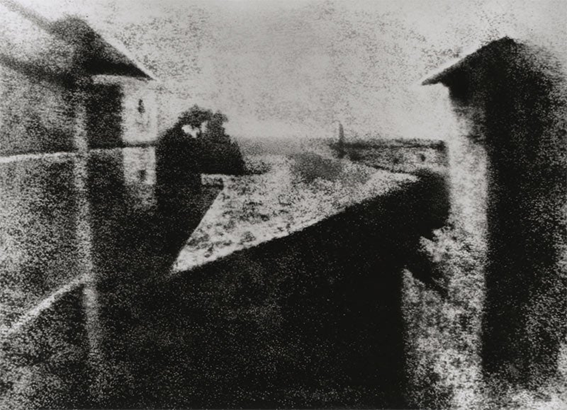
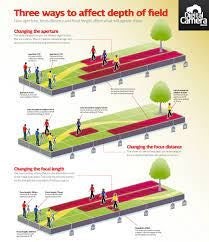
Formalism describes the critical position that the most important aspect of a work of art is its form – the way it is made and its purely visual aspects – rather than its narrative content or its relationship to the visible world.

This photo is an example of formalism, it has a large, focused depth of field, the photo is taken in natural light as the photo has then been edited into black and white it highlights the light parts and shadows making them stand out more. The tone of the photo goes from dark to light which implies that the photo would have been taken around late morning or early evening i can gather this information because of the angle of the shadows, the buildings on either side of the photo adds the element of a frame within a frame as the centre of the photo has no buildings in the centre. The top of the buildings is what draws the audience to the photograph as it is the lightest part of the photograph.
Visual language
Visual language in photography is a photograph which tells a story. The visual language shown on a photography work implies a pictorial communication media in telling a story or a particular event. The presence of a sequence of portraits seri is sometimes important to explain the things happening.
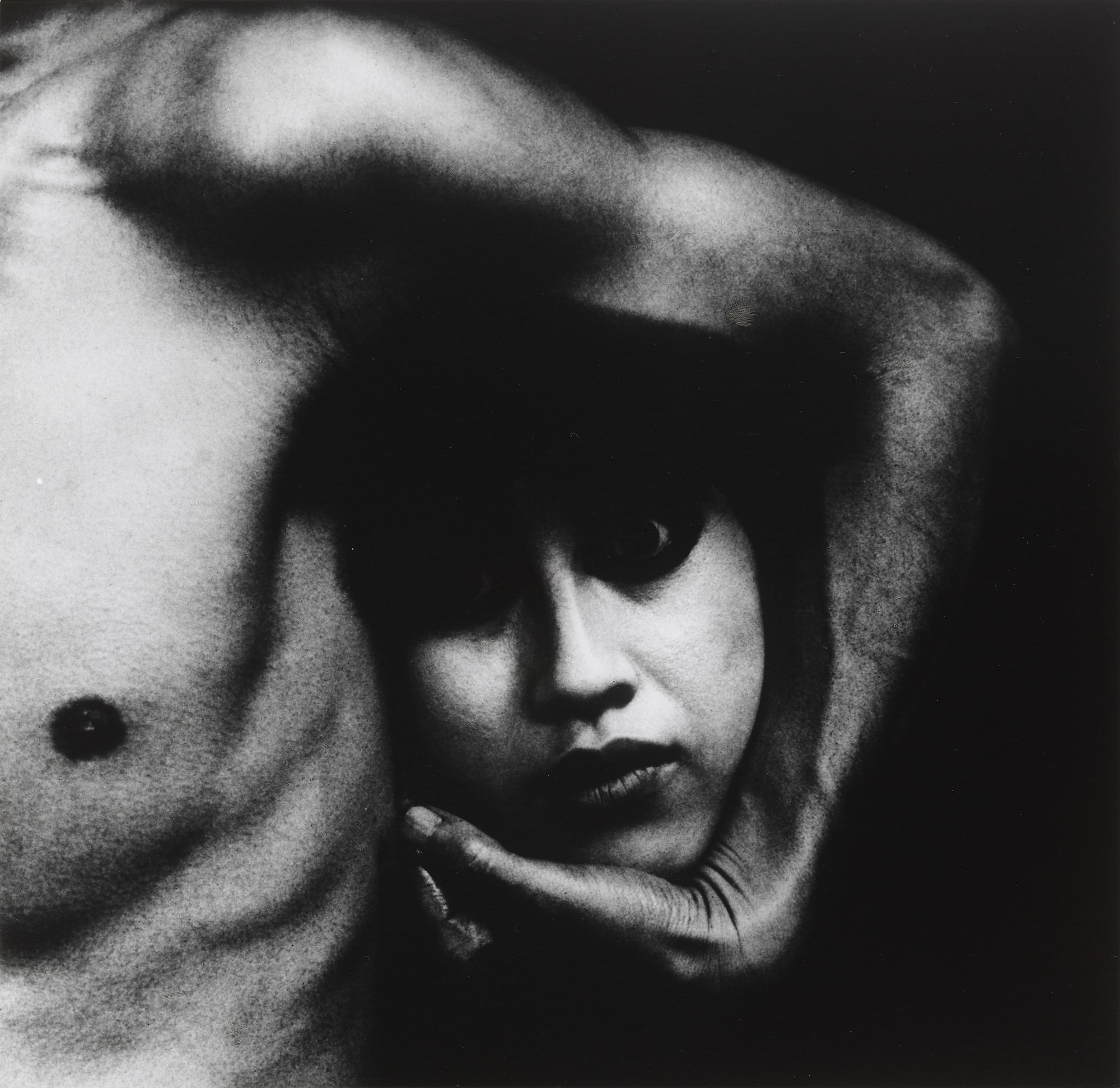

This photograph is a visual language photo as when the consumer of the photo looks at it they begin to think of a story behind it and question the intentions behind the photo and why it was taken, the lightest points on the photo draws you in as they are the high points on the photo, the girls facial expression in my opinion implies a lot about the photo. The photo shows the texture of the body as you see the veins on the arm and the texture of the rough looking skin. The lighting highlights certain aspects of the photo such as the ribcage and the creases on the hand.
Walker Evans

Walker Evans began to photograph in the late 1920s, making snapshots during a European trip. Upon his return to New York, he published his first images in 1930. During the Great Depression, Evans began to photograph for the Resettlement Administration, later known as the Farm Security Administration (FSA), documenting workers and architecture in the Southeastern states.
Darren Harvey-Regan

Harvey-Regan was known for entwining image and object together, his work was inspired by Walker Evans as he montaged together Walkers tools before recreating the objects, he bought the tools and deconstructed them and then reconstructing them.
Harvey-Regan’s work is eye catching because at the first glance you can see it as a normal tool but when you look at it in depth you can see the reconstructed tool and how the two tools seamlessly, he has also eliminated all shadows making the photo look sharp and well put together.