Identity
Identity is ‘the fact of being who or what a person is’, it is a combination of your physical and behavioural traits that define who you are. For example, your name is part of your identity, as is the form and colour of your eyes and your fingerprint. This set of characteristics allows you to be definitively and uniquely recognisable. For example here are five words that ‘define’ identity:
- personality.
- character.
- selfhood.
- individuality.
- individualism.

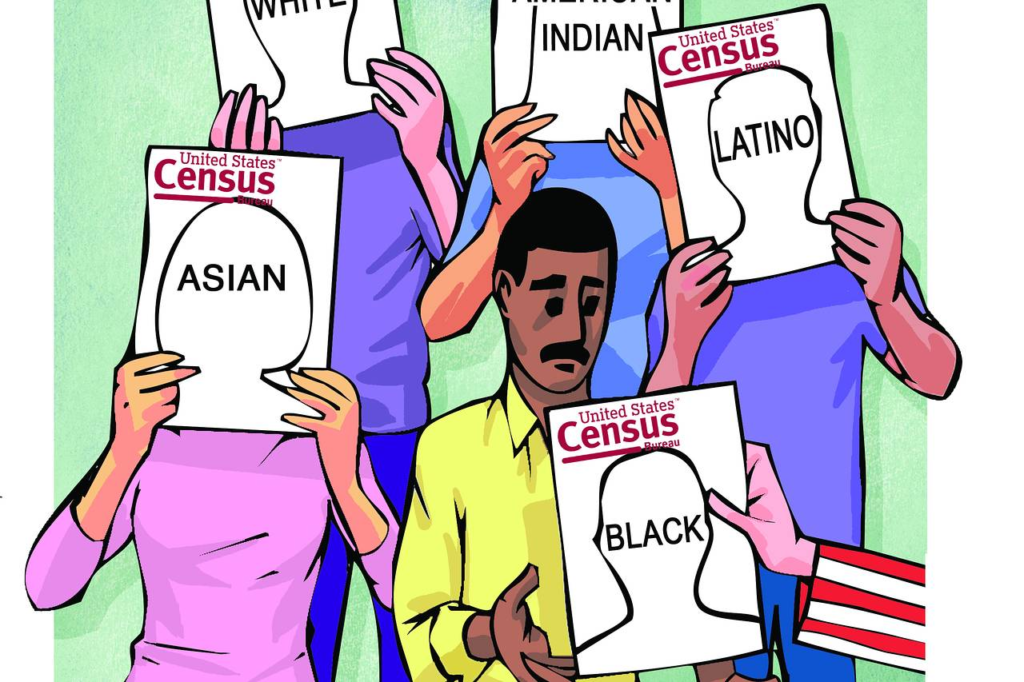
Identity politics
Identity politics is politics based on a particular identity, such as race, nationality, religion, gender, sexual orientation, social background, caste, and social class. The term was coined by the Combahee River Collective in 1977. It took on widespread usage in the early 1980s, and in the ensuing decades has been employed in myriad cases with radically different connotations dependent upon the term’s context. It has gained currency with the emergence of social activism, manifesting in various dialogues within the feminist, American civil rights, and LGBT movements, disabled groups, as well as multiple nationalist and postcolonial organizations, for example: Black Lives Matter movement. Harnessing your identity with someone else and banding together can be a very positive thing, you may come to learn more about yourself but also see how you relate to other peoples identity’s, this can help you know that you are not alone. On the other hand joining identity’s may end out bad, as you might feel like your not the same as everyone else and you may try change yourself, loosing your true identity.
What is the argument against identity politics?
The nationalist argument against identity politics is, therefore, that, regardless of one’s individual ancestry, cultural background, religion, statehood, race, creed, etc.


Culture Wars
‘cultural conflicts’, In political science, a culture war is a type of cultural conflict between different social groups who struggle to politically impose their own ideology (beliefs, virtues, practices) upon their society.
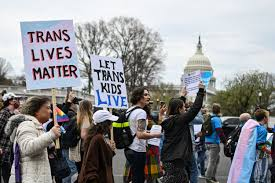
What was the culture wars in 1980?
The culture wars had flared up during the 1980s, enjoined by a rising movement of conservatives who charged that American society had lost its way. The root of the problem, in their view, was a decline of cultural and moral values, rather than economic or other political issues.
Dangers of tribalism dividing communities
These negative aspects of tribalism are often fueled by competition and the perception of a common threat. They promote fear, anxiety, and prejudice, all of which make us more susceptible to fake news, propaganda, and conflict. Tribalism can take many forms in our modern society. Main problems include:

- Poverty and exploitation.
- Economic and technological backwardness.
- Socio-cultural handicaps.
- Problems of assimilation with the non-tribal population.
- Illiteracy among tribals is a major hindrance to their development.
