Moodboard
Identity

“Identity” is basically who you are, it’s made up of the things that define you, like your values, beliefs, and how you see yourself. It also includes how others see you. Your identity can be shaped by lots of things, like your background, experiences, and the society you’re part of. It’s not fixed and can change over time as you grow or as you’re exposed to new ideas.
Femininity

Femininity is the set of qualities or behaviors that society often associates with women, like being nurturing, emotional, or gentle. These ideas about femininity can vary from culture to culture and can change over time. It’s not something that everyone who is female has to follow, and today, many people are pushing back against these old stereotypes of what women should be like.
Masculinity
“Masculinity” is similar to femininity, but it’s about the traits traditionally linked to men, like being strong, independent, and assertive. Just like femininity, ideas about masculinity are shaped by culture and society, and they’ve evolved a lot in recent years. Now, more people are recognizing that there are many ways to express masculinity, and it’s not limited to just a few behaviors.
Gender Identity
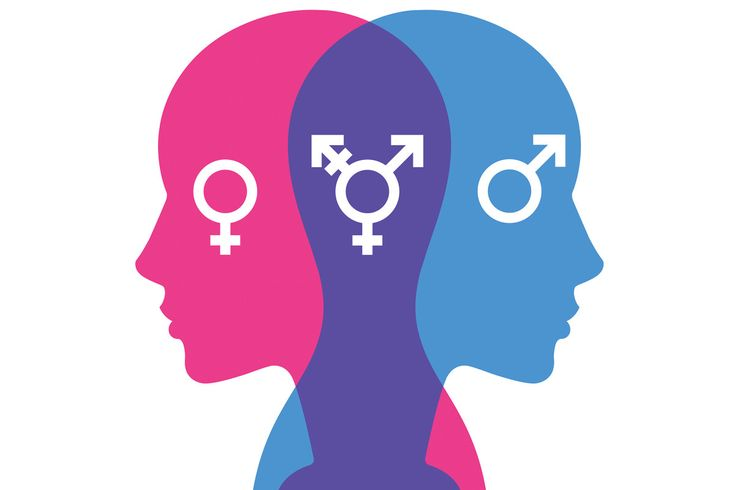

Gender identity is how you personally feel about your gender, whether you feel like a man, a woman, or something else entirely. Society often has certain ideas about how men and women should act, but those ideas aren’t the same everywhere, and they’re always changing. Growing up in a place where there’s a lot of pressure to act a certain way based on your gender can affect how you see yourself, but so can being in an environment where people are more open-minded about gender.
Cultural Identity

Cultural identity is about feeling connected to the culture or traditions of the group you’re from, like language, food, religion, or customs. If you grow up in a place where that culture is important, it can become a big part of who you are. But if you move to a new country or grow up in a mixed community, your cultural identity might become more fluid as you blend influences from different places.
Social Identity

Social identity is how you define yourself based on the groups you belong to, like your family, community, or class. Your social identity affects how you see yourself in relation to others and how you feel about your place in the world. For example, if you grow up in a working-class family, that might shape how you think about success or what kinds of opportunities are possible for you.
Geographical Identity

Where you’re from, whether it’s a specific country, city, or neighborhood, can shape who you are. The place you live affects your values, your lifestyle, and how you relate to the world. If you’re from a small town, you might have a different sense of community or pace of life compared to someone from a big city, for example.
Political Identity
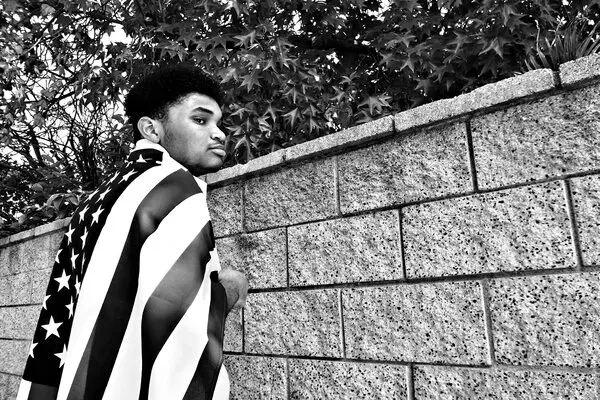

Political identity is about where you stand on issues like government, rights, and power. This is often influenced by the values you were taught growing up, the society you live in, and the political climate of your country. So, someone raised in a conservative family might have a different political identity than someone from a progressive background.
Loss of or Lack of Identity
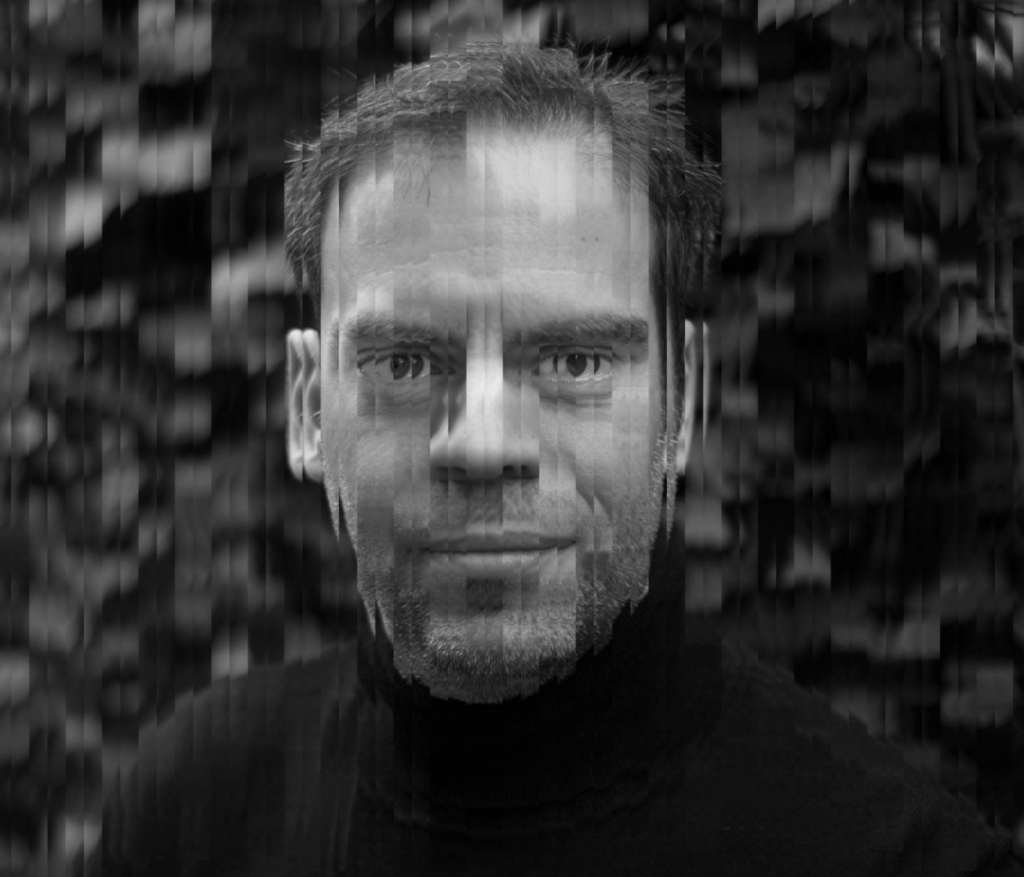

Sometimes people feel like they’ve lost their sense of identity or never really figured out who they are. This can happen if you go through big life changes, like moving to a new place or dealing with personal struggles, or if you’re stuck in a situation where you don’t feel like you belong. It can be confusing and leave you unsure of where you fit in.
Stereotypes and Prejudices
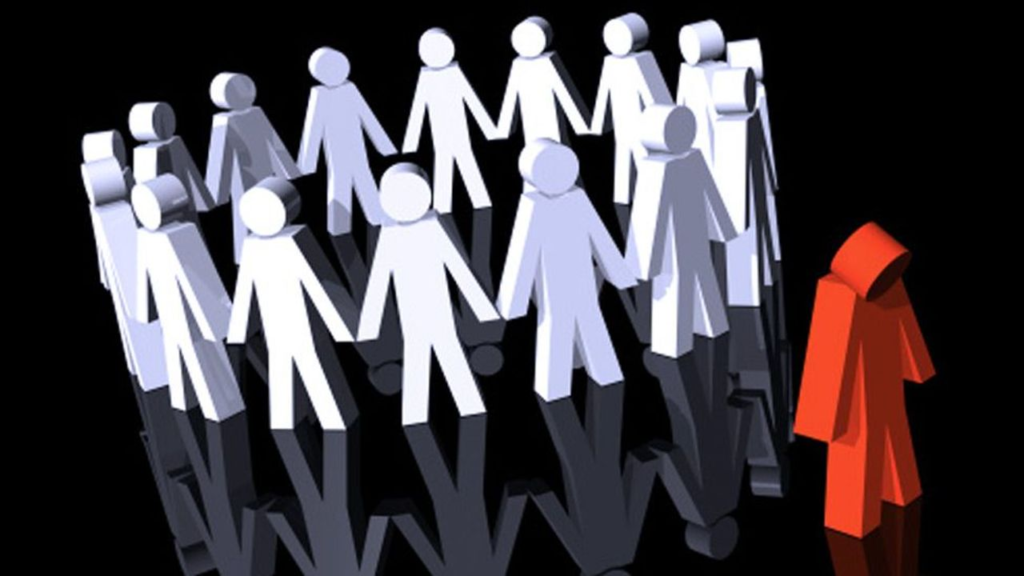

Stereotypes are oversimplified ideas about certain groups of people, and prejudices are biased attitudes based on these ideas. These can influence how you see yourself or how others see you. For example, if society expects women to be nurturing, a woman who doesn’t fit that mold might feel like she doesn’t belong, or she might be judged unfairly.
