What is identity Politics?
IDENTITY POLITICS is a phrase that describes a political approach where in people of a particular religion, race, social background and class or other identifying factor form special socio-political alliances. It makes the distinct experiences and challenges faced by these groups and advocates for policies and practices that address their specific needs and rights.
The term was coined by the Combahee River Collective in 1977. It took on widespread usage in the early 1980s, and in the ensuing decades has been employed in myriad cases with radically different connotations dependent upon the term’s context.
It has gained currency with the emergence of social activism, manifesting in many dialogues within the feminist , American civil rights , and LGBT movements , disabled groups, as well as multiple nationalist and postcolonial organizations, for example: Black Lives Matter movement.
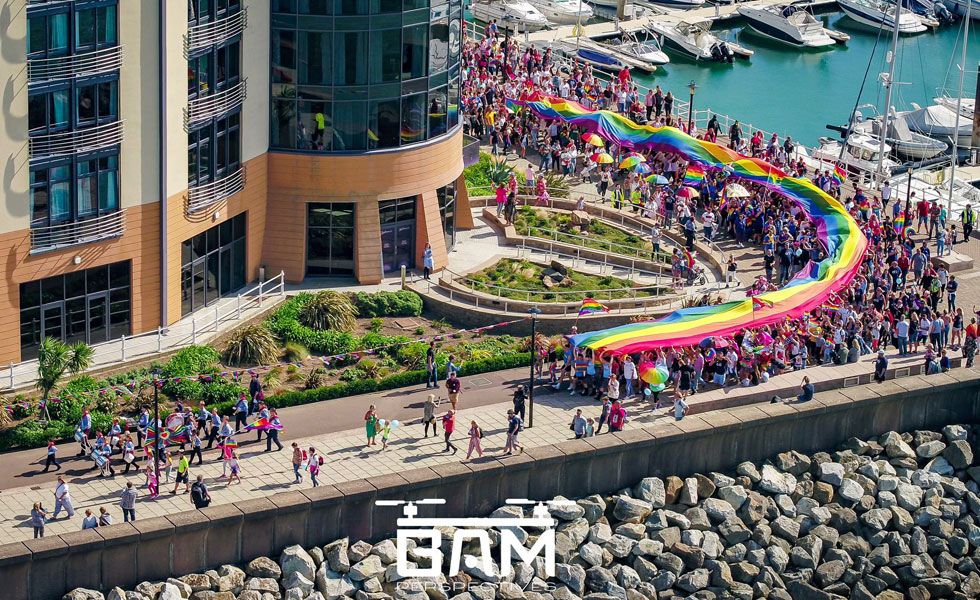


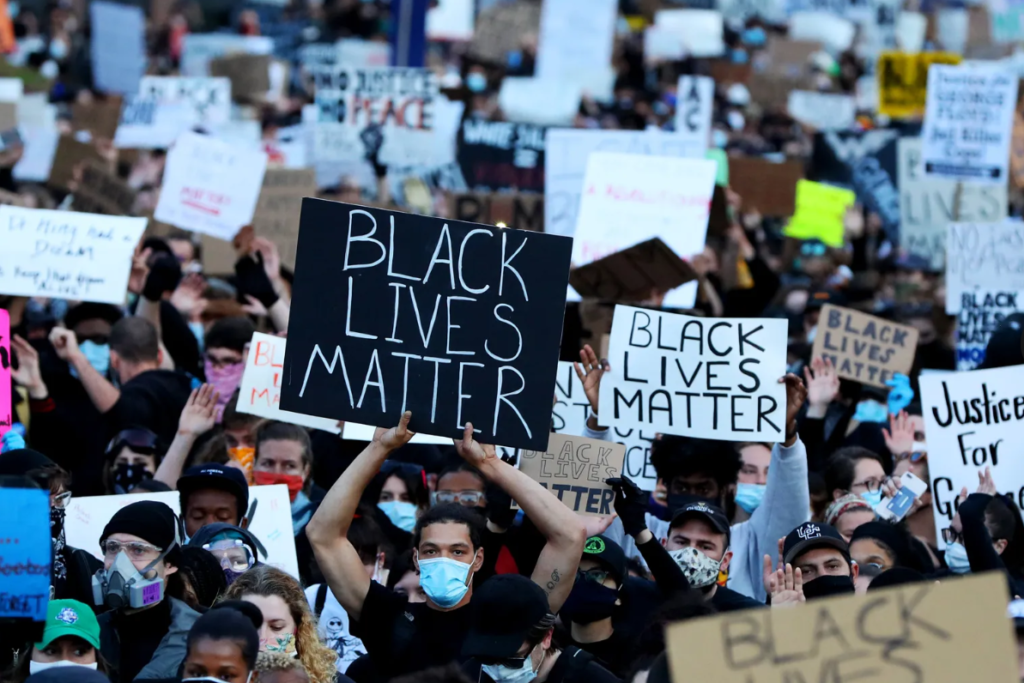
How does Identity Politics link to Culture Wars?
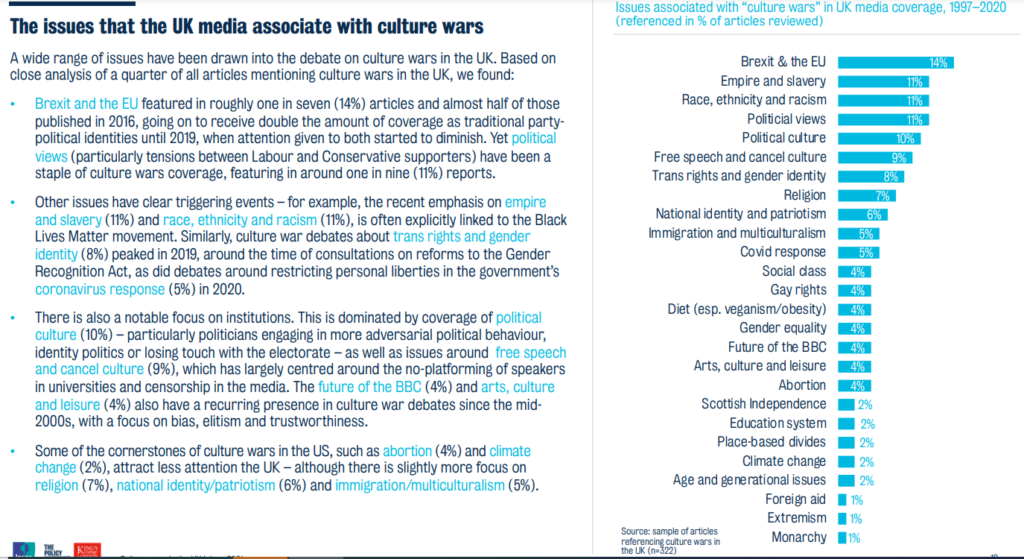
CULTURE WARS are cultural conflicts between social groups and the battle for dominance of their values, beliefs, and practices. It commonly refers to topics on which there is general social disagreement and polarization in societal values is seen.
A “culture war” will signal much more than a disagreement. It will describe an impression of conflict between two irreconcilable worldviews in what is “fundamentally right and wrong about the world we live in” (1991).
This term is commonly used to describe contemporary politics in western democracies with issues such as abortion, homosexuality ,transgender rights, pornography, multiculturalism, racial viewpoints and different cultural conflicts based on values, morality , and lifestyle being stated as the major political cleavage.

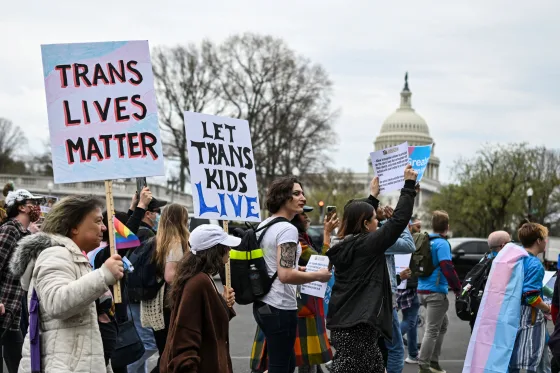

What are some of the positives associated with Identity politics?
Identity politics will help centre the experiences of those as they will view as they will be facing some systemic oppression so that society can get better understanding the interplay of different forms of demographic-based oppression and ensure that no one group is disproportionately or affected by political actions.
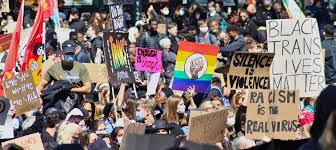
Dangers of Tribalism
Tribalism is defined as
“behavior and attitudes that stem from strong loyalty to one’s own tribe or social group.”
The definition of as “a social division in a traditional society consisting of families or communities linked
by social, economic, religious, or blood ties, with a common culture and dialect, typically having a
recognized leader.” When we listen to the word tribe, we may think of Native Americans, but in modern
usage the term can also refer to people who share common ideas and allegiances.
Tribalism
Tribalism can have extremely negative consequences when it is used to eliminate individuals or groups or to
banish their rights, status, and/or independence. These negative impacts of tribalism are often sustained
by competition and the perception of a very common threat. They will promote fear, anxiety, and prejudice, all of
which make us more susceptible to fake news, propaganda, and conflict.
Tribalism can take lots of forms in our modern society. One example of tribalism is individuals’
strong connections with sports teams. These partnership are frequently built on regional identities and
approved through the use of symbols. We often see deep connection between fans of a specific
team who classify strongly with each other and against fans of opposing teams.
