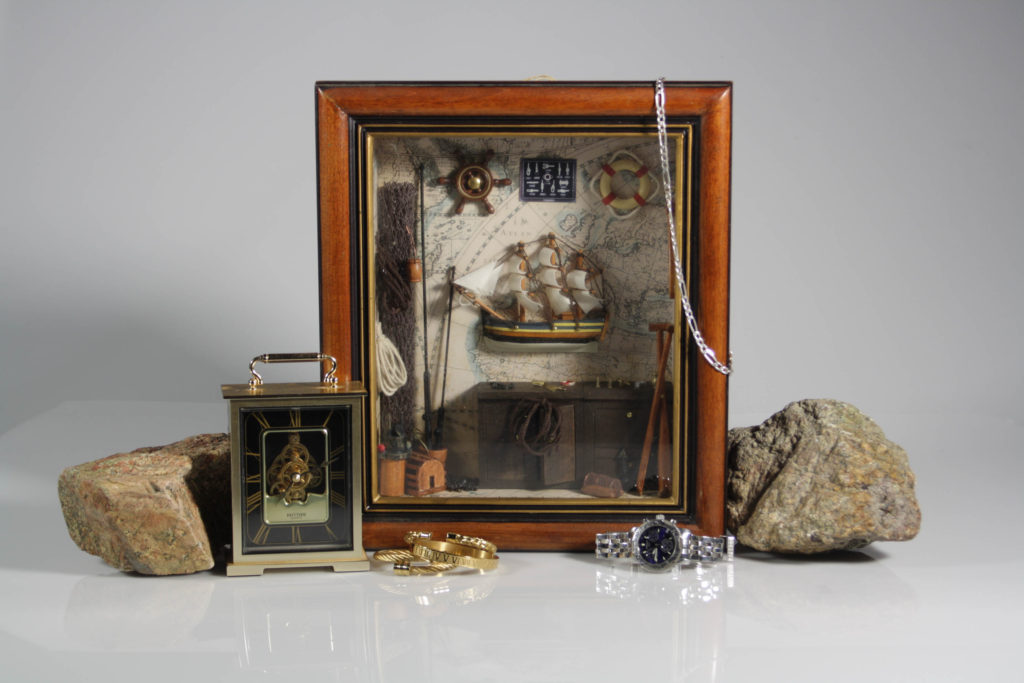
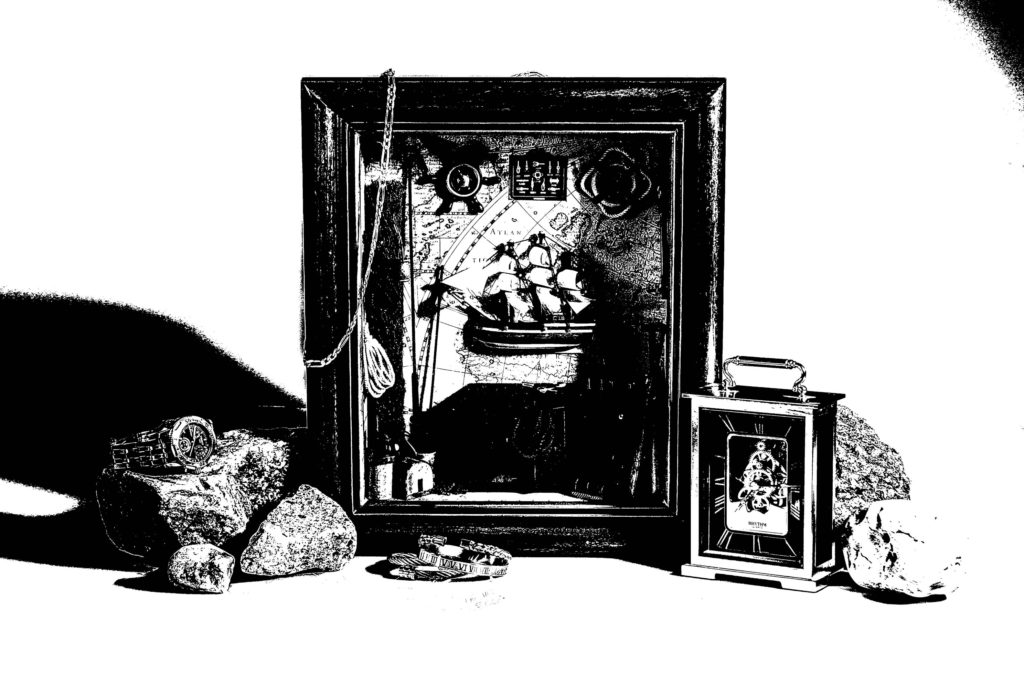




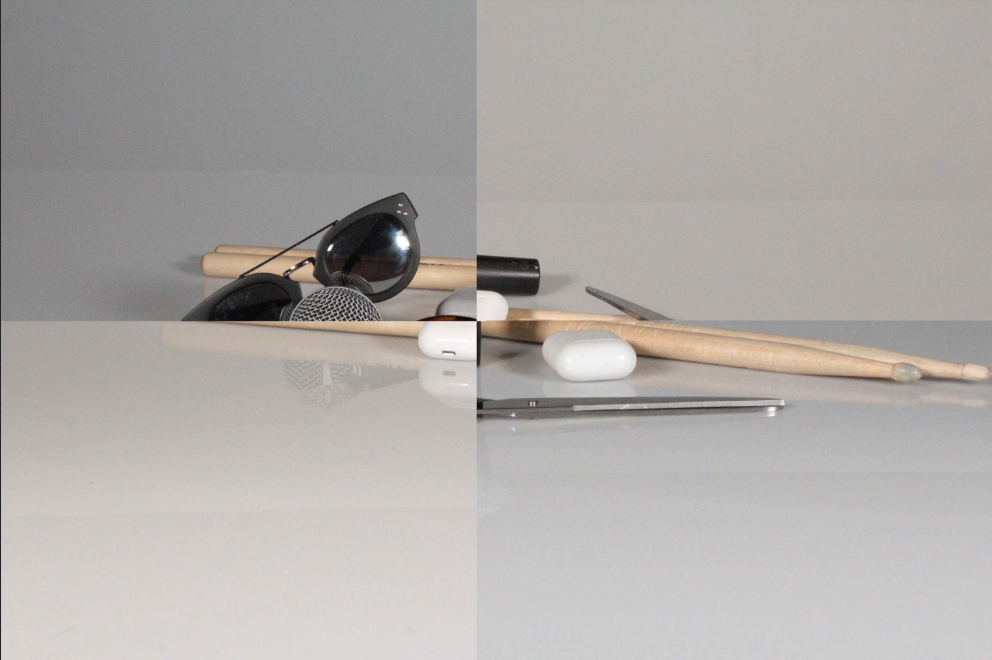
these are the final images they have been edited and its shows a colourless photo a coloured photo and a the original photo. also there is another photo




these are the final images they have been edited and its shows a colourless photo a coloured photo and a the original photo. also there is another photo
for photography at the start of the course I wasn’t here join a bit late however I believe I caught up, I have learned about how shutter speed works and how it make a difference between a good photo and a bad photo, I have also learn about aperture and how it effects how much light is let into the camera. I have also learned how to edit on Lightroom classic and photoshop which I have never used before. I have also learned physical photography by learning how to frame pictures and put them on foam board. over all I believe that I have gotten better at photography but I can improve.

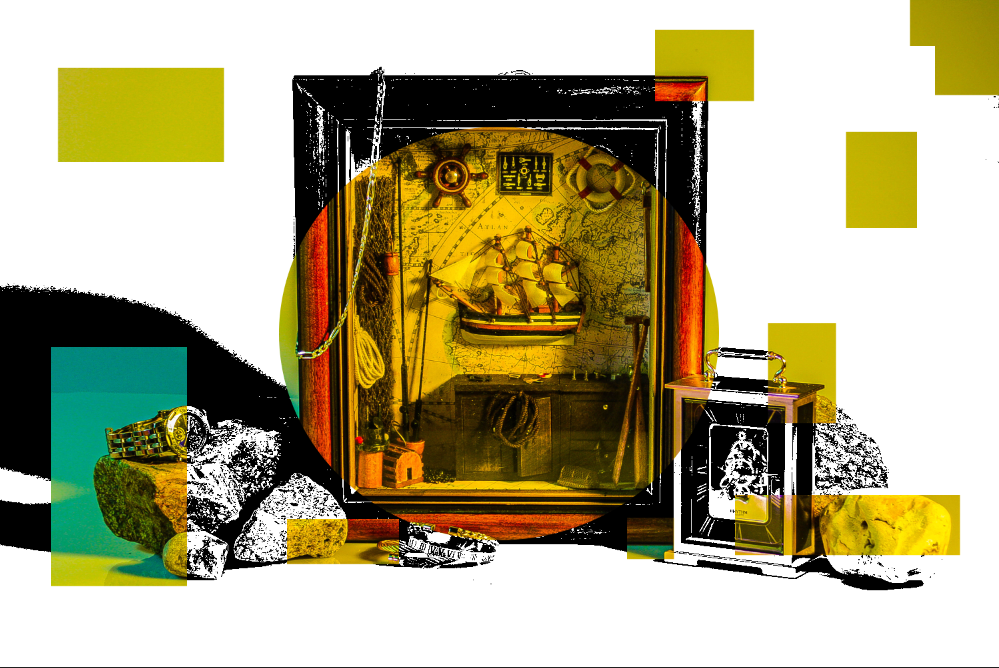
I made a separate blog post about the picture above this but I edited a photo of a photo gallery and put some of my photos in it.

When talking about landscape it is typically talked about as an image wider than it is tall that is shot horizontal, they tend to contain aspects of nature and natural land.
There are three typical types of landscape photography mountain, flat and costal landscape, it commonly involves daylight photography.
Landscape photography shows the spaces within the world, sometimes vast and unending, but other times microscopic. Landscape photographs typically capture the presence of nature but can also focus on man-made features or disturbances of landscapes.
The earliest known evidence of a landscape photograph was taken between the years of 1826 and 1827. It was an urban landscape photo taken by a French inventor by the name of Nicephore Niepce.
Formalism specifies the critical position that the most main aspect of a art object is its form – the way it is fashioned and its purely ocular aspects – alternatively its narrative content or its friendship to the visible experience.
The visual language shown on a fine arts work implies a pictorial ideas media in telling a lie or a particular event.

Continuous lighting is lighting that’s always on. Its used mostly in cinematography and videography, photographers also use it to determine how the shot will come out.

Flash lighting is where the lights flash (1/200 to 1/1000 of a second) when the photographer takes a photo. You can use a flash to get rid of shadows from your photo. You can also use flash and a slow shutter speed when photographing a moving subject.

Key Light is the primary source of light in a scene. The Key light is most often placed in front of your subject, at an angle, and thus illuminates one section of your subject.

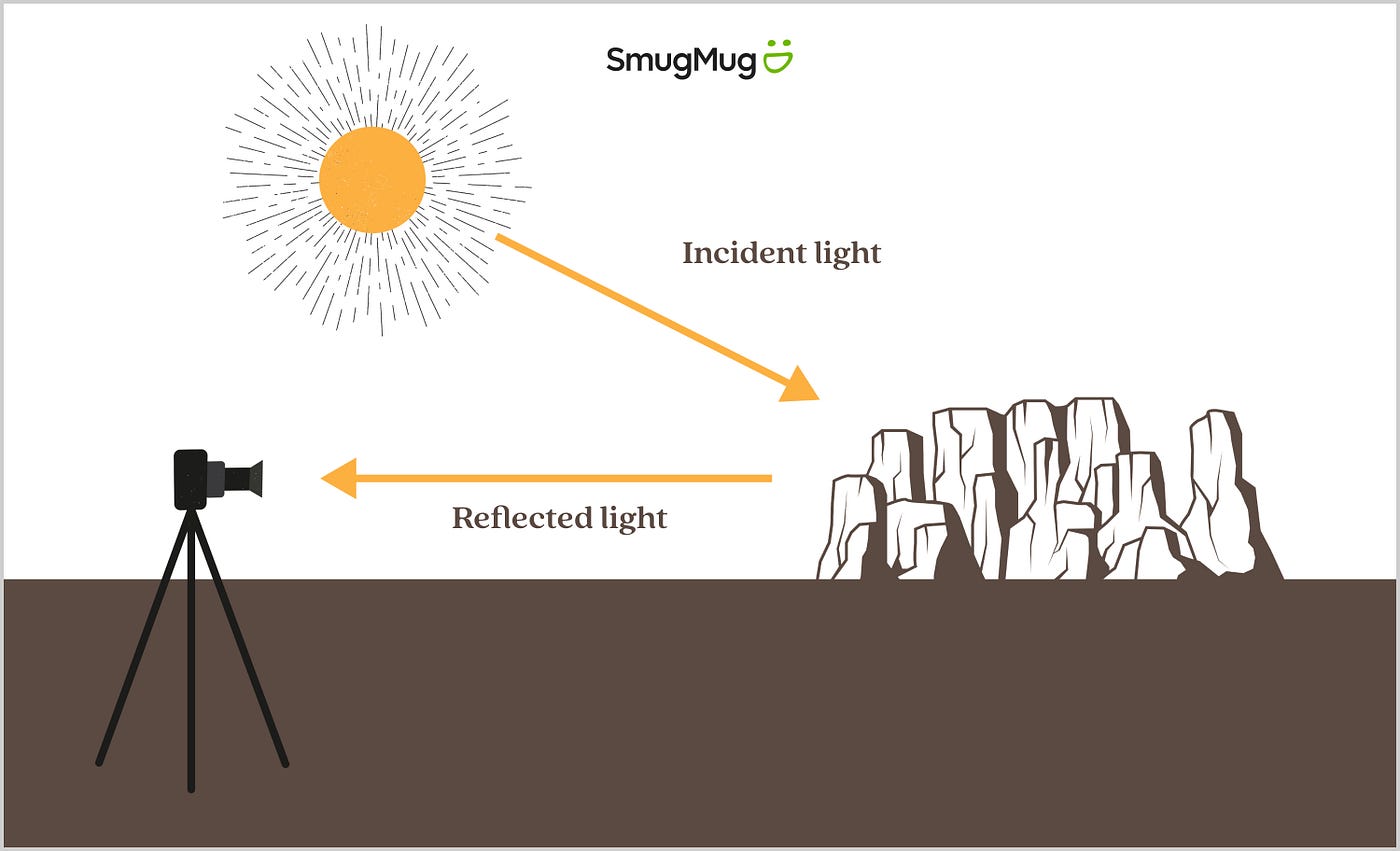
Reflected light is light that reflects off the subject. Regardless of the light source, light is altered by whatever it reflects off.
Backlight photography emphasizes the depth behind the subject and gives images a greater sense of place. Backlighting can produce a dramatic contrast between the subject and the background.

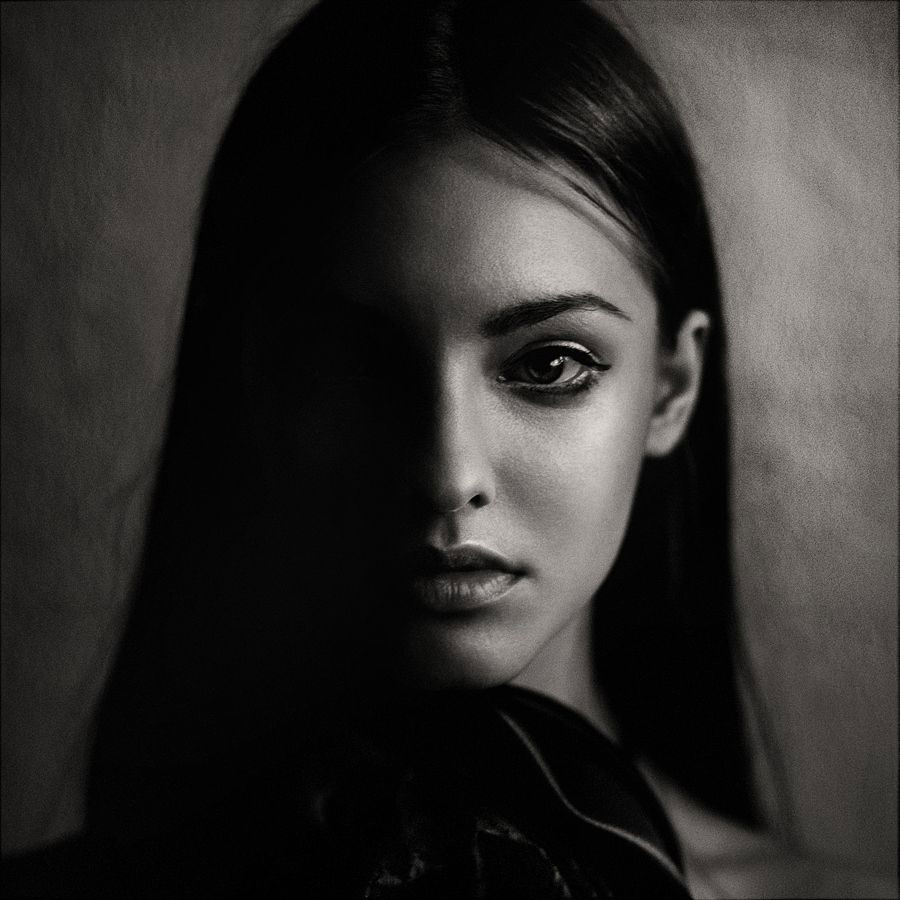
the light in this photo is coming from behind the subject giving the illusion of the subject being a silhouette.
As well as with digital photo montages, the ones done in Photoshop, I have also had a go at experimenting with different forms of montages done by sticking some images together , cutting some up, gluing, and taping different parts of images together and combining things manually , in real life.
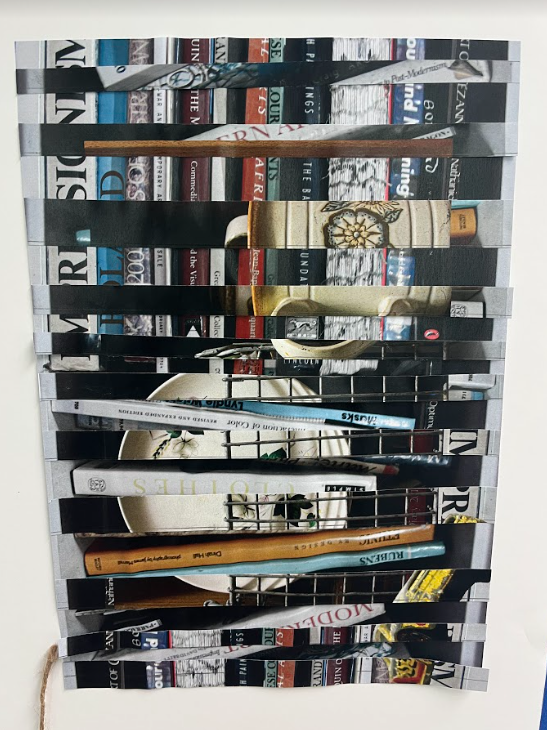

With the above image , after printing 2 different images I have measured and drawn horizontal lines with a pencil and a ruler on one of the images. These lines were uneven as I made one bigger then the other and then when they would reach a certain point I would make them go smaller, this pattern repeated until I’ve reached the end of the image. Aliening the strips again i have glued each other strip onto another image, leaving gaps in where every 2nd strip would be.
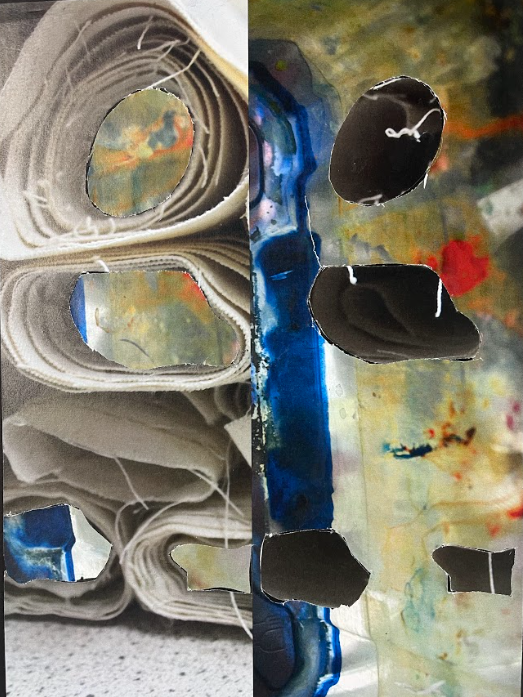

With an image that was already montaged with another one in Photoshop,by slitting one in half and having a split between 2 different photographs. I have cut out the above image using a utility knife, the darkest, inside areas that the canvas rolls created. Then I layered them over the other half of the image and cut around them, then when I had 2 identical shapes I have switched them around so that it looked like the paint on the right was in thee canvas rolls.
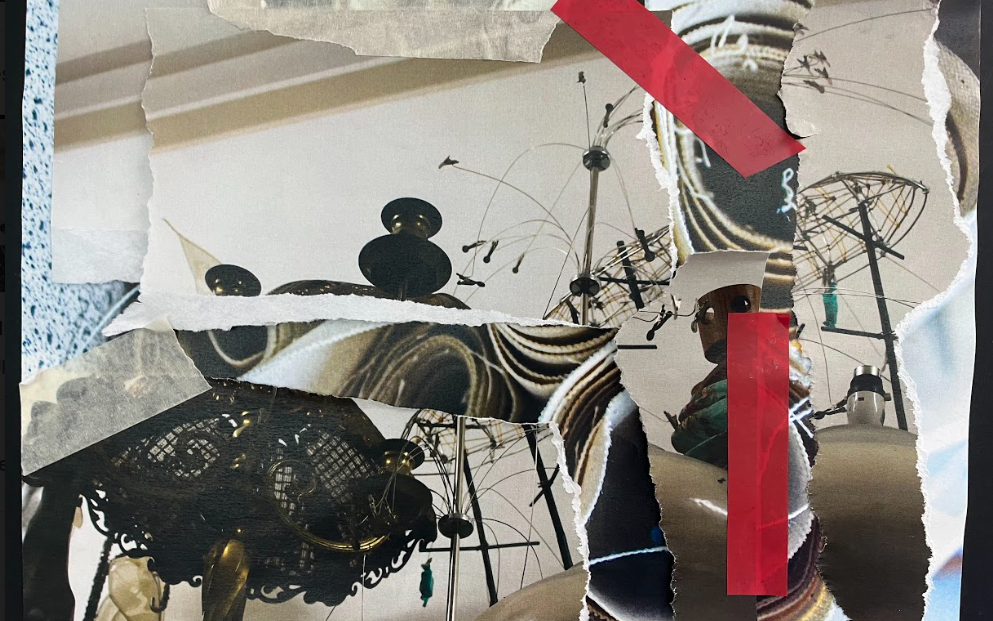

With the last image I have got 2 separate ones and not touching one , as the bottom photograph was sort of as a background. Using different tapes and glue I simply ripped parts of an image and stuck it onto the other. Since both images were matching tones and quite messy, I decided to make the final image chaotic, therefore that’s why I went for an unprepared form of montage like ripping the image and using tape.
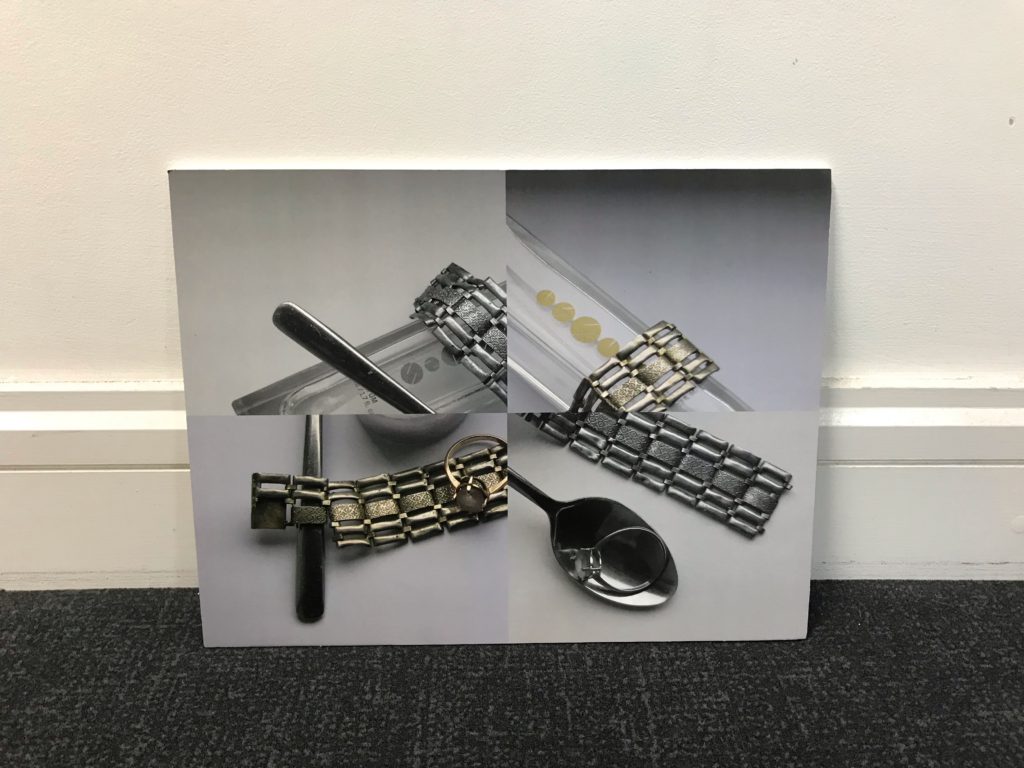





There are various lighting techniques in photography that can enhance or stand out from your images. These techniques can be used in a variety of other ways in addition to highlighting specific areas of your photo to give the final product more impact.
Flat Light

When you place your light source in front of your subject, you create flat light, which evenly lights your subject and eliminates any shadows. This isn’t a technique that is highly sought after because it’s crucial to show shadows in order to give your subject life, but it works well for hiding textures and other image flaws.
Broad light

With broad light, the face of your subject is at an angle with the most well-lit side of the face is closest to the camera and the shadow on the back side of the face. This type of light can make a face look fuller so it’s ideal for those with very narrow faces.
Short light

The face is at an angle and the shadow falls on the side of the face closest to the camera in short light, which is the opposite of broad light. A thinner face responds well to this kind of light.
Split light

Another type of side lighting is split lighting, which can be identified in an image by half of the subject being lit and the other half being in the shadows. You can see the shadow line running directly down the middle of a face’s forehead, nose, and chin.
Backlight

Backlight is the light coming from behind your subject. Photos taken during the golden hour, when the sun is low in the horizon and just beginning to set, frequently display this. This can be accomplished by purposefully using a background light or by utilizing natural lighting.
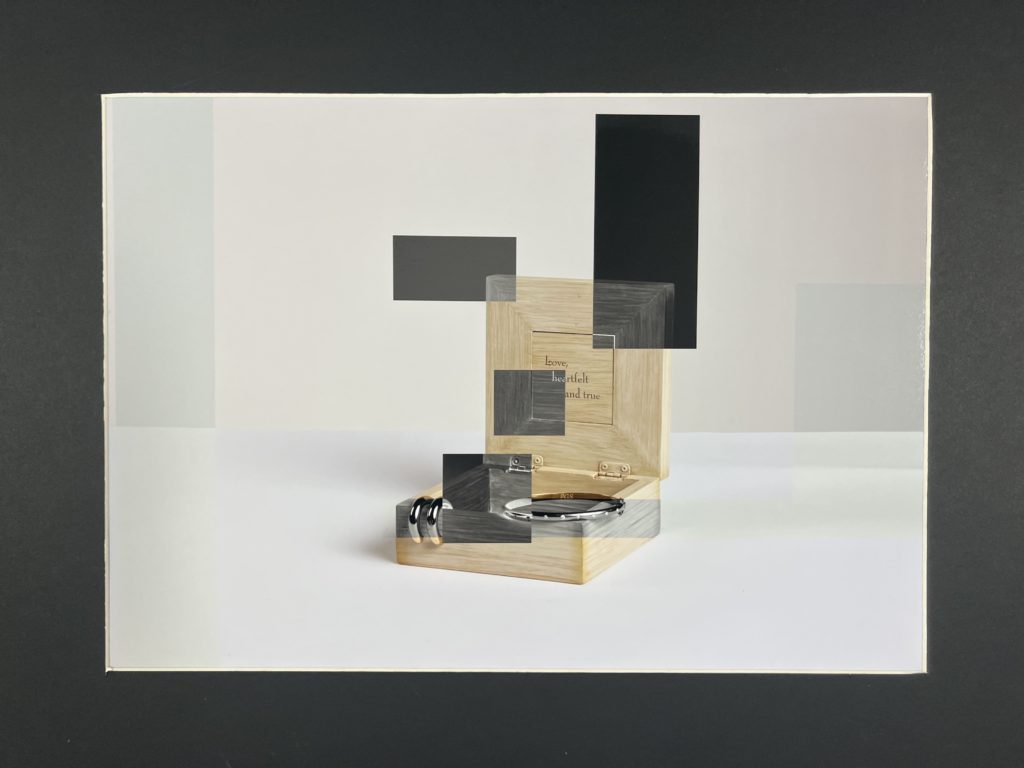





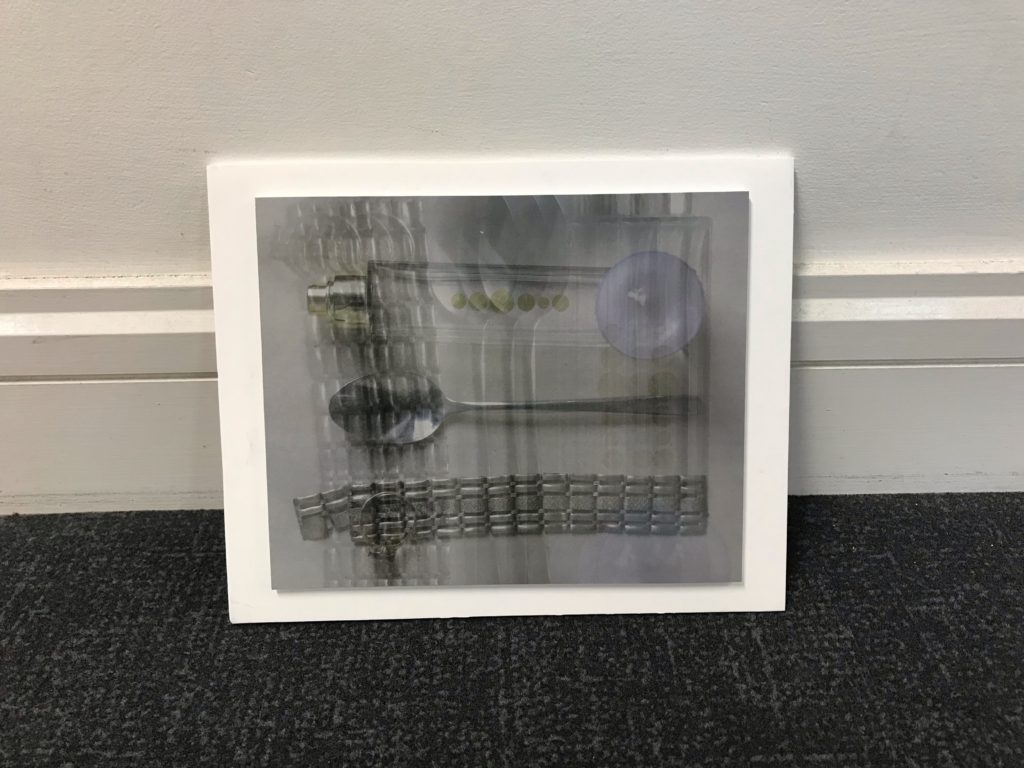
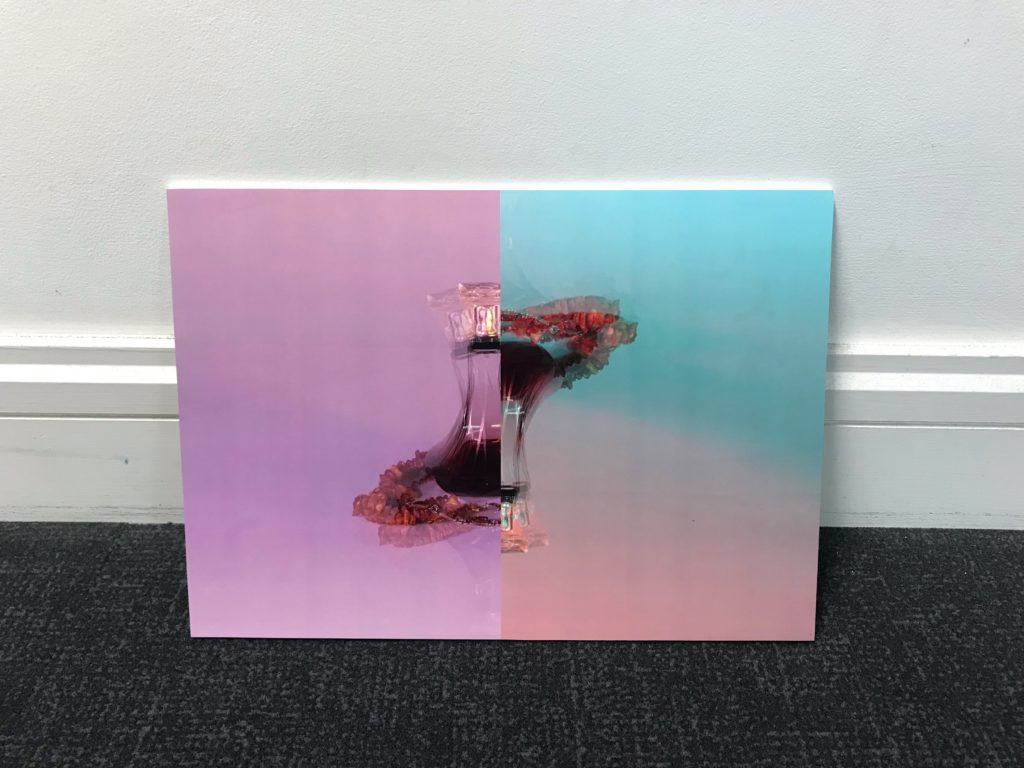
For my final outcome I decided to mount this A3 image. I chose this image because it was simplistic yet due to the editing it had a unique difference. I found this final piece challenging as I had never done anything like this before and had never experienced using the tools I needed to. For this final outcome I created a window mount to make a high quality smart image so I could avoid creating an unprofessional outcome.
Reflecting on this fragment of my project of ‘HOME’ I believe that it was a challenging and informative experience. I discovered how to use a online blog and how to create creative and smart blog posts to the best of my ability, this was one of the first challenges and differences I had to overcome because I had never used a internet blog before. I have taken a numerous amount of photoshoots which lead to me having a variety of images so I could create more unique edits, however I am aware that I have not worked on photoshop nor used it to the best of my abilities. Therefore I hope in my future projects I show my progress and abilities on photoshop and make time to create more edits, as I believe that it was my blog is lacking. I also believe I should take more images and inspect my images so I have a clear view of the images so I know later in editing I know what images I have and have an easier work. However taking this all into consideration I will use this to improve on in my next project, and I hope in future projects I can act thorough throughout this project.