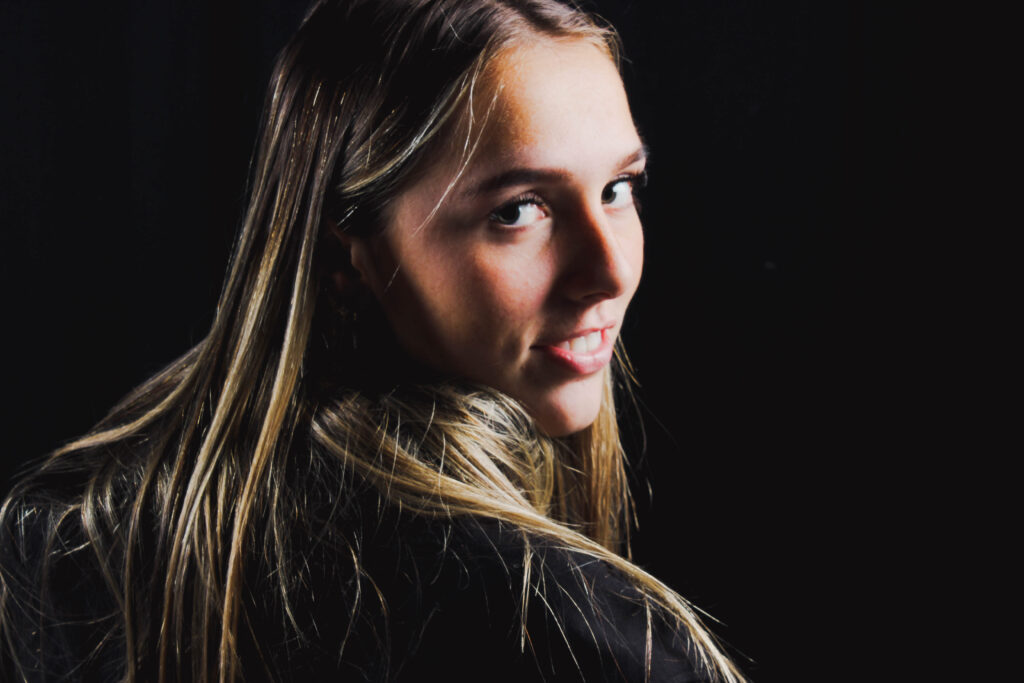
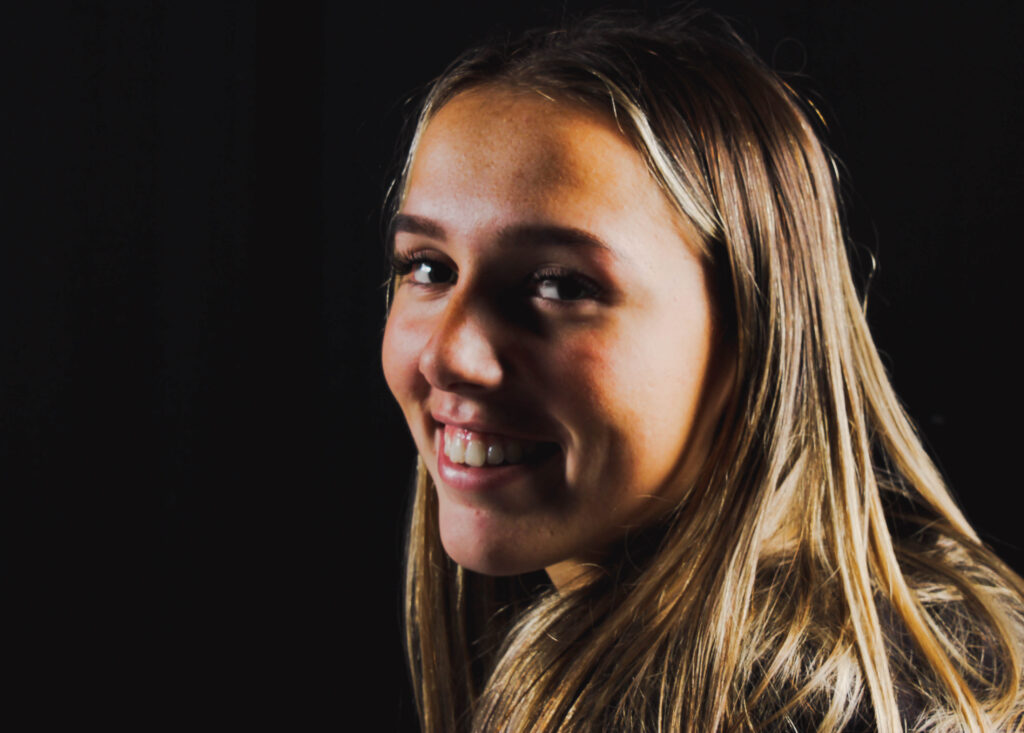
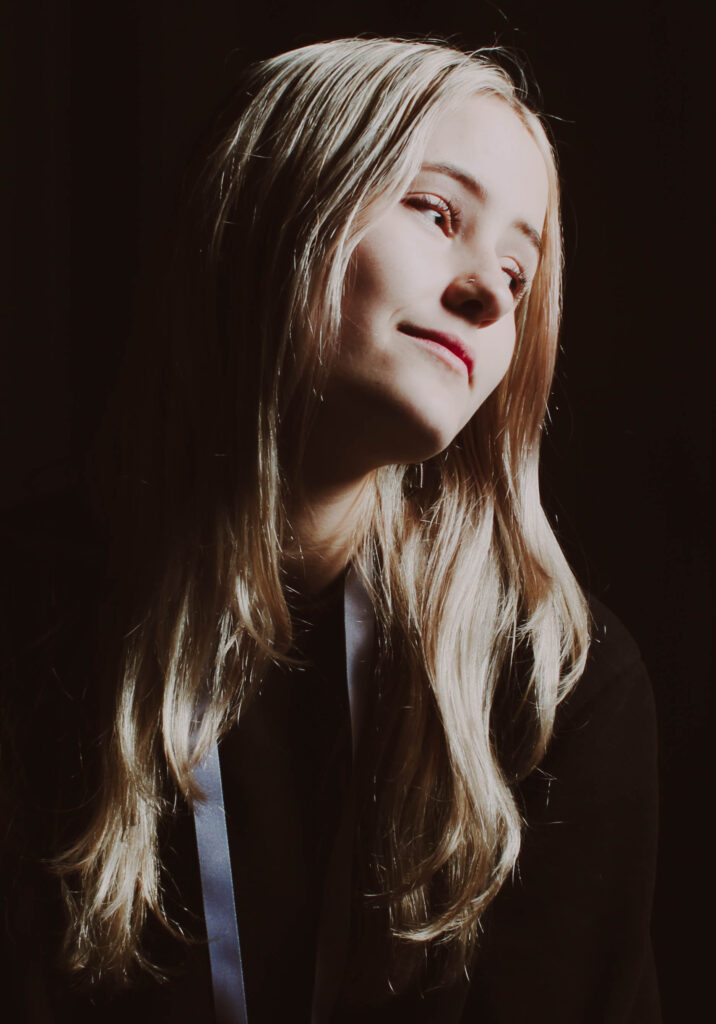
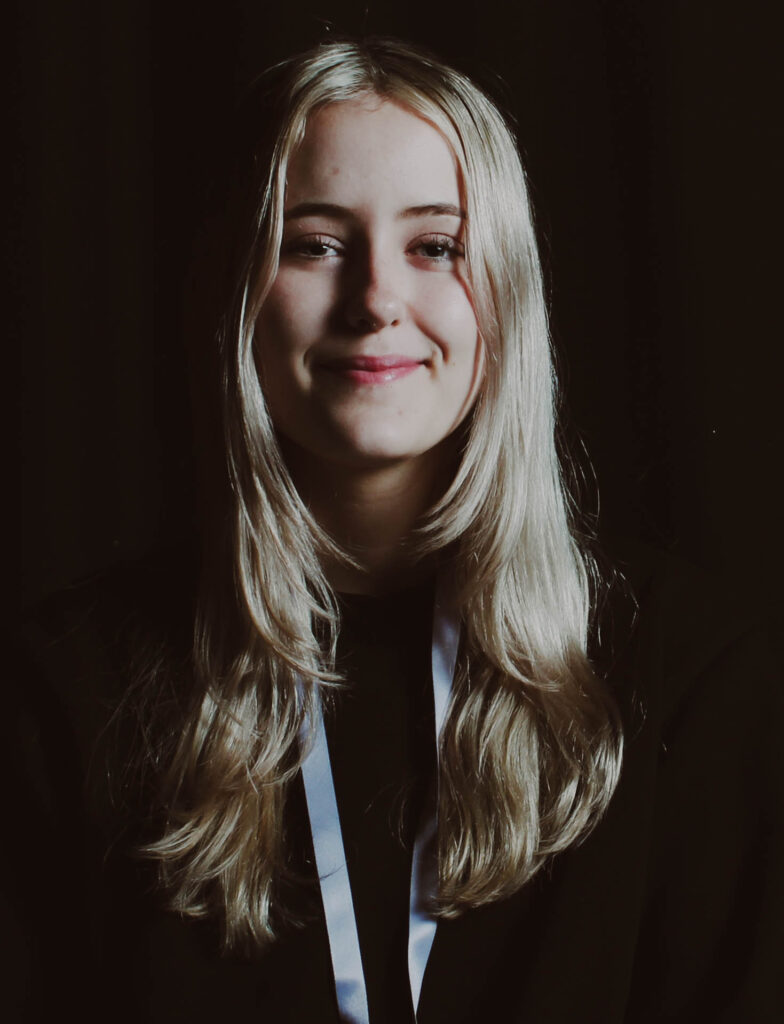
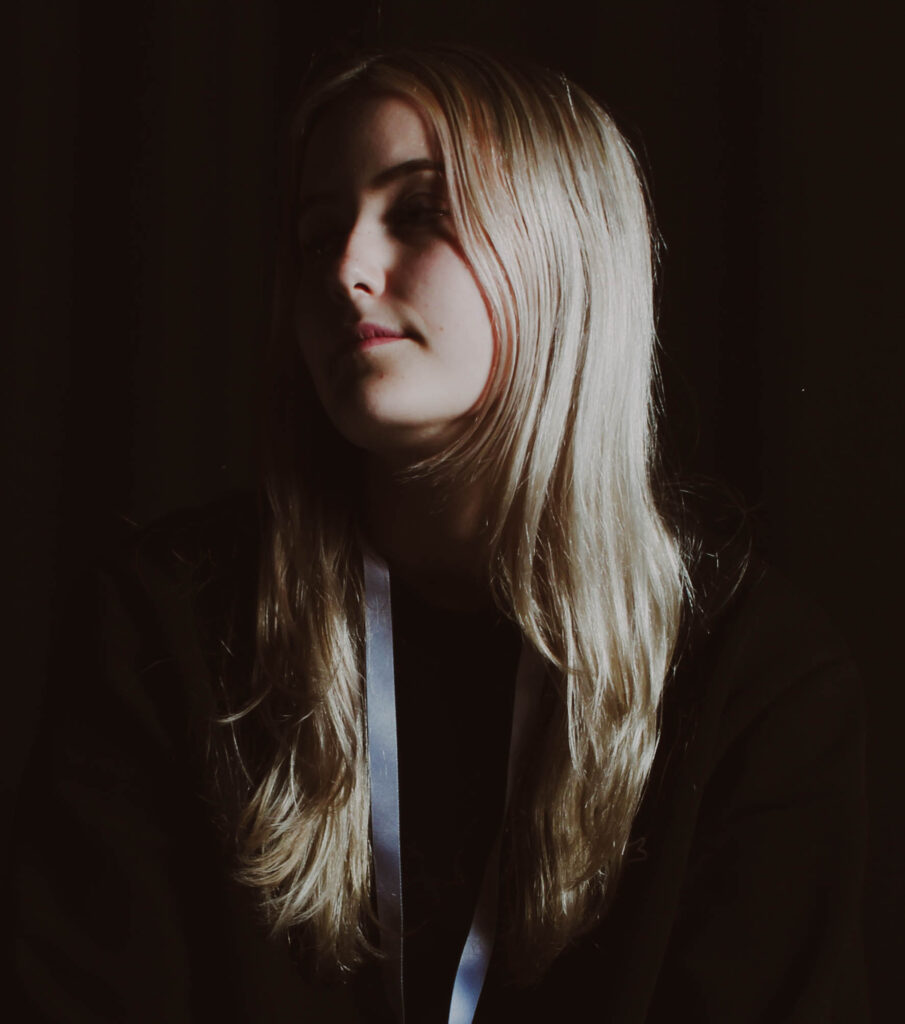
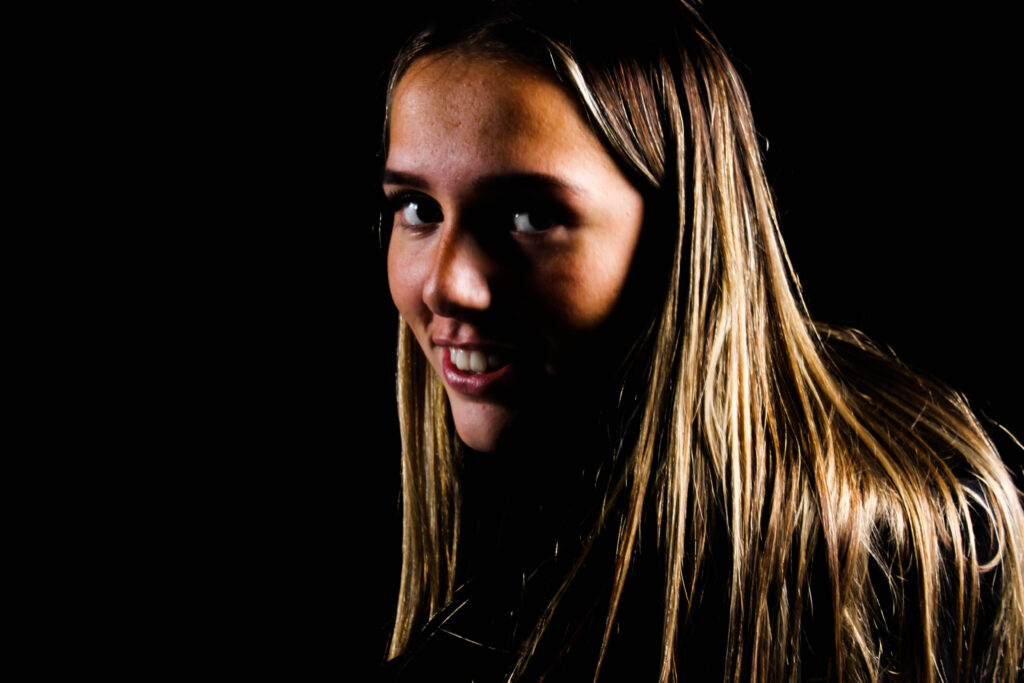
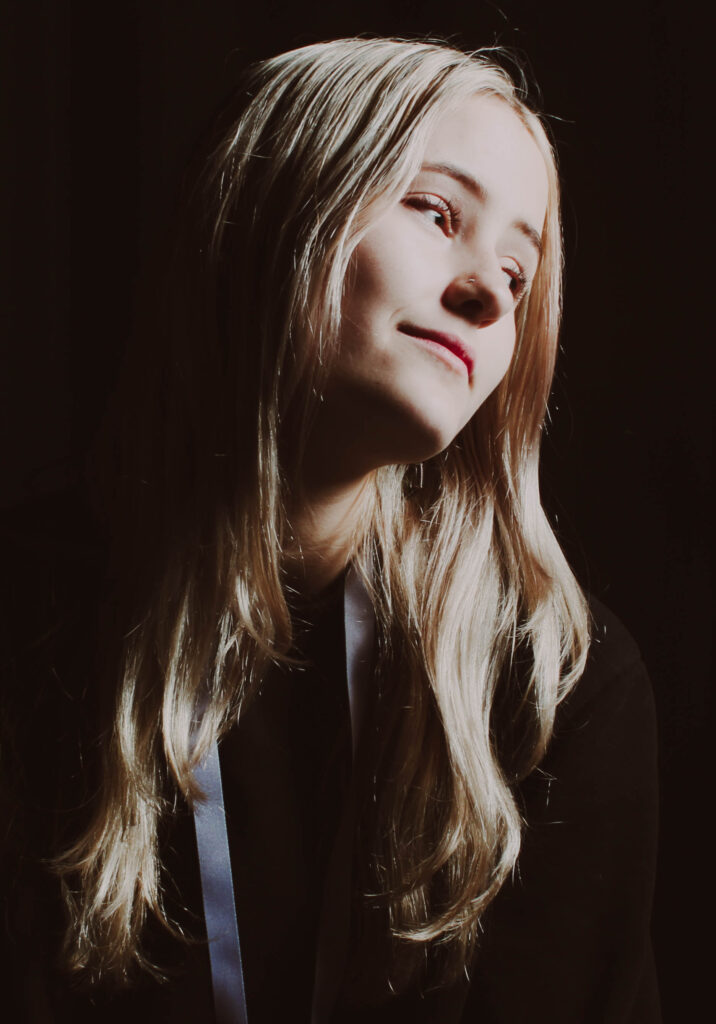
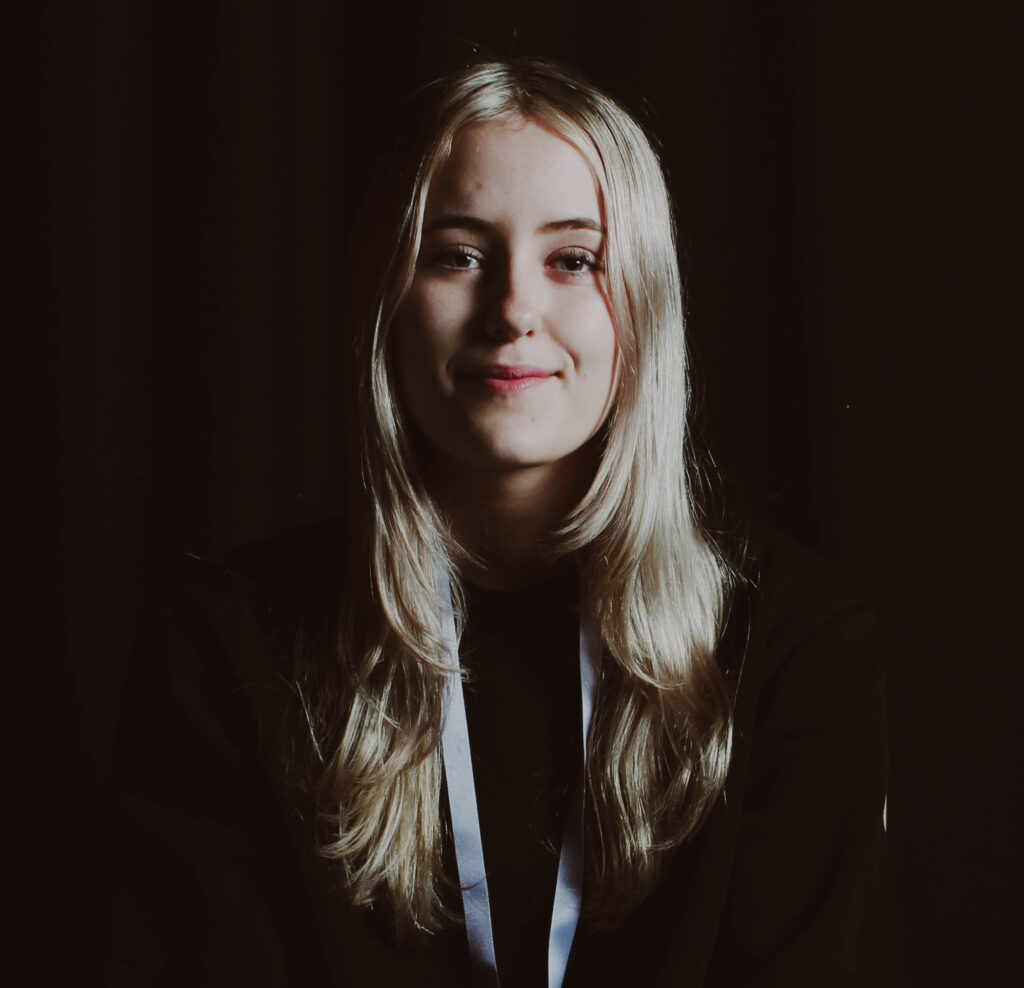
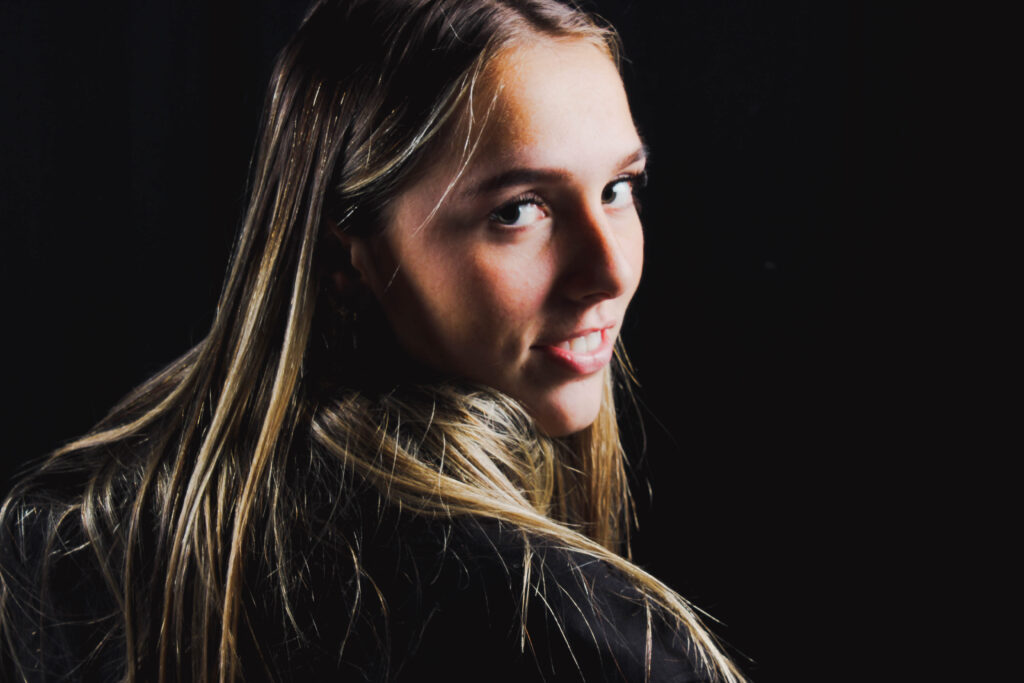
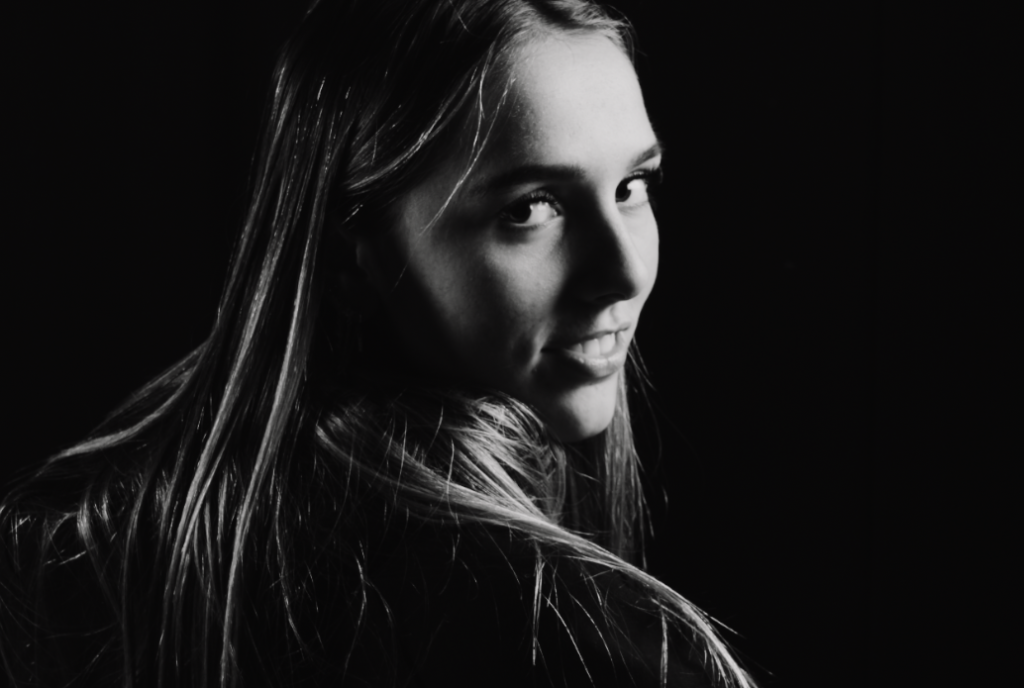
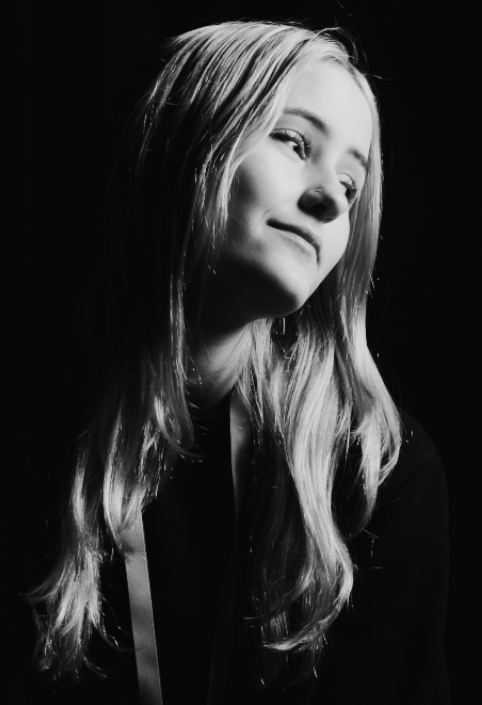
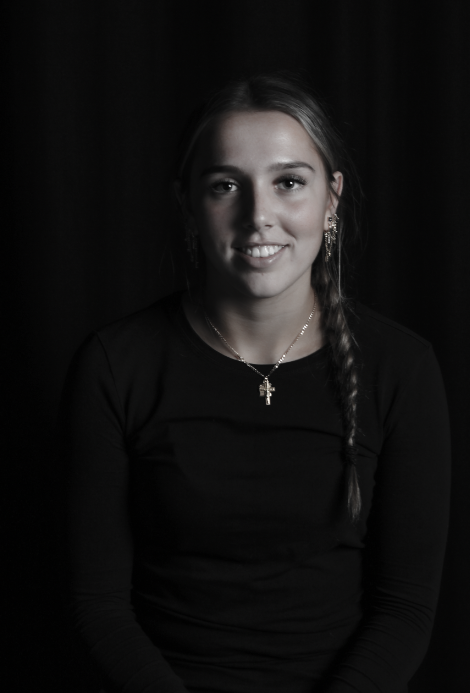
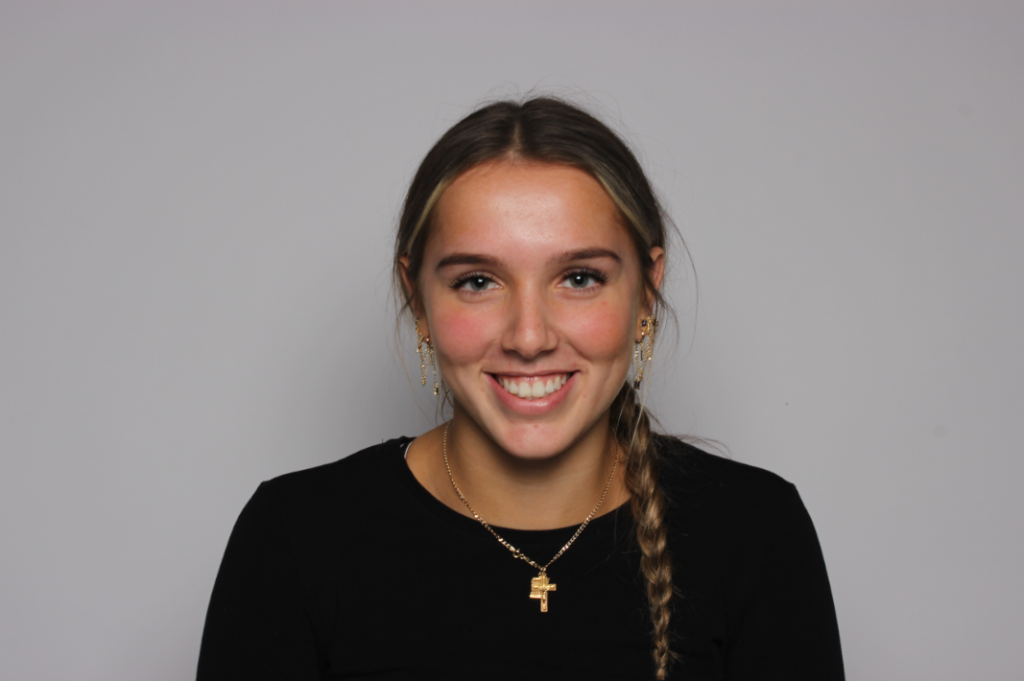
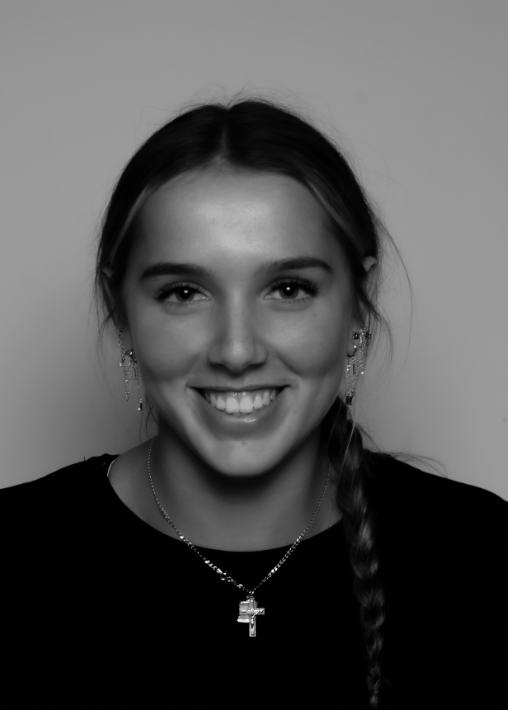
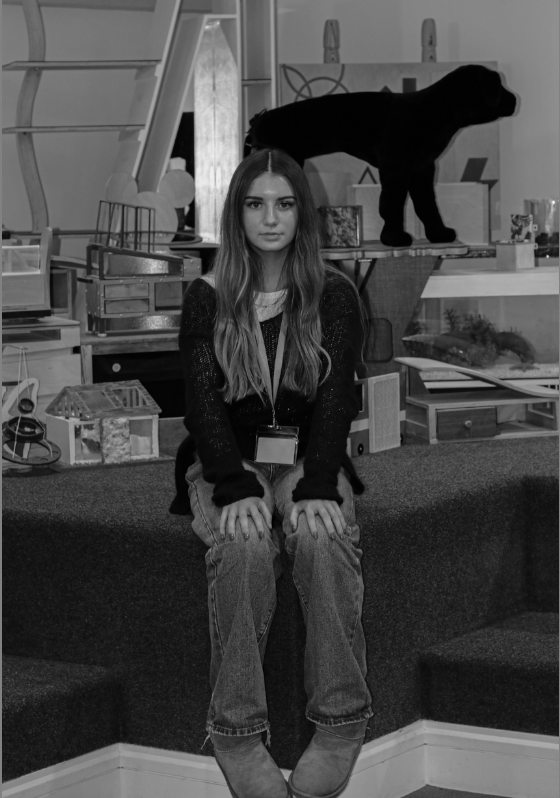
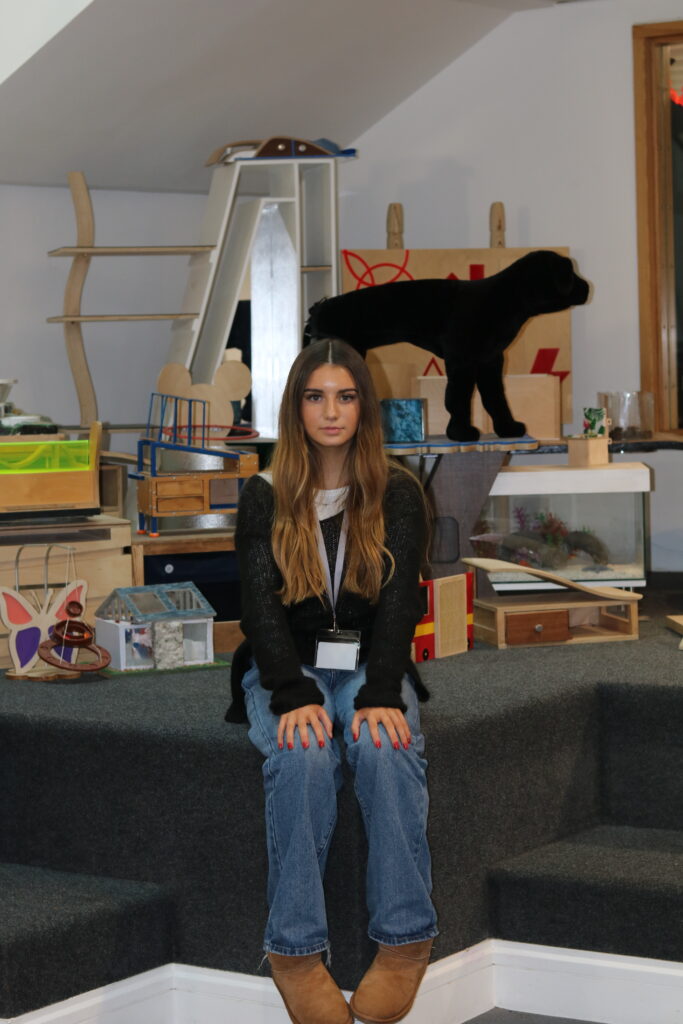
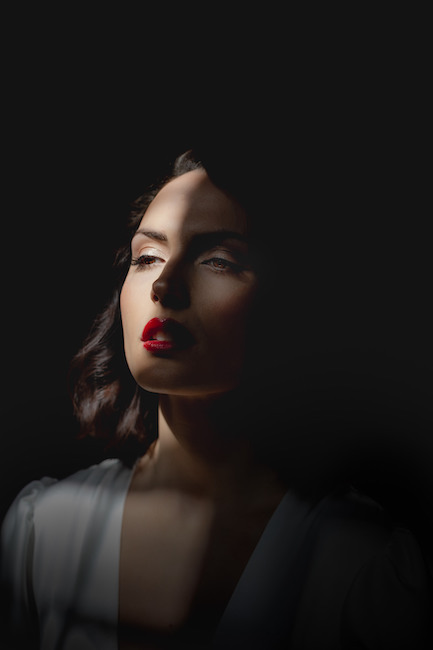
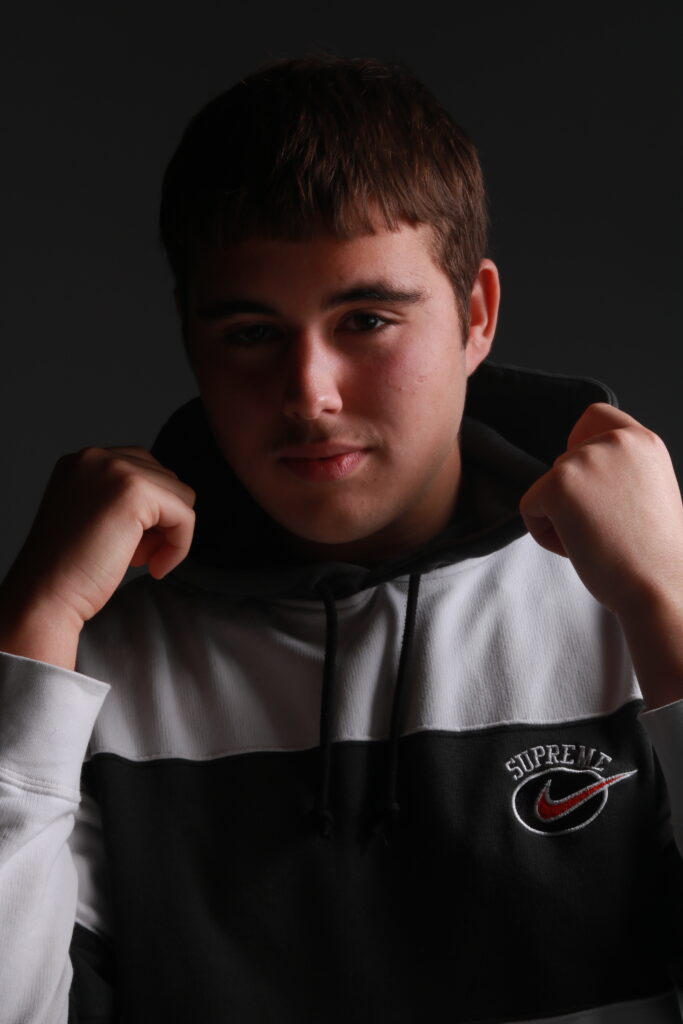
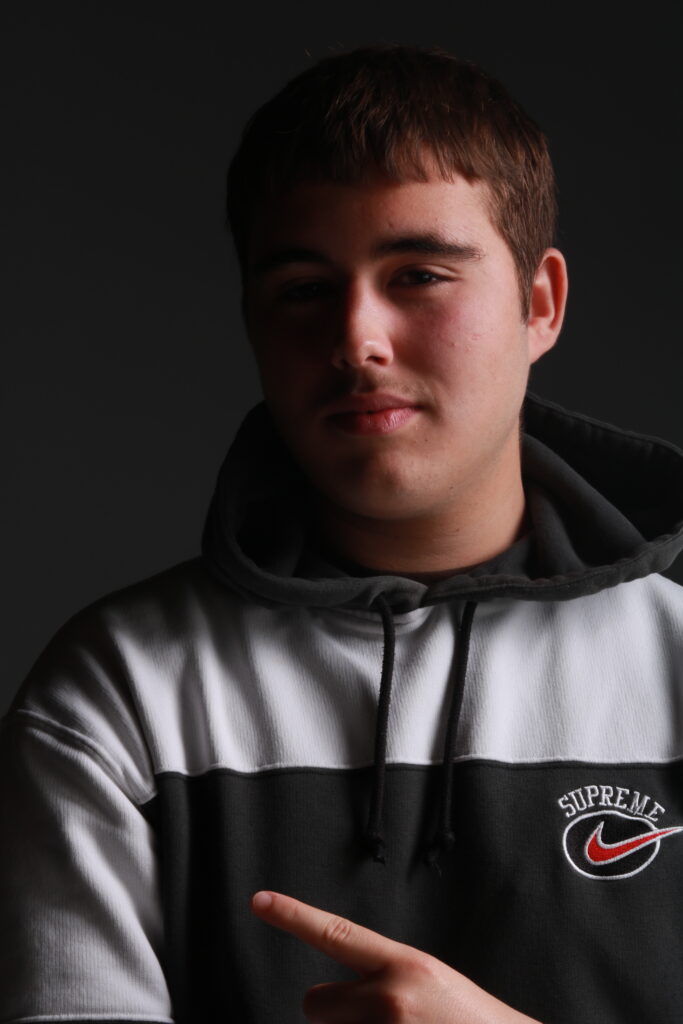
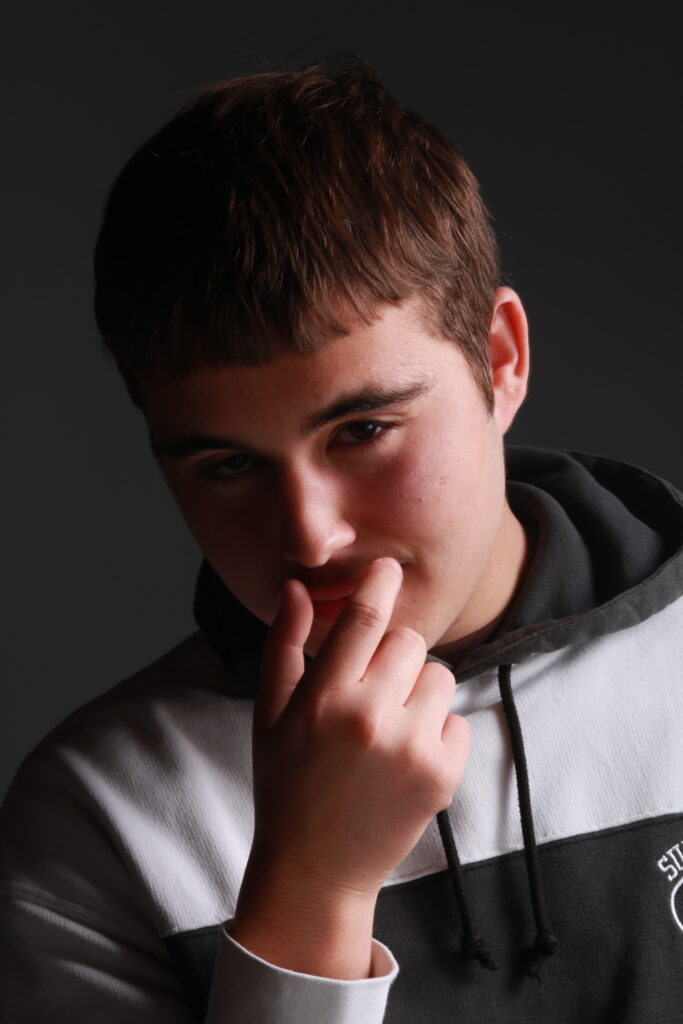
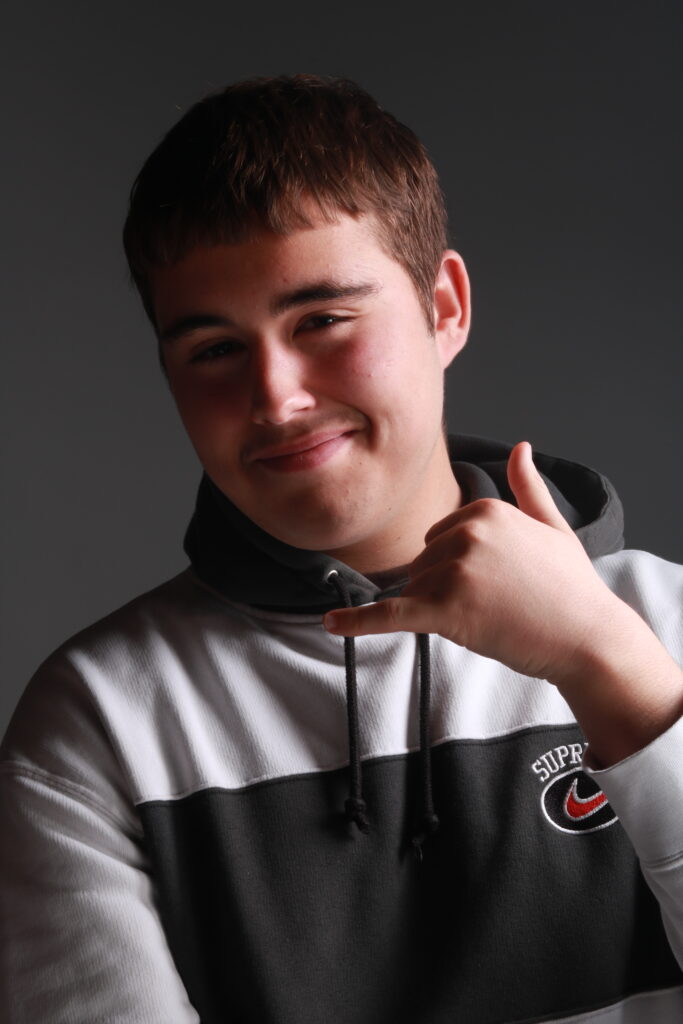
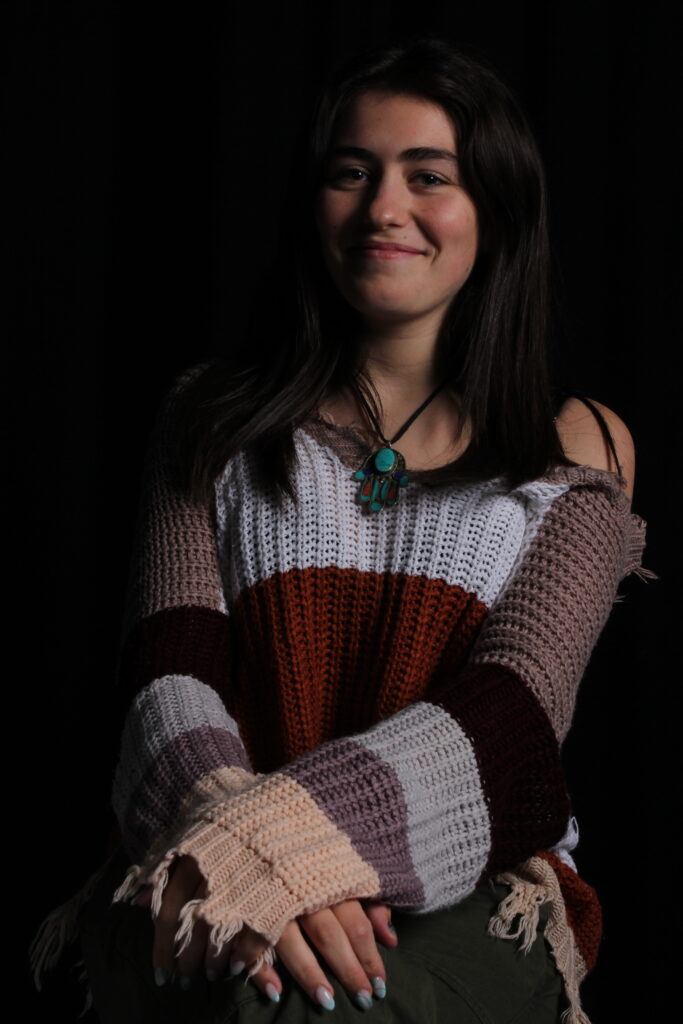
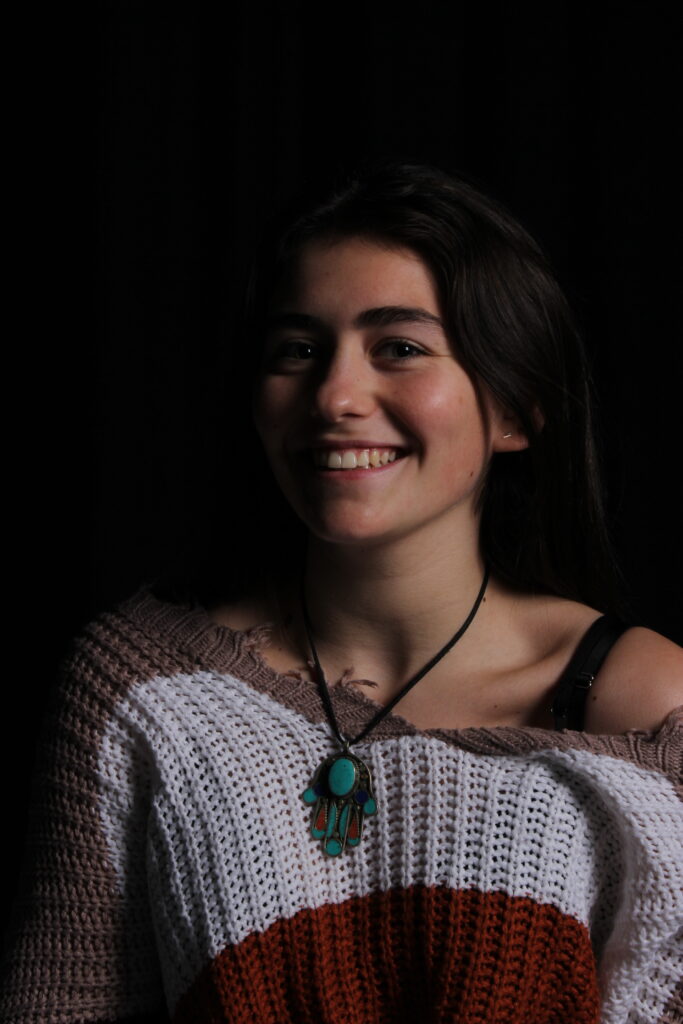
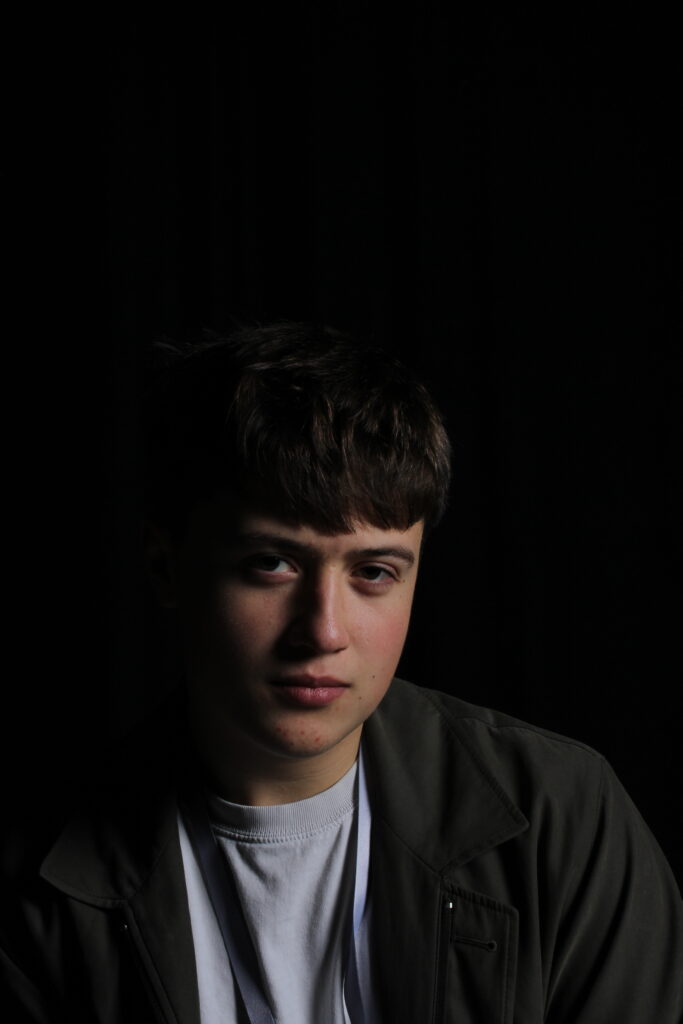
“Rembrandt lighting adds an element of drama and psychological depth to the character of your sitter.“
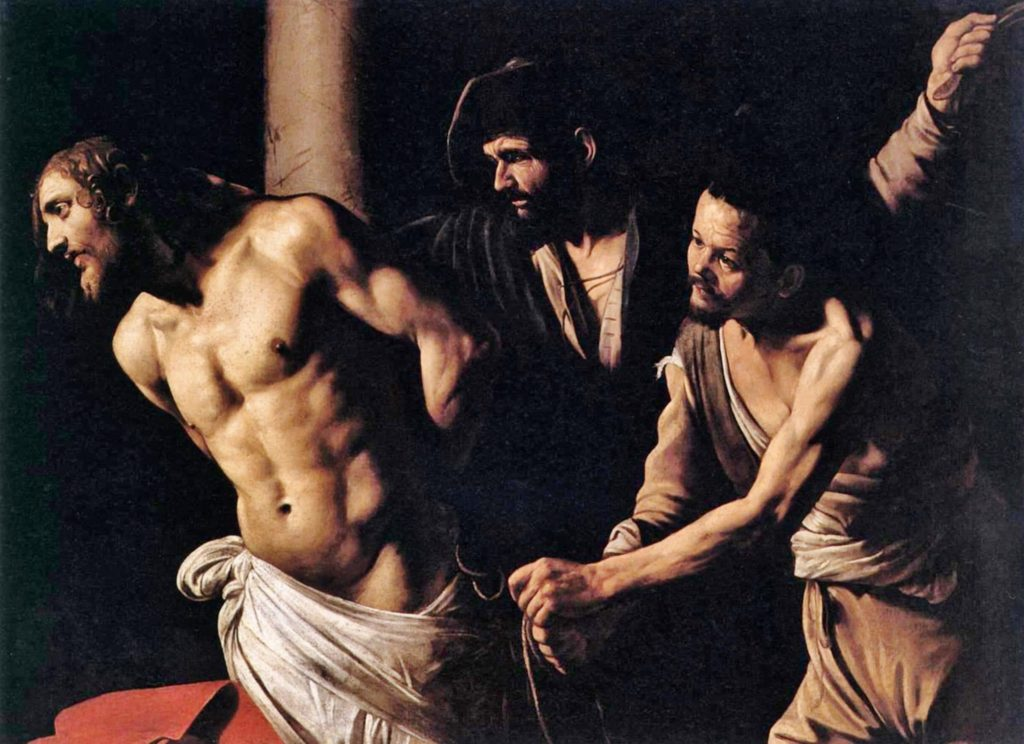
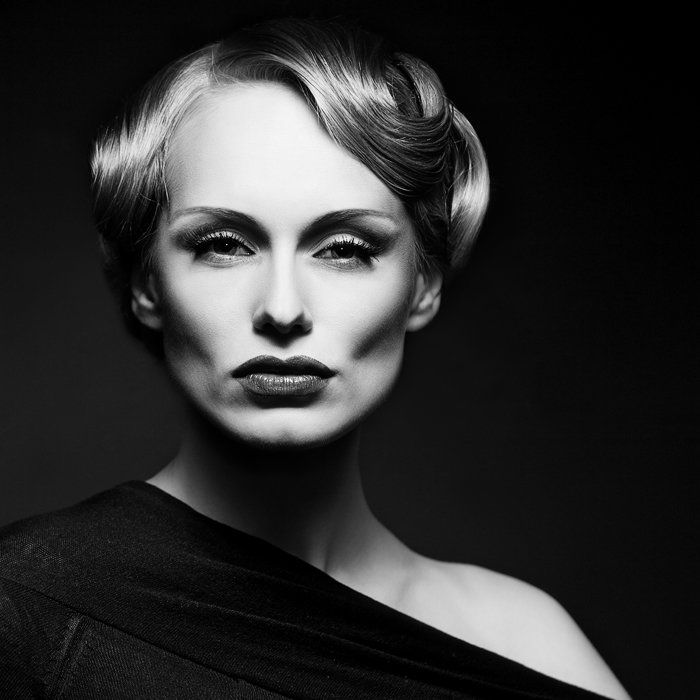
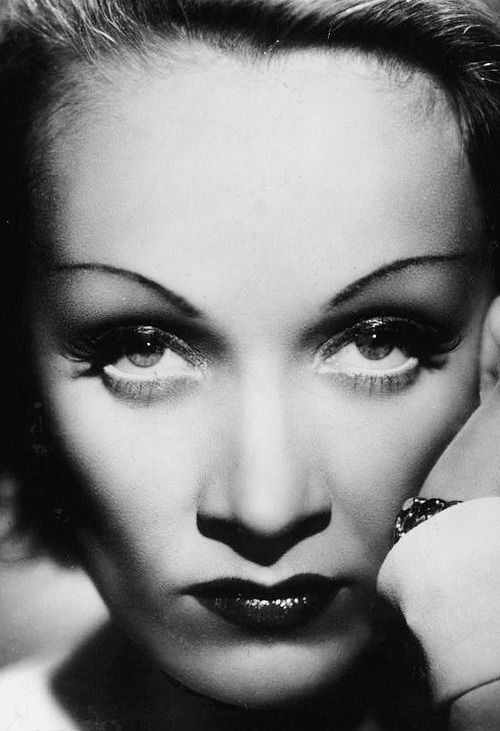
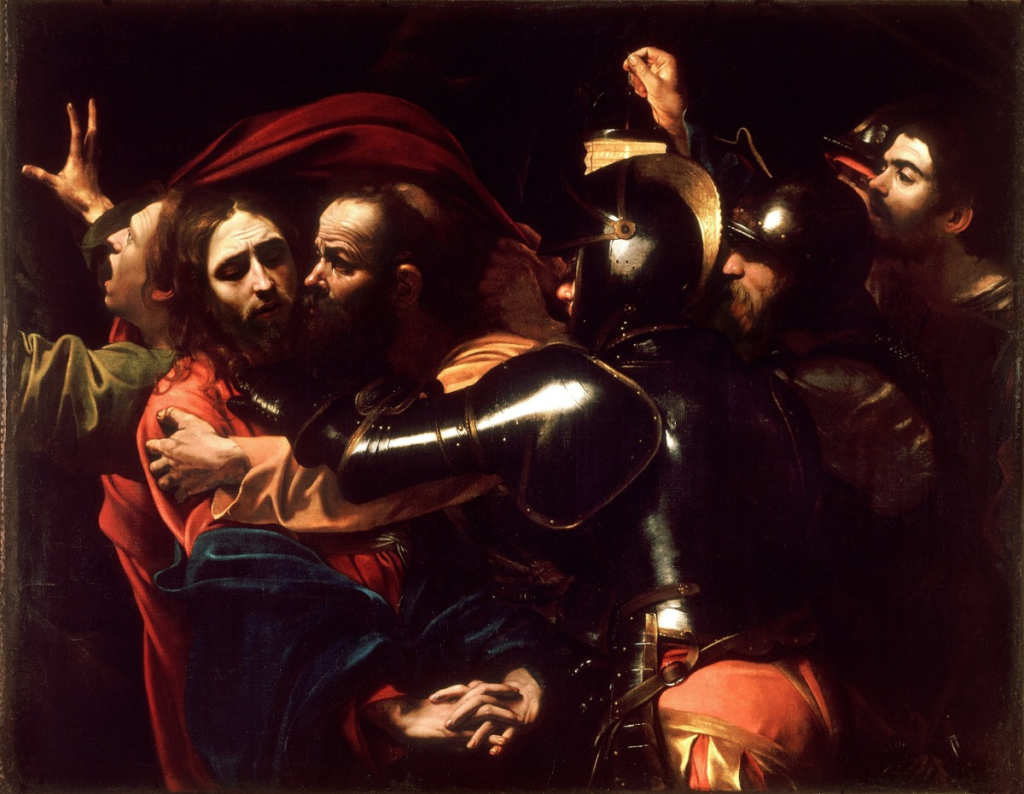
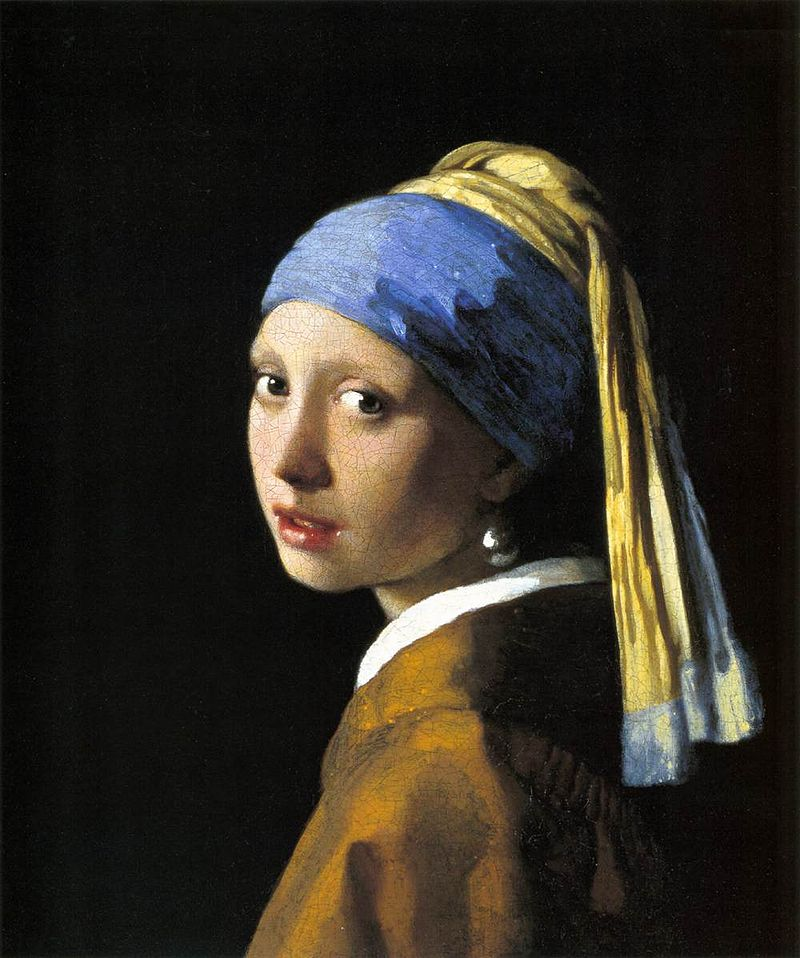
Rembrandt lighting takes its name after Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, a 17th-century Dutch painter who was known for using earthy tones and golden highlights to frame the faces of his portraiture subjects. What made his painting style distinct was focusing lighting on the subject’s face and adding detail around it, tapping into an innate human attraction to the face.
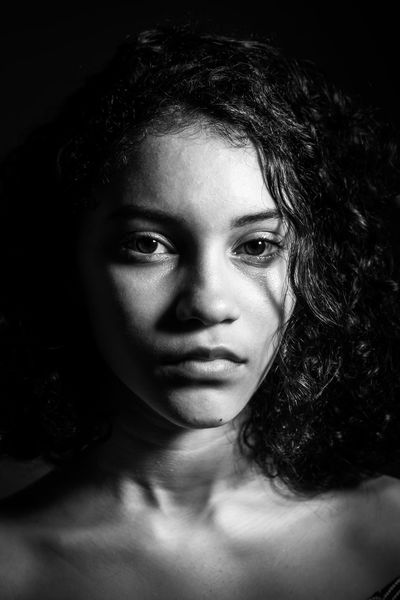
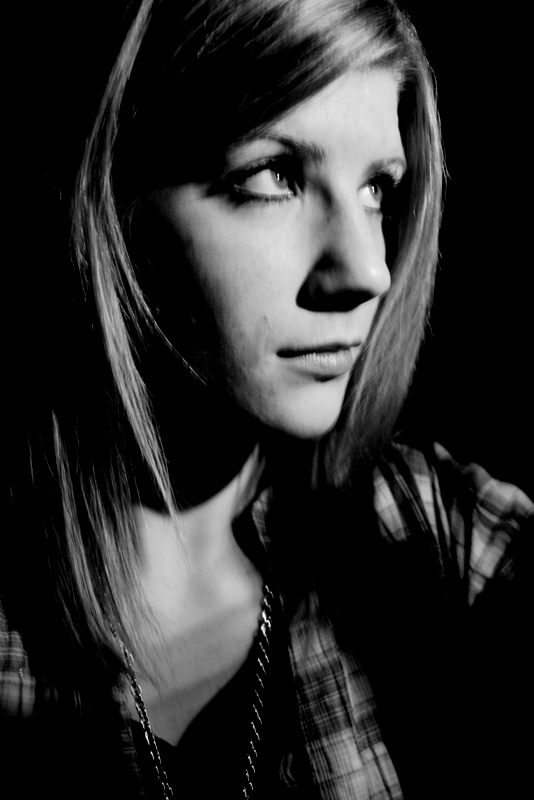
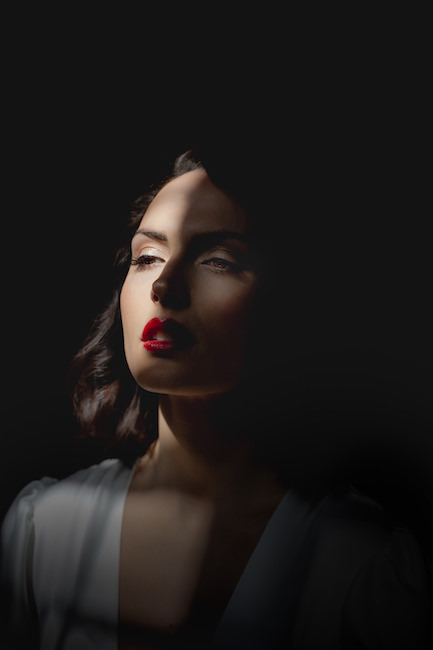
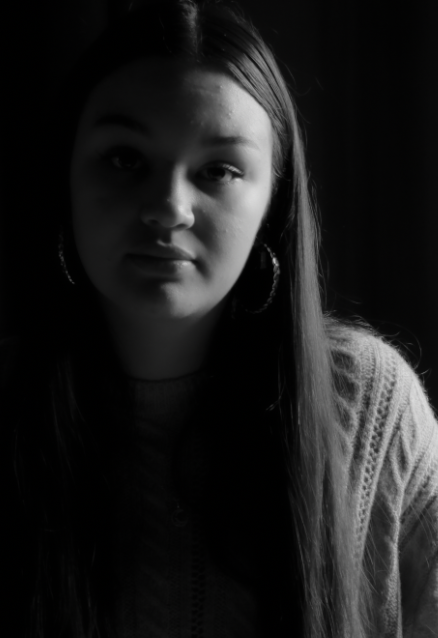
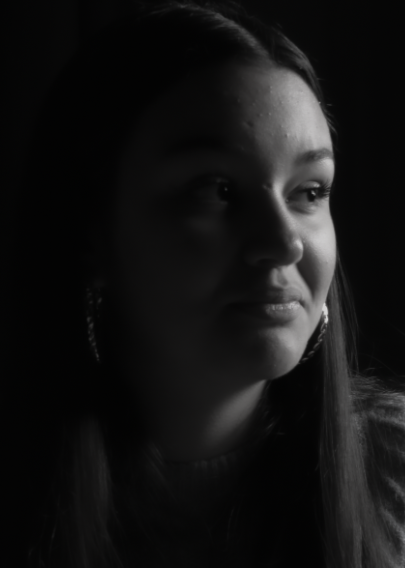
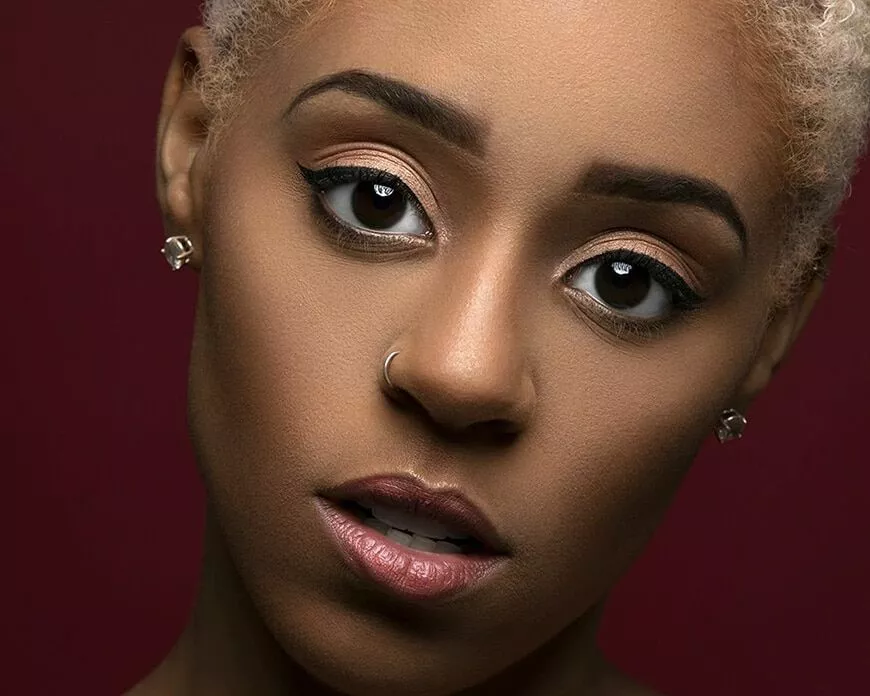
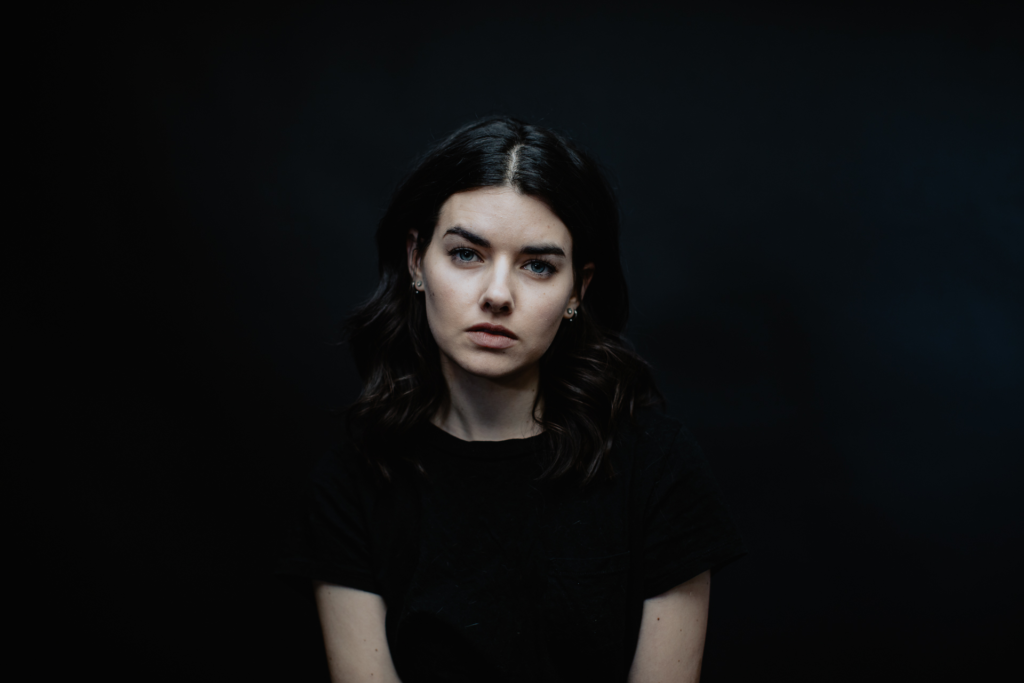
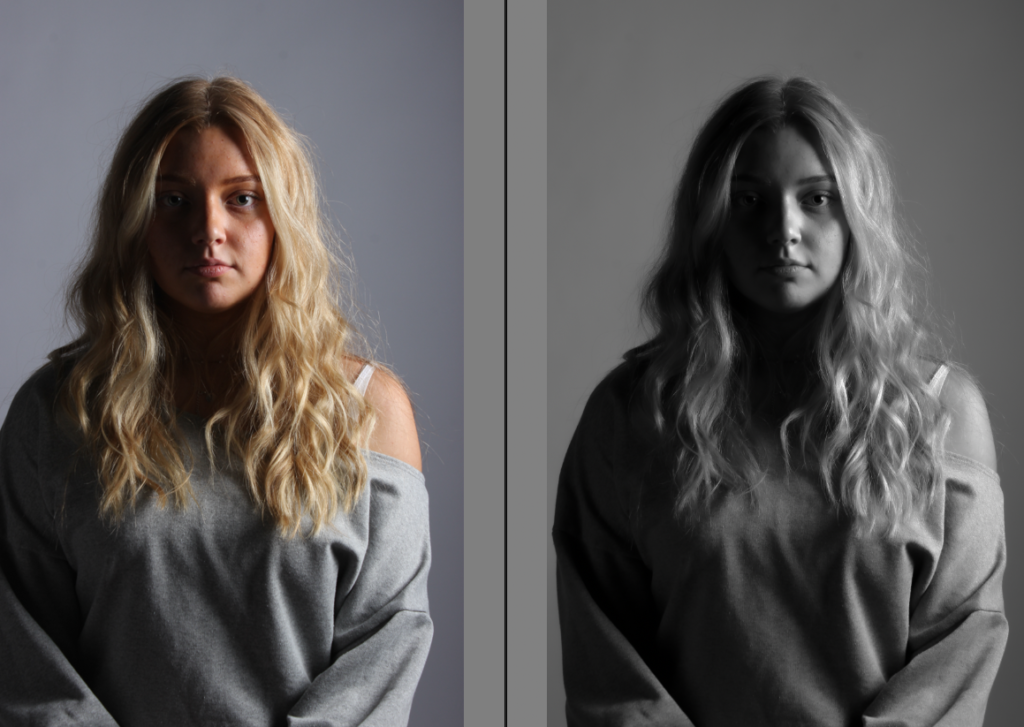
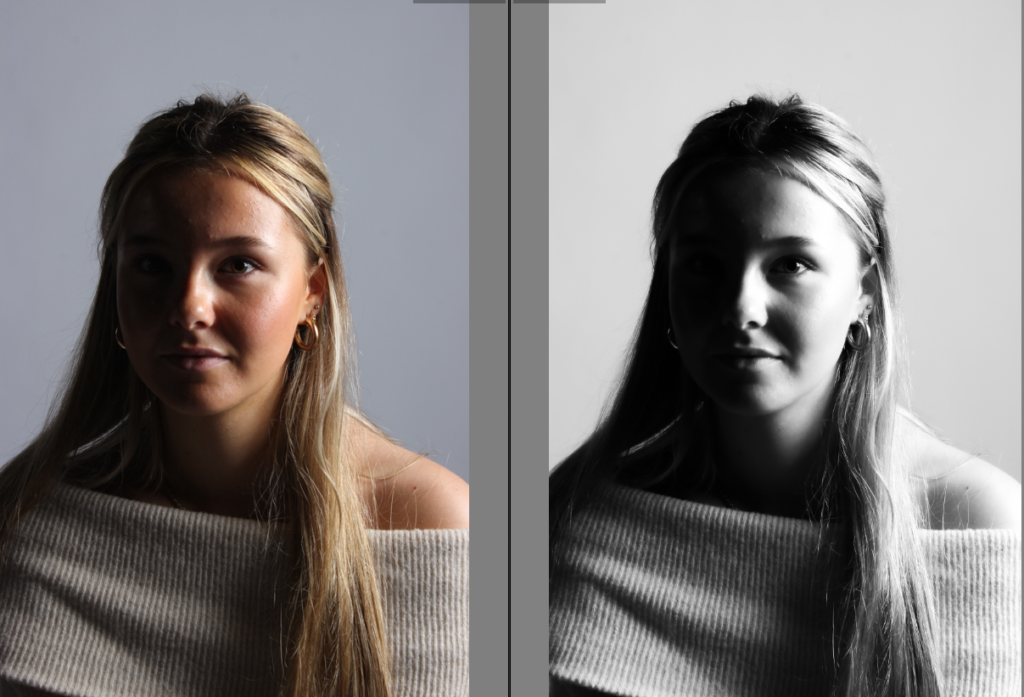
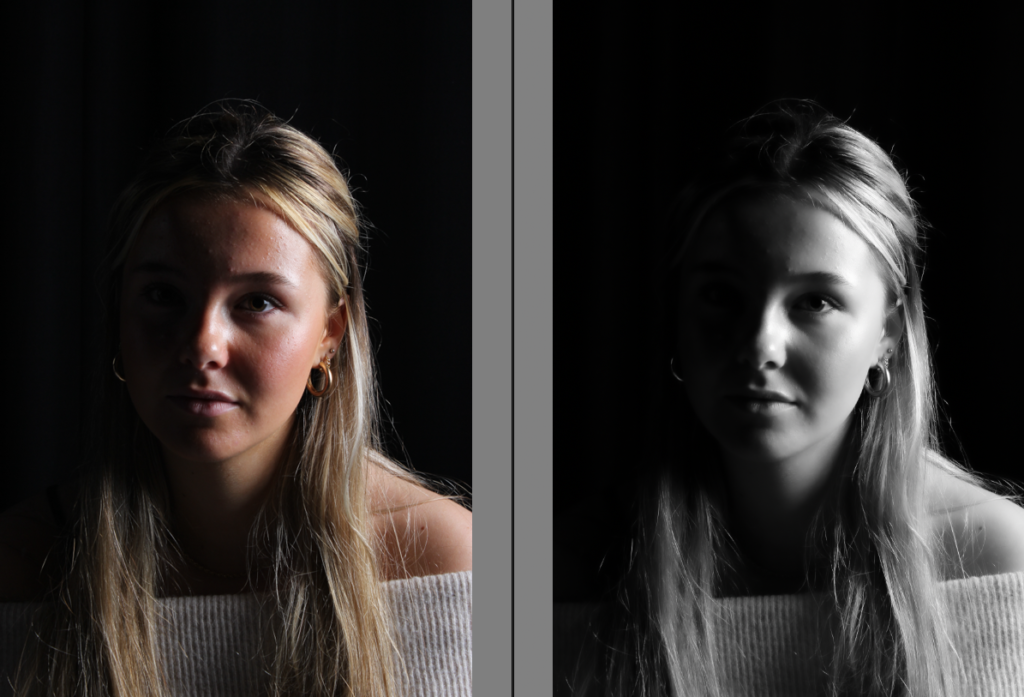
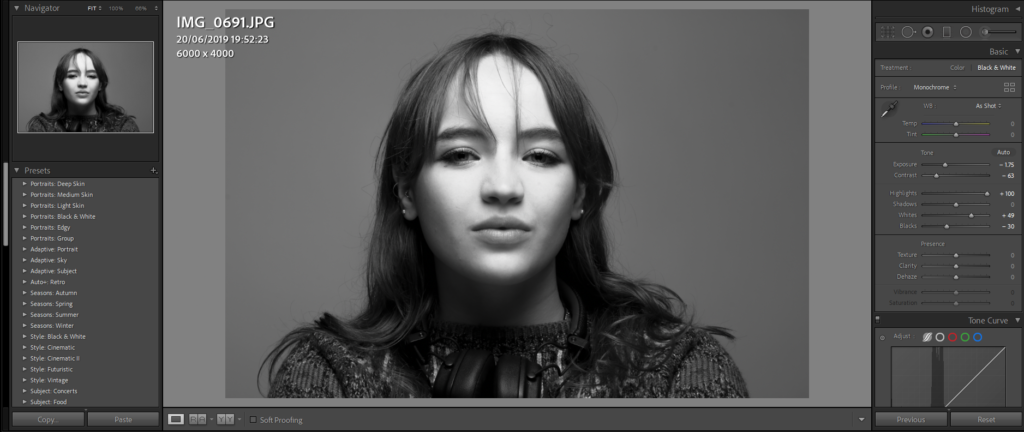
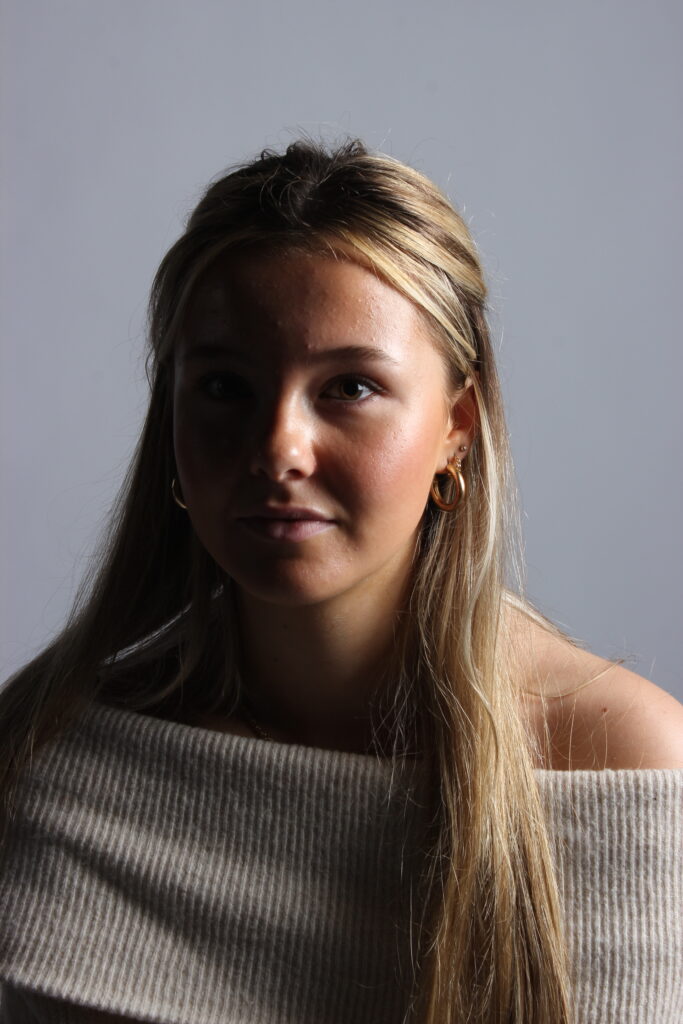
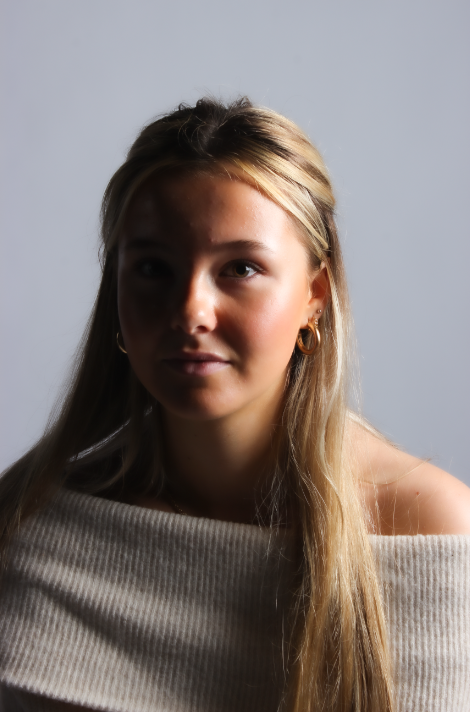
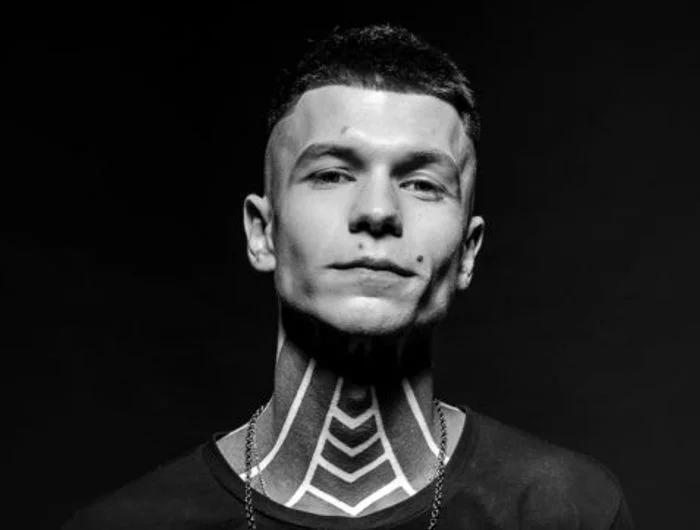
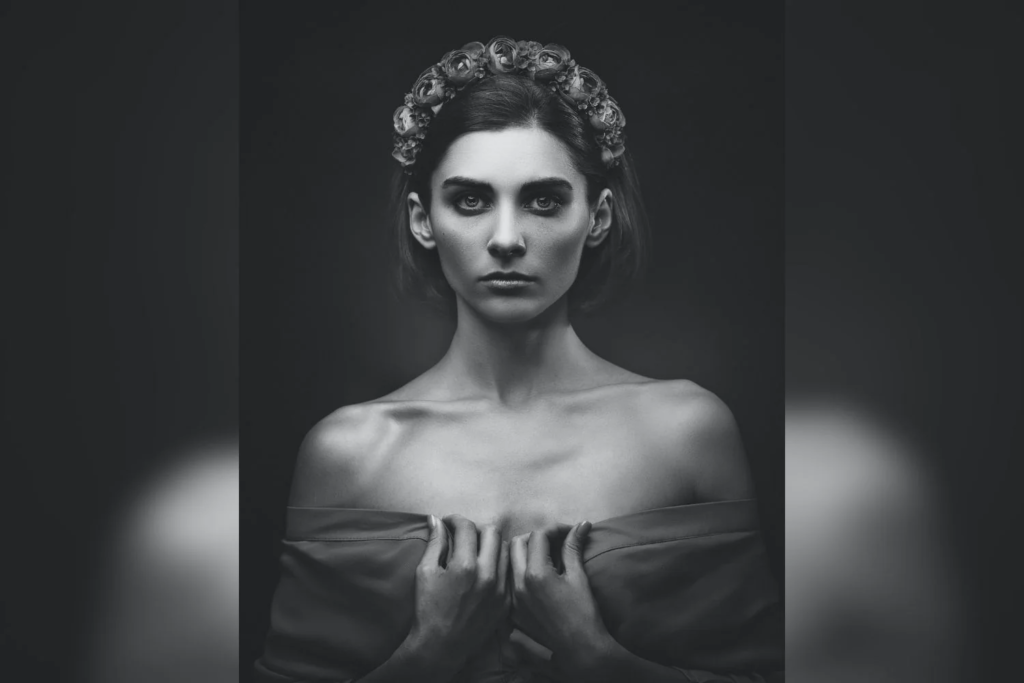
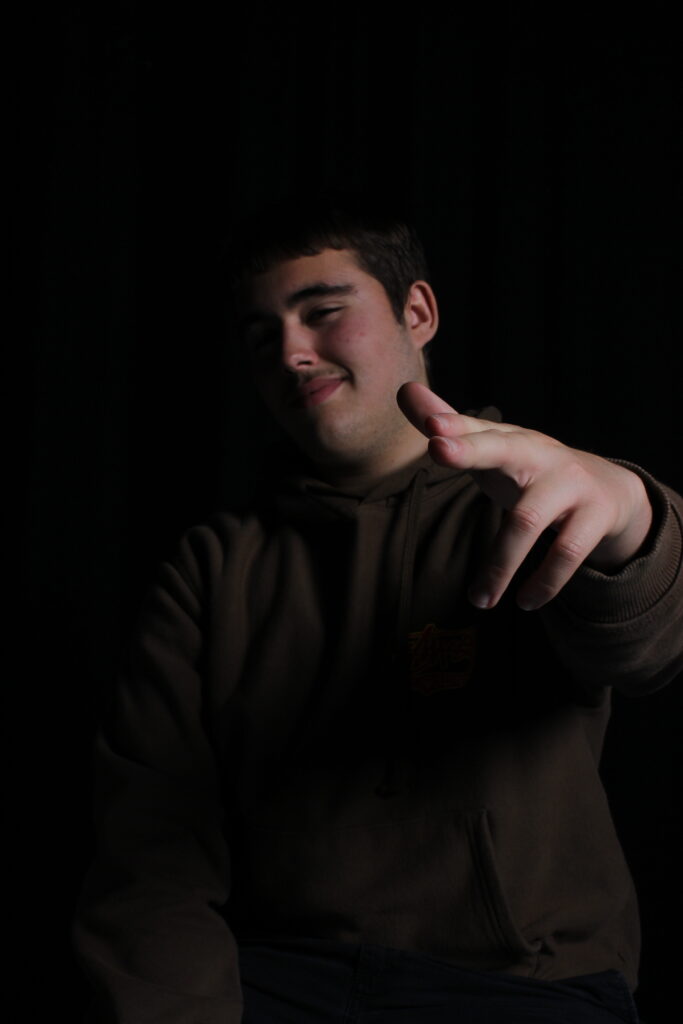
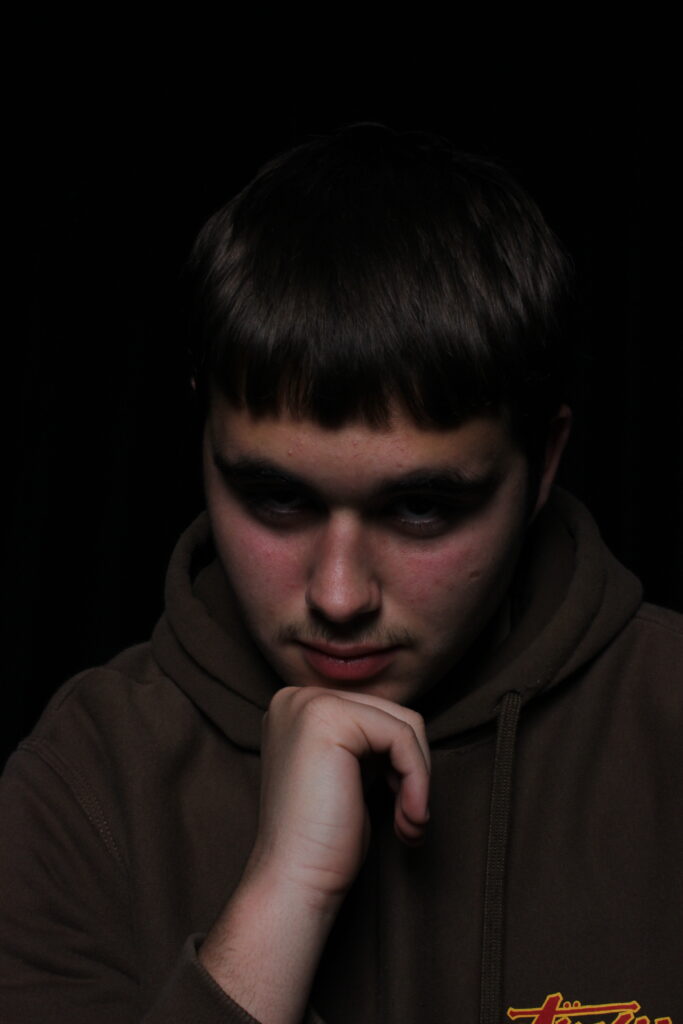
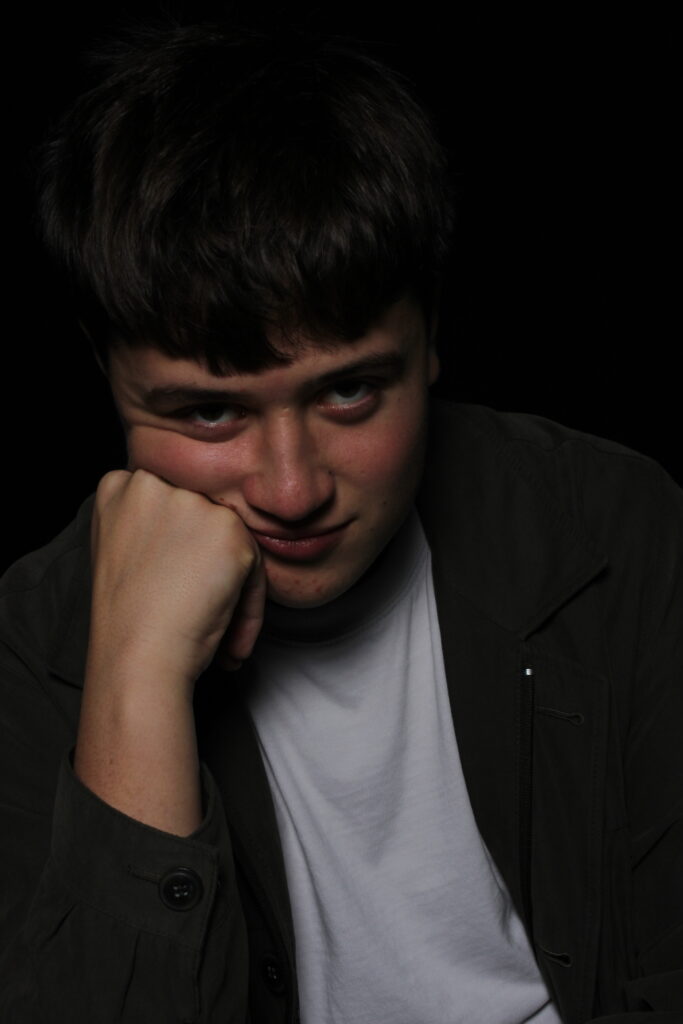
His approach results in one half of the subject’s face is fully illuminated, while the other half is in partial shadow. One tell-tale sign of Rembrandt lighting is the presence of a small inverted triangle of light below the subject’s eye, usually along the cheek, which is a result of the lighting setup. For perfect execution of this type of lighting, the triangle of light shadow must be no wider than the length of the eye, and no longer than the subject’s nose.
The Rembrandt lighting technique results in a moody and dramatic effect. This type of lighting technique often features a dark or black background behind the subject, putting the subject front and center.
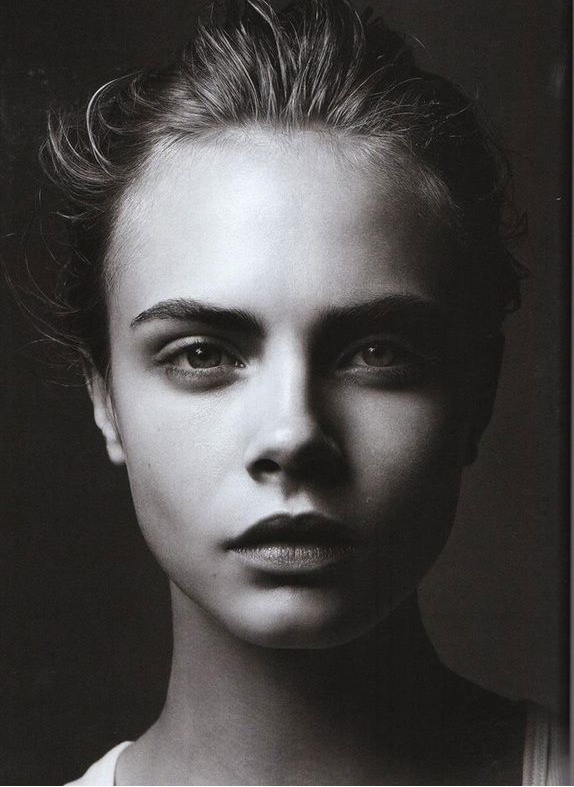
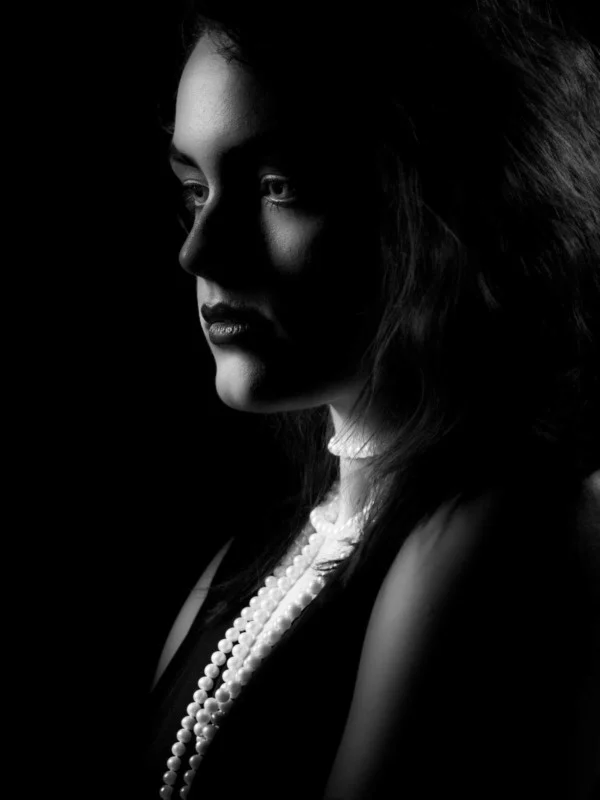
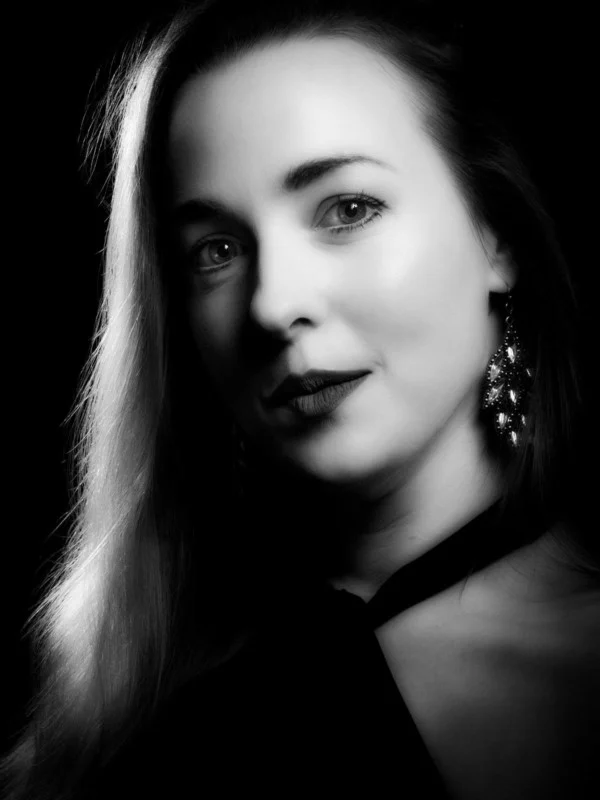



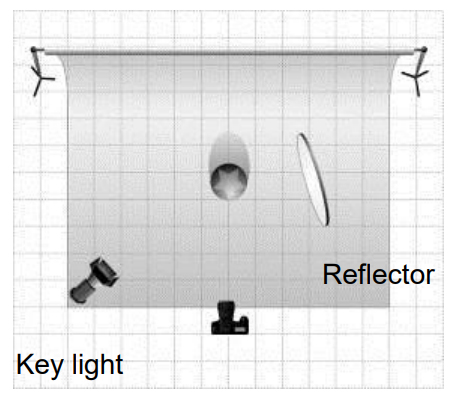
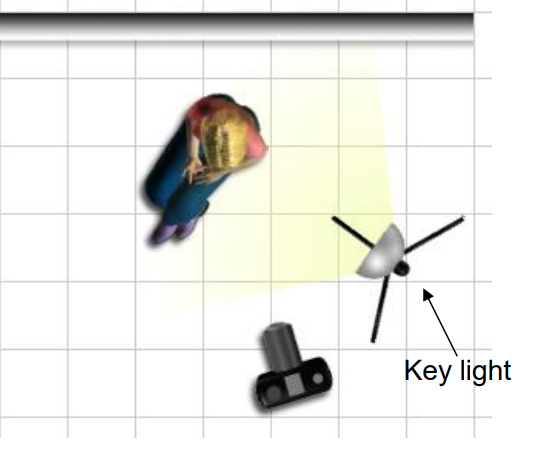
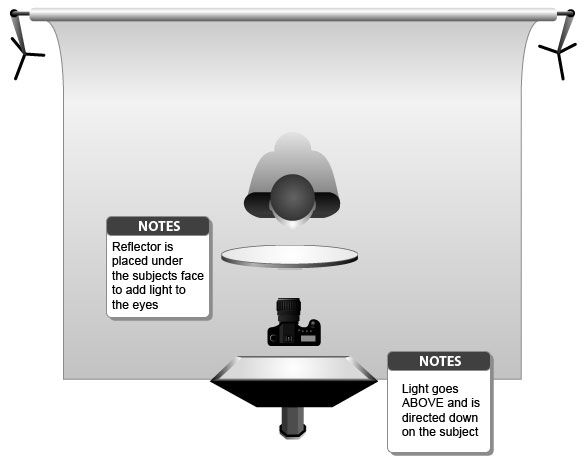
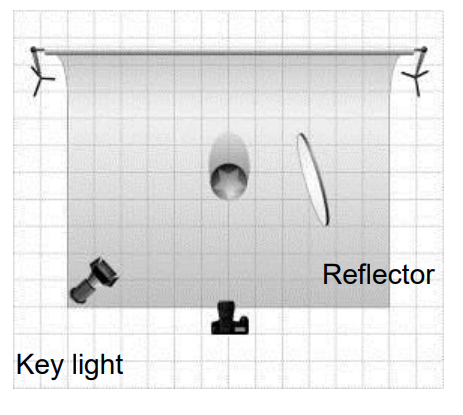
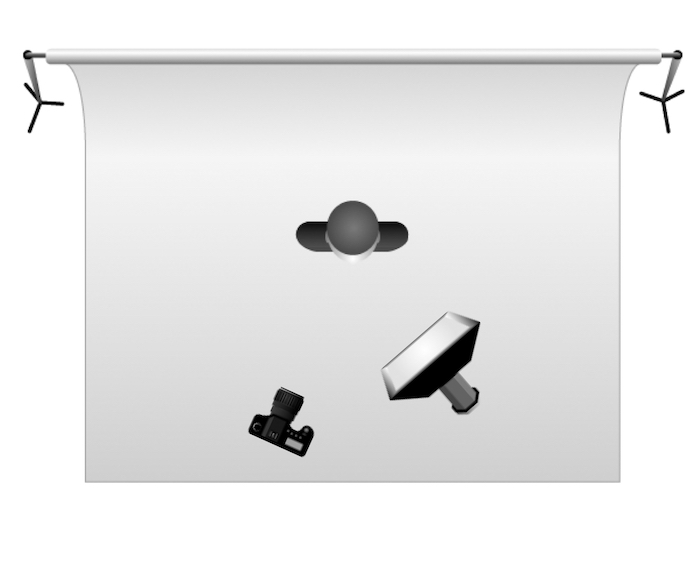
Rembrandt lighting is a technique utilizing one light and one reflector or two separate lights. It’s a popular technique because it creates images that look both dramatic yet natural. It’s predominantly characterized by a lit-up triangle underneath the subject’s eye on the less illuminated area of the face (fill side).
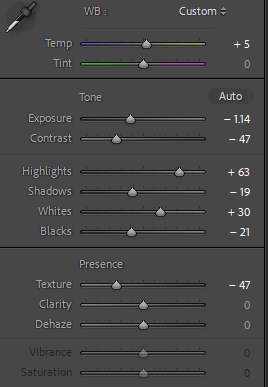
Camera settings (flash lighting)
Tripod: optional, better so you dont have a shake in the photo.
Use transmitter on hotshoe
White balance: daylight (5000K)
ISO: 100
Exposure: Manual 1/125 shutter-speed > f/16 aperture
– check settings before shooting
Focal lenght: 105mm portrait lens
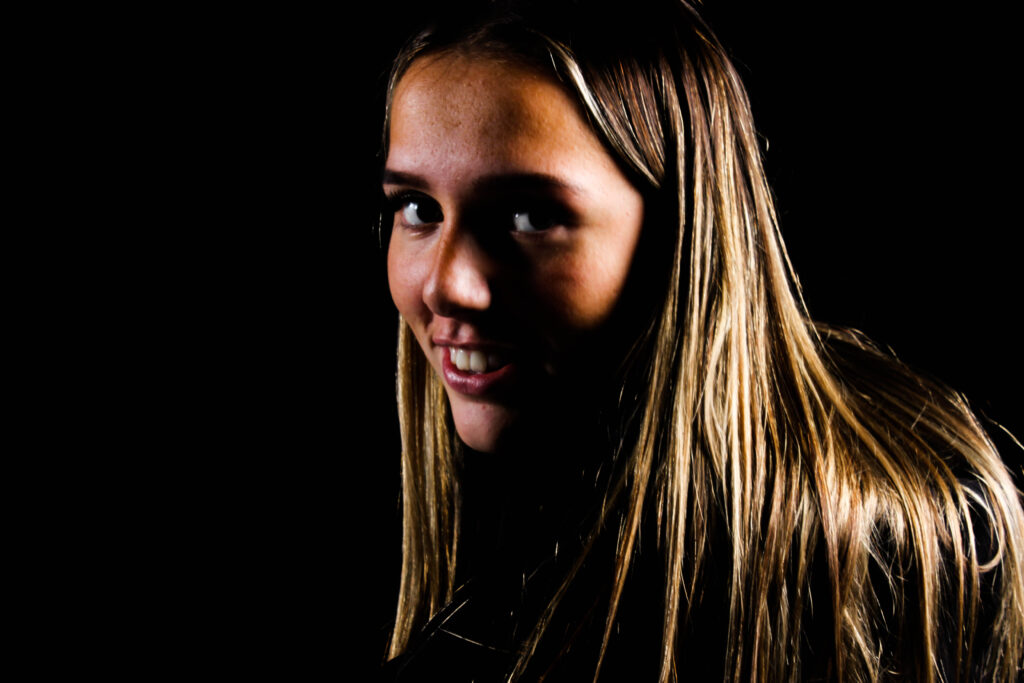
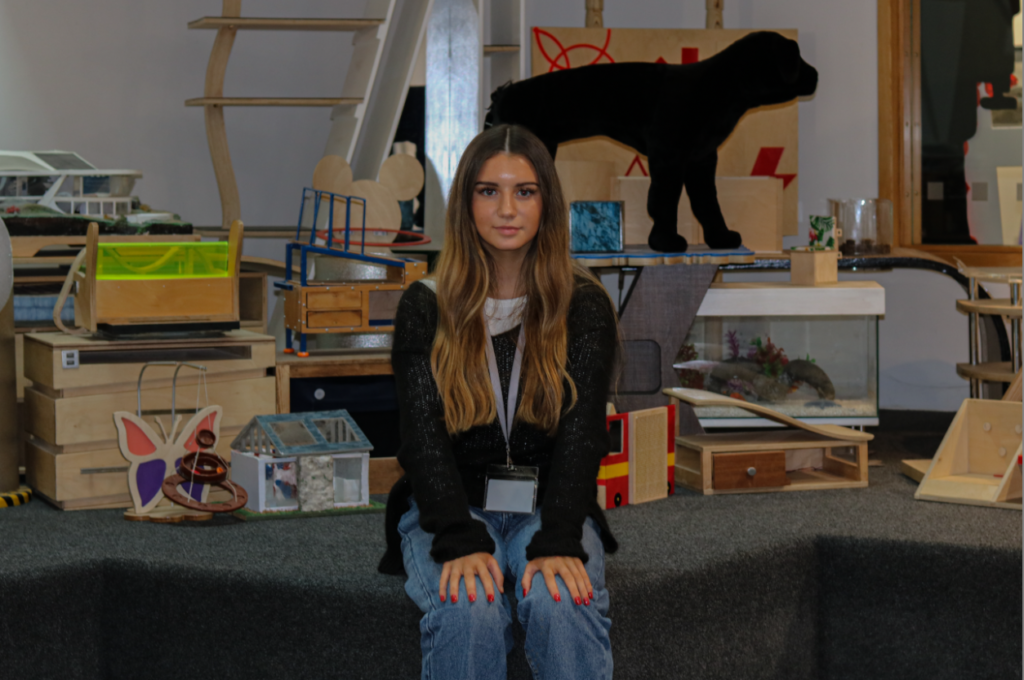
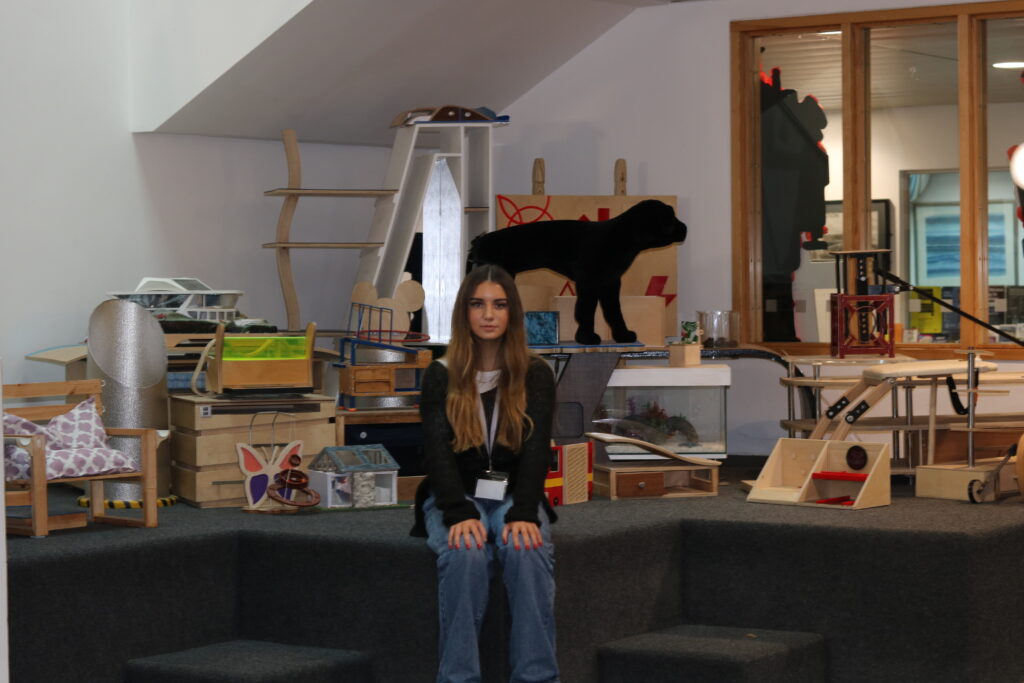
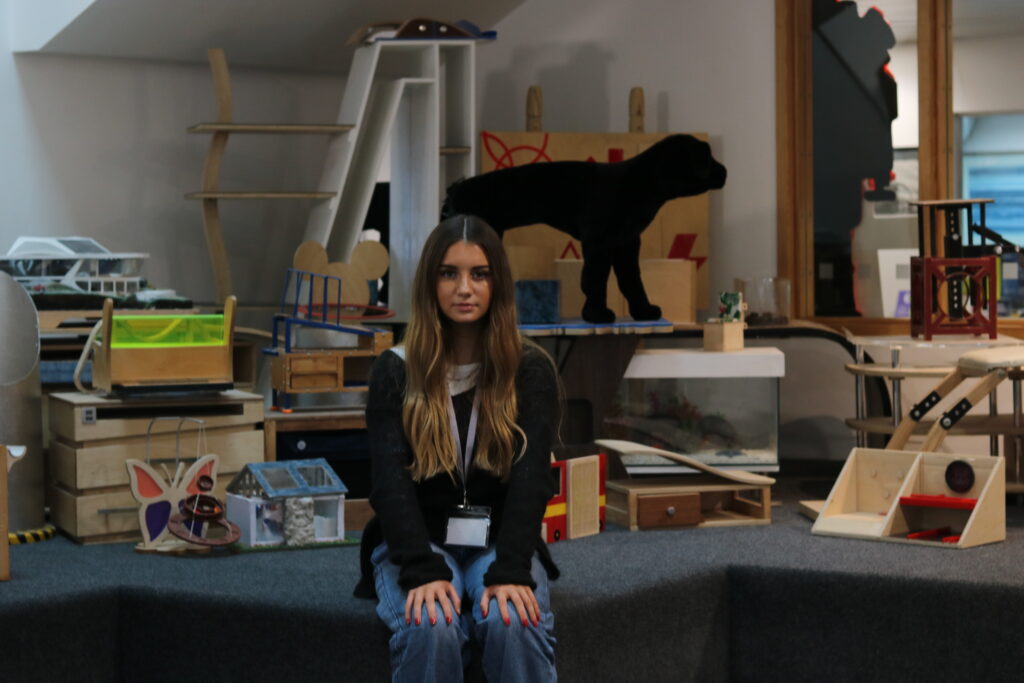
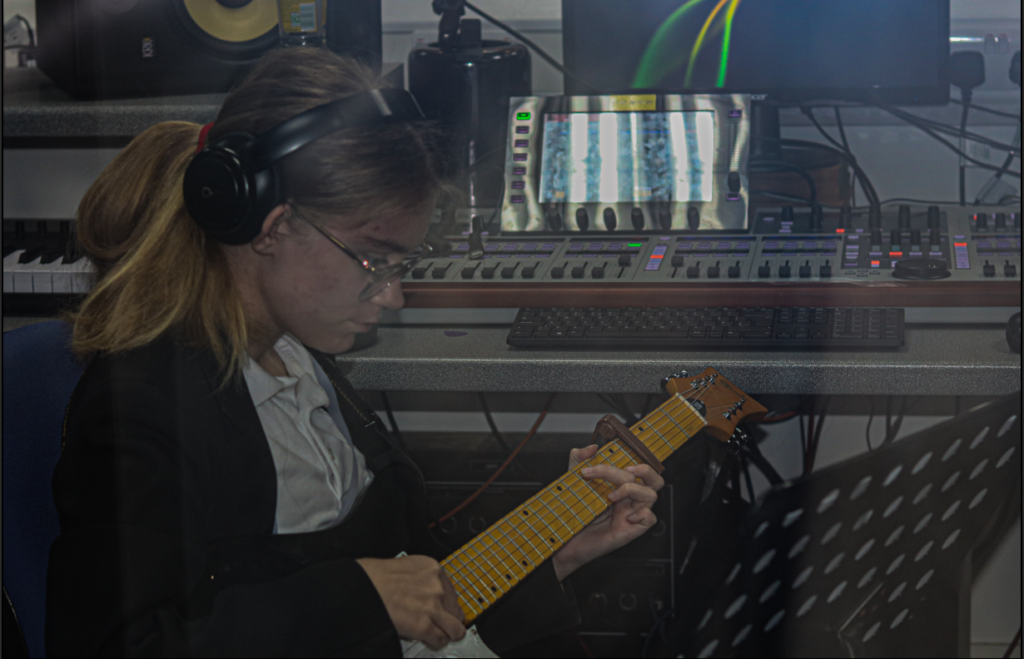
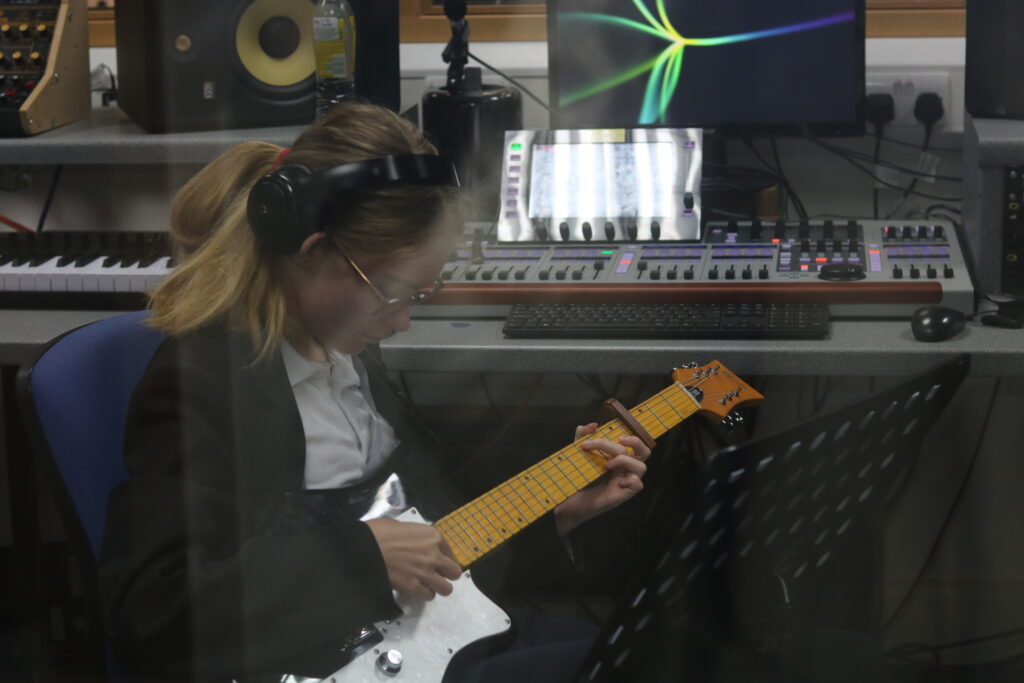
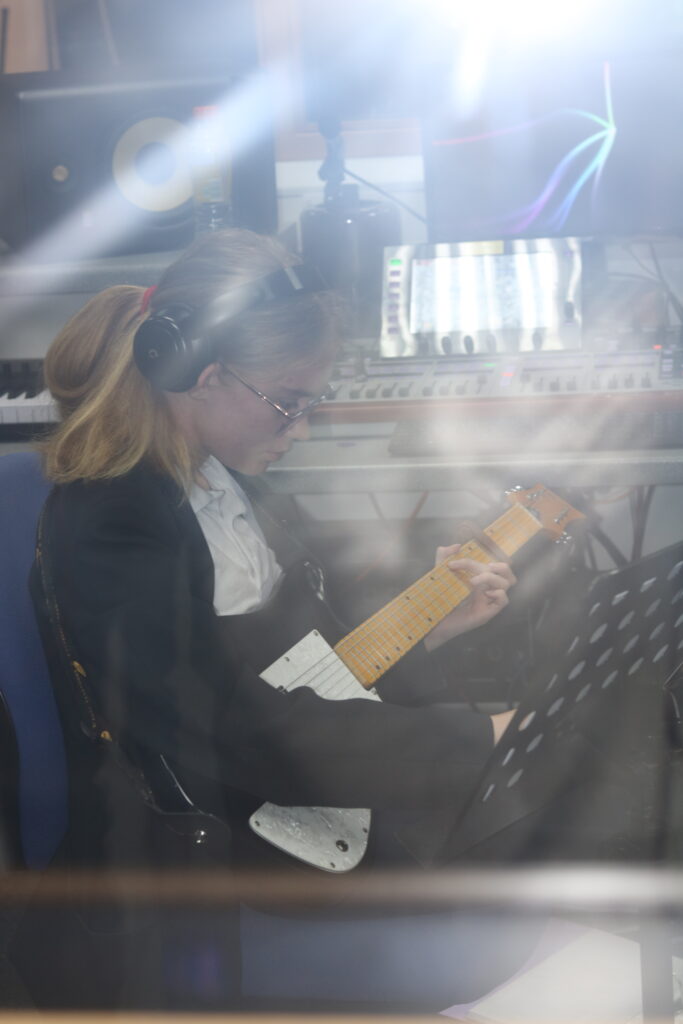
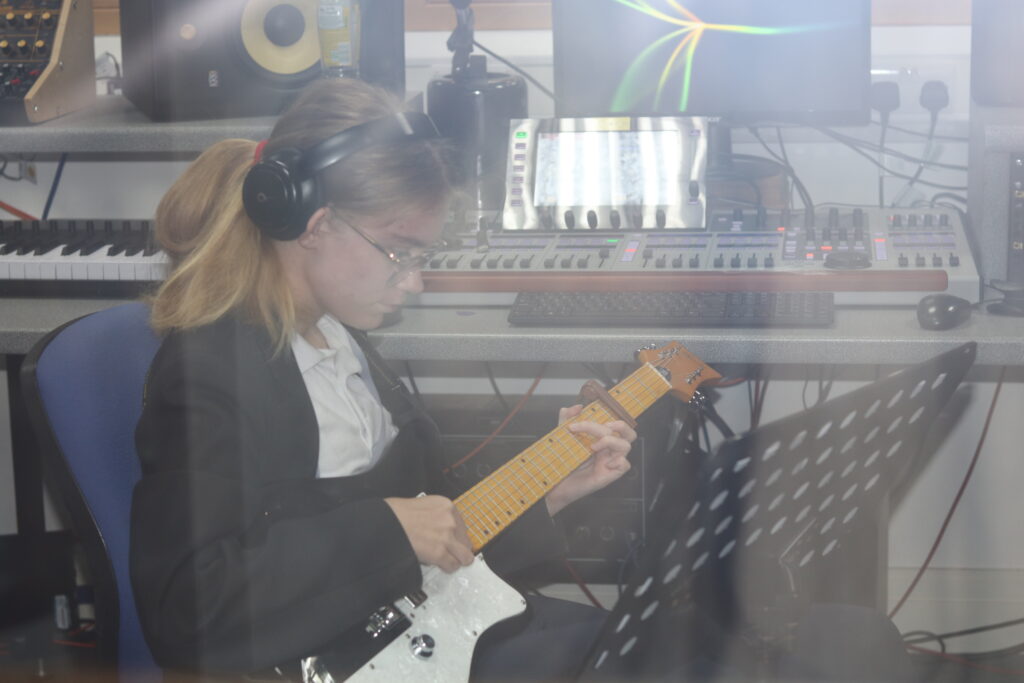
My OWN PHOTOSHOOT:
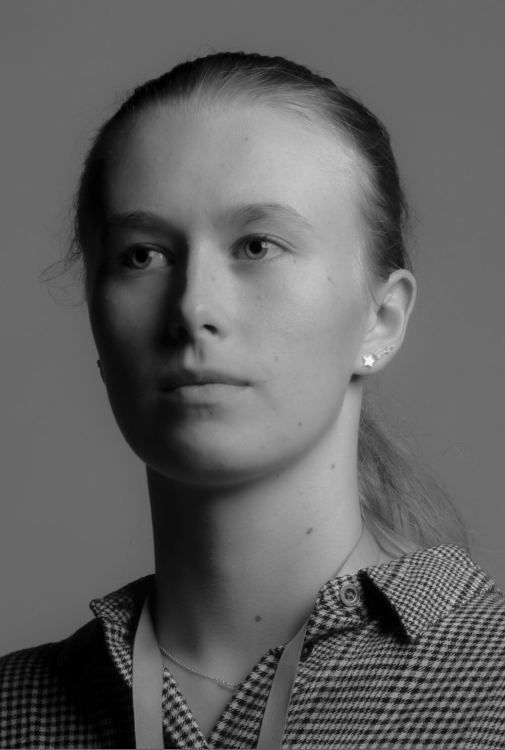
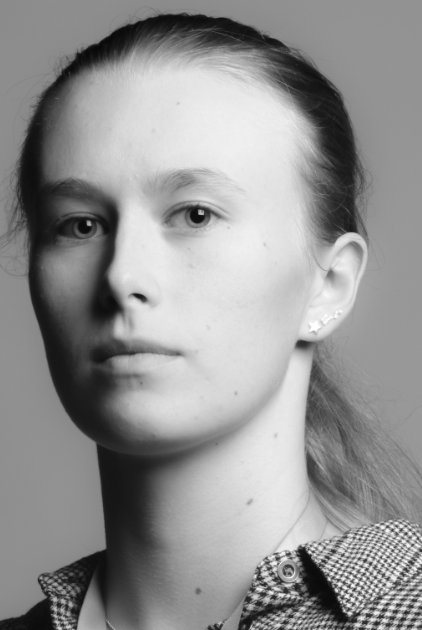
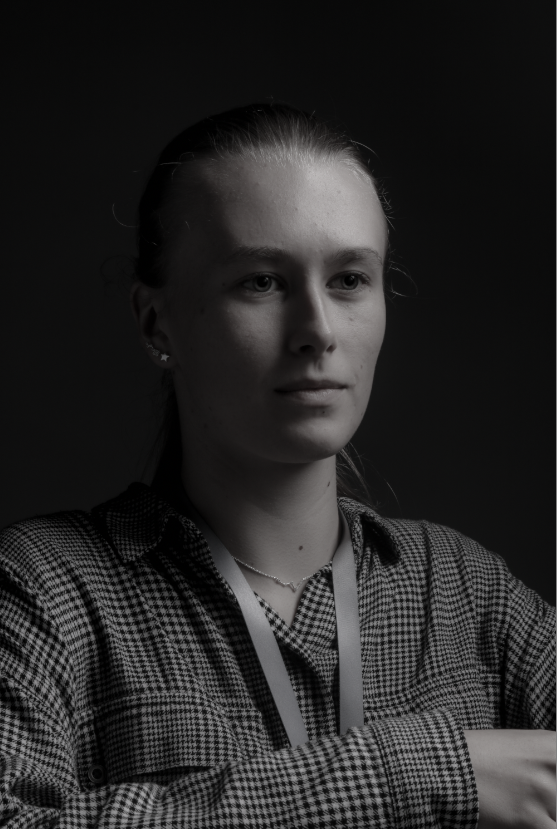




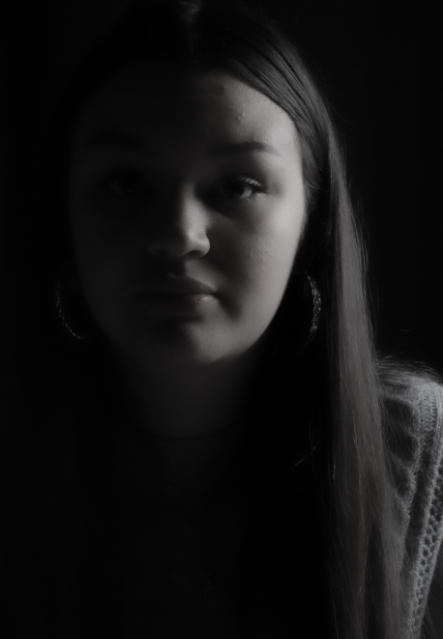
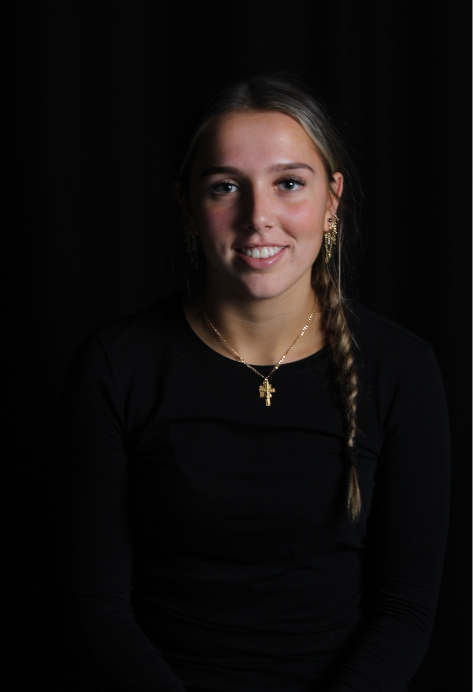
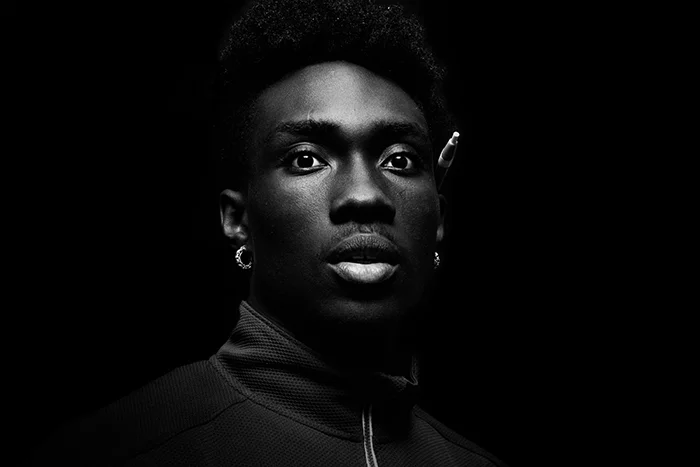
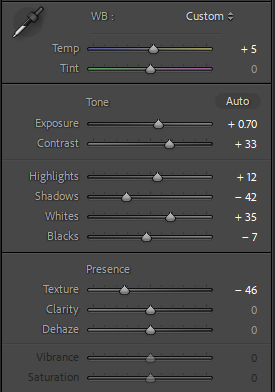
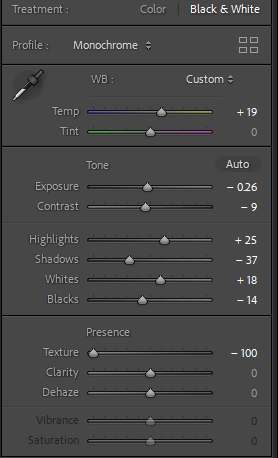
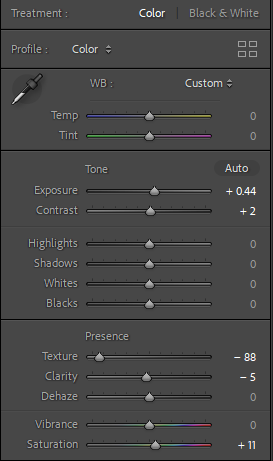
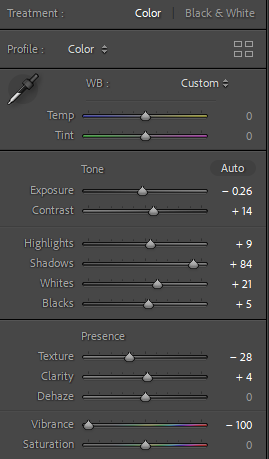
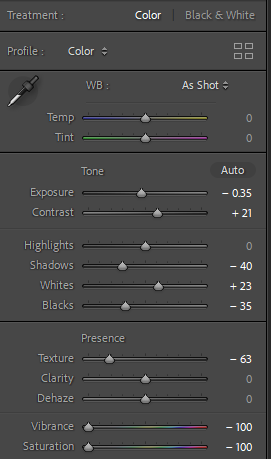
Personally I really like how this photo has turned out as it looks exactly like a Rembrandt photo, however I would have preferred to have made the triangle around the eye more clear and visible to see, the background is quite dark which clashes with the shadowing on the models face. If I were to redo this again I would have tried to get a white background so that the shadows on the face were more vibrant and stood out of the picture, however I do really like how it turned out as everything is in the right place. If i were to make the triangle smaller it would have been less noticeable and if the triangle was my bigger it would have changed the shape and ruined the point of the photo. If I were to change something about the model I would have changed the clothes and made them more vibrant so that some colour was in the photo however the clothes she had on were simple and didn’t catch my eye too much which is a good as my focus is only on the type of lighting used on the model. I would have also taken of the models lanyard as it sort of clashed with the models clothes and gets in the way. Lastly I would have changed the models posture and i would have made her pose as if she wan more comfortable as she seems to be posing more professionally. I would have possibly made the model hold a prop or even just position her in a more unique style.