IDENTITY POLITICS is a term that describes a political approach wherein people of a particular religion, race, social background, class or other identifying factor form exclusive socio-political alliances, moving away from broad-based, coalitional politics to support and follow political movements that share a particular identifying quality with them. Its aim is to support and centre the concerns, agendas, and projects of particular groups, in accord with specific social and political changes.
Femininity vs Masculinity
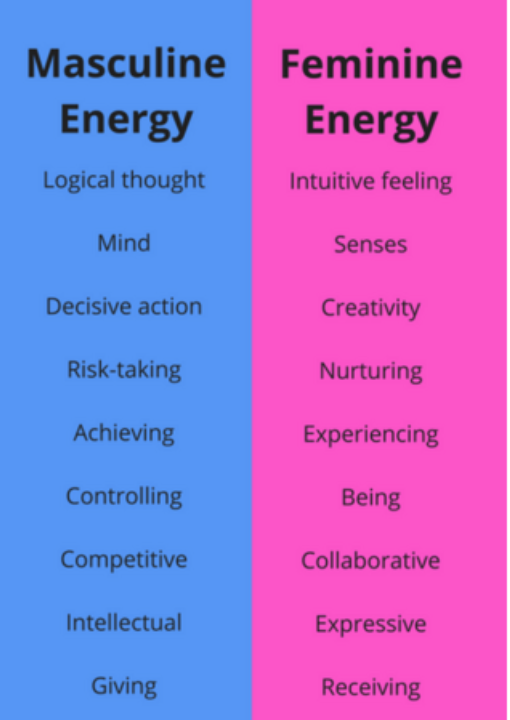
The themes of ‘FEMININITY and MASCULINITY’ are a binary opposite – a pair of related terms or concepts that are opposite in meaning.
Masculinities and femininities refer to the social roles, behaviours, and meanings prescribed for men and women in any society at any time. Such normative gender ideologies must be distinguished from biological ‘sex,’ and must be understood to be plural as there is no single definition for all men and all women.
In my opinion as new generations are born the views, opinions and ideas of femininity and masculinity are being challenged and changed as people are being given and allowed more freedom to discover who they are and how they like to present themselves. Creating different visions on the views on femininity and masculinity.
Masculinity describes the degree to which society focus on assertiveness and achievement. When in contrary, femininity describes the focus of society to quality-of-life issues, such as caring for others, group solidarity and helping the less fortunate are valued. In other words, society still recognizes a gap between male and female values. This dimension is frequently viewed as taboo in highly masculine societies.
Masculinity
- Masculinity: Strong egos – feelings of pride and importance are attributed to status. Money and achievement are important. Examples of masculinity cultures are Slovakia, Japan, Hungary, Austria, Venezuela.
Femininity
- Femininity: Relationship oriented, more focus on quality of life. Examples of femininity culture are Sweden, Norway, Netherlands and Denmark.
Identity can be influenced with many factors one of the main factors is your environment for example if you grew up in a patriarchal place or family men are going to show more dominant attributes and females are going be seen as more submissive.