Biography :
Walker Evans, was an American photographer and photo journalist best known for his work for the Farm Security Administration (FSA) documenting the effects of the Great Depression. He said that his goal as a photographer was to make pictures that are “literate, authoritative, transcendent”. Evans took up photography in 1928, around the time he was living in new York. His influences included Eugene catgut and .August Sandler. In 1930, he published three photographs in the poetry book The Bridge by Hart Crane. In 1931, he made a photo series of Victorian houses in the Boston vicinity sponsored by Lincoln Kirstein.
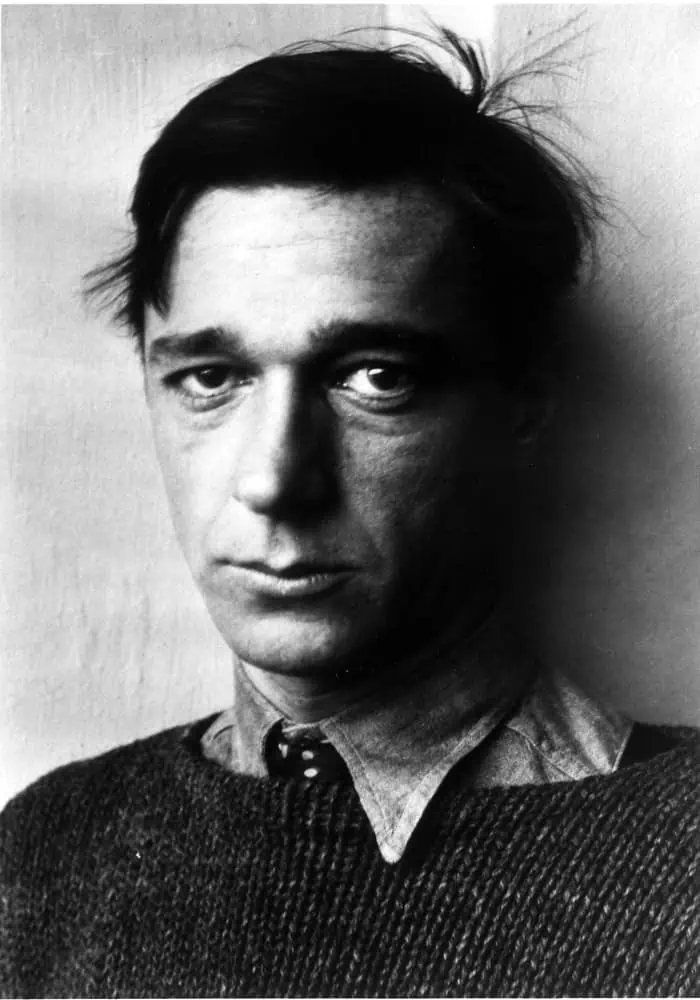

Walker Evans Photography :
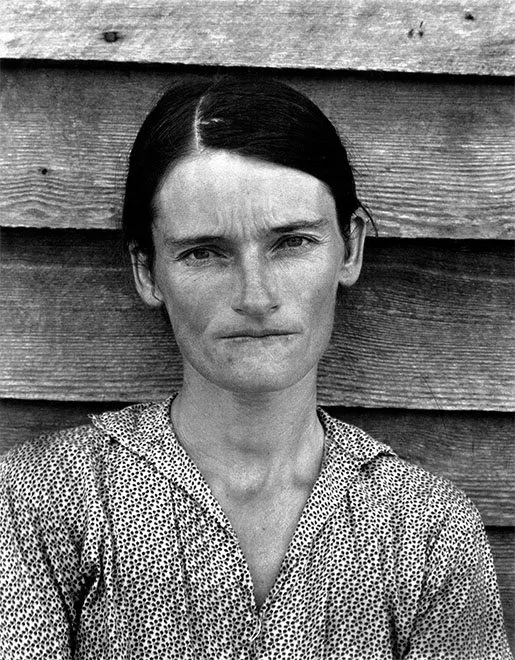
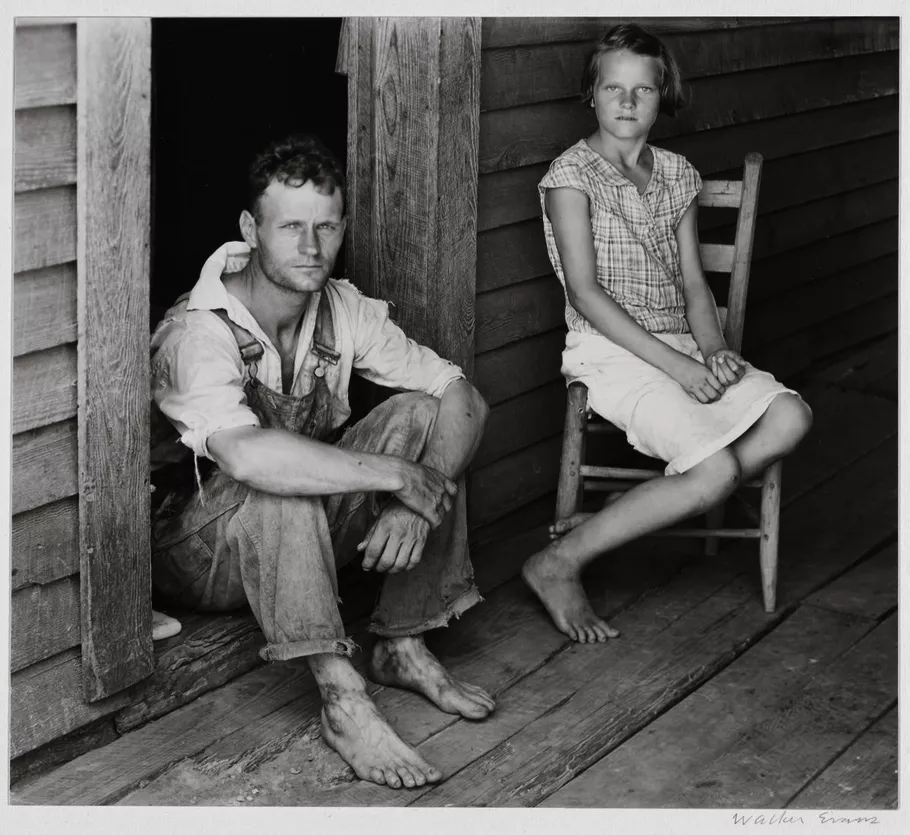
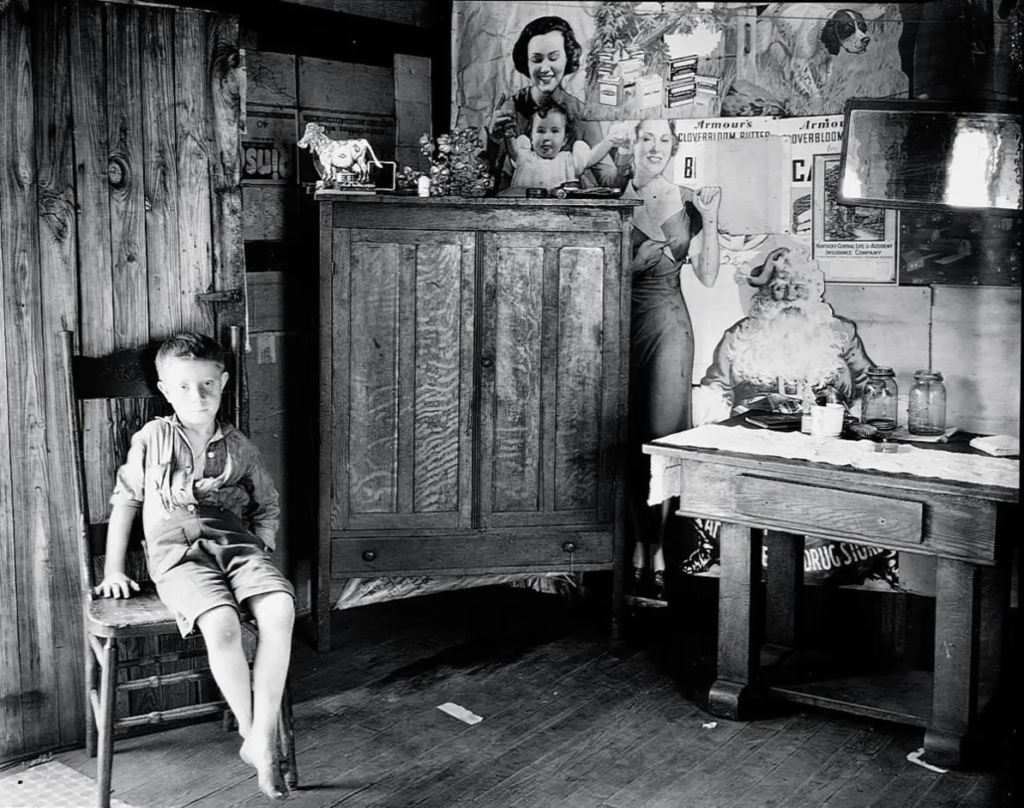



Image analysis :
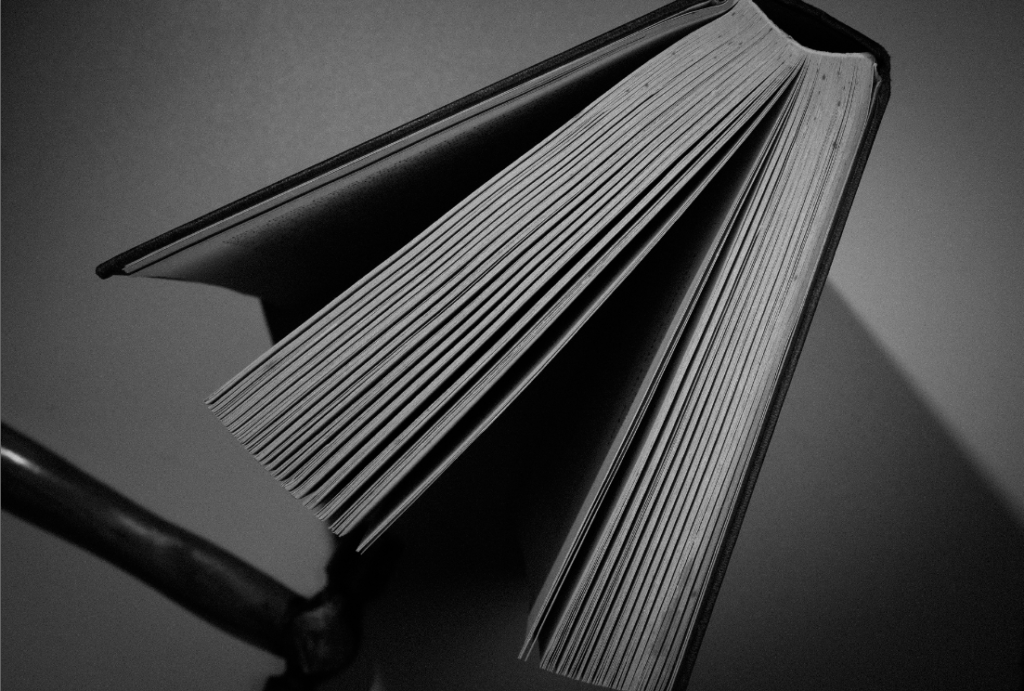
Walker Evans photography have a narrow depth of field to keep the man in focus. The pictures are in black and white which gives the pictures a dramatic and ominous feel to them.
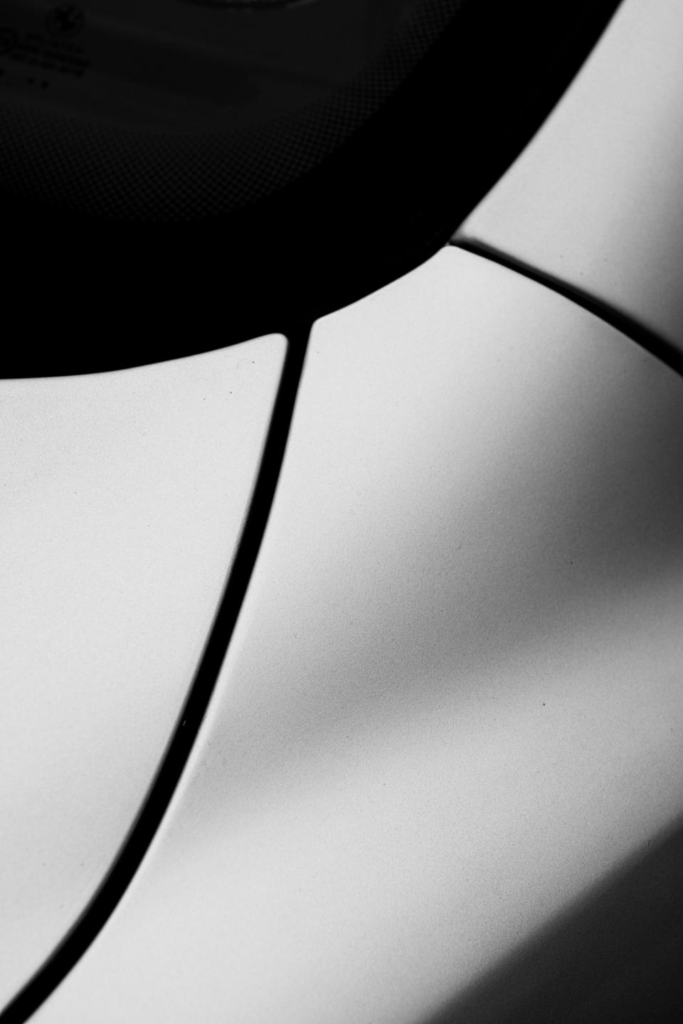
Darren Harvey-Regan
Darren Harvey-Regan is a graduate of the Royal College of Art. His work has been in Exhibitions and Publications all over the world. His work focuses on photography but has an emphasis on the mediums relationship to language and to sculpture.

Image Analysis :
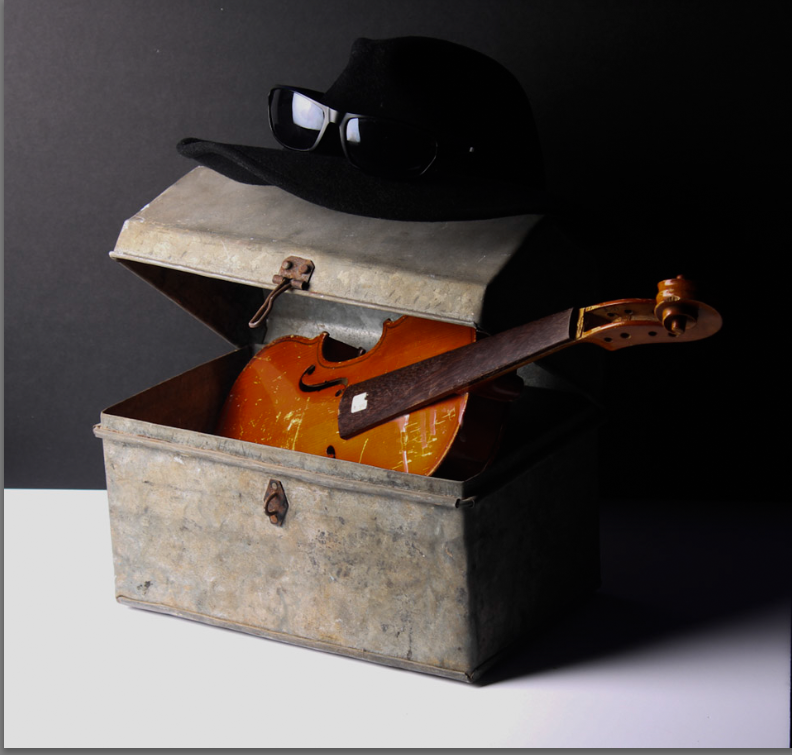
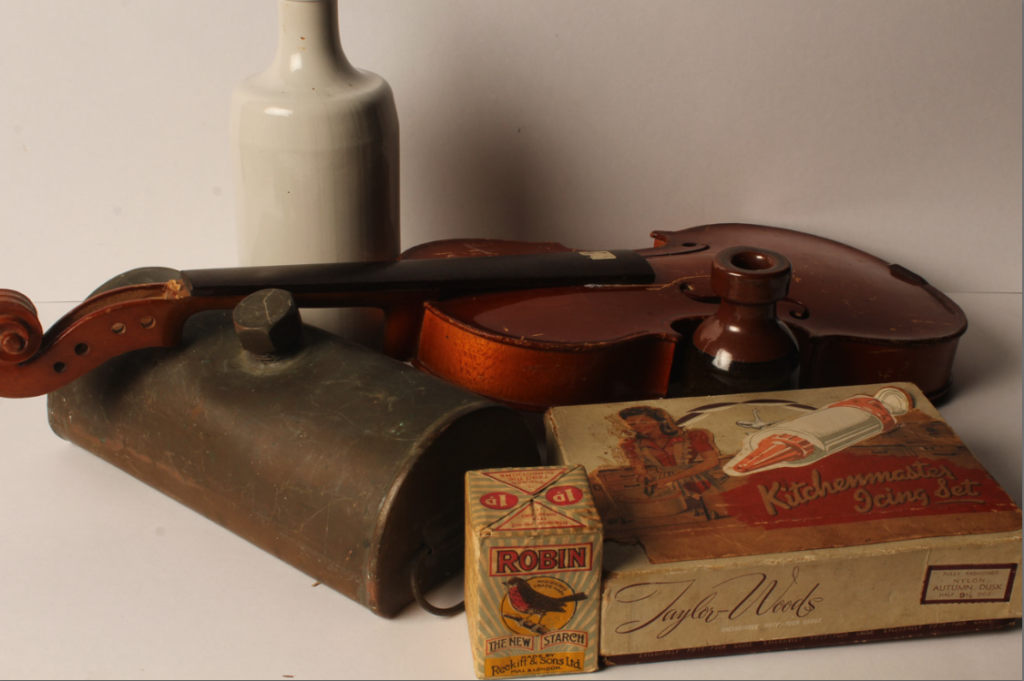
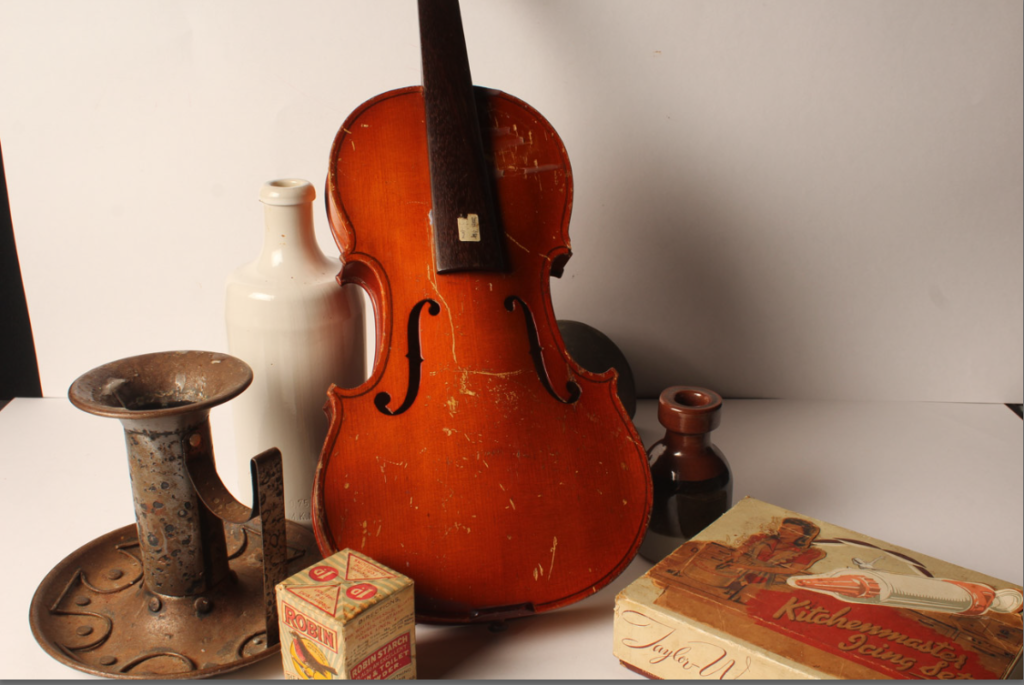
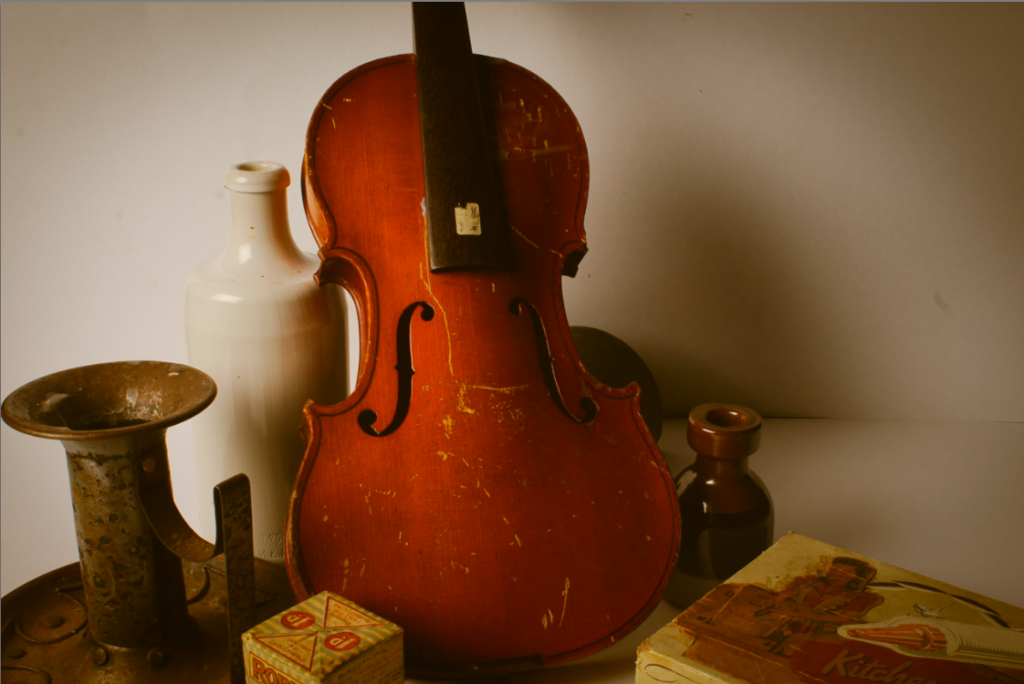
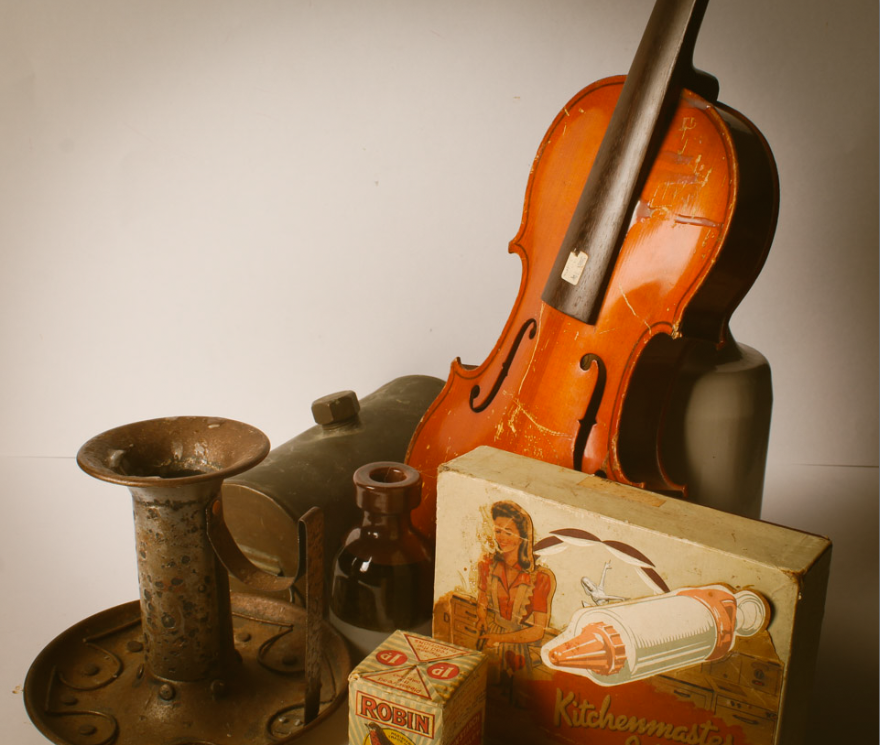
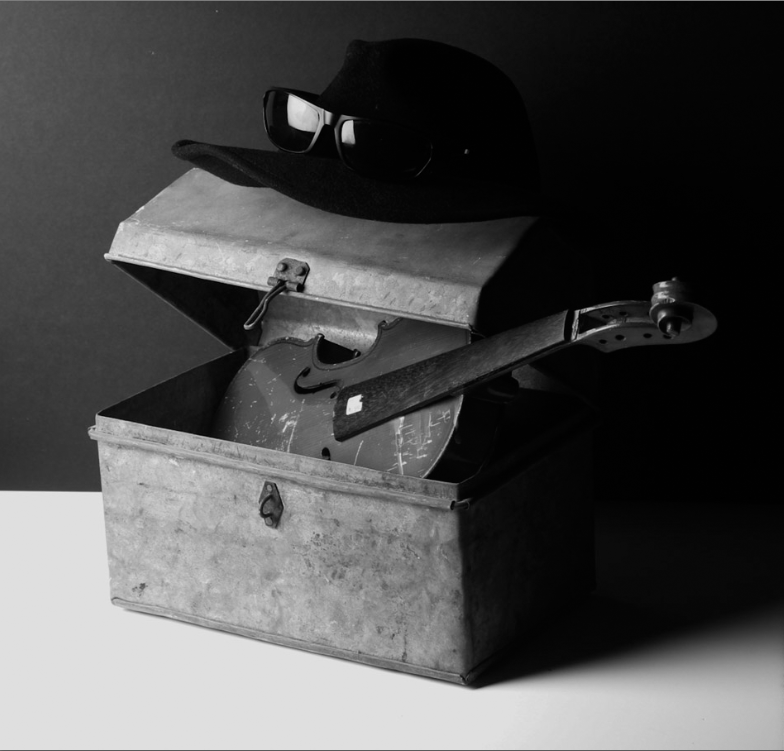
Darren Harvey-Regan’s photos are very bold and powerful and this picture in particular has a very strong contrast between the block and the shadow. This makes the object used stand out and look more powerful. The use of shape and line in this image makes the object appear more interesting to look at and gives the object a different composition.
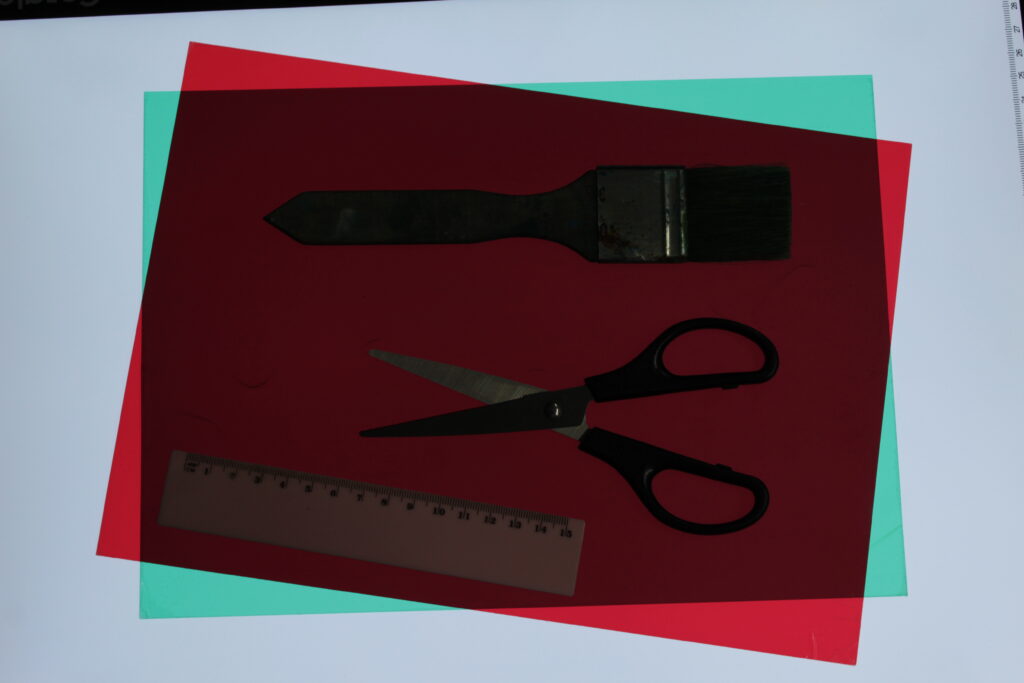
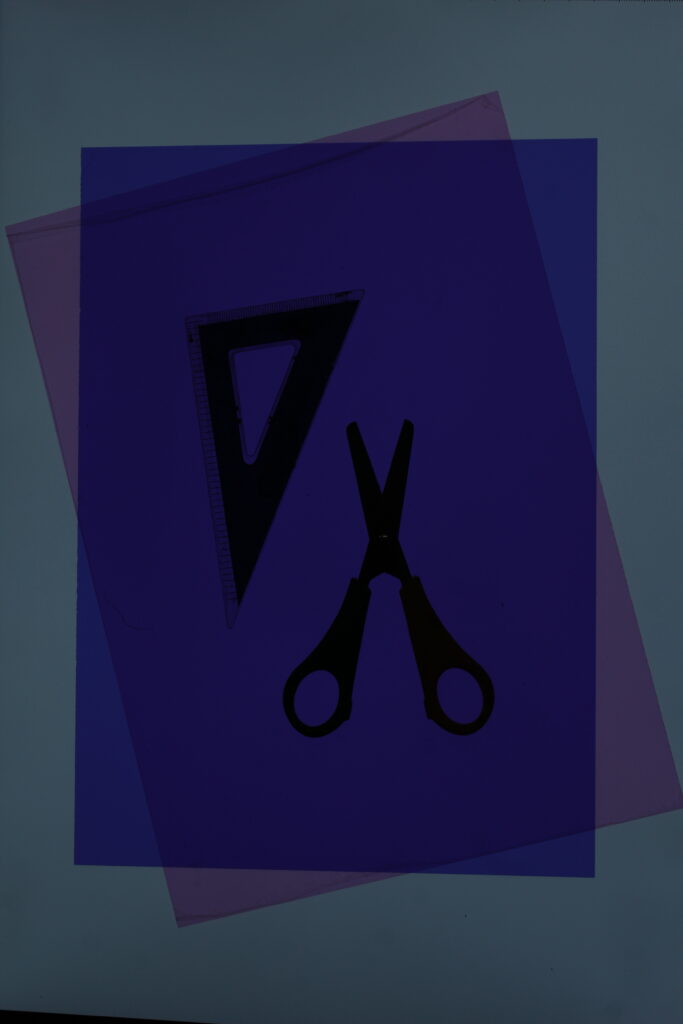
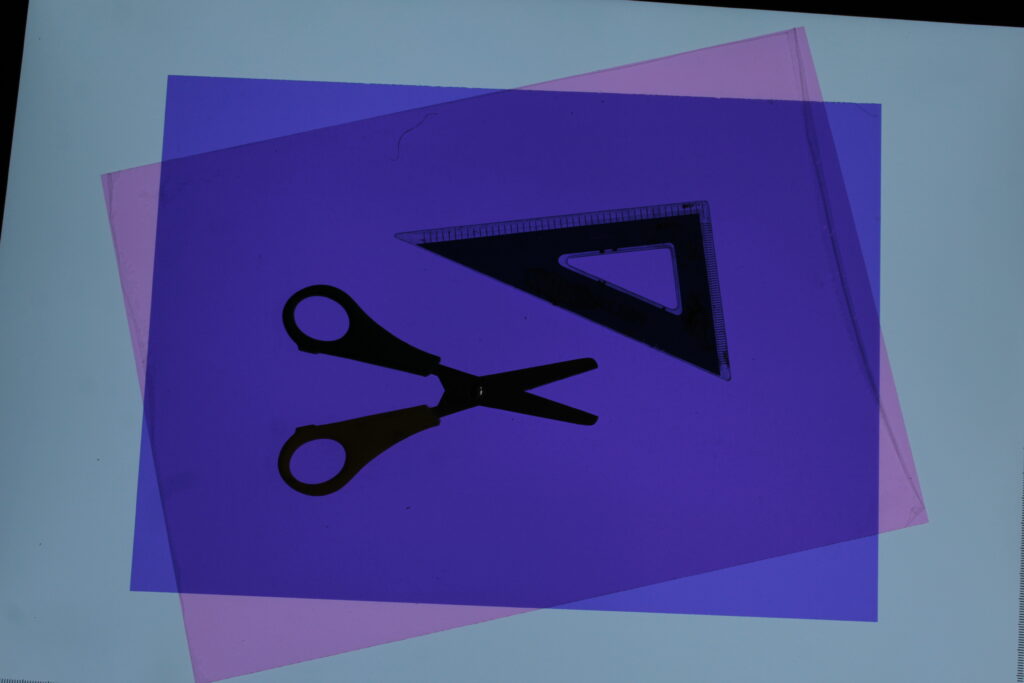
How did Walker Evans’ work inspire Darren Harvey-Reagan?
Harvey-Regan first constructed a montage of Evans’s images to make new forms. He then sourced matching tools, cut them in half and re-joined various halves together, with the resulting physical objects being photographed to create his final work.
Comparrison :
Darren Harvey – Reagan :

Walker Evans :

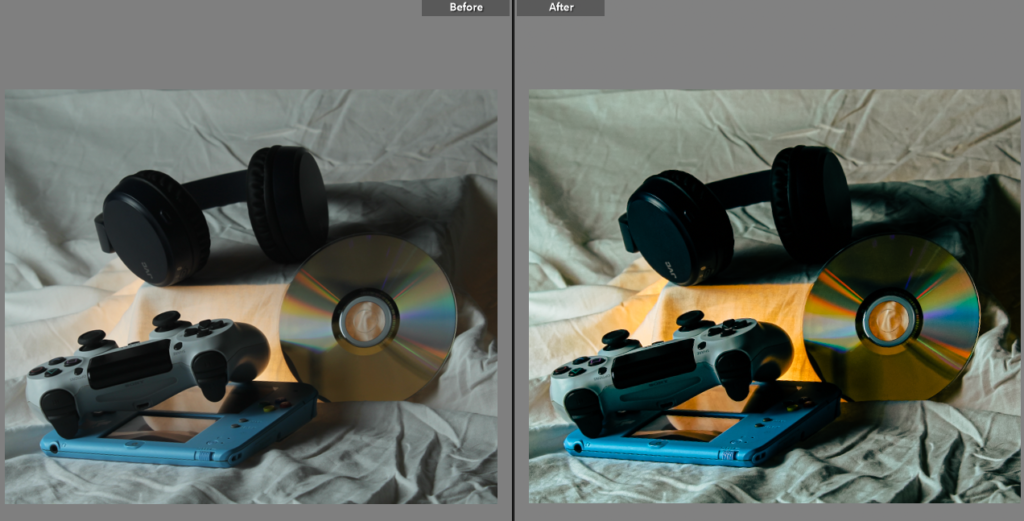
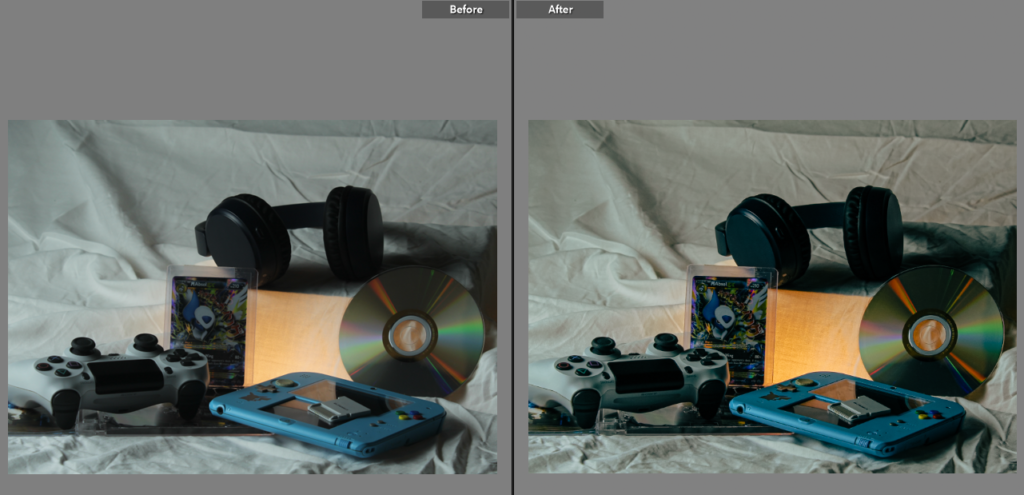
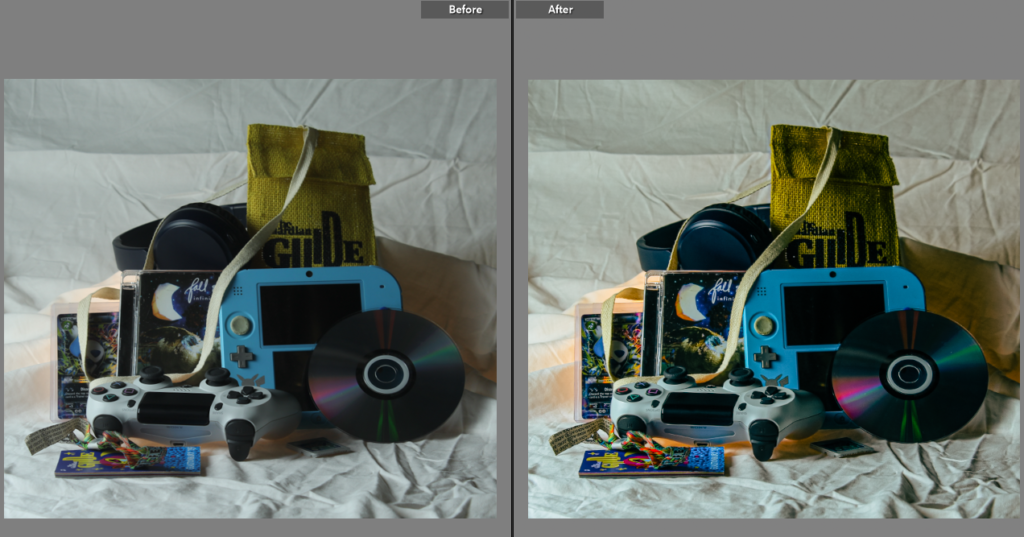
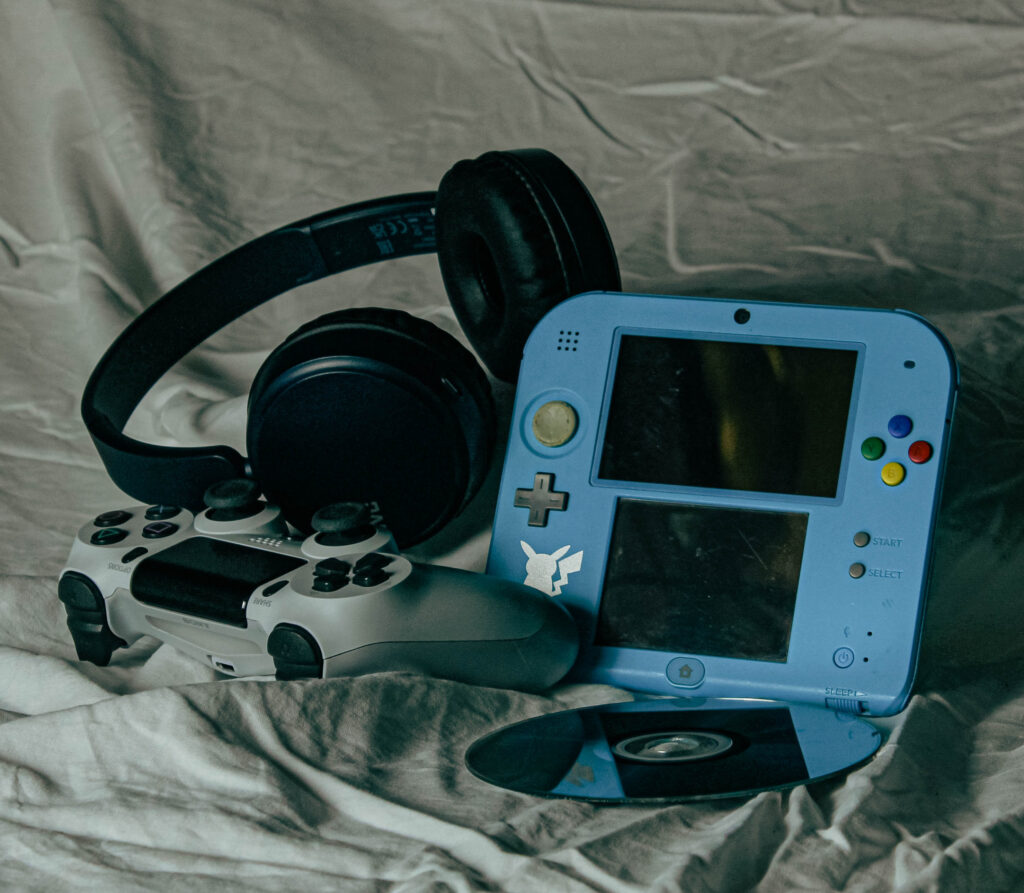
with both walker Evans and Darren Harvey-Reagan you can clearly see that Darren was inspired by walker when getting into still life photography, walkers work is very much real life situations turned into still moments whereas Darren has used objects and slightly altered walkers way of work and created it his own by using non alive objects and different layouts within that category of work.















































 .
.






