Photography is very good at turning the ordinary into the extraordinary. A usual everyday occurrence could be captured in a photograph and be completely transformed. Something such as as clouds in the sky, which is a usual thing for people to see in their everyday lives, could be captured in a photo to make it more dramatic and unique.
Camera Obscura
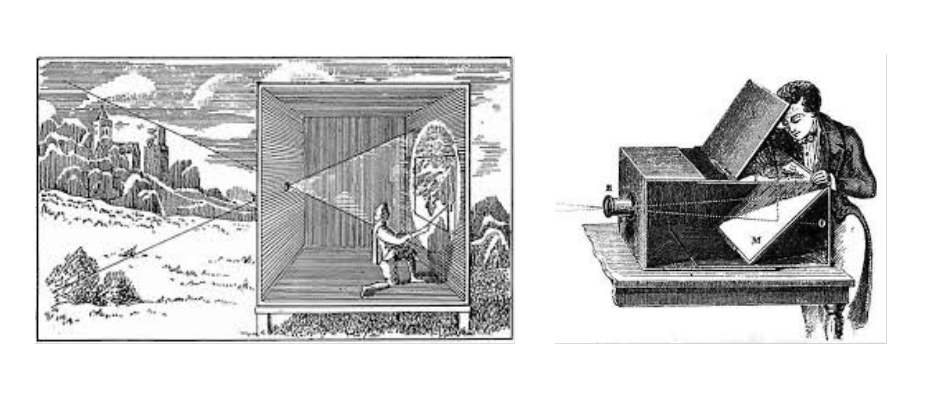
The camera obscura (dark chamber), is a device that has been very important in the history of photography. Its function involves light passing through a small aperture into a darkened room or box which would then project an inverted image of the outside scene onto a plain surface inside. During the Renaissance, artists and scientists began to utilize the camera obscura as a tool for drawing and understanding perspective.
Describe how an image is produced using a camera obscura – making the room pitch black and making sure there is no light coming through anywhere. create a hole somewhere where the light will be able to pass through. This process of waiting for the light to show could take up to an hour or two until the cut out shape is able to be shown on the other side of the room
Nicephore Niepce
Nicephore Niepce is known for creating one of the earliest permanent photographs. He was born in 1765 in Chalon-sur-Saône, France. In 1826 or 1827, his first successful photograph was titled “View from the Window at Le Gras.” The exposure time for his image was around eight hours which ended up producing a blurred image however it was recognisable. He studied law at the University of Dijon but developed a keen interest in science and mechanics. Niépce came from a well-off family and was the son of a wealthy merchant. He later inherited his father’s estate. In 1829, Niépce partnered with Louis Daguerre, who was a theatrical designer and inventor. Although their collaboration was cut short by Niépce’s death, it set the stage for significant advancements in photography.

Heliograph- To make the heliograph, Niépce dissolved light-sensitive bitumen in oil of lavender and applied a thin coating over a polished pewter plate. He inserted the plate into camera obscura and positioned it near a window in his second-story workroom. After several days of exposure to sunlight, the plate yielded an impression of the courtyard, outbuildings, and trees outside.
Louis Daguerre
Louis Daguerre 18 November 1787 – 10 July 1851) was a French artist and photographer, recognized for his invention of the eponymous daguerreotype process of photography. In 1829, Daguerre partnered with Nicéphore Niépce, an inventor who had produced the world’s first heliograph in 1822 and the oldest surviving camera photograph in 1826 or 1827.
After Niépce’s sudden death, Daguerre continued experimenting, and evolved the process which would subsequently be known as the daguerreotype. To create this, he exposed a thin silver-plated copper sheet to the vapour given off by iodine crystals, producing a coating of light-sensitive silver iodide on the surface. The plate was then exposed in the camera.


Henry Fox Talbot
William Henry Fox, 11 February 1800 – 17 September 1877, was an English scientist, inventor, and photography pioneer who invented the salted paper and calotype processes. Shortly after.Louis Daguerre’s invention of the daguerreotype was announced in early January 1839, Talbot asserted priority of invention based on experiments he had begun in early 1834.
Differences
Henry Fox Talbot experimented using paper and shoe boxes which he called “mousetraps” to create his image where as Louis Daguerre used a mirrored metal plate instead of paper. Talbot was not an experienced artist as it was known that he couldn’t draw very well whereas Daguerre was an academically trained painter who sold his own work. Daguerre’s invention of the Daguerreotype eventually became less successful and Talbot’s Calotype became more popular.
similarities
Both processes are long and tedious. Both invented in 1839 which meant there would be a competition between the two as they were invented in the same year. both processes fix an image.
He took unremarked photos of Murdock Ans turned ordinary into extraordinary. Andre. Control that transformation- art of photography. “how can something that reveals so much keep so much to itself”. shows the secret strangeness. instantaneous. secrets behind the world
Richard Maddox
Richard Leach Maddox was born at Bath, England, on 4 August 1816. Maddox was prominent in what was called photomicrography, which was photographing minute organisms under the microscope.
In photography, the Collodion process was invented in 1851 by Frederick Scott Archer. This invention required only two to three seconds of light exposure to produce an image. When he noticed that his health was being affected by the ‘wet’ collodion’s ethervapor, Maddox began looking for a substitute

George Eastman
George Eastman (July 12, 1854 – March 14, 1932) was an American entrepreneur who founded the Eastman Kodak Company. This was an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in film photography. Working as the treasurer and later president of Kodak, he oversaw the expansion of the company and the film industry.
Kodak (Brownie)
The Brownie was a series of camera models made by Eastman Kodak and first released in 1900. This was a basic cardboard box camera which was initially aimed at children. An improved model, called No. 2 Brownie, came in 1901, which produced larger 3.25-by-2.25-inch photos, cost $2, and was also a huge success. Many iconic shots were taken on brownies such as images produced from the Titanic disaster or even taken to war by soldiers. The cameras continued to be popular, and spawned many varieties such as Boy Scout edition in the 1930s. Six-20 Flash Brownie in 1940, Kodak’s first internally synchronized flash camera, using General Electric bulbs. In 1957, Kodak produced the Brownie Star flash, Kodak’s first camera with a built-in flash.

Film/Print Photography
The first film that was in a roll and flexible was made by George Eastman in 1885, but it wasn’t synthetic but on paper. “Safety film” was introduced by Kodak in 1908, made of cellulose acetate and was invented as a replacement for dangerous nitrate film. in 1855, The first Photographic plates that could produce images in colour appeared however this included long exposure time which was very unpractical. Colour film was used for home movies and photographic cameras but was still too dark and much more expensive than black and white. It took 40 years for colour film to become standard and for black and white to be used for low-light and art photography.

Digital Photography
The history of digital photography began in the 1950s. in 1957, American computer engineer Russell Kirsch developed the first rotating drum scanner and software that could digitally record images. Digital photography is a complex technological process that utilizes optical physics, materials engineering, and data science to transform light into electrical signals that are converted into photo elements that comprise a digital image.

