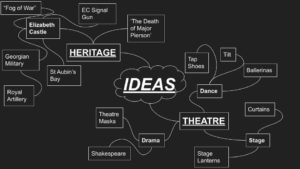
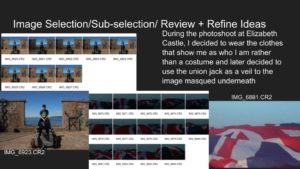
History of Photography
Q1: What is the etymology (origin & history) of the word photography?
Writing with light.
Capturing light.
Painting with light.
Filming light.
Writing with light.
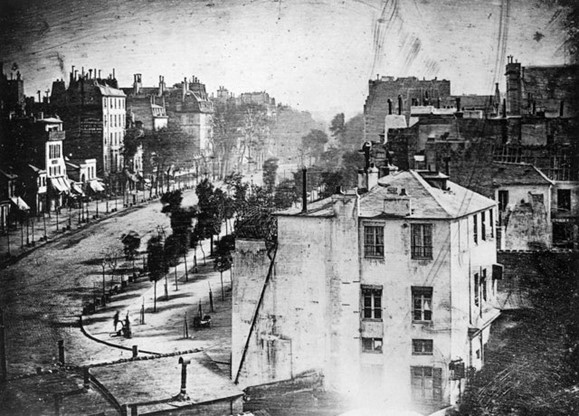
Q2: What year was the first photograph made in camera?
1739 (Joseph Wright)
1839 (Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre)
1826 (Joseph Nicéphore Niépce)
1904 (Salvadore Dali)
1826 (Joseph Nicéphore Niépce)
Q3: When did the first photograph of a human appear?
1874 (Julia Margeret Cameron)
1838 (Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre)
1856 (Henry Mullins)
1939 (Ropert Capa)
1838 (Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre)
Q4: Who made the first ‘selfie’
Kim Kardashian (2015)
Robert Cornelius (1839)
Cindy Sherman (1980)
Claude Cahun (1927)
Robert Cornelius (1839)
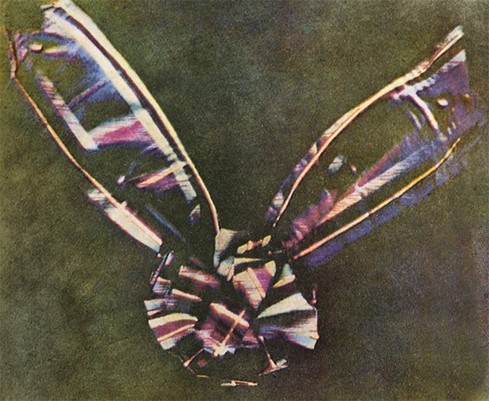
Q5: When did the first colour photograph appear?
1907 (Lumière brothers)
1961 (Andy Warhol)
1935 (Kodachrome)
1861 (James Clerk Maxwell)
1861 (James Clerk Maxwell)
Q6: What do we mean by the word genre?
A study of an artwork
A depiction in art
A style or category of art
A creative process in art
A style or category of art
Q7: What do we mean by the genre of still-life?
In image where a person is sitting still and not moving.
An arrangement of flowers.
A picture of food.
An image that shows inanimate objects from the natural or man-made world.
An image that shows inanimate objects from the natural or man-made world.
Q8: What was the main purpose of the Pictorialist movement?
To capture moving objects
To record reality
To affirm photography as an art form
To be scientific
To affirm photography as an art form
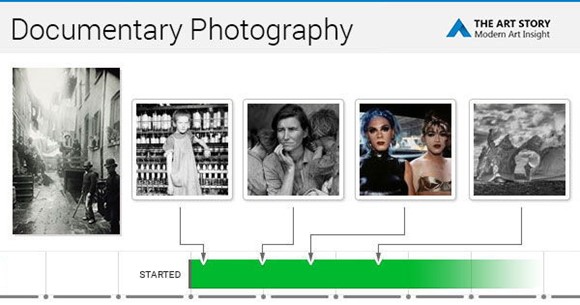
Q9: How do we describe the term documentary photography?
Capture images that truthfully portray people, places and events.
Staging images for maximum effect.
Provide in-depth information about a subject over a long period time.
An interpretation of reality as witnessed by the photographer.
Capture images that truthfully portray people, places and events.
Staging images for maximum effect.
Provide in-depth information about a subject over a long period time.
An interpretation of reality as witnessed by the photographer.
Technical Aspects of Photography
Q10: What is exposure in photography?
To expose hidden elements in our society.
To record fast moving objects.
To capture bright light.
The amount of light that reaches your camera’s sensor.
The amount of light that reaches your camera’s sensor.
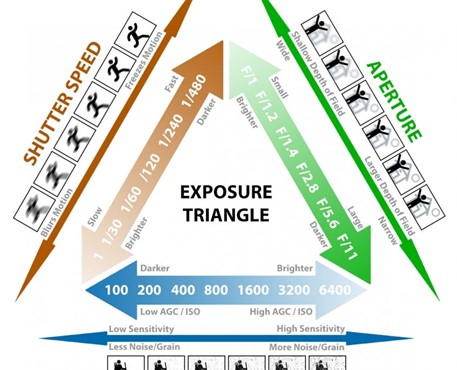
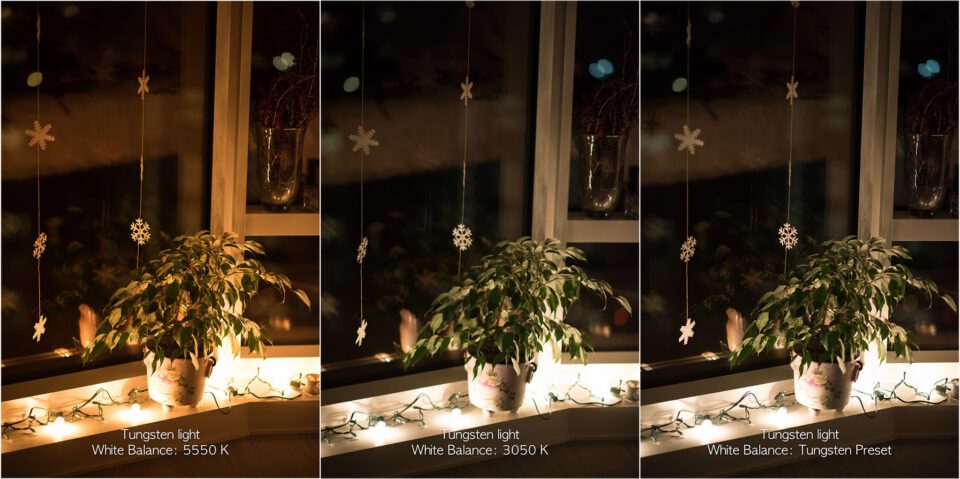
Q11: What controls exposure on your camera?
Depth of field, composition, distance to subject.
Aperture, focal length, ISO.
Aperture, shutter speed, ISO.
Shutter speed, distance to subject, depth of field.
Aperture, shutter speed, ISO.
Q12: What control on our camera records moving objects?
Aperture
White balance
Shutter
ISO
Shutter
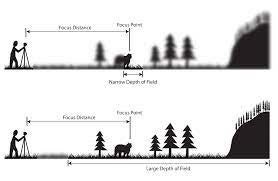
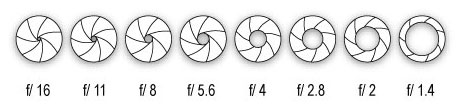
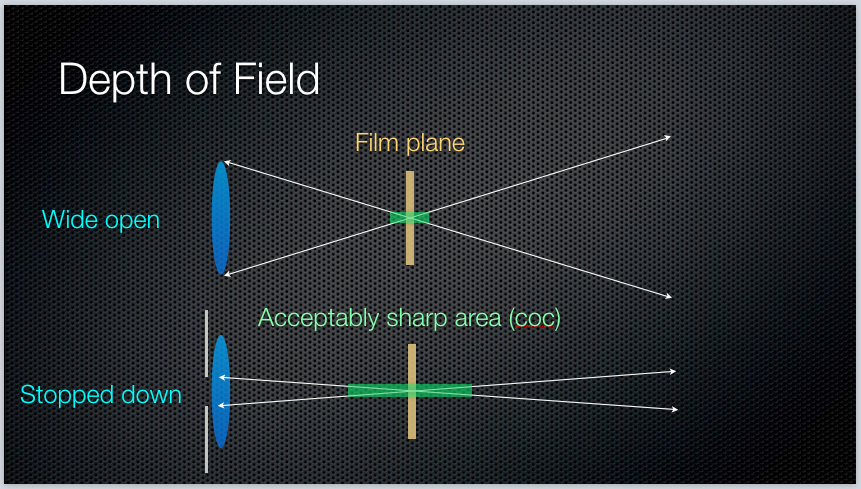
Q13: How do we explain depth of field?
How much of your image is in focus.
To photograph from a high vantage point.
A view across a field.
A deadpan approach to image making.
How much of your image is in focus.
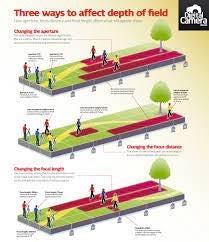
Q14: What factors affect Depth of Field?
Shutter speed, distance from camera to subject, and sensitivity to light.
Lens aperture, distance from camera to subject, and lens focal length.
Lens focal length shutter speed and lens aperture.
Sensitivity to light, shutter speed and lens focal length.
Lens aperture, distance from camera to subject, and lens focal length.
Q15: What is composition in photography?
Capturing the quality of light.
A piece of music with different instruments.
Staging a portrait with props.
The arrangement of visual elements within the frame.
The arrangement of visual elements within the frame.
Q16: What is your understanding of aesthetics in art?
Concerned with the nature of beauty and taste.
It is subjective and in the eye of the beholder.
Aesthetic qualities refer to the way and artwork looks and feels.
Making a critical judgement based on observation and understanding.
Concerned with the nature of beauty and taste.
It is subjective and in the eye of the beholder.
Aesthetic qualities refer to the way and artwork looks and feels.
Making a critical judgement based on observation and understanding.
Q17: What are contextual studies in photography?
To provide historial, cultural and theoterical understanding of images.
Consider factors outside of the image, as well as inside the frame.
To give an opinion without any research.
To seek a definite answer.
To provide historical, cultural and theoretical understanding of images.
General Knowledge of Photography
Q18: How many images are captured on average every day worldwide?
1.5 billion
4.7 billion
800 million
6.9 billion
4.7 billion
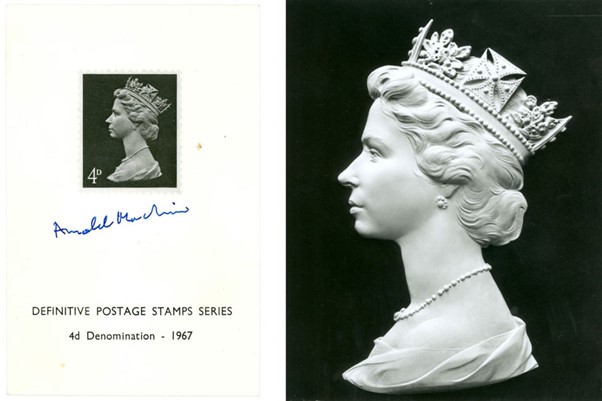
Q19: Which portrait is the most reproduced in the world?
Mona Lisa
Lady Gaga
Ernesto ‘Che’ Guevara
The Queen (Elizabeth II)
The Queen (Elizabeth II)


























![Lesson 4] Understanding Shutter Speed](https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcS_A1OBhLALbJHoVSpcdaiZbVZmjtYJBe1hgpYxw5IxZte-Ofyk8A7dnGp9b9KmiHOFFG4:https://d1hjkbq40fs2x4.cloudfront.net/images/324.jpg&usqp=CAU)