Identity is the set of qualities, beliefs, personality traits, appearance, and/or expressions that characterize a person or a group. Identity emerges during childhood as children start to comprehend their self-concept, and it remains a consistent aspect throughout different stages of life
Femininity
Femininity (also called womanliness) is a set of attributes, behaviours, and roles generally associated with women and girls. Femininity can be understood as socially constructed, and there is also some evidence that some behaviours considered feminine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors.
Masculinity
Masculinity involves displaying attitudes and behaviours that signify and validate maleness, and involves being recognised in particular ways by other men and women.
Masculinity Photography MoodBoard






How identity can be influenced by “place”, or belonging, your environment or upbringing.
There are many factors that shape identity, and they can be both external and internal factors. Society, family, friends, ethnicity, culture, location, media, interests, self-expression, and life experiences are all common factors that shape identity.
Multiple pathways exist through which families may influence adult identity formation, including levels of social control and monitoring, warmth and closeness, responsibility, and hierarchical family relations
When we are in familiar surroundings, we tend to feel more secure and strengthen our sense of identity. We feel more in control of our lives and boost our self-confidence. On the other hand, when we lack an established place, a home, we may feel lost and disconnected.
“Placefulness” is an awareness of the place—where one is or where one comes from. And remembering that places shape one’s expectations and understandings of the world. Feeling a sense of belonging is very important.without it, we’re unmoored in the world.but it can also lead to a lack of awareness.
Our sense of identity and belonging is impacted by various factors, including our experiences, relationships, and our environment. The journey to find identity and belonging can often be a struggle, since we ask ourselves, ‘who am I?
Claude Cahun (1894–1954)

Who:
Claude Cahun, born as Lucy Schwob in Nantes, France, was a pioneering photographer, poet, and writer. She adopted the name Claude Cahun as a gender-neutral persona, reflecting her resistance to societal gender norms and her exploration of identity beyond the binary. Cahun’s work was highly experimental, challenging conventional notions of gender, sexuality, and the self.
What:
Cahun is best known for her self-portraiture, which she used as a tool for gender exploration and identity fluidity. She transformed herself into various personas using makeup, costumes, and props, blurring the lines between masculine and feminine. Her works often included surrealist elements, utilizing symbolic imagery and dreamlike compositions to challenge perceptions of reality and identity. Cahun’s photographs also explored the performative nature of identity, questioning how roles and gender are constructed.
When:
Cahun’s most significant photographic work was created in the 1920s and 1930s, during her involvement with the surrealist movement in Paris. Her later works, particularly during the 1940s, became politically charged as she and her partner, Marcel Moore, were involved in resistance activities during World War II.
Where:
Born in Nantes, France, Cahun moved to Paris during the 1920s, where she became part of the avant-garde and surrealist circles. In the late 1930s, she and Moore relocated to the Channel Island of Jersey, where they lived during the German occupation in WWII. It was in Jersey that Cahun’s work took on a more political tone as she used photography for resistance propaganda.
How:
Cahun’s photography was deeply performative, with the artist using herself as the subject to create multiple constructed personas. She utilized props, costumes, and makeup to transform her identity, playing with gender ambiguity and challenging the traditional notions of the feminine and masculine. Her works often included surreal, dreamlike compositions and symbolic imagery. Cahun’s approach to self-portraiture was collaborative, particularly with Marcel Moore, who assisted in capturing many of her most iconic works.
Why:
Cahun’s photography was a direct challenge to societal norms around gender and identity. By using self-portraiture as a tool for experimentation, she questioned the fixed nature of gender roles and explored how identity is shaped by culture. Cahun’s work, much of which was feminist in nature, critiqued the traditional expectations placed on women and offered an early commentary on gender fluidity and sexuality. Her photographs also explored the performative aspects of identity, positioning her as a significant figure in the history of self-representation and early critiques of fixed gender norms.
World war II activism
In 1937, Cahun and Moore moved to Jersey, where they became active in resisting the German occupation during World War II. Opposed to war, they produced anti-German propaganda, including rhythmic poems and critical messages derived from BBC reports on Nazi atrocities. Using the pseudonym Der Soldat Ohne Namen (The Soldier With No Name), they secretly distributed these flyers at German military events, placing them in soldiers’ pockets, on chairs, and in cars. One notable act was hanging a provocative banner in a church that mocked Hitler’s authority. Their resistance was not just political, but also artistic, reflecting their desire to challenge and undermine authority.
In 1944, they were arrested and sentenced to death, but the sentence was never executed due to the liberation of Jersey in 1945. Despite this, Cahun’s health suffered from her imprisonment, and she died in 1954. During her trial, she reportedly told the German judge that they would have to shoot her twice, as she was both a resistor and a Jew, which led to laughter in the courtroom and may have saved her life. Cahun and Moore are buried together in St Brelade’s Church. Their resistance efforts were a deeply personal, lifelong fight for freedom.
LEGACY
Claude Cahun’s work, which remained largely unrecognized during her lifetime, has since gained significant attention for its social critique and revolutionary impact on art and gender norms. She used her photography and writing to challenge societal expectations, particularly those related to gender, beauty, and logic, destabilizing conventional notions of reality. Cahun’s involvement in the Surrealist movement added new perspectives, especially with her portrayal of women not as erotic symbols but as fluid, gender-nonconforming figures. Her work has been described as “prototransgender,” with some considering her a precursor to modern trans self-representation.
Cahun’s life and legacy have gained renewed recognition in recent years. A street in Paris was named after her and her partner Marcel Moore in 2018. Cahun’s WWII resistance work, along with Moore’s, was highlighted in the 2020 book Paper Bullets. She was also honoured by Google in 2021 with an animated Doodle for her birthday. A novel based on her life, Never Anyone But You, was published in 2018, and in 2023, a graphic novel about her life, Liberated: The Radical Art and Life of Claude Cahun, was released, further exploring her artistic and political activism.
Image Analysis

Visual Aspects
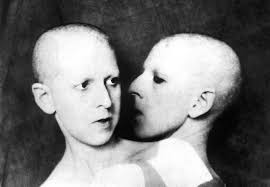
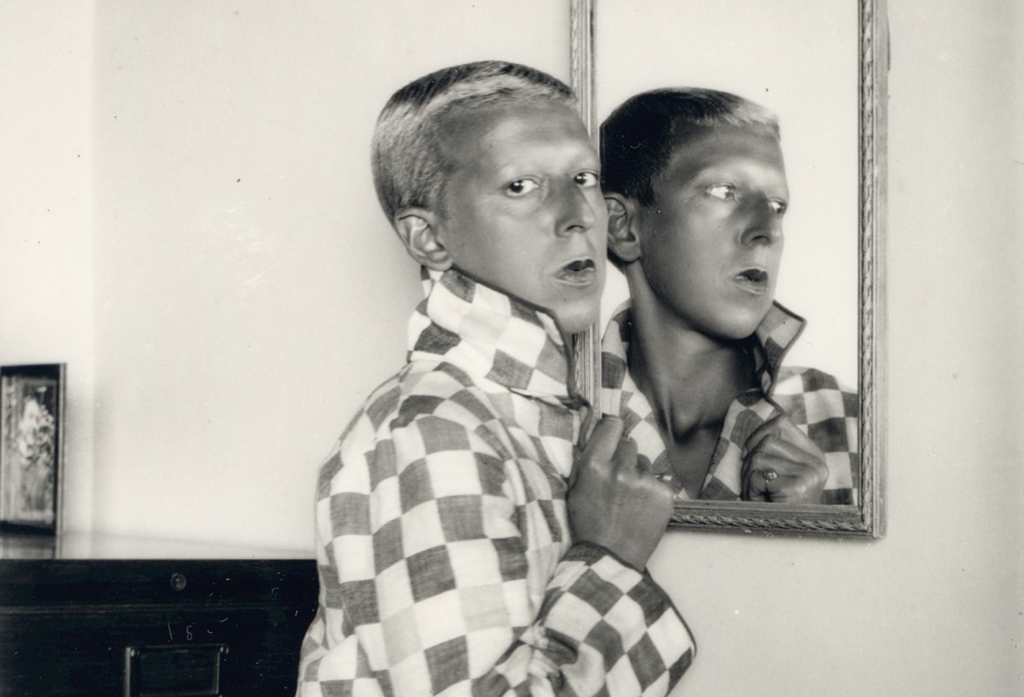
Claude Cahun’s black-and-white self-portrait immediately draws you in with its strong composition and exploration of identity. The image is split between two versions of Cahun: her physical form on the left and her reflection in the mirror on the right. This duality feels deeply personal, almost like a visual representation between how she sees herself and how the world perceives her.
Her androgynous appearance is striking. The short hair, checkered shirt, and upturned collar challenge conventional ideas of femininity. The raised collar seems to suggest she’s hiding a part of herself, while the reflection, showing her bare neck, hints at a more vulnerable side. Creating a interesting contrast between what’s concealed versus what’s revealed.
Her serious expression adds emotional weight. She looks directly at the viewer, almost challenging us, yet she turns away from the mirror, as if rejecting her own reflection. The plain background keeps all the focus on her, amplifying the intensity of her presence and the interplay with the mirror.
Technical Aspects
The soft, natural lighting in this photo enhances the fluency of the photograph , Shadows are gentle, giving depth to her face and texture to her clothing. The absence of harsh contrasts makes the image feel intimate and smooth.
The composition feels deliberate, with the mirror perfectly aligned to create balance. The camera is at eye level, making the connection between Cahun and the viewer feel direct and personal. Her sharp focus ensures both she and her reflection demand equal attention, forcing us to at least acknowledge the tension between the two.
Conceptual Aspects
This portrait is a conversation about identity, duality, and self-perception. Traditionally, mirrors in art symbolize vanity or beauty, but here, Cahun flips the script. She doesn’t admire her reflection. she seems to reject it. Her pose suggests discomfort with what the mirror reveals, yet she confronts the viewer head-on, as though asking us to consider the same questions about identity.
The raised collar adds layers to this narrative. It hints at concealment. something she’s choosing not to show us. But the mirror exposes her neck, a symbol of vulnerability and openness. This interplay between hiding and revealing feels universal. Highlighting the internal conflicts we all face about how much of ourselves we show to the world.
Cahun’s choice of clothing and androgynous style were radical for her time. By rejecting societal expectations of femininity, she challenges us to think about gender as something fluid , not as a fixed and deeply cemented concept. This bold self-representation speaks to themes that feel just as relevant today as they did during her time, as she battles her own physical reality with how she really feels.
Contextual Aspects
Cahun created this photograph in the early 20th century, a time when gender roles were rigid and societal expectations weighed people down heavily. As a French artist associated with Surrealism, she was part of a movement that loved to explore dreams, illusions, and hidden truths. This aligns perfectly with her use of mirrors to delve into identity and self-perception.
During this period, photography was gaining traction as an art form, and Cahun used it not just to create striking images but also to push boundaries. Her work feels like a quiet rebellion/ refusal to conform to the era’s strict ideas of gender and identity.
Emotional Response
Looking at this photograph, you can’t help but feel a mix of unease and empathy. The direct gaze pulls you in, almost demanding your attention, while the turned-away reflection creates a sense of conflict. It’s as if Cahun is wrestling with self-acceptance, a struggle that feels both deeply personal and universally human.
The raised collar and the mirror deepen this emotional tension. They remind us of the parts of ourselves we keep hidden and the vulnerability of having them exposed. Her serious expression feels heavy, as though she’s carrying the weight of these questions. questions we might ask ourselves, too. In the end, the portrait leaves you thinking about the complex, often contradictory nature of identity, making it as impactful today as it was then.
Clare Rae: Exploring the Body, Landscape, and Performance
Melbourne-based artist Clare Rae is known for her evocative photographs and moving image works that challenge traditional representations of the female body by exploring its relationship with physical environments. In 2017, Rae participated in the Archisle International Artist-in-Residence programme in Jersey, where she delved into the Claude Cahun archive. During her residency, she created new photography and film, ran workshops, and examined Cahun’s connections to Jersey’s cultural and physical landscapes.
Her residency culminated in the creation of the series Entre Nous (Between Us): Claude Cahun and Clare Rae, which debuted at the Centre for Contemporary Photography in Melbourne (March 22–May 6, 2018) and later exhibited at CCA Galleries in Jersey, UK (September 7–28, 2018). Accompanying the series, Rae published Never Standing on Two Feet in April 2018, featuring an introduction by Susan Bright and an essay by Gareth Syvret.
Never Standing on Two Feet: A Feminist Perspective on Landscape and Identity
In this series, Rae investigates how Claude Cahun’s engagement with Jersey’s landscapes shaped her work, particularly in relation to its coastal geography and Neolithic ritual monuments. Rae reflects:
“Like Cahun’s, my photographs depict my body in relation to place; in these instances, sites of coastal geography and Jersey’s Neolithic ritual monuments. I enact a visual dialogue between the body and these environments and test how their photographic histories impact upon contemporary engagements.”
Rae builds on Cahun’s legacy of using self-portraiture to critique the male gaze, positioning her work as a feminist exploration of self-representation. Her practice integrates gesture and performance to reimagine the female body in landscapes, contrasting and unsettling traditional depictions.
Artistic Influences and Methodologies
In an artist talk, Rae contextualized her practice, drawing connections to artists such as Claude Cahun, Francesca Woodman, and Australian performance artist Jill Orr. She highlighted the role of performative photography in her work, where gesture and the body become tools for disrupting conventional narratives. Rae also discussed her engagement with architecture and the body, her methodologies for image-making, and the conceptual outcomes of her projects.
Her work invites viewers to reconsider the interplay between identity, landscape, and performance, building on historical contexts while addressing contemporary feminist concerns. For a deeper exploration of her process and its influences, see the blog post Photography, Performance, and the Body.
Identity self portrait mini project.
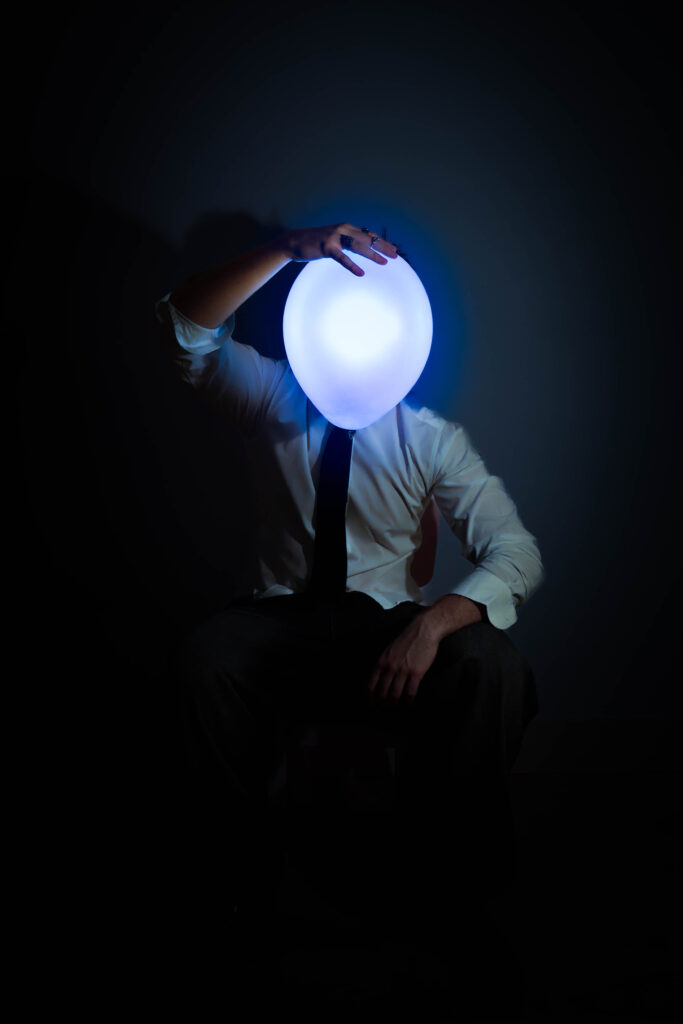
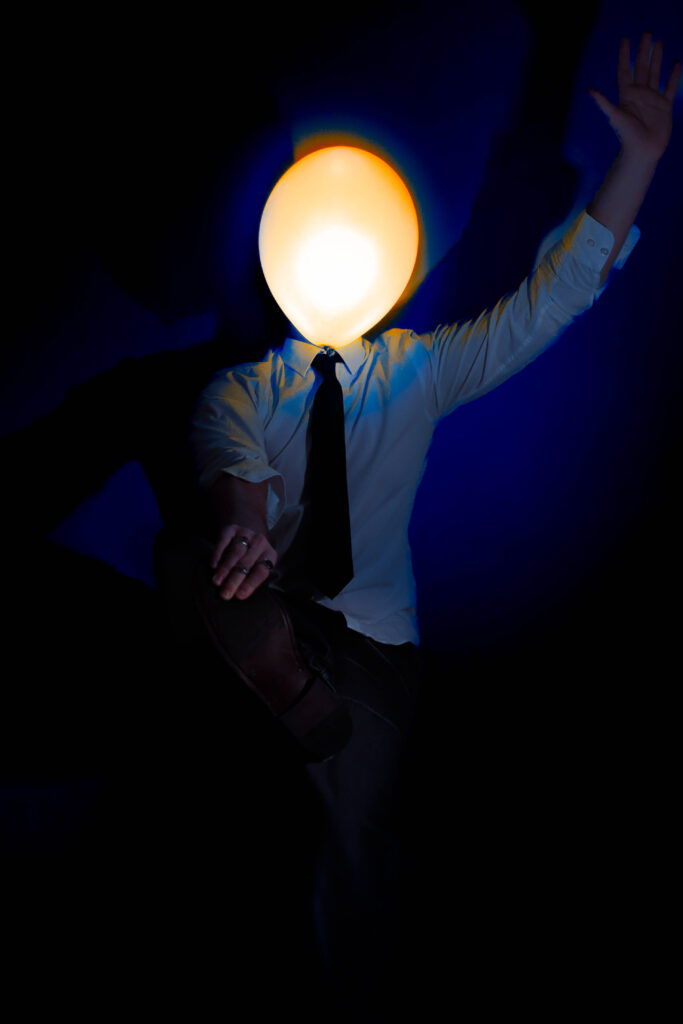
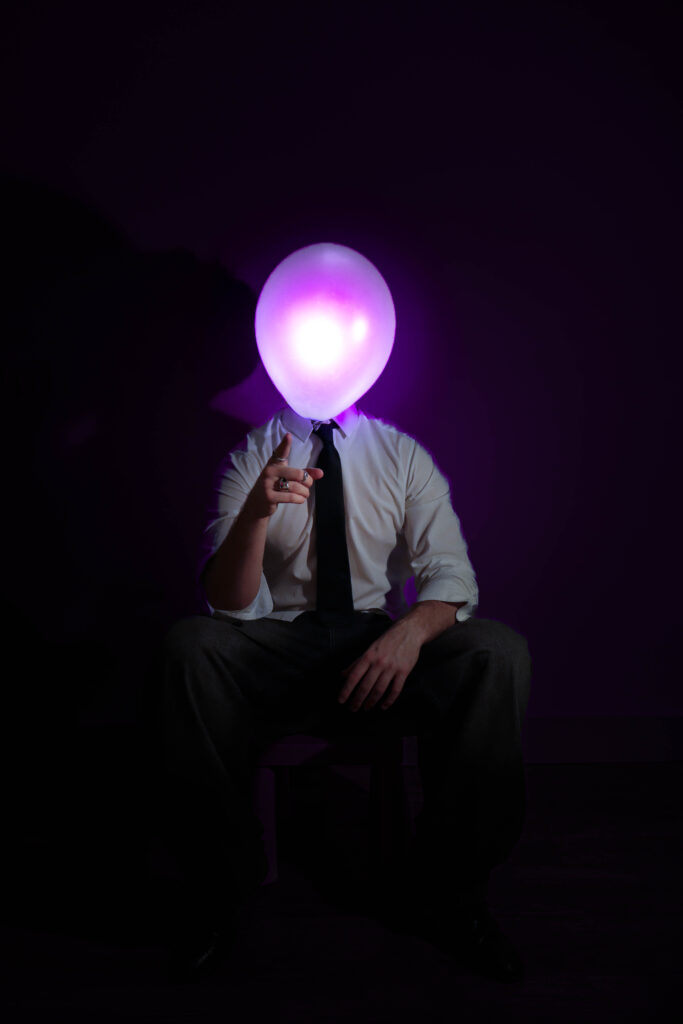
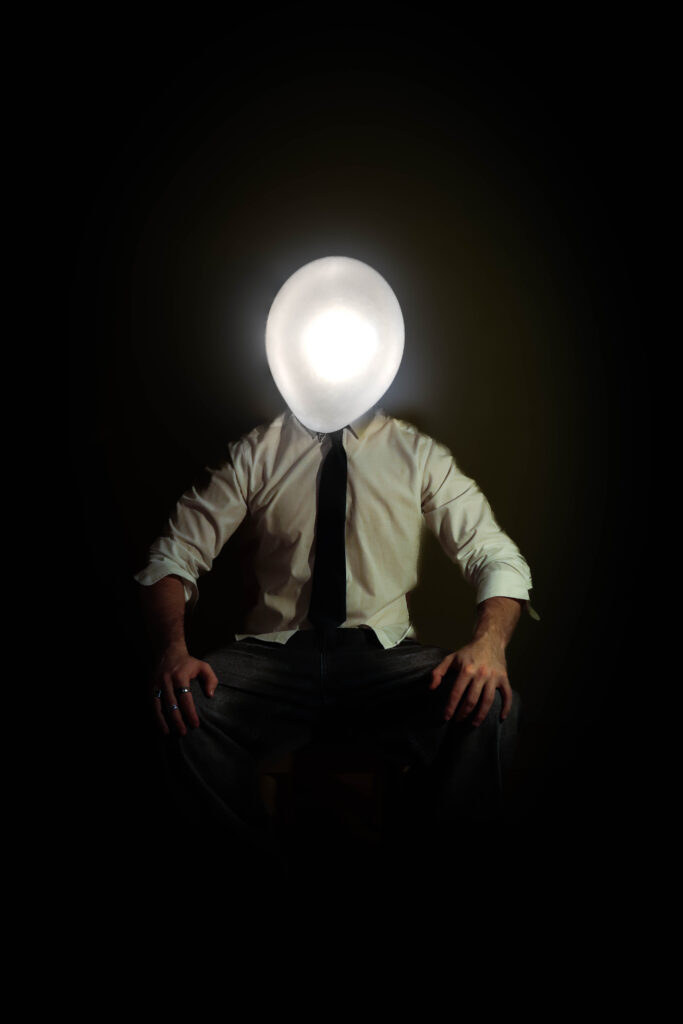
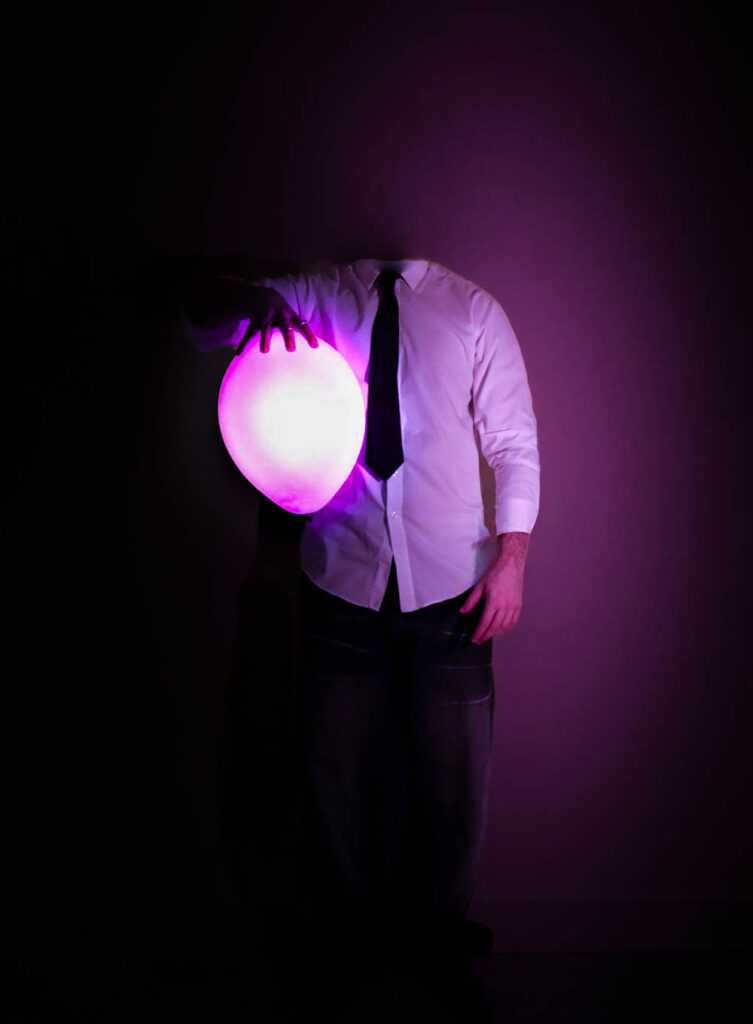

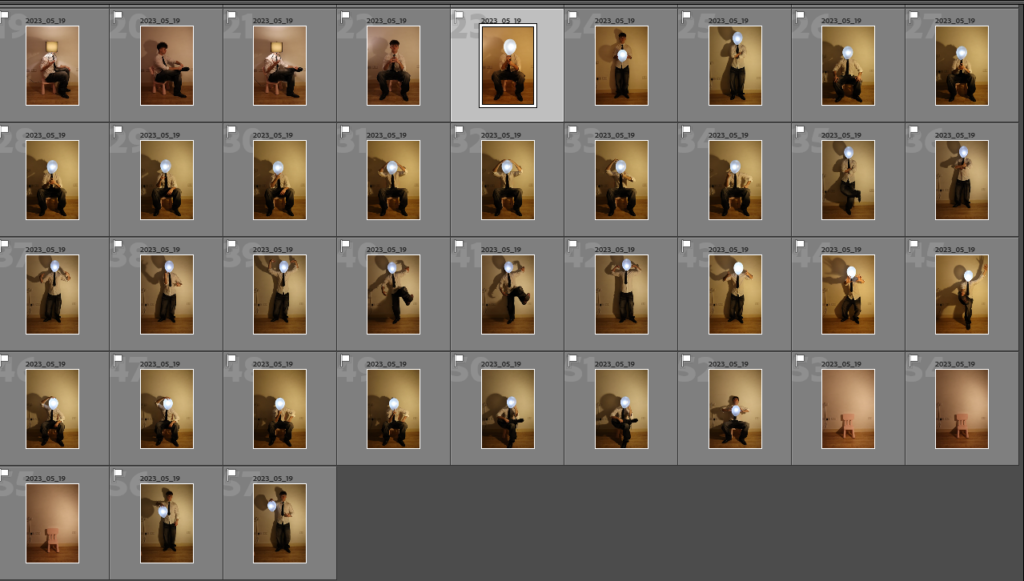





This series of photographs delves deeply into themes of identity, self-discovery, and the conflict between societal expectations and personal desires. The illuminated balloon replacing the subject’s head becomes a powerful metaphor, serving both as a mask and a representation of the subject’s emotions and turmoil. The balloon, glowing with a surreal, almost childlike quality, evokes nostalgia for the simplicity and freedom of childhood—a time unburdened by the rigidity and monotony of adult life. Its weightlessness contrasts sharply with the heavy symbolism of the suit the subject wears, a uniform of professionalism that hints at his role as an office worker trapped in the endless loop of societal conformity. The suit signifies the oppressive nature of his identity, reduced to being just another cog in the machine, an “ant” in the larger structure of a system that suppresses individuality.
The balloon also serves as a visual representation of his inner conflict—its glow suggests fleeting moments of clarity and self-awareness, while its fragile, impermanent nature symbolizes his longing to escape the identity forced upon him. The balloon’s presence acts as a mask, concealing the emotions and dissatisfaction beneath, while amplifying his hatred toward the person he has become. The use of color strengthens this narrative: blue evokes sadness and the monotony of routine, purple reflects introspection and the deep yearning for escape, and yellow hints at fleeting hope or memories of a happier, untainted self.
The subject’s body language—tense and reflective—paired with the dramatic interplay of light and shadow, further emphasizes his internal struggle. The darkness around him reinforces his feelings of isolation, while the illuminated balloon stands out, as if mocking him with its surreal brightness, a symbol of both his desire for freedom and his inability to achieve it. By removing the subject’s facial features, the series universalizes its narrative, inviting viewers to project their own feelings of nostalgia, dissatisfaction, or longing onto the imagery. Ultimately, the photographs capture the haunting idea of a man who despises his identity and longs to shed the mask of adulthood, yearning to return to a time when life was defined by freedom, playfulness, and authenticity.
Statement of intent
The intention behind this series of photographs was to explore themes of identity, nostalgia, and the conflict between personal desires and societal expectations. The images were created in my living room, using household lamps as lighting sources to craft dramatic and moody atmospheres. I utilized a tripod to keep the camera steady and relied on a timer to capture self-portraits. To achieve the surreal illusion of the balloon replacing my head, I held a lit-up balloon in my mouth, allowing it to appear as though it were my head glowing with emotion and inner turmoil.
By wearing a formal suit, I aimed to symbolize the restrictive nature of adulthood, particularly the monotonous life of an office worker. The suit represents societal conformity and the feeling of being trapped in an endless cycle of professional obligations, reducing individuality to mere functionality. The illuminated balloon, serving as both a mask and a metaphor for my emotions, embodies the tension between self-awareness and dissatisfaction. Its glow evokes fleeting moments of clarity, while its fragility and playful, weightless nature reflect a yearning to return to the innocence and freedom of childhood.
The colour choices and lighting were intentionally dramatic to convey specific emotions: blue suggests melancholy, purple reflects introspection, and yellow symbolizes fleeting hope or moments of self-discovery. The series aims to capture the struggle of defining one’s identity within societal constraints while expressing the longing to shed the burdens of adulthood and rediscover authenticity and joy.