What does Landscape mean?
“Landscape” means how a piece of land looks, including hills, trees, rivers, and buildings. It can also refer to pictures of nature or describe the overall vibe of a place, like in business or politics.



When did landscape emerge as a genre in western culture?
Landscape emerged as a genre in Western culture during the Renaissance period, around the 14th to 17th centuries. Artists began to focus more on nature and the environment in their works, moving away from solely religious themes. This shift allowed landscapes to become a popular subject in painting, with artists like Leonardo da Vinci and later, the Dutch masters in the 17th century, contributing significantly to its development. By the 18th century, landscape painting had solidified its status as a distinct genre, especially with the Romantic movement, which emphasized the beauty and emotional power of nature.
When did classical landscapes emerge as a genre?
Classical landscapes emerged as a genre during the Renaissance, particularly in the 15th and 16th centuries. Artists began to depict idealized natural scenes, drawing inspiration from ancient Roman and Greek art. This genre continued to evolve through the Baroque period and into the 18th century, with artists like Claude Lorrain and Nicolas Poussin creating works that emphasized harmony and balance in nature. These classical landscapes often featured dramatic skies, serene waters, and carefully arranged compositions, which became influential in shaping the landscape genre in Western art.
What prompted the rise of Landscape Art during the late 18th / 19th century?
The rise of Landscape Art during the late 18th and 19th centuries was influenced by several factors. One major reason was the Romantic movement, which emphasized emotion and the beauty of nature. Artists began to focus on capturing the sublime aspects of the natural world, showcasing its power and majesty. Additionally, the Industrial Revolution led to rapid urbanization, prompting a longing for the countryside and a simpler way of life. This nostalgia was reflected in art as artists like J.M.W. Turner and Caspar David Friedrich created stunning landscapes that highlighted nature’s beauty and its contrasts with industrialization. Overall, these social, cultural, and emotional shifts played a significant role in the popularity of landscape art during this period.


When did landscape photography originate?
Landscape photography originated in the early 19th century, around the 1830s and 1840s. The invention of photography itself in the 1820s laid the groundwork for this genre. Early photographers, like Carleton Watkins and Ansel Adams, began to capture the beauty of natural landscapes, showcasing mountains, forests, and other scenic views. The development of new photographic techniques and equipment allowed for greater detail and clarity, further popularizing landscape photography as an art form. By the late 19th century, it had become a well-established genre, appreciated for its ability to document and celebrate the natural world.
What is Romanticism?
Romanticism was an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement that originated in the late 18th century and peaked in the early to mid-19th century. It emerged as a reaction against the Enlightenment’s emphasis on reason and the Industrial Revolution’s focus on industrialization and mechanization.

Key characteristics of Romanticism include:
1. Emphasis on Emotion: Romanticism places a strong emphasis on individual feelings, emotions, and the sublime. It values personal experiences and the expression of deep emotions over rational thought.
2. Nature: Romantic artists and writers often celebrated the beauty and power of nature, viewing it as a source of inspiration and a reflection of the human spirit. Nature was seen as a place for solace and spiritual renewal.
3. Individualism: The movement championed the individual and the unique perspective of the artist or writer. It often highlighted the importance of personal freedom and self-expression.
4. Imagination: Romanticism valued imagination and creativity, often exploring themes of fantasy, the supernatural, and the mysterious. It encouraged artists to break away from traditional forms and experiment with new ideas.
5. Historical and Cultural Inspiration: Many Romantic works drew inspiration from history, folklore, and the past, often idealizing medieval times or exploring national identities.
Notable figures associated with Romanticism include poets like William Wordsworth, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and John Keats, as well as authors like Mary Shelley and Victor Hugo. In visual arts, painters like Caspar David Friedrich and J.M.W. Turner are often linked to the movement. Overall, Romanticism had a profound impact on literature, art, music, and philosophy, shaping the way we understand emotion, nature, and the individual’s role in society.
Fact file about Romanticism:
Who: The movement included a variety of artists, writers, and musicians. Notable figures include poets like William Wordsworth, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, John Keats, and authors like Mary Shelley and Victor Hugo. In visual arts, artists like Caspar David Friedrich and J.M.W. Turner are significant.
What: Romanticism was an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement characterized by an emphasis on emotion, nature, individualism, imagination, and a focus on the sublime. It sought to express the beauty of nature and the depth of human experience.
Where: The movement originated in Europe, particularly in countries like Germany, France, and Britain. It later spread to other parts of the world, influencing various cultures and artistic expressions.
When: Romanticism began in the late 18th century, around the 1770s, and peaked in the early to mid-19th century, roughly until the 1850s. Its influence continued into the late 19th century and beyond.
How: Romanticism emerged as a reaction against the Enlightenment’s focus on reason and the Industrial Revolution’s mechanization. Artists and writers sought to highlight the importance of emotion and the beauty of nature, often using vivid imagery and expressive language.
Why: The movement arose from a desire to break free from the constraints of rationalism and to celebrate the individual experience. It aimed to explore deeper emotional truths and to reconnect with nature and the past, reflecting a longing for a more authentic and meaningful existence.
The Sublime
“The Sublime” is a concept in aesthetics that refers to an experience of beauty that is overwhelming and transcendent, often evoking feelings of awe, admiration, and sometimes fear. It is associated with vastness, grandeur, and the power of nature, which can inspire both wonder and a sense of insignificance in the face of something much greater.
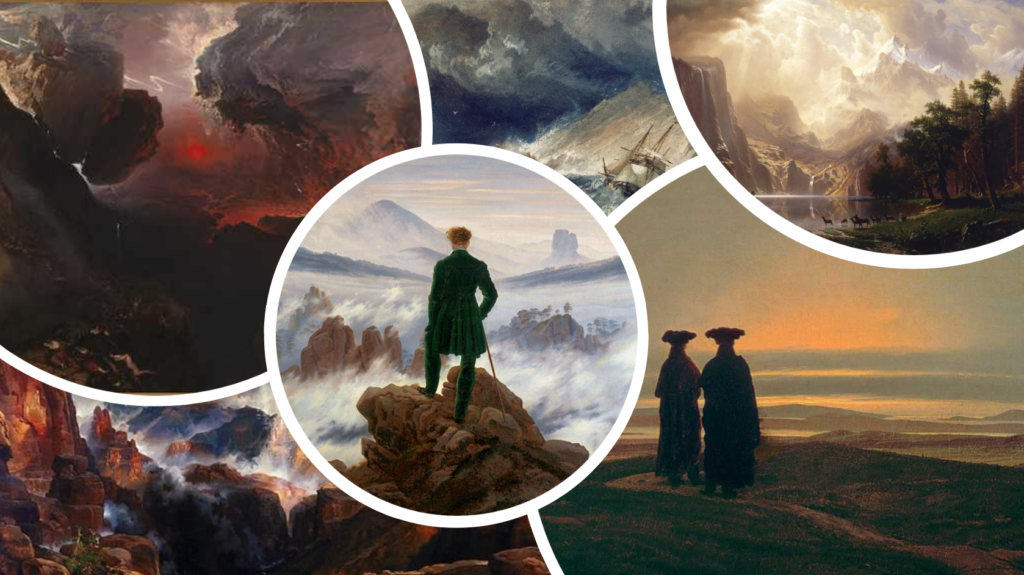

In Romanticism, the sublime was a key theme, as artists and writers sought to capture the emotional intensity of experiences that go beyond ordinary beauty. This could be seen in depictions of dramatic landscapes, powerful storms, or monumental mountains, where the beauty of nature is both captivating and intimidating. The sublime often challenges the viewer’s perception and evokes deep emotional responses, making it a significant aspect of Romantic art and literature.
Importance of British Painters
J.M.W. Turner and John Constable are two of the most important British painters of the Romantic era, and they significantly contributed to the development of landscape painting.
J.M.W. Turner: Turner is known for his innovative use of colour and light, often depicting the effects of atmospheric conditions in his landscapes. His works, such as “The Fighting Temeraire” and “Rain, Steam and Speed,” evoke a sense of drama and emotion, capturing the sublime aspects of nature. Turner’s ability to convey movement and the transient nature of light paved the way for future movements, including Impressionism. He is considered a precursor to modern art due to his expressive style and exploration of colour.
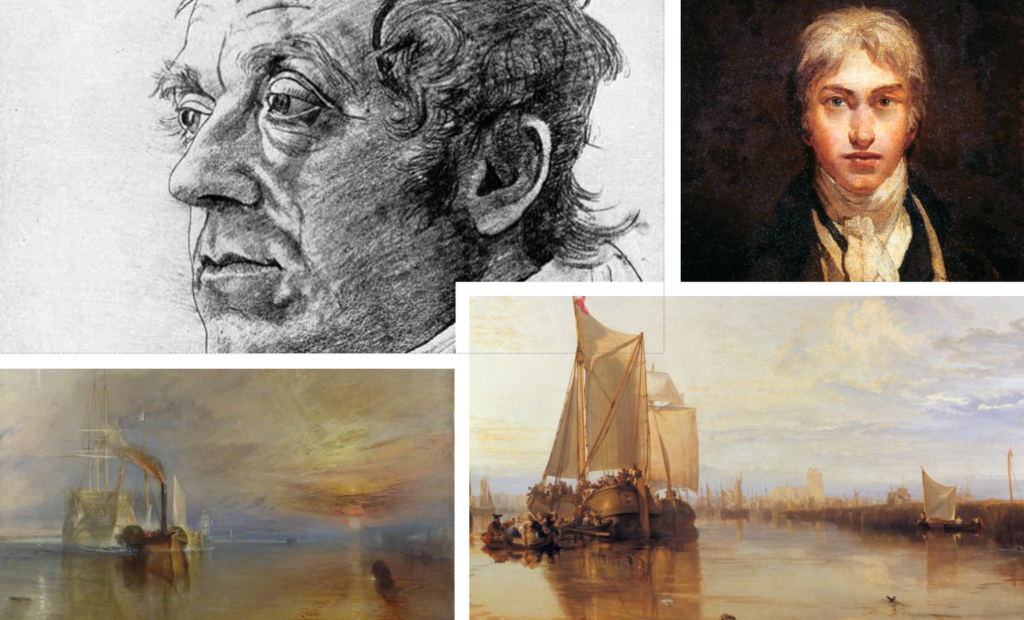

John Constable: Constable, on the other hand, focused on the beauty of the English countryside, often painting scenes from his native Suffolk. His works, like “The Hay Wain” and “Dedham Vale,” are celebrated for their realistic portrayal of nature and the changing seasons. Constable emphasized the importance of light and atmosphere, using techniques like plein air painting to capture the essence of the landscape. He is known for his emotional connection to the land, which resonates with viewers and has influenced generations of artists.
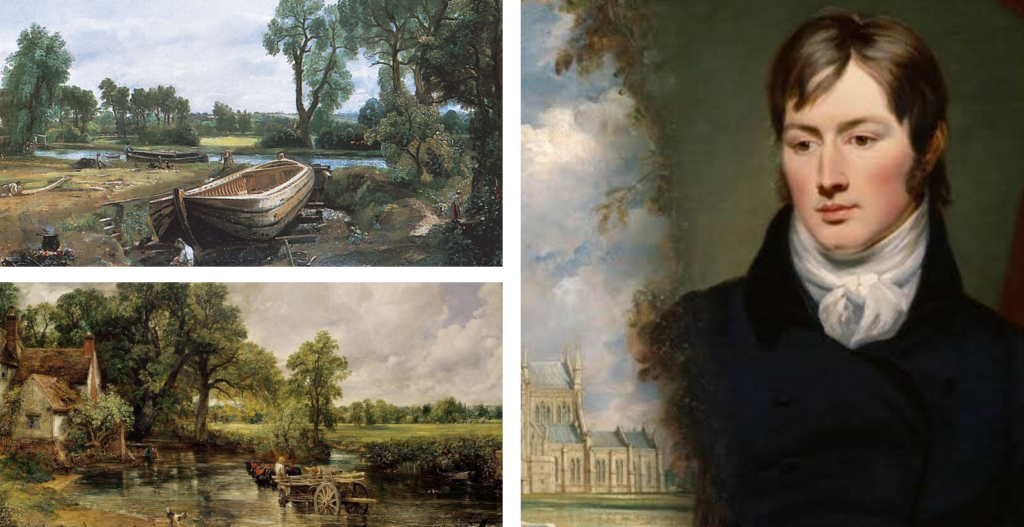

John Constable Painting
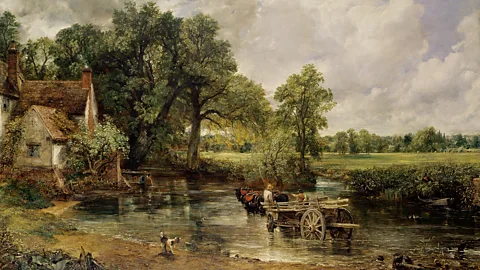
- Romanticism – Pastoral scene, Known now as a British Cliché, but was once quite radical
- Very large landscape – but very low on the genre hierarchy
- Constable’s father was a land owner in Suffolk
- The painting is of the Stour River where he grew up
- Biggest painting for it’s time
- This is a time when the land is fraught, there are economic stresses and unemployment among workers
- Early industrial revolution – machines were perceived to be taking employment away. There was extreme poverty
- But we see none of this here… It’s a beautiful working and thriving landscape
- Additional focus on the sky – Constable had studied Meteorology, capturing a specific time of day
- Was originally called Landscape Noon
- The farmers in the background are at one with nature
- Finding beauty in the most humble of landscapes
- “The sound of water escaping from mill-dams, willows, old rotten planks, slimy posts, and brickwork, I love such things. … As long as I do paint, I shall never cease to paint such places. They have always been my delight.“
- Completed from sketches – cery quickly over 5 months
- Green – radical. Very realistic and close to nature. Other artists painted landscapes that were brown… old masters were used to working in rooms with fire and smoke in
- Red accent to balance out the green
- Broad marks – contemporary for its time – deliberate in creating rough texture that reflected the textures of the landscape. We can feel the water moving across the stream, or the clouds in the sky
- It captures the nostalgic memory of the place
- Curator of the Louvre called Constable the messiah of landscape painting
Together, Turner and Constable helped elevate landscape painting to new heights, emphasizing the emotional and sublime qualities of nature, which became central themes in Romantic art. Their legacy continues to inspire artists and art lovers today.
Landscape Photoshoot Response
Choose 1 Location to make all the images Cohesive

