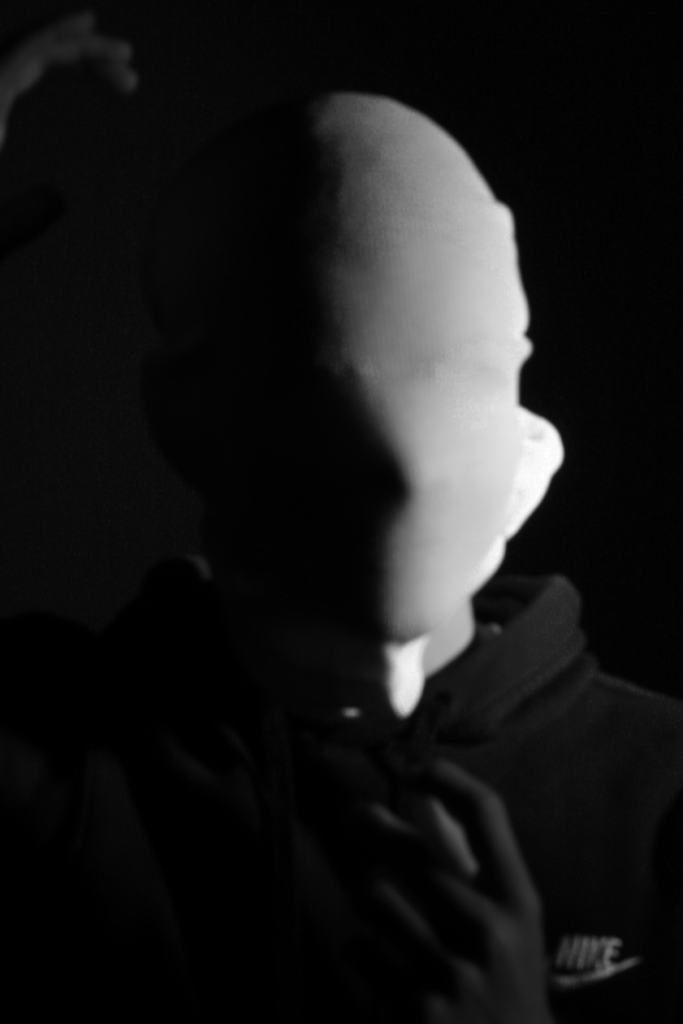
Final Photos
These are my Final images that have been produced/edited. There were 56 Images taken and as I said before I used Adobe Lightroom Classic to browse through my photos and select my Best Images from my Photoshoot. In this case, I chose these 14 images and applied all the filters and overlaying as said in the previous Section.
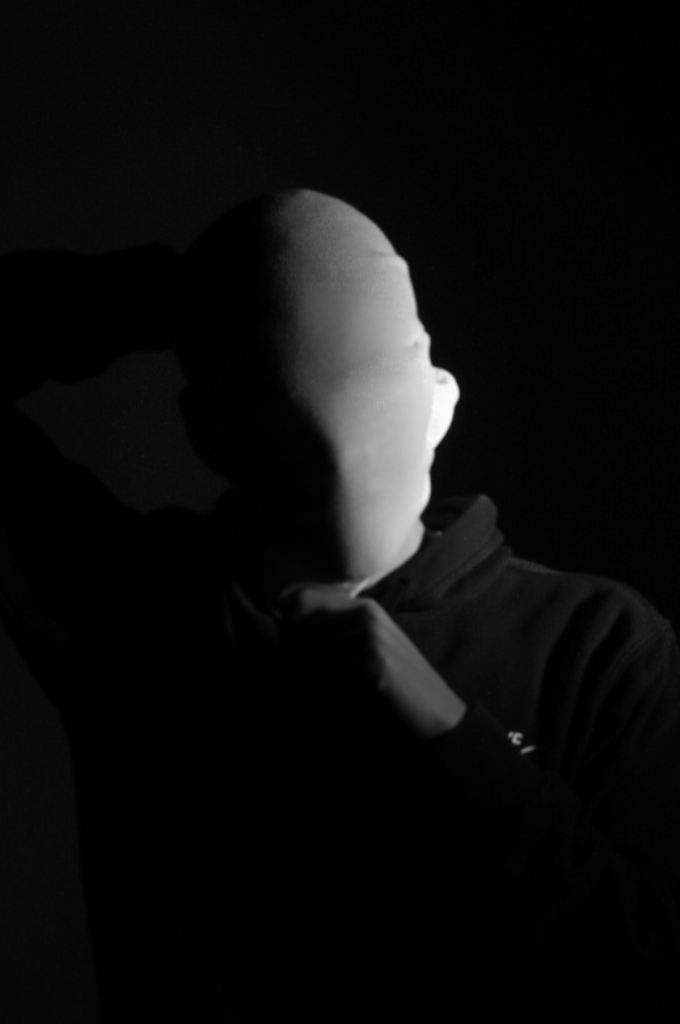
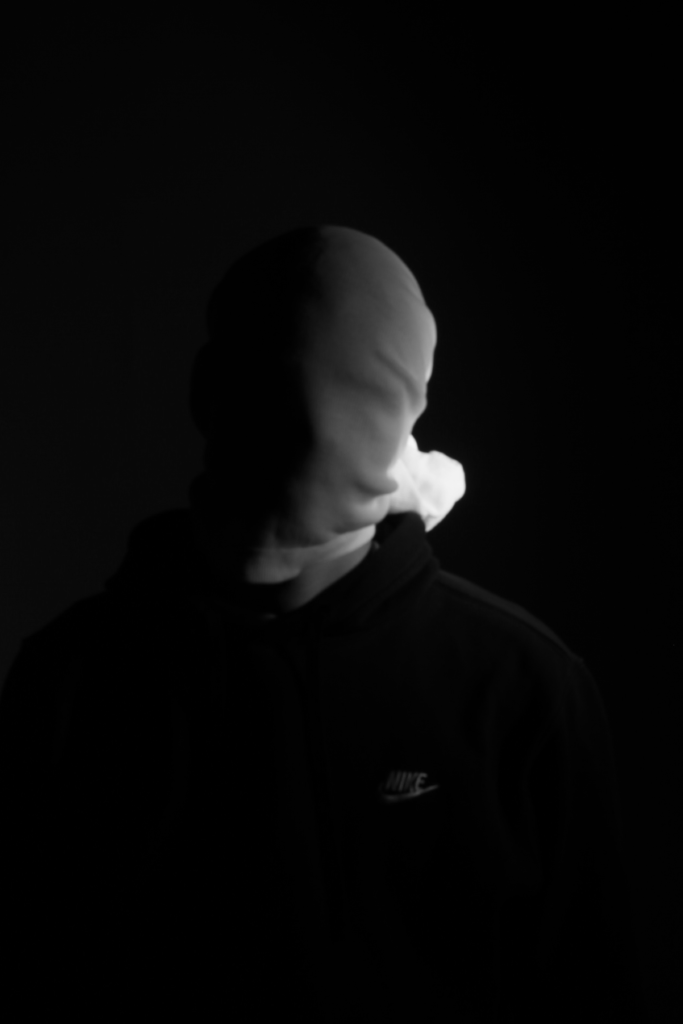
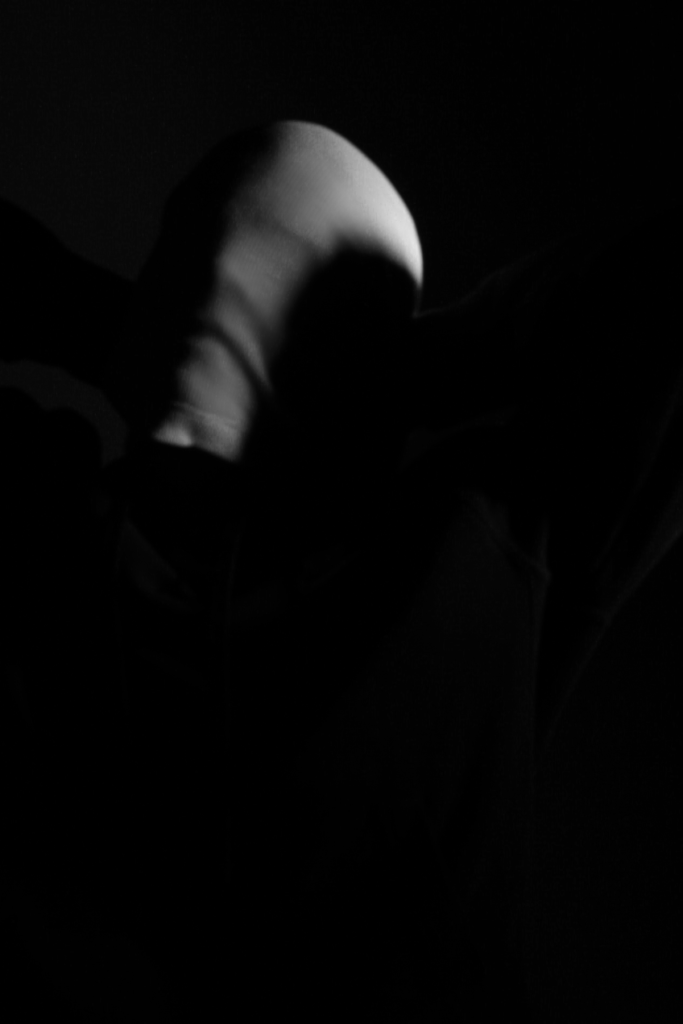
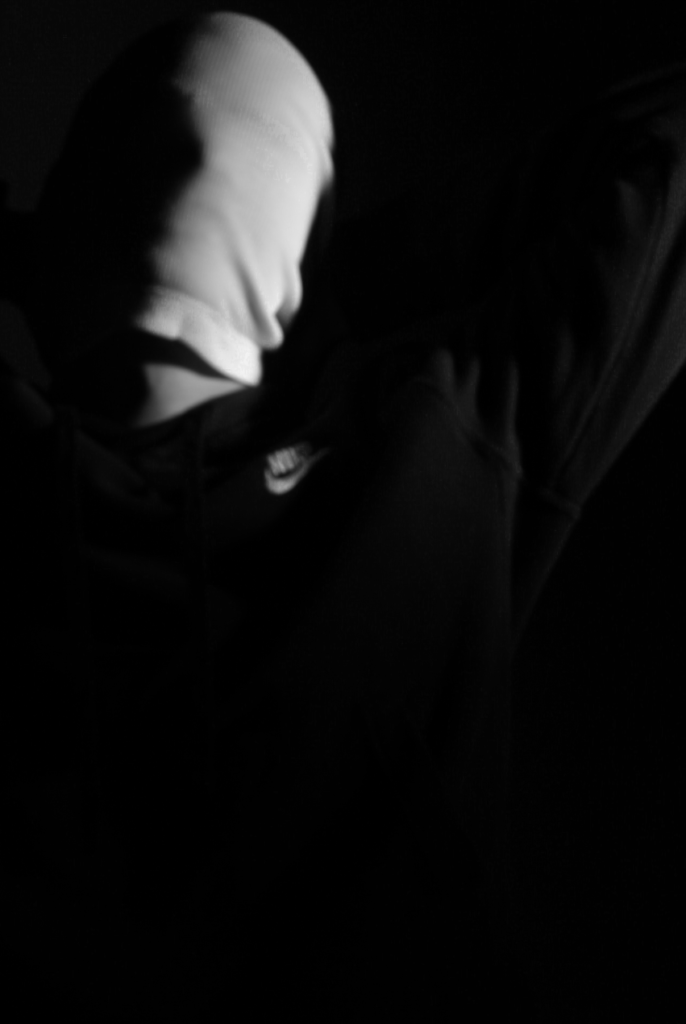
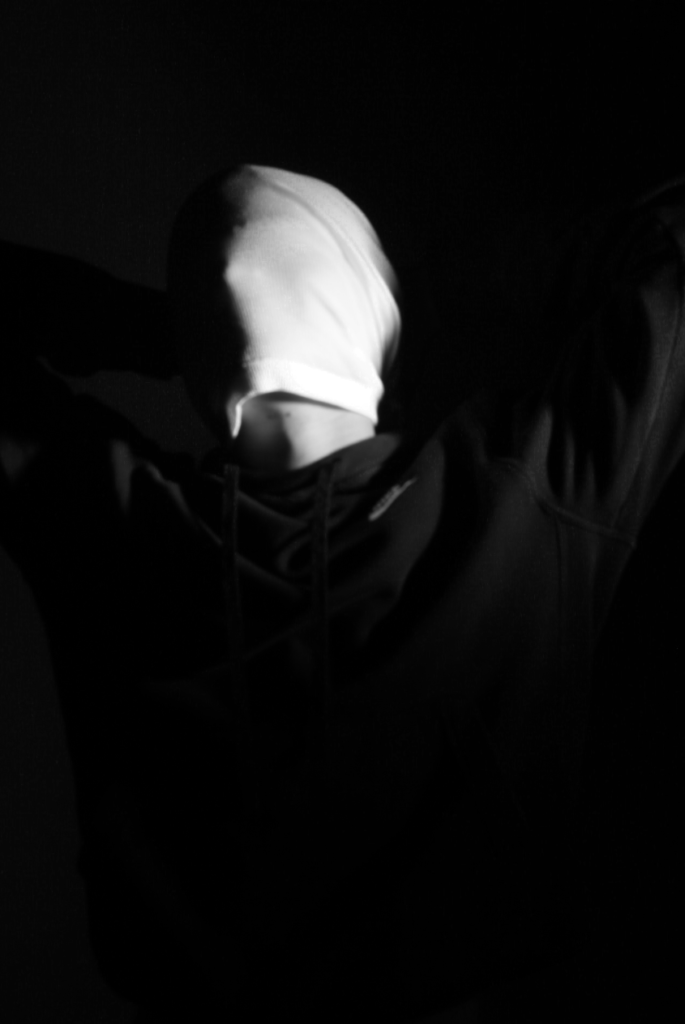
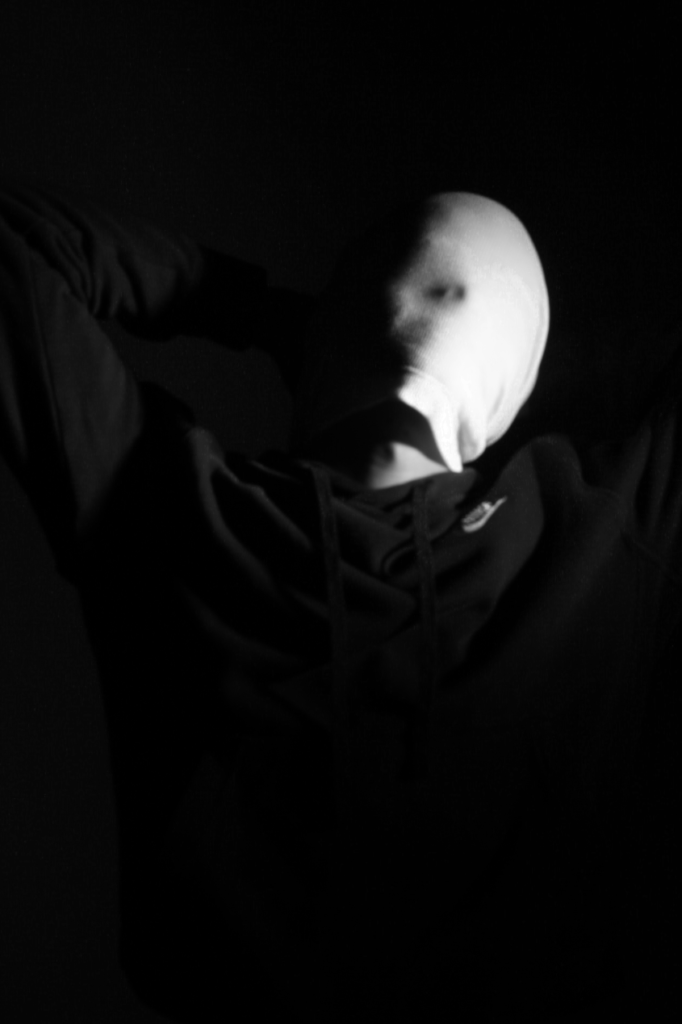
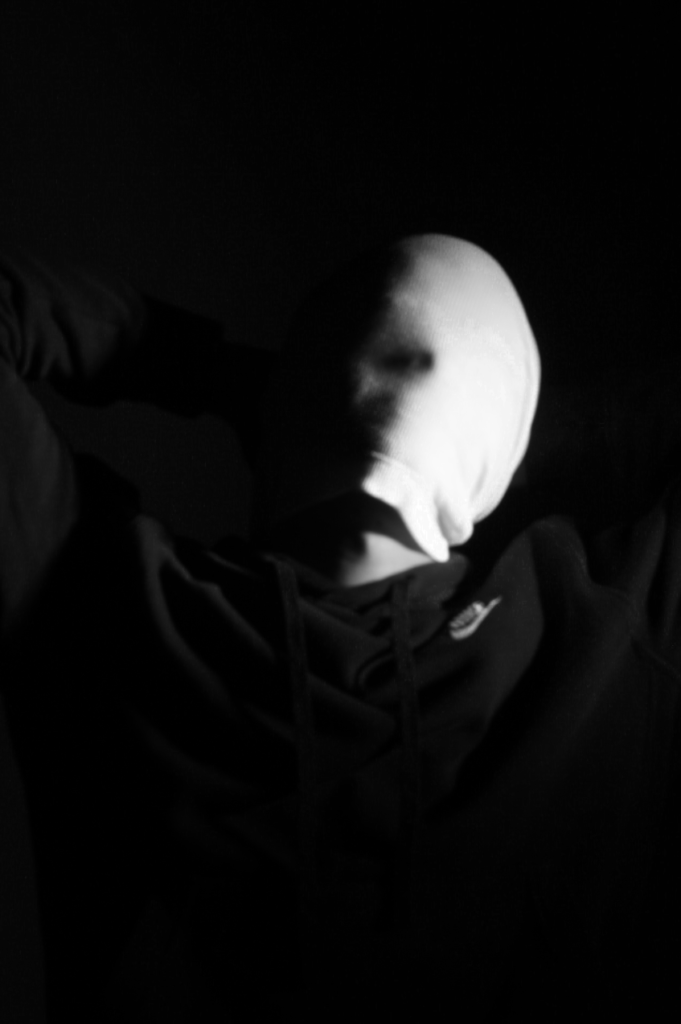
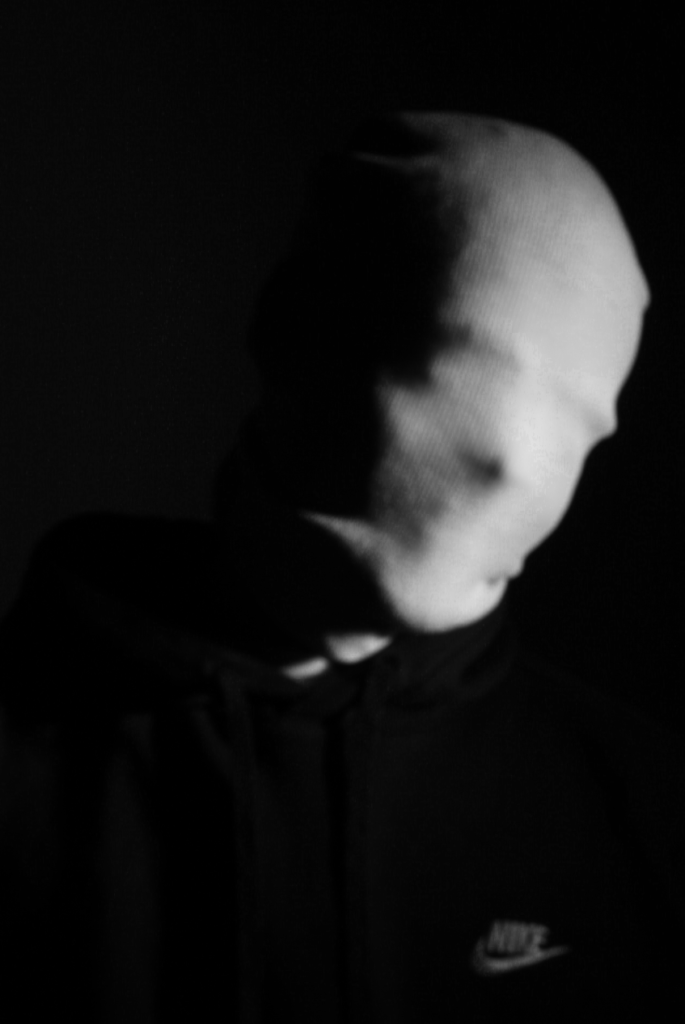














Now comes the hard part. For my Exam I have to choose a certain amount of images to be sent and printed off to be displayed on a visual canvas of our choice. What I mean by this is that Firstly, I need to decide on which images to use. Secondly, I need to decide how big or how small I want my Images to be printed off and Lastly, I need to decide how big I want the canvas that’s going to be holding my images to be cut out.
Chosen Images For Printing
After careful thought and consideration, these are the photographs that I want to be Displayed/Printed.






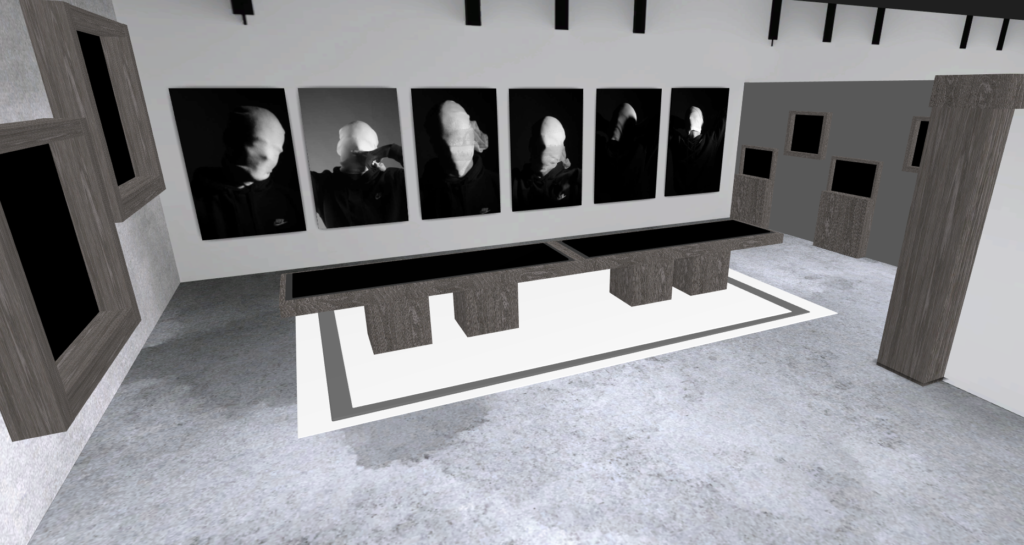
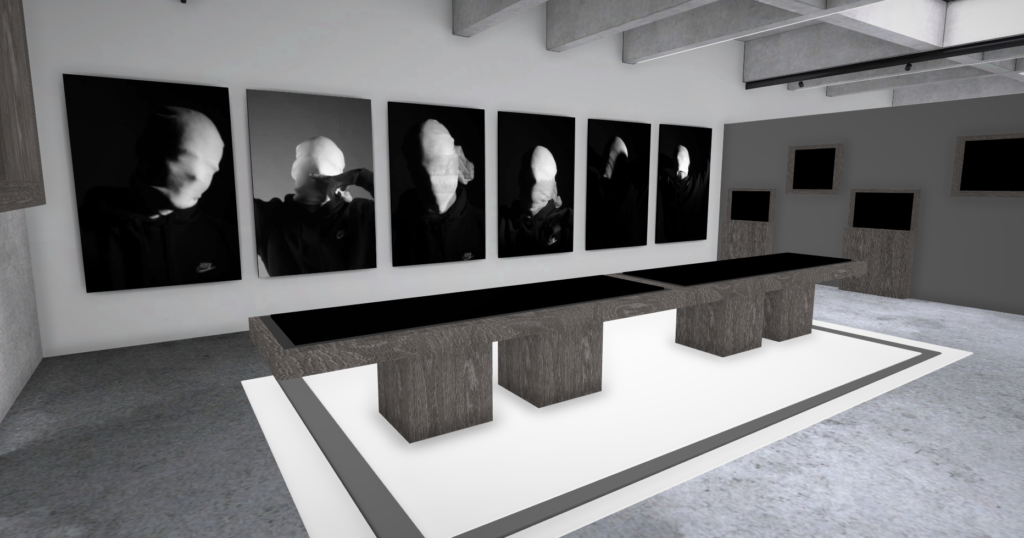
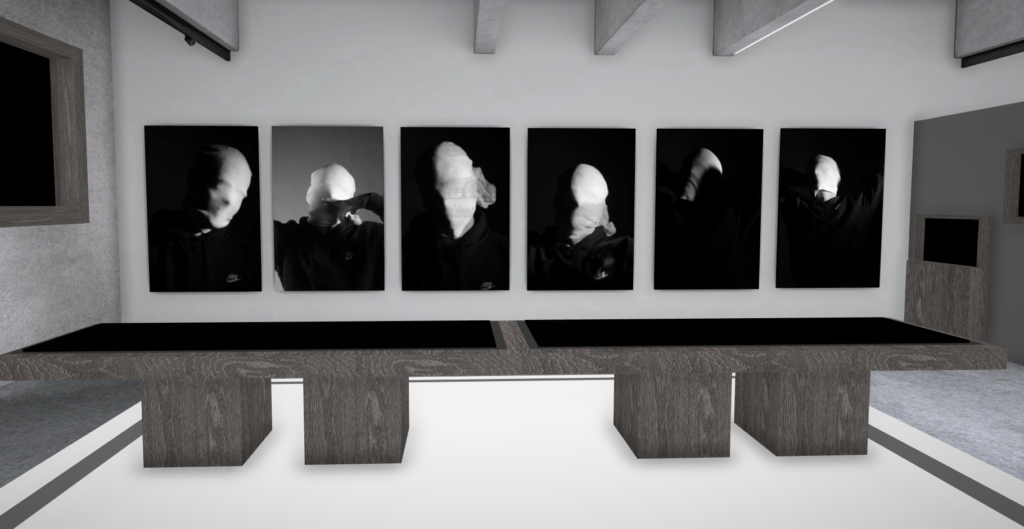
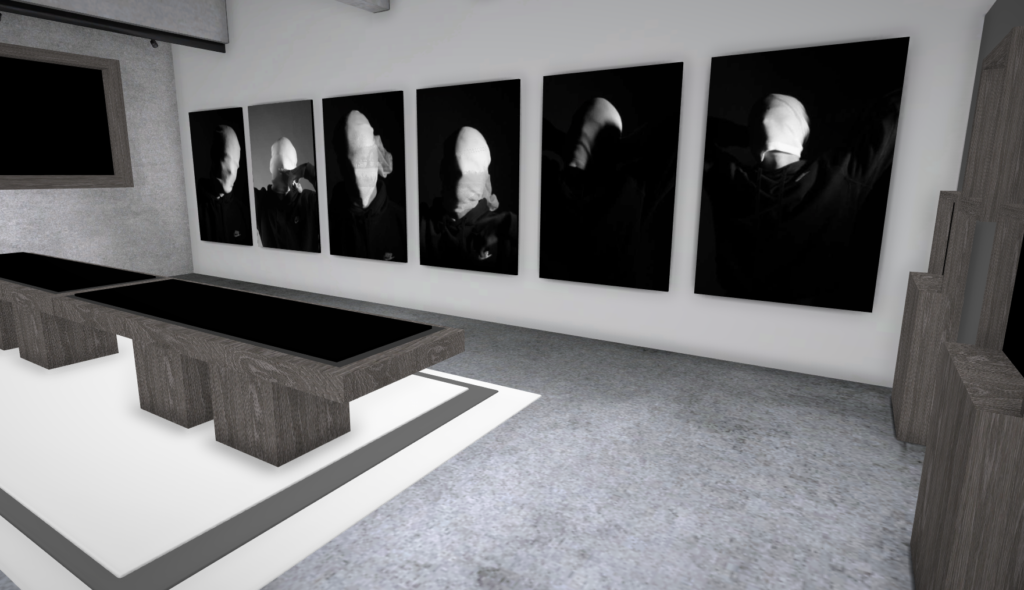
Andreas Poupoutsis shows his theme of identity through the uniqueness of facial expressions. He takes his images from a close-up shot, and makes the background extremely dark to highlight the figure to being the main focus. These 6 images I think have achieved the closest resemblance of Andreas Poupoutsis work. There is a photograph that utilises a grey background, this was intentional as Poupoutsis uses both a vignette effect for the background or changes the background to be fully black.
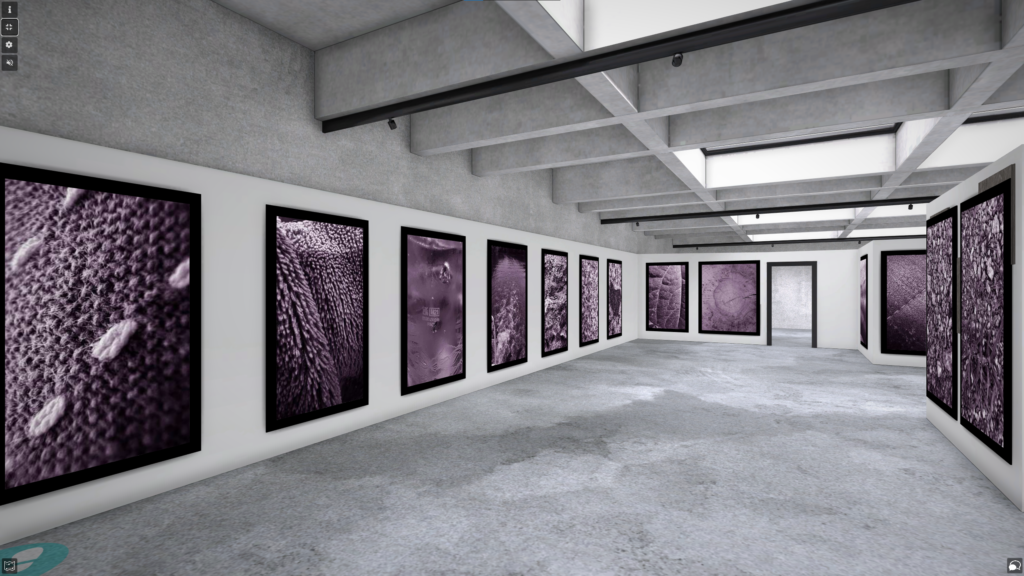
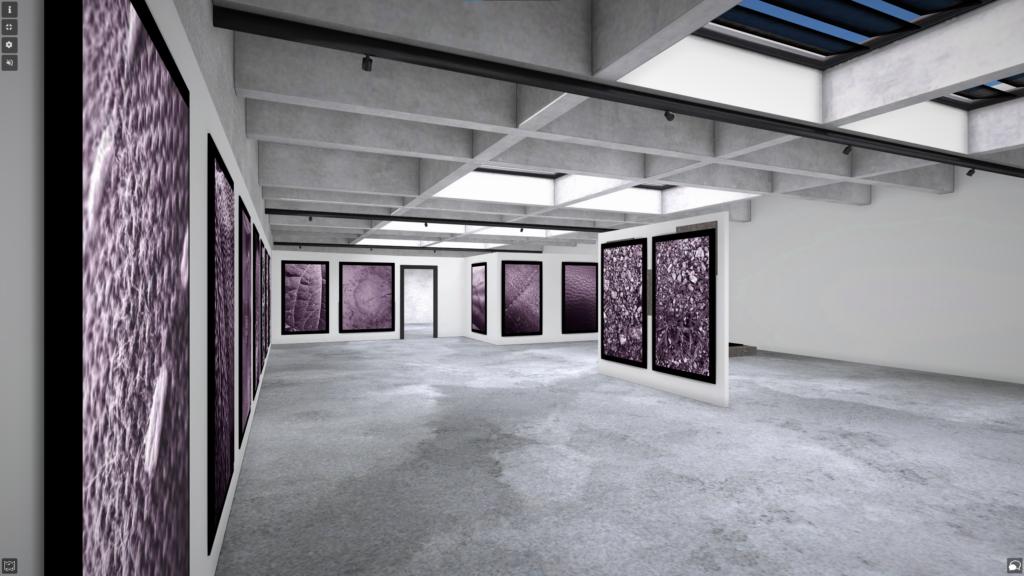
I transferred my Images into Art Steps so that I can visualize what my Images would look like in real life at Exhibition/Museum/Display etc..