What is Romanticism?
Romanticism was an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe in the late 18th century and peaked in the early to mid-19th century. It was characterized by an emphasis on emotion, individuality, imagination, and the beauty of nature. Romanticism rejected the rationalism and restraint of the Enlightenment, instead focusing on the expression of personal feelings and experiences. Romanticism was embodied in various forms of art, including literature, music, painting, and sculpture, and had a profound impact on Western culture. Key themes of Romanticism include the celebration of nature, the importance of intuition, the exploration of the supernatural and mystical, and the exaltation of the individual and the artist.
What is the history of Romanticism?
Romanticism emerged in the late 18th century as a reaction against the values and ideals of the Enlightenment, which prioritized reason, logic, and scientific inquiry. The movement began in Europe, particularly in Germany and England, before spreading to other countries such as France, Italy, and the United States.
The Romantic era was characterized by social, political, and economic upheaval, including the French Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, and the Napoleonic Wars. These events influenced the development of Romantic ideals, as artists and thinkers increasingly turned to nature, emotion, and the individual as sources of inspiration and meaning.
Some of the key figures associated with Romanticism include poets like William Wordsworth, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and John Keats; writers like Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Victor Hugo, and Mary Shelley; composers like Ludwig van Beethoven and Franz Schubert; and artists like Caspar David Friedrich and Eugene Delacroix.
Romanticism reached its peak in the early to mid-19th century but continued to influence artistic and intellectual movements well into the 20th century. Its legacy can be seen in the emphasis on emotion and subjectivity in modern art and literature, as well as in the continued celebration of nature and the individual in contemporary culture.
Mood board
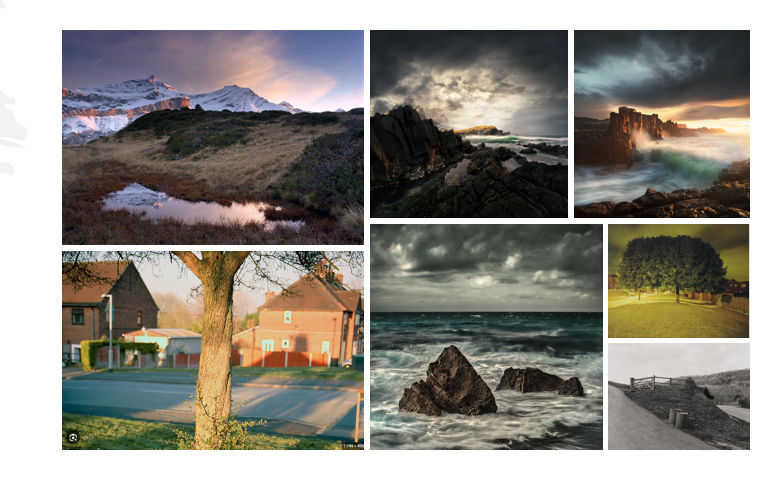

What is The Sublime?
In Romanticism, the concept of the sublime refers to a sense of awe, astonishment, and reverence for the grandeur and power of nature. The sublime often evokes feelings of both beauty and terror, as well as a sense of the infinite and the unknowable. It is associated with the overwhelming experience of the natural world and the emotions it can inspire in the viewer.
In photography, the sublime is often represented through images of vast landscapes, dramatic weather conditions, and powerful natural phenomena such as storms, mountains, and oceans. Photographers use composition, lighting, and perspective to create images that evoke a sense of the sublime, inviting viewers to contemplate the beauty and power of the natural world.
Photographers such as Ansel Adams, Edward Burtynsky, and Hiroshi Sugimoto have explored the sublime in their work, capturing the grandeur and mystery of nature in ways that transcend mere representation. By harnessing the power of photography to capture moments of awe and wonder, these artists invite viewers to connect with the sublime and experience the transformative power of nature.
John Constable – The Haywain
John Constable was an English landscape painter who lived from 1776 to 1837. He is considered one of the greatest painters of the Romantic era, known for his realistic and detailed depictions of the English countryside. Constable’s works often focused on rural scenes, particularly those in Suffolk and Essex, where he grew up and spent much of his life.
One of Constable’s most famous paintings is “The Hay Wain,” completed in 1821. The painting depicts a horse-drawn cart, known as a hay wain, crossing a shallow stream in the heart of the English countryside. The scene is set in the picturesque Stour Valley on the border between Suffolk and Essex, a place that held great significance for Constable.
“The Hay Wain” is celebrated for its vibrant colors, meticulous attention to detail, and atmospheric effects, which capture the beauty and tranquility of the English landscape. The painting has become an iconic image of the Romantic ideal of nature and has inspired generations of artists and admirers.
Constable’s dedication to capturing the beauty of the natural world and his ability to convey a sense of peace and harmony in his landscapes have made him a beloved figure in art history. His works continue to be celebrated for their timeless beauty and emotional resonance.
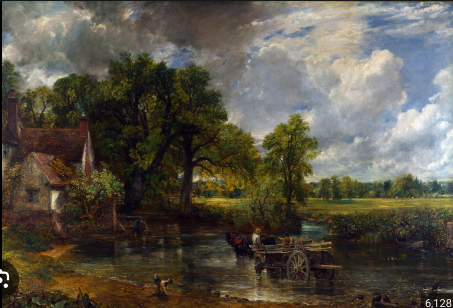
What is social Commentary?
Social commentary is a form of expression that critiques or reflects on societal issues, norms, or behaviors. It is a way for artists, writers, filmmakers, and other creators to engage with and comment on the world around them, often intending to spark awareness, dialogue, and change.
Social commentary can take many forms, including art, literature, music, film, theater, and even social media. It can address a wide range of topics, such as politics, inequality, injustice, discrimination, environmental issues, and cultural norms. By highlighting and questioning these issues, social commentary can challenge viewers or listeners to think critically about the world they live in and consider different perspectives.
Artists use various techniques and mediums to convey social commentary, including satire, symbolism, allegory, irony, and direct representation. Through their work, they may shed light on systemic problems, advocate for social justice, give voice to marginalized communities, or critique the status quo.
Overall, social commentary serves as a powerful tool for provoking thought, raising awareness, and promoting empathy and understanding of the complexities of the human experience. It plays a vital role in facilitating conversations about important social issues and inspiring positive change in society.
