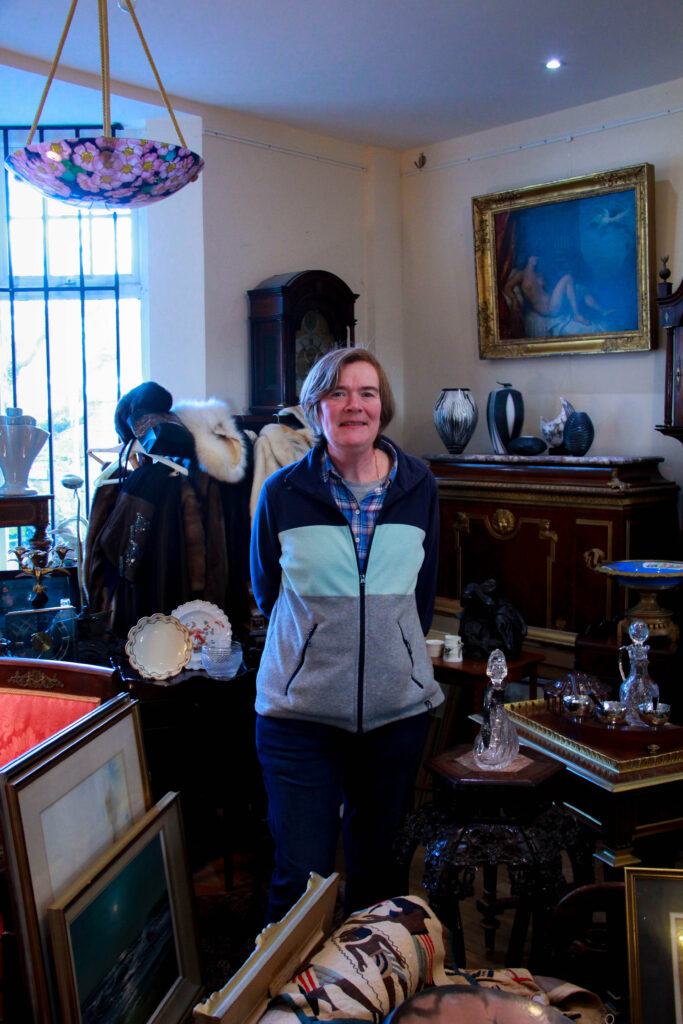
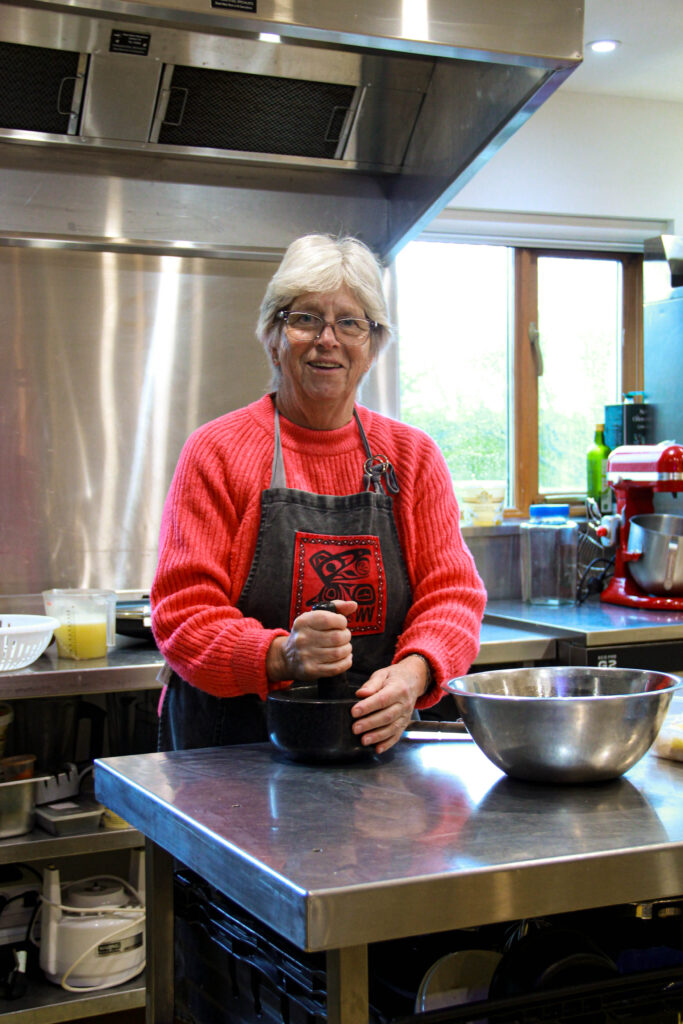
I spent time on 3 different days taking photos at the Arts Centre, a house in St. Peters and multiple locations in St. Lawrence and St. Helier.
During my photoshoot with Jaime I used a tripod with camera settings approximate to this for most photos:
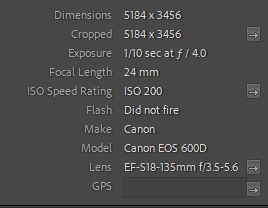
Most other photos I stuck to a low aperture (4-6.3), 400-800 ISO and a shutter speed of about 1/60.
Most my photos were rejected because I was not happy with the exposure, focus or pose. Because I had medium-dim indoor static lighting I had trouble figuring out how to take clear photos without blurs.
Some photos were taken with a mix of natural light which contrasted heavily with the indoor lighting and also meant I had a hard time selecting white balance.

Photos that I deemed to have potential made it into the so-so rating as there wasn’t anything inherently great about them and they could have been improved by sharper focus or lighting, or a more intentional pose. Others in the yellow category had good composition but too harsh lighting.
Finally, the 32 photos I have approved are sharp, have balanced exposure and capture the formality of environmental portraits.
Most of the photos I have selected where taken after I had experimented with the cameras settings in the same shot to understand and intentionally capture what I wanted.
Best Photos (unedited):
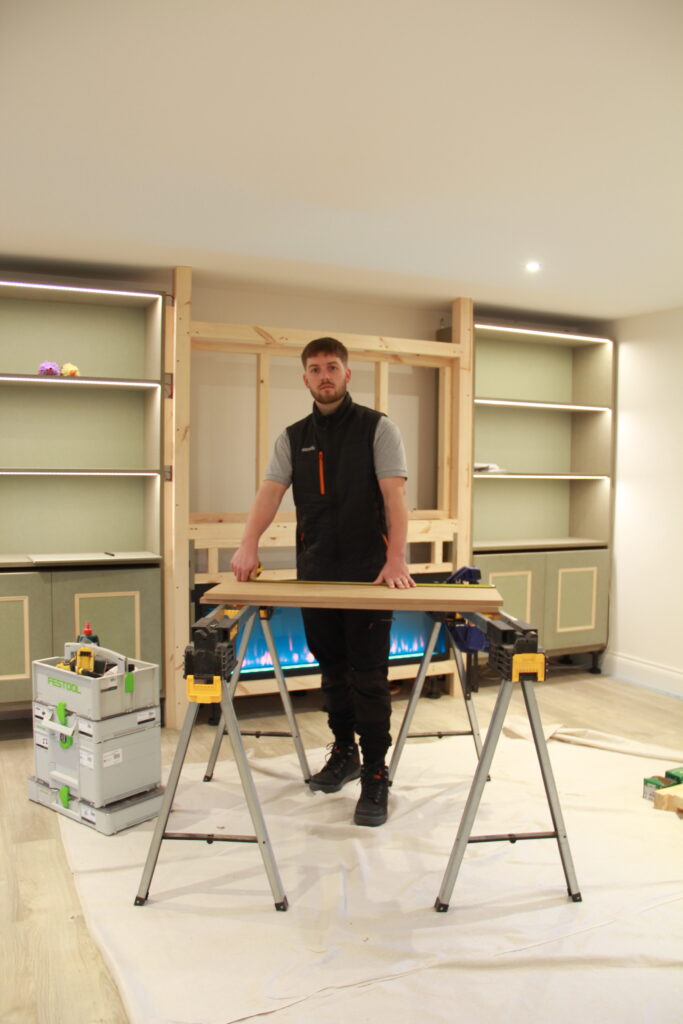
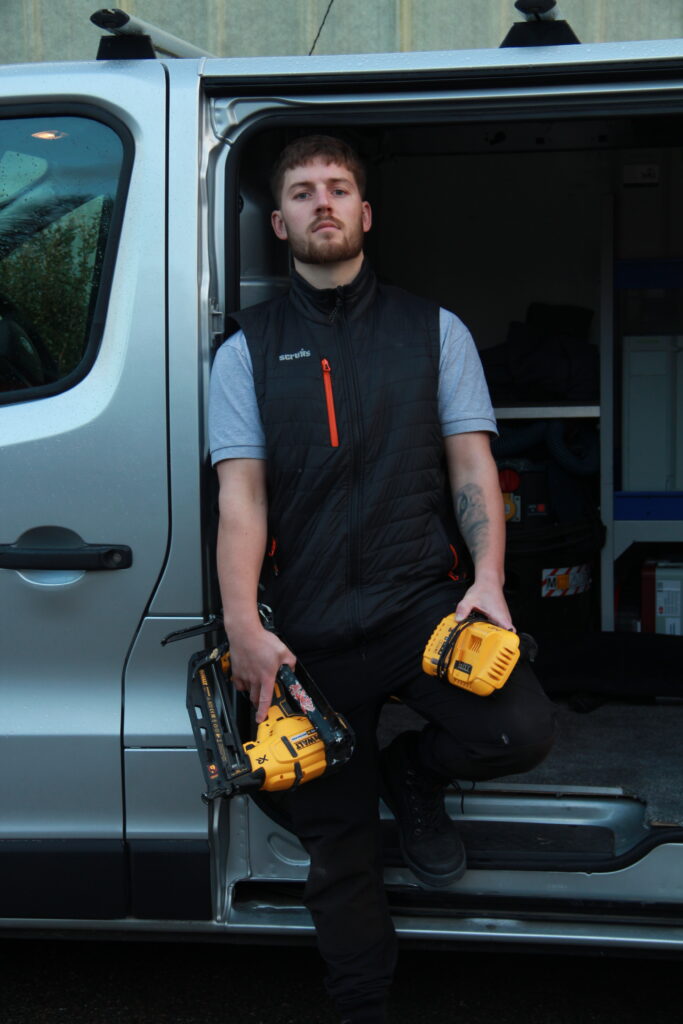
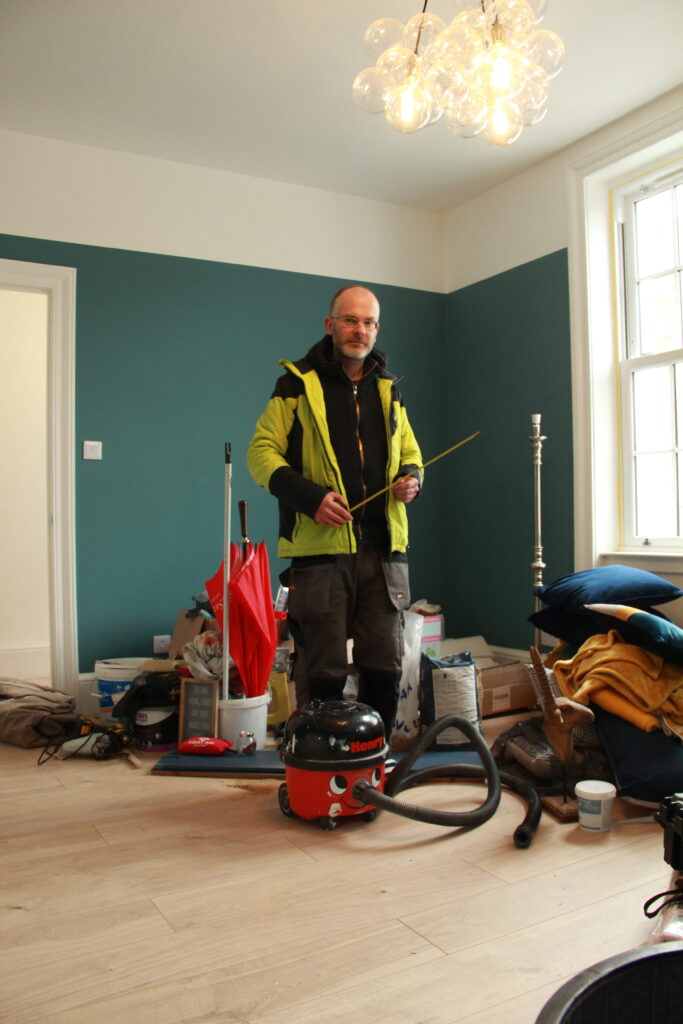
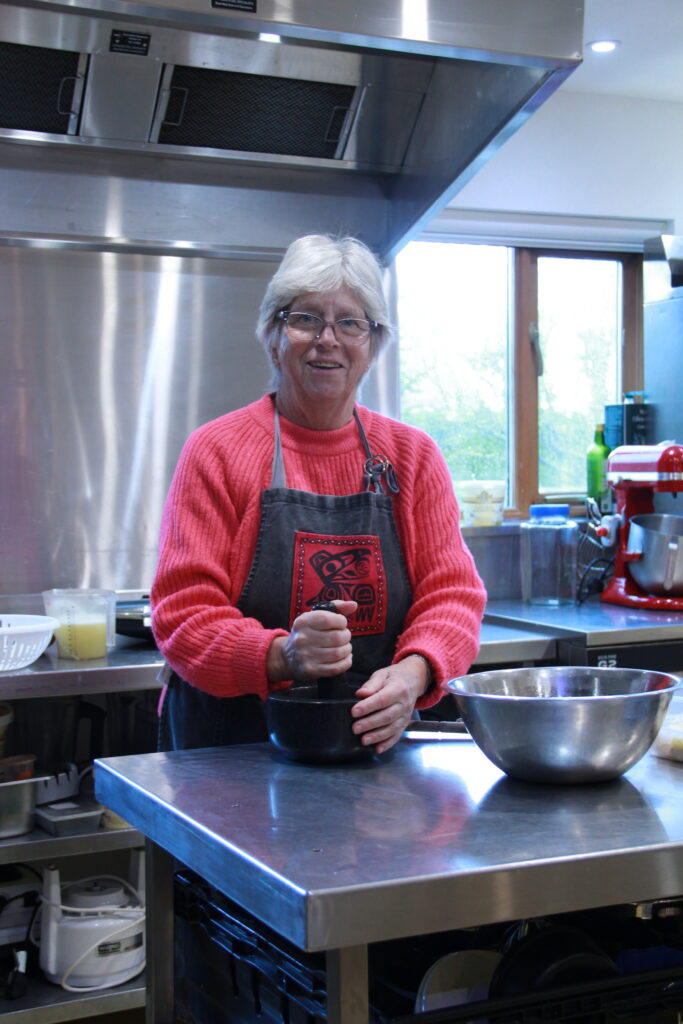
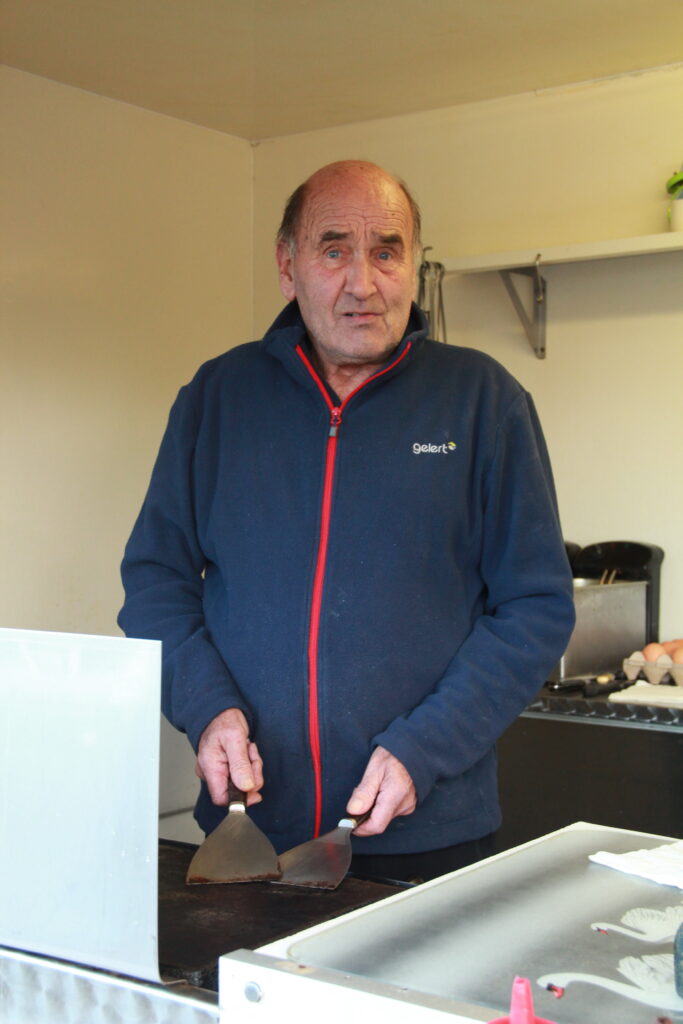
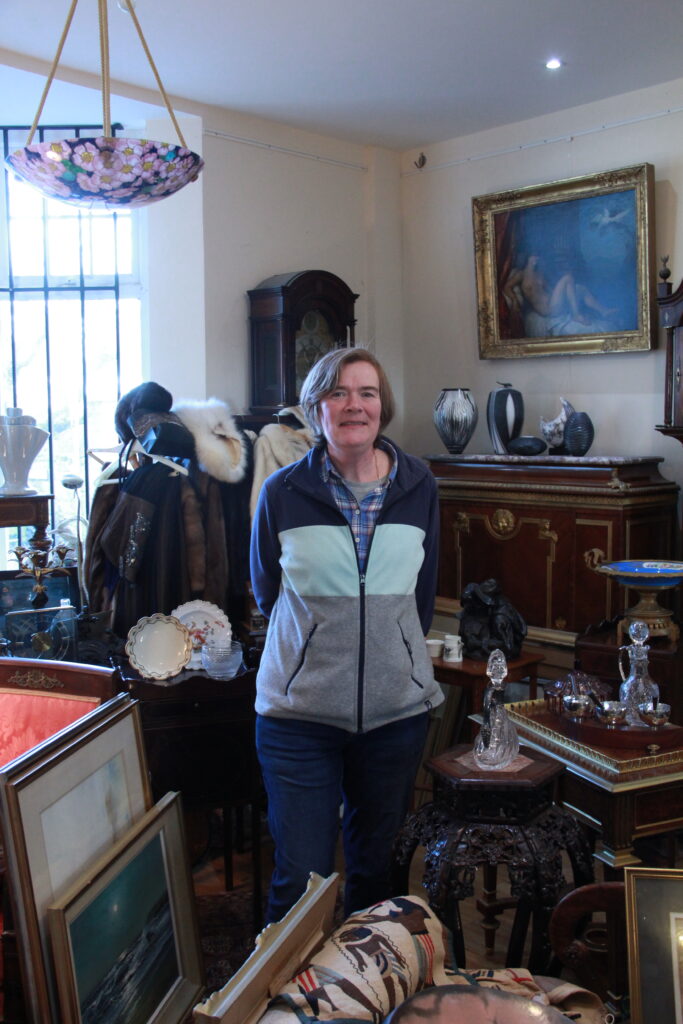






Final Edits:
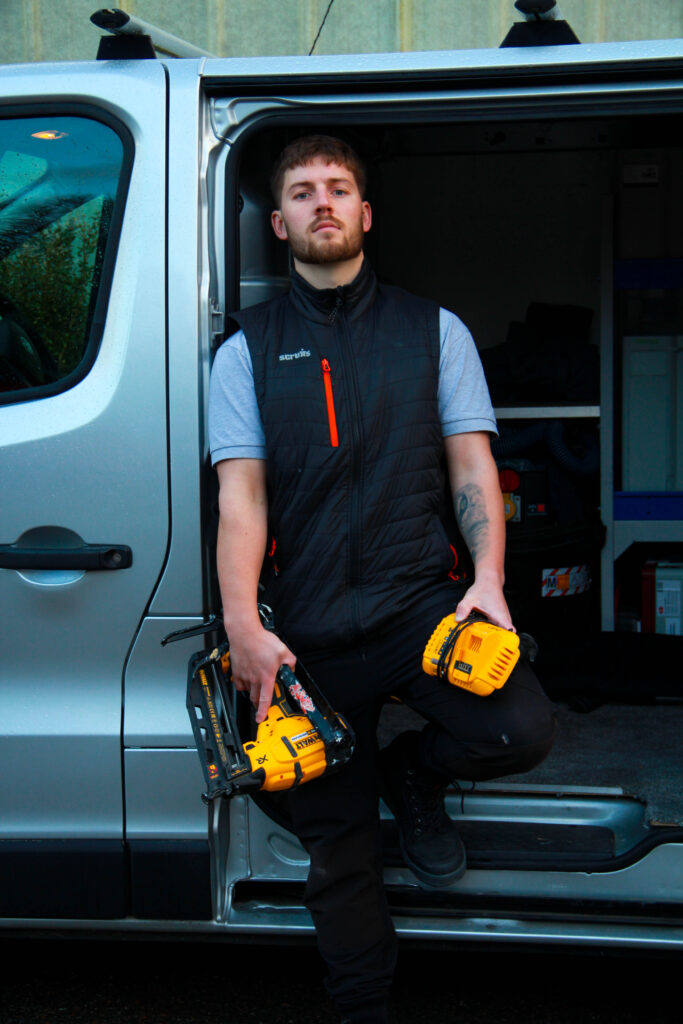

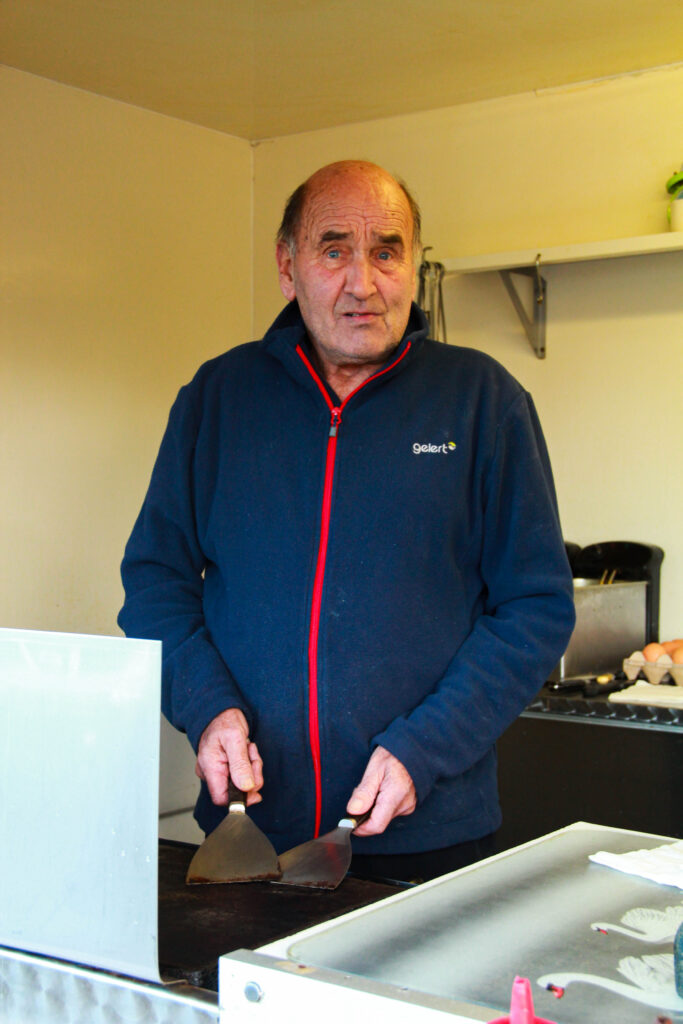
This photo was taken in the early morning (8:30ish) to have a soft lighting coming in from the right side and is taken outside of his work van where he carries all of his equipment and resources.
Using the van door frame I framed Jaime against the dark interior of his work van for some contrast. Additionally, the saturated power tools strike quite boldly against the monochrome background.
I think the photo is quite sharp, so I increased the saturation as much as I could to accentuate different objects, bone structure and shadows.
Also, to remove any distraction from the background above and beneath the vehicle I placed a light vignette which also softens of the sides of the image as a nice break from the strong colours and lines in the focal point.