Auto Focus and Manual Focus (AF and MF)
Auto focus is for general use, so you can use it for a large variety of things as it is the basic use for a camera. It automatically focuses the image. Whereas, manual focus is for specific photos you want to take, like close ups and detailed images, so it enables you to control the focus of the image.
Auto focus is typically used to track a subject when it’s moving around the frame, as it’s easier to get a clear image since auto focus will capture the subject without making it blurry.

The Focal Length
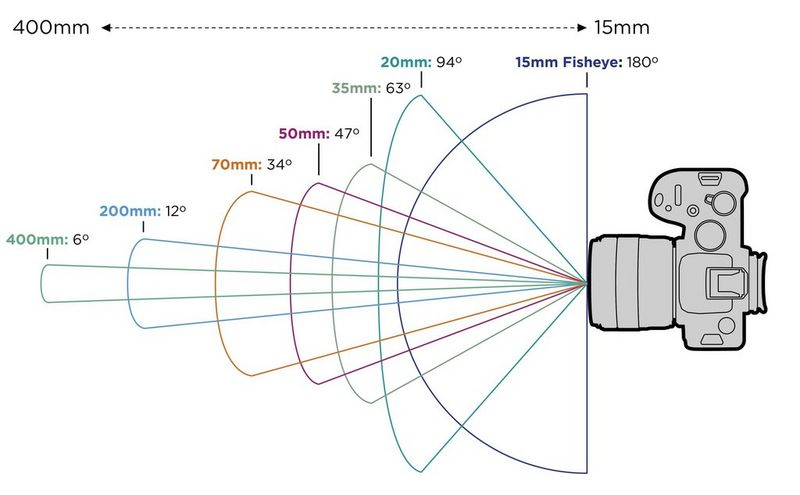
Focal length is the optical distance (usually measured in mm) from the centre of its lens and its focus. This helps to determine how much you can see from the camera.
For example, in this image below, you can recognise that the picture taken on the far left has been from up close, whereas the image on the far right is using a high focal length and a shallow depth of field as the background’s blurry. By using the focal length, the man’s face is now more symmetrical, as it’s taken from afar but zoomed in to make him look more proportionally accurate.

Depth of Field and Aperture
depth of field is the range of distance in an image that is sharp and in focus. A shallow depth of field means that only a small area is in focus, whereas a deep depth of field means a large portion of the image is in focus.

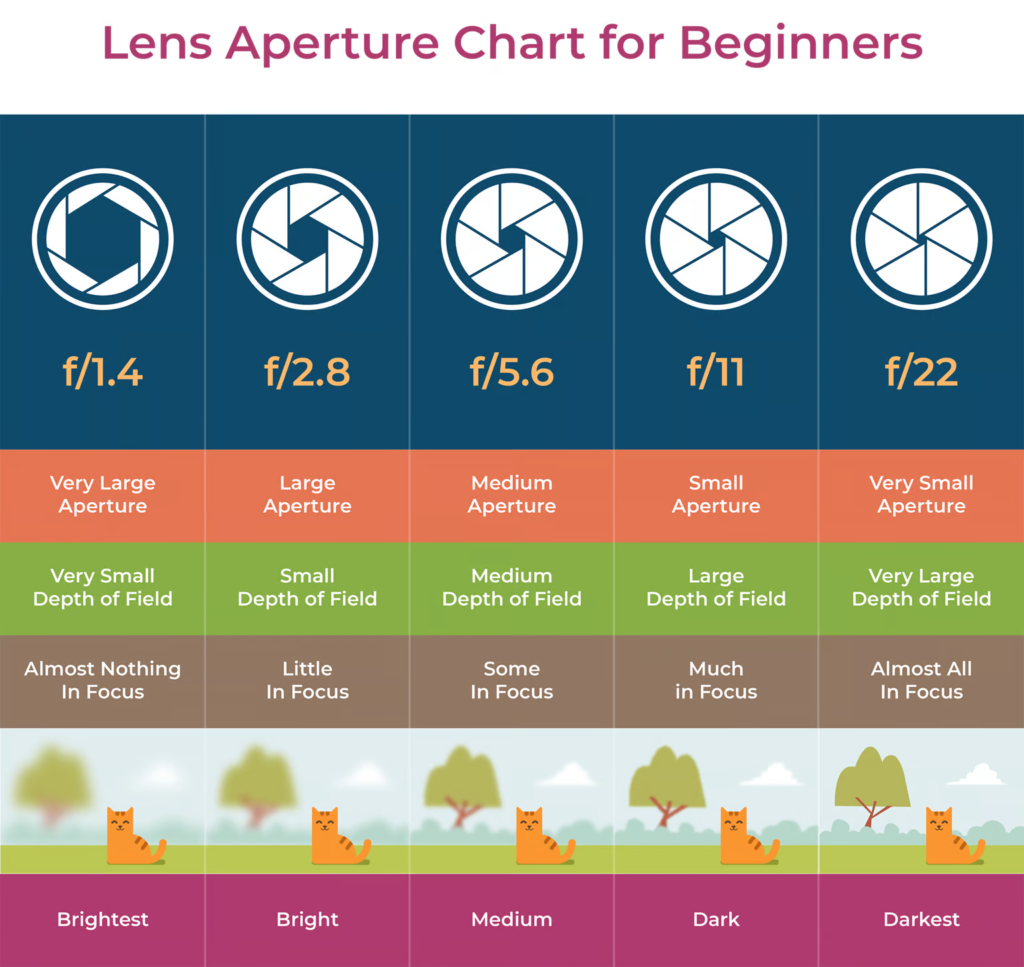
Aperture controls the amount of light let into the camera by adjusting the lens. The higher the f/stop number, for example, f/22, the smaller the lens hole will mean there will be a small aperture. This enables the entire image to be in focus, with all the details being clearly visible. Whereas, with a lower f/stop number, like f/2.8, only the subject will be visible with the rest being more blurry. You can look at other examples on this chart below:
My examples from the Canon Camera Simulator:

Shutter Speed: 1/3
Aperture: 22
ISO Setting: 400
At this aperture, you can notice that everything is in focus, as the higher the aperture, the clearer the image will be. This is useful when you take photos where you want everything to be in focus, like if you were to take a photo of landscapes as all the minuscule details are captured.

Shutter Speed: 1/60
Aperture: 8
ISO Setting: 1600
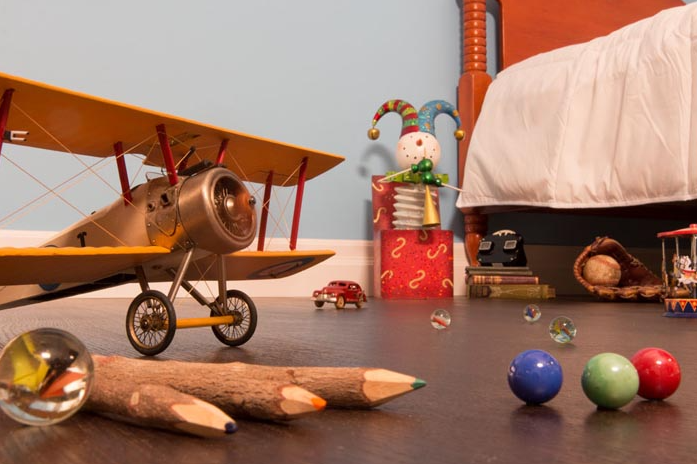
As you can see, in this image the plane is still in focus, however around the edges the objects are slightly blurred. This is because the aperture number is in the middle between out of focus and clear.

Shutter Speed: 1/180
Aperture: 2.8
ISO Setting: 400
In this image, it is recognised that only the subject (the plane) is in focus whilst everything else is blurred and out of focus. This is due to the low aperture number, but this is good for taking images where you only want one subject to be the main focus.
Artist Research
Ralph Eugene Meatyard
Ralph was born in 1925 and passed in 1976, but in his lifetime Meatyard pursued his passion for photography in various ways, like his most famous work ‘Zen Twigs’ and his no focus work. His ‘Zen Twigs’ are photos of zoomed in twigs (using large aperture and a small depth of field) to make the twigs the main subject and the rest blurred. His no focus images are made by putting the camera on manual focus and changing the lens to create a foggy effect.






Ralph specialised in changing the cameras focus and depth of field, as well as motion blur and a range of exposure to invent an interesting look, as your mind tries to assemble what some of the images actually are, like in the ones above where you can partially figure out what it is.
Contact Sheet



Best Photos: Edited



