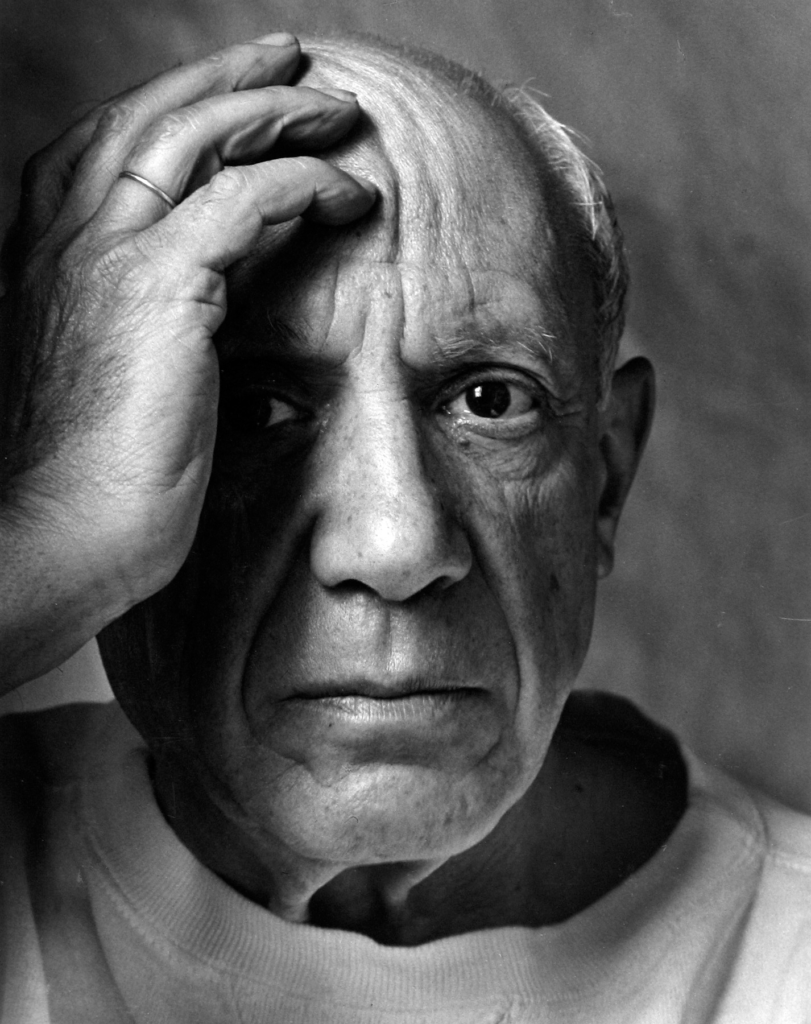
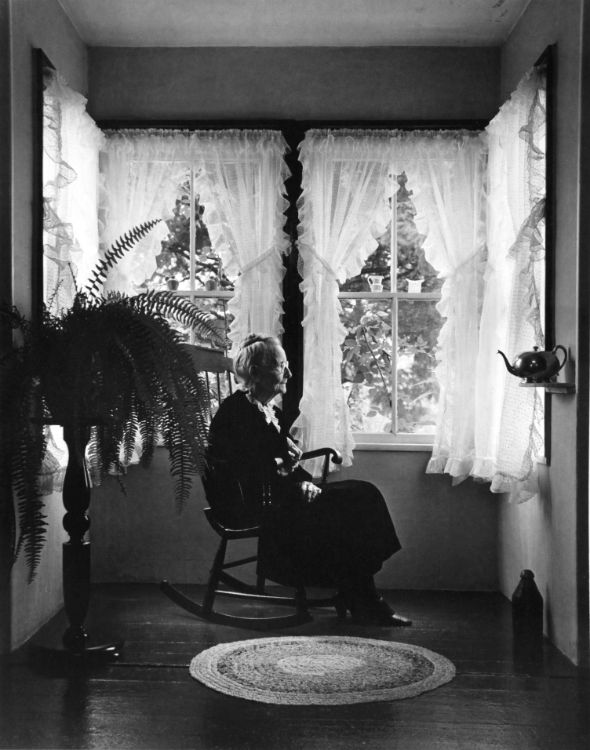
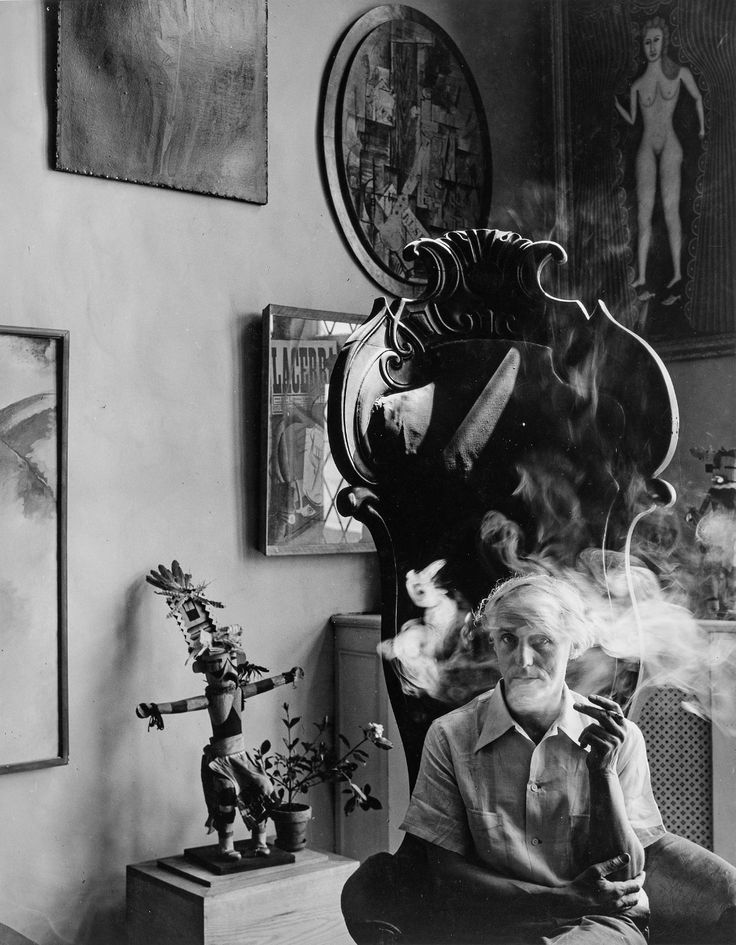
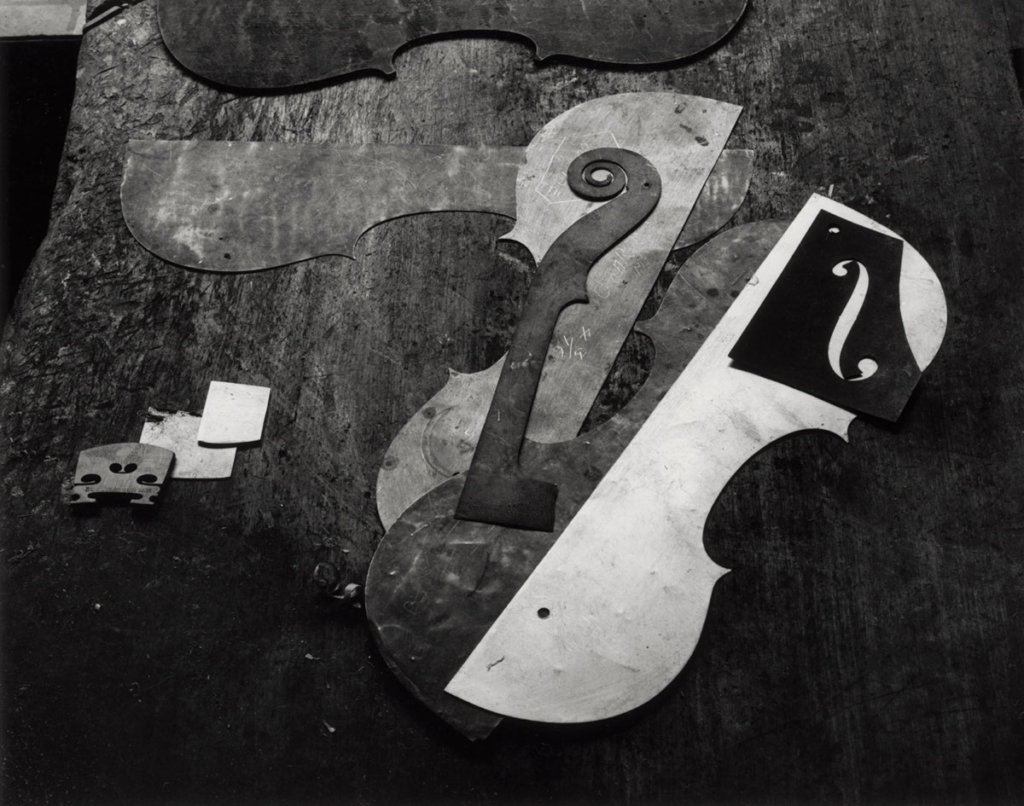
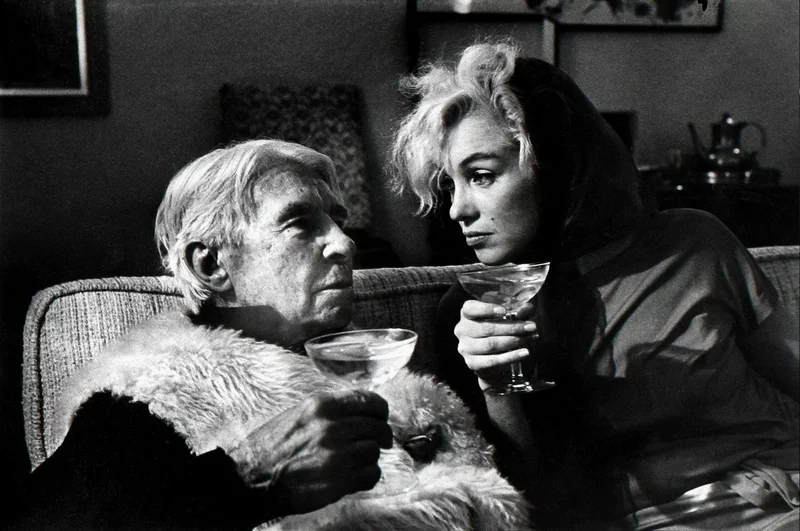
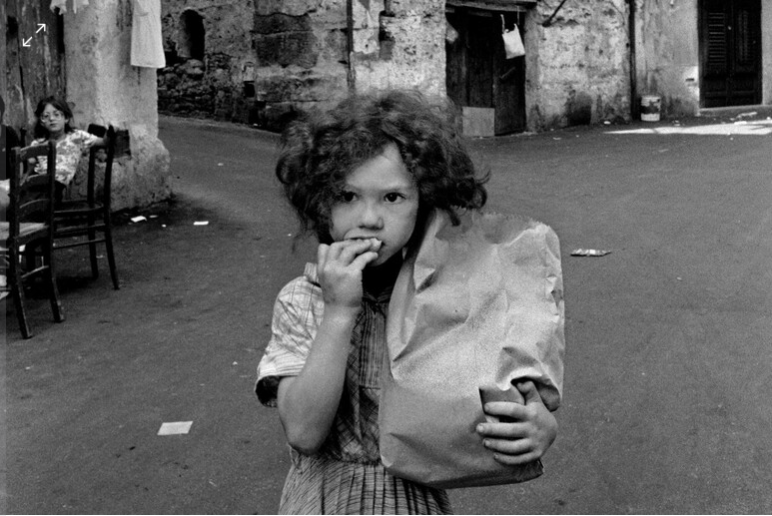
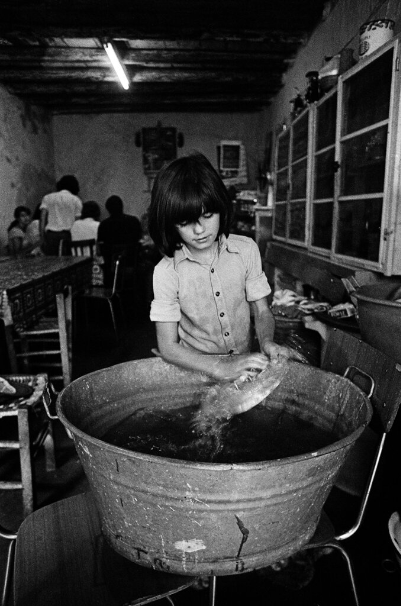
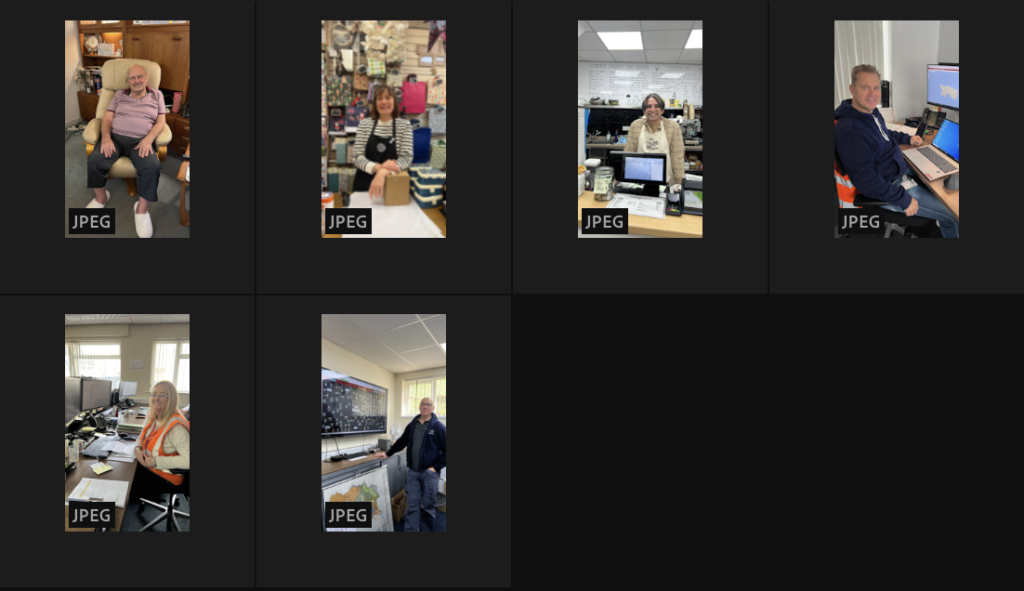
Arnold Newman, Newman was an American photographer born in 1918 and passed away in 2006. Arnold Newman was well known for his portraits of high-profile individuals such as artists, politicians and celebrities. He is usually acknowledged with making the environmental portraits popular, a style of photography which places the subject in a context or background relevant to their work or personality.
Newman`s portraits normally use a strong sense of composition and he would pay careful attention towards the lighting and the surroundings. Most of Newmans work is in monochrome (black and white) which i really like because it gives off the feeling of nostalgia and it also makes the images alot more dramatic. Arnold Newmans participation to photography and his unique style of portraiture has made himself one of the most important people in the history of photography.
here are some of Arnold Newman`s Images:

Arnold Newman has various museum collections and exhibitions such as: “The great British”, “Five Decades”, “Arnold Newman`s americans” and many more which can be found here, https://arnoldnewman.com/biography.html
Image Analysis
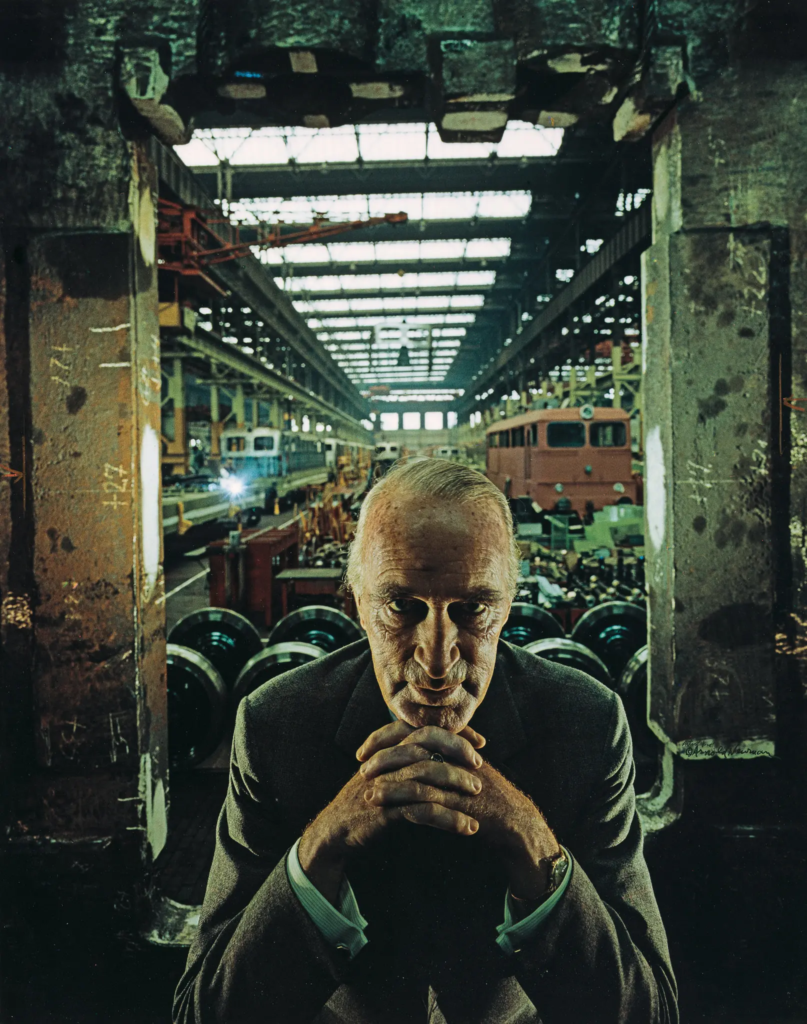

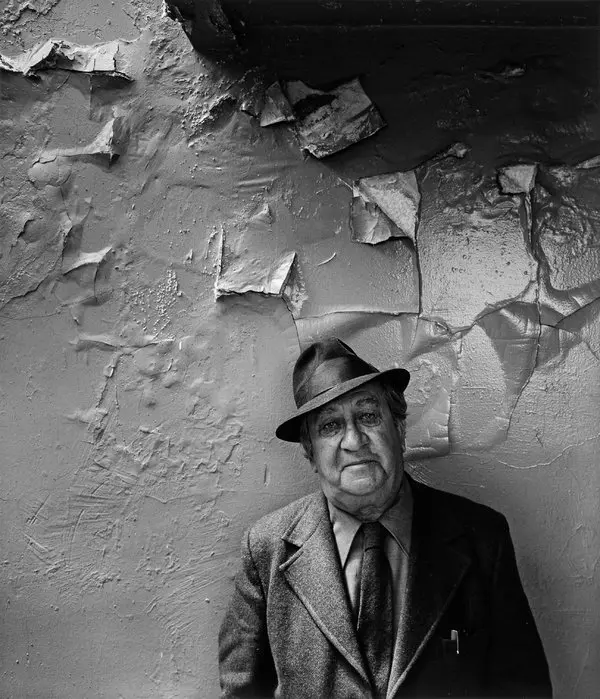
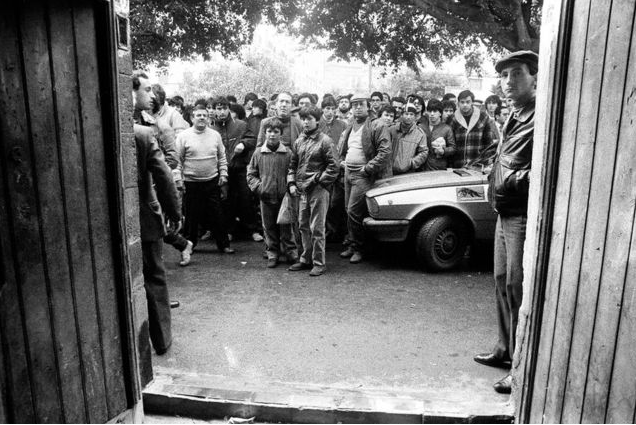
Alfried Krupp, industrialist, Essen, Germany, 1963, Arnold Newman
Visual: The man is the main subject in this image, the background is pretty dark with white artificial lighting which makes it look like a cold environment, its in a industrial place and it has leading lines towards the back of the photo which gives more depth and perception to the image. The train station/factory looks abandoned due to the graffiti on the walls and the overall look of the place.
emotional: Intimidated, cold , serious. these are the feelings I get from this image because the man is staring straight at the viewers and he is in a dark place.
Technical: the photo has a sense of balance because the image uses symmetry this is done with the two pillars being either side of him which makes the image more central and puts the focus on him. the lighting is also done from the top to the bottom and we cant properly see the mans face so this could be to create a sense of anonymous.
Context– Arnold Newman is a Jewish American photographer who took this photo and in the image is Alfred Klupp who is a German who owned many factories in Germany. Arnold Newman did not want to take the photograph at first because Alfred Krupp helped the Germans, but in the end he went through with the job.