What is identity?
Identity is the set of qualities, beliefs, personality traits, appearance, and/or expressions that characterize a person or a group. Identity emerges during childhood as children start to comprehend their self-concept, and it remains a consistent aspect throughout different stages of life.

What is femininity?
Femininity (also called womanliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with women and girls. Femininity can be understood as socially constructed, and there is also some evidence that some behaviors considered feminine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors.

What is masculinity?
Masculinity involves displaying attitudes and behaviours that signify and validate maleness, and involves being recognised in particular ways by other men and women. Traits traditionally viewed as masculine in Western society include strength, courage, independence, leadership, and assertiveness.

How can Identity be affected?
Identity can be affected in lots of different ways, for example:
Gender Identity:
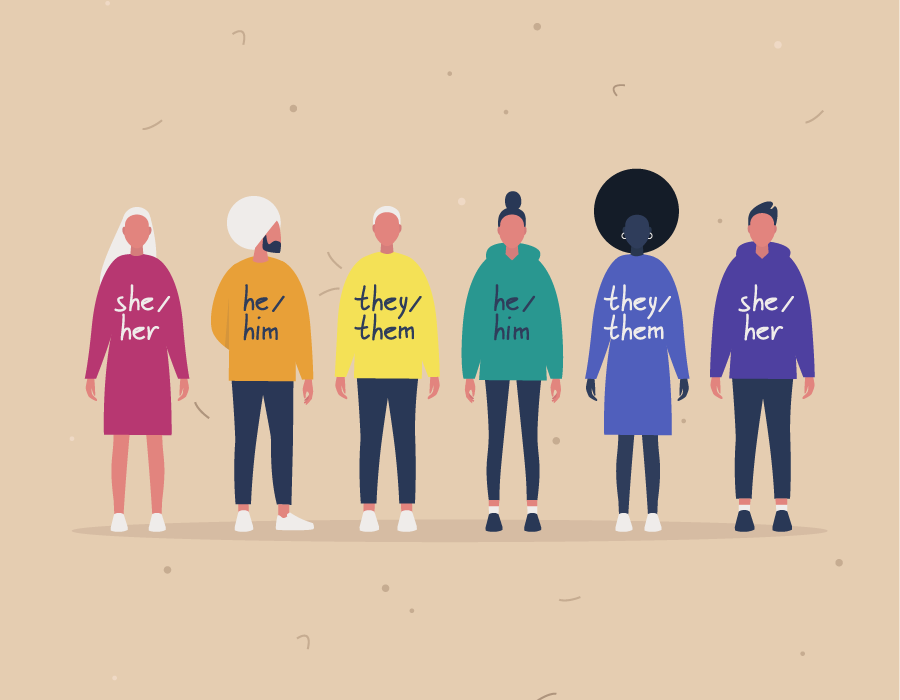
Gender identity is defined as a personal and internal sense of oneself as male, female, or other. Gender expression is defined as the way in which an individual publicly expresses their gender, for example, through aspects such as clothing, hair, makeup, and body language.

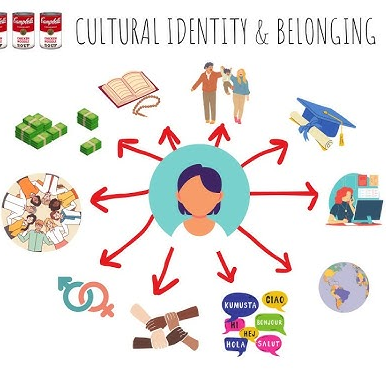
Cultural Identity:
Cultural identity refers to an individual’s sense of belonging and connection to a particular cultural group or community encompassing the shared values, traditions, customs, language, beliefs, and behavioral norms that define and distinguish a specific cultural or ethnic group.
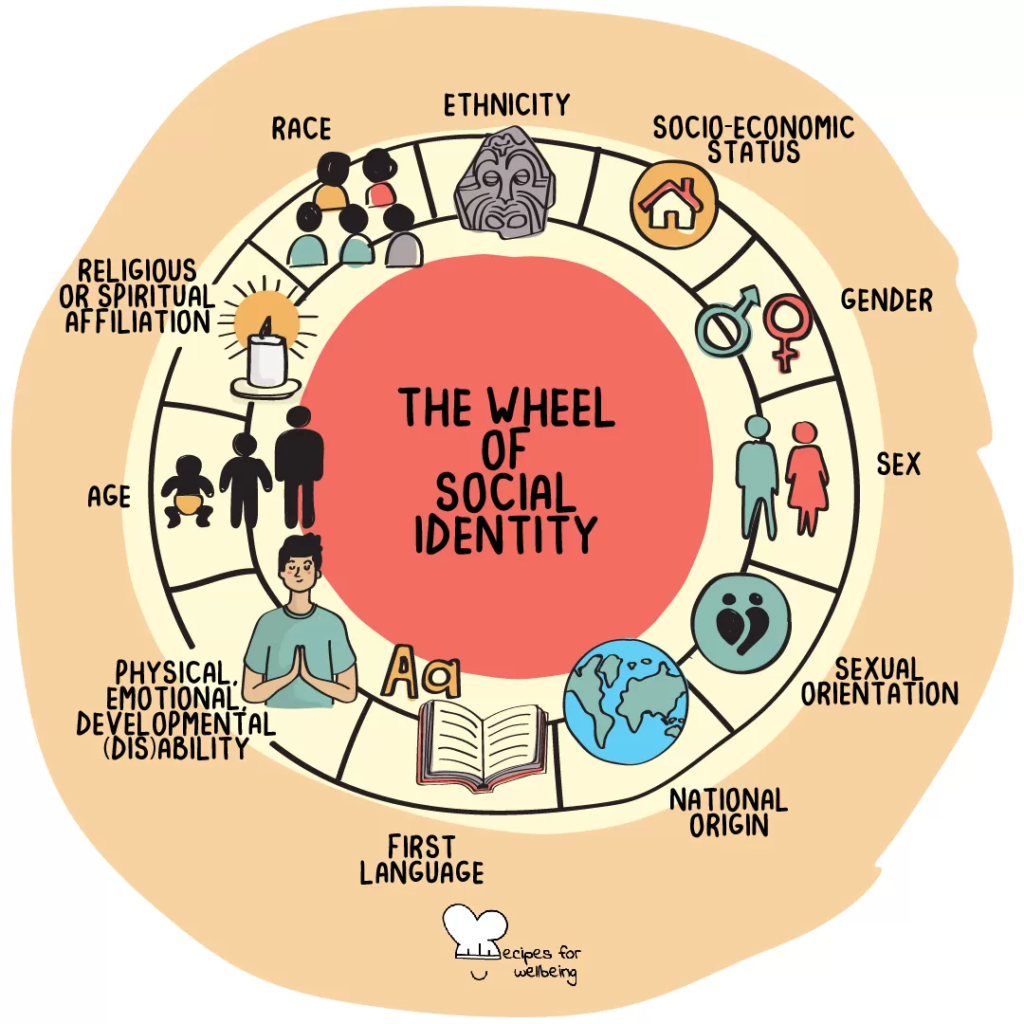
Social Identity:
Social identity refers to people’s self-categorizations in relation to their group memberships (the “we”). These categorisations are often assigned to us or something we are born into.
Geographical Identity:
Geographical identity refers to an individual or group’s sense of attachment to the country, region, city, or village in which they live.
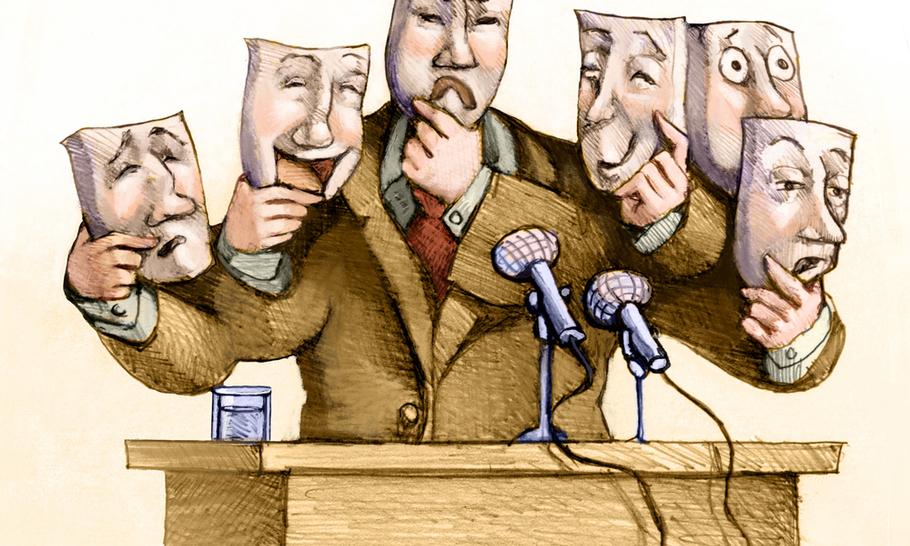
Political Identity:
Political identity is how a person or group of persons think of themselves in relation to the politics and government of a country. Everything that makes up our sense of self are components of our political identity. This includes our ethnicity, religion, gender, class, ideology, nationality and even our age and generation.

Lack of/ Loss of Identity:
Loss of identity may follow all sorts of change; changes in the workplace, loss of a job or profession, loss of a role that once defined us, as a child, as a parent, as a spouse, as an employee. This leaves a gap, an abyss, an empty space.

Stereotypes:
A stereotype is a fixed general image or set of characteristics that a lot of people believe represent a particular type of person or thing.
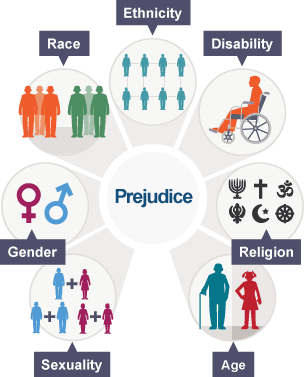
Prejudices:
Prejudices is a favoring or dislike of something without good reason, unfriendly feelings directed against an individual, a group, or a race. prejudice.