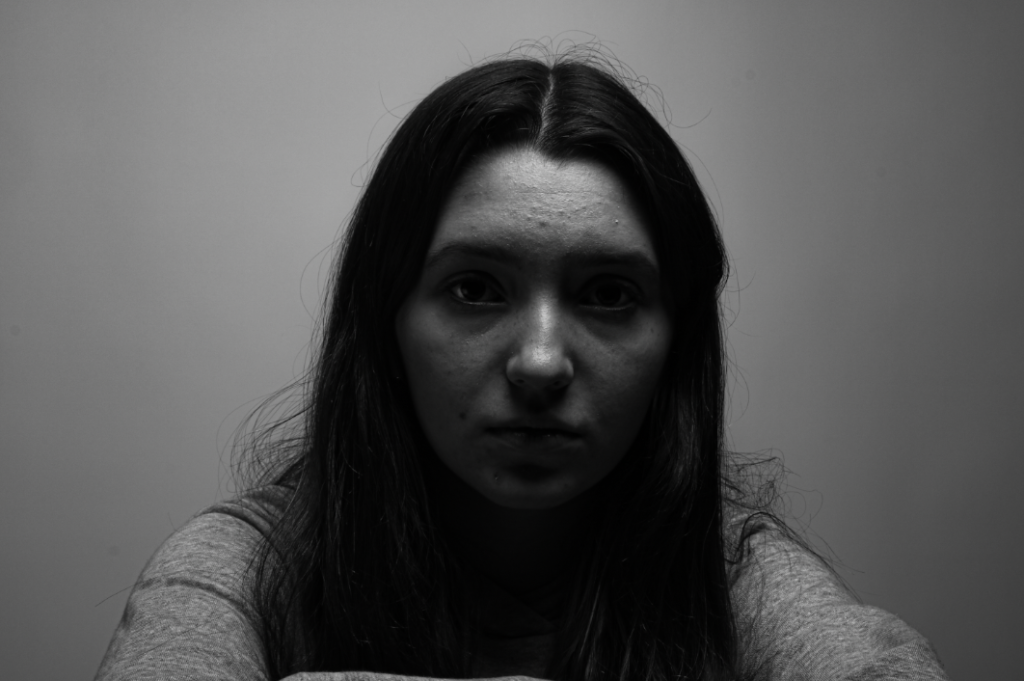
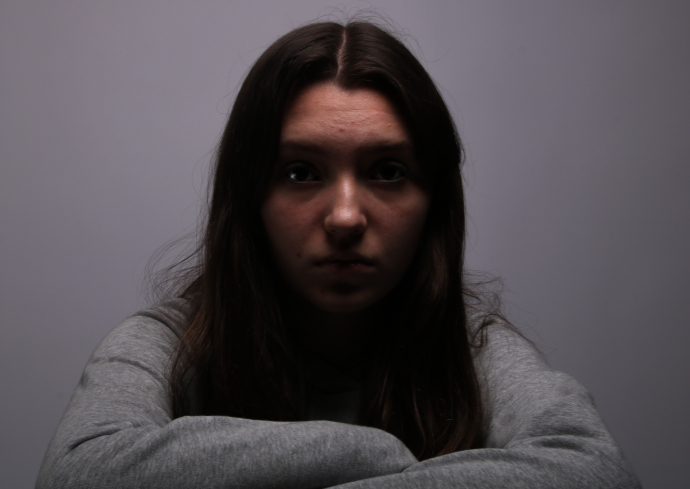
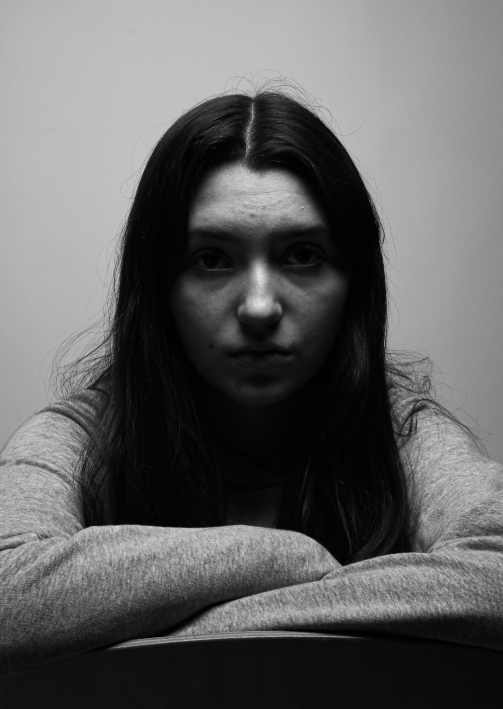
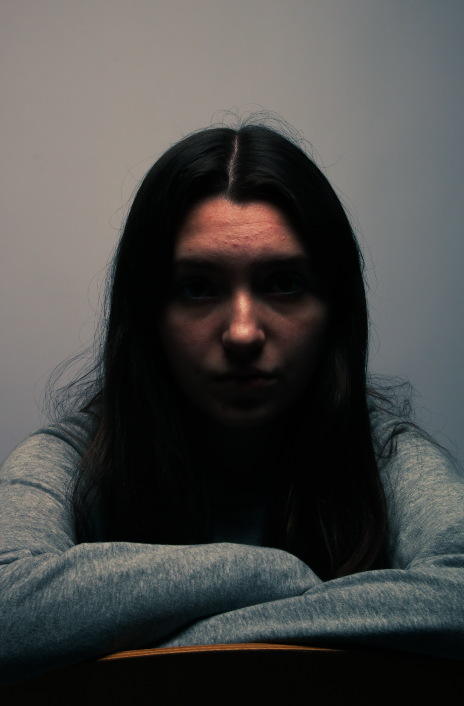
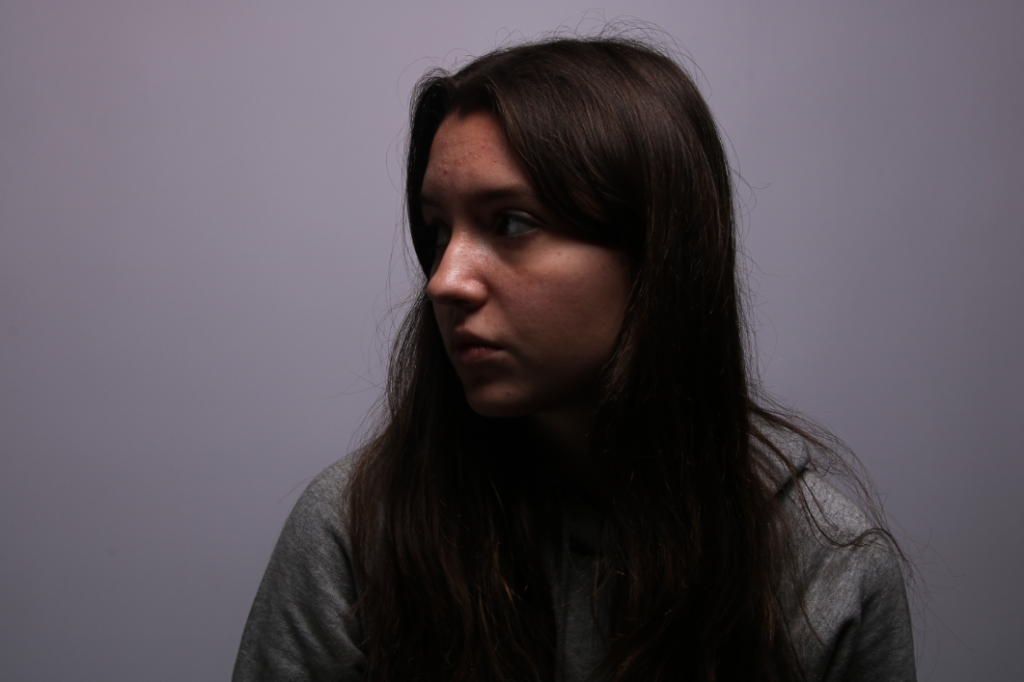
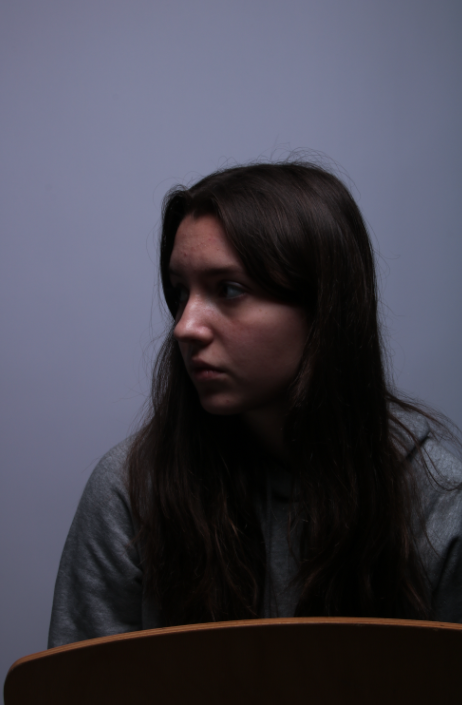
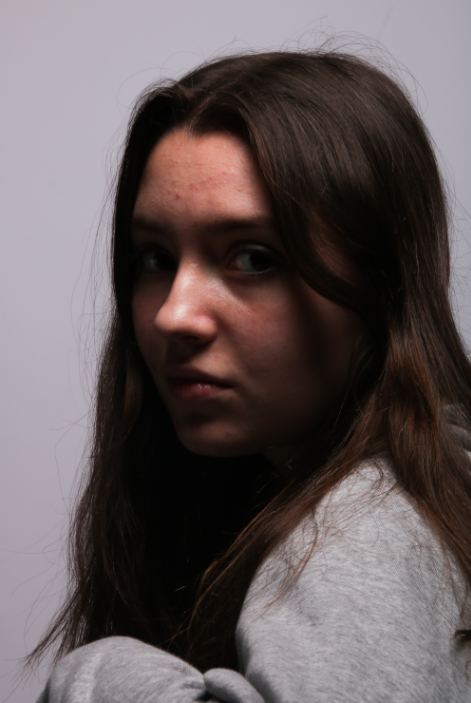
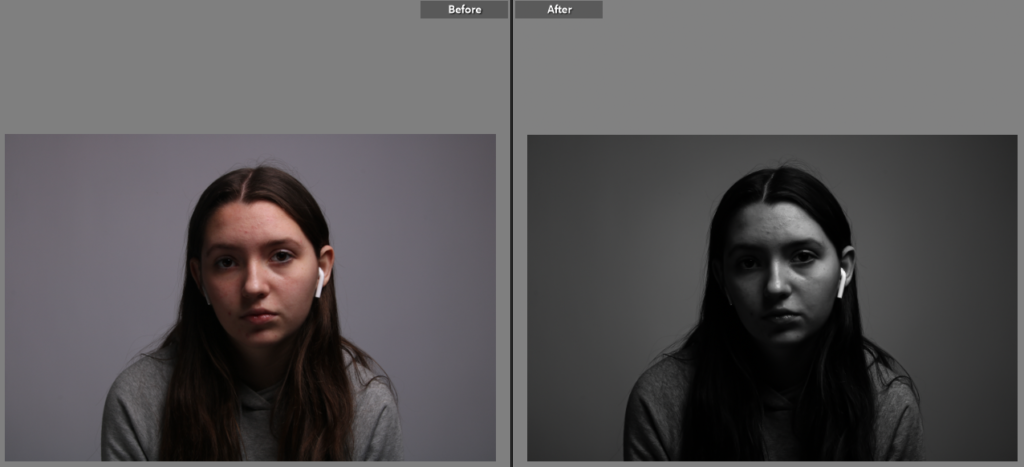
Femininity

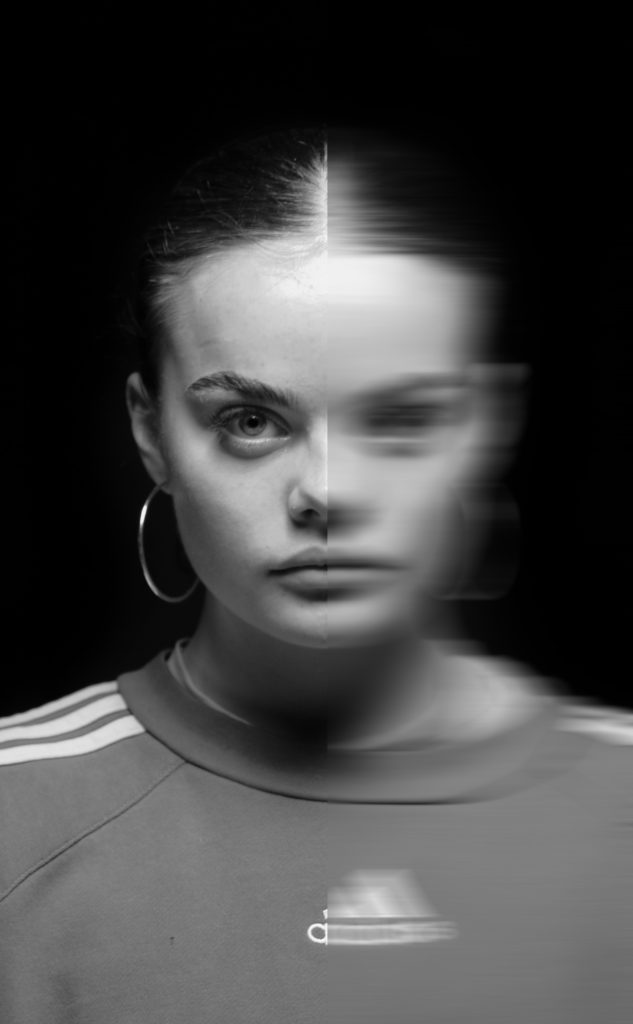
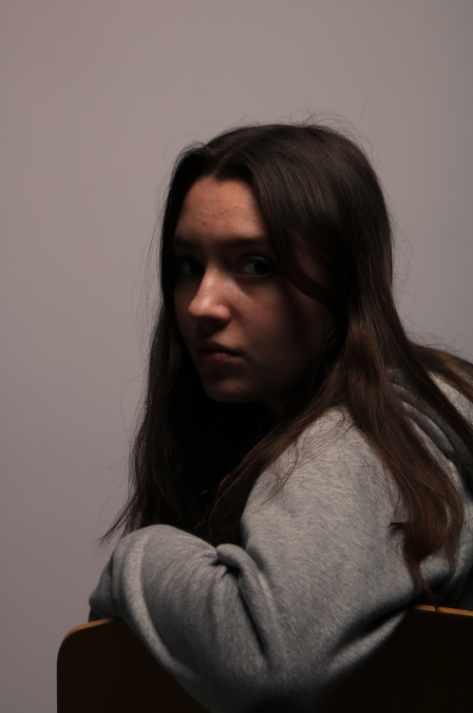
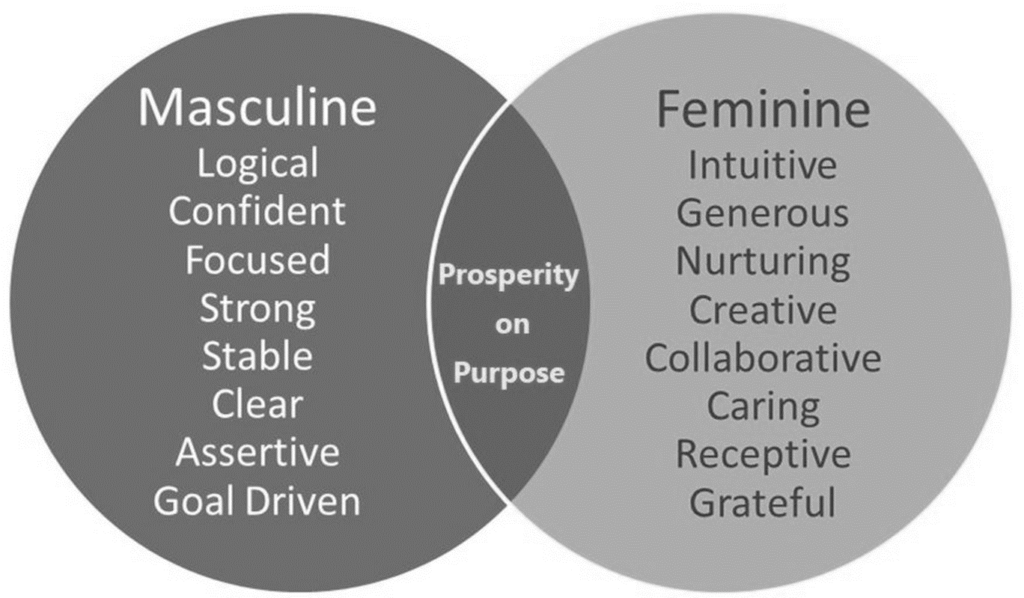
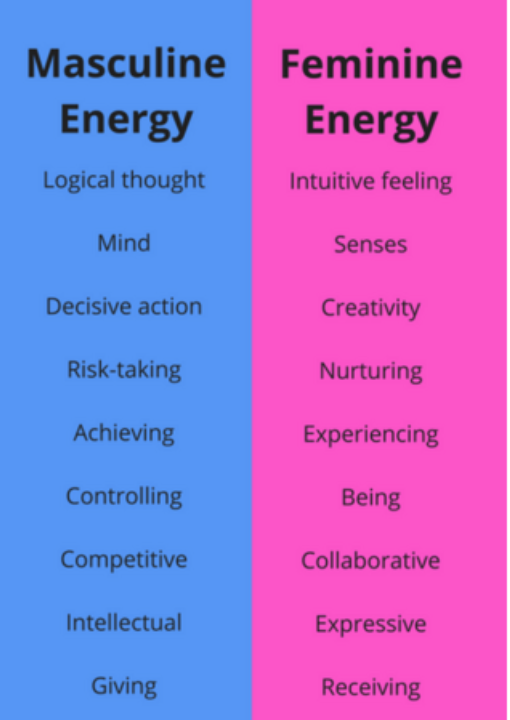
femininity is defined as the quality or nature of the female sex. which over the years during old tradition was challenged by men and masculinity, and sometimes even now.
Femininity years ago used to be shown through obeying men and looking after the house and kids, but as the years went on, it evolved into the individuality of women and how they don’t need men to survive and live, and even the quality and freedom of woman’s life’s broadened into what they could do.
This influenced women’s identity and strengthened it. But it didn’t just come to women, they had top prove and fight for the right to be viewed as self sufficient and capable of similar things.
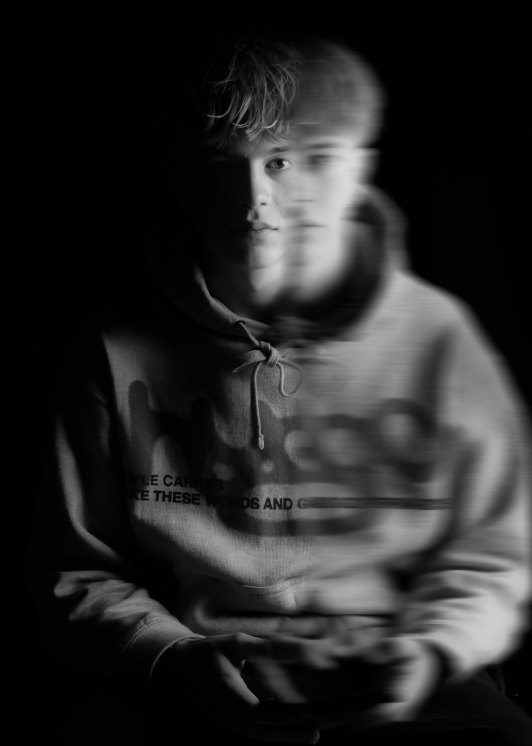
Masculinity

Masculinity is defined as qualities or attributes regarded as characteristic of men or boys.
Masculinity years ago was challenged to what made you a man, especially towards younger boys, they had to prove to become and man and to be strong with little emotion, with its main component being power.
Although it was easier during this time for a man in comparison to women it still had its struggles. Now masculinity is more flexible and is in a similar state to women’s, for example self worth, pride in who and what you are, but it definitely still has a difference, and still includes aspects of what it means to be a man years ago. It can be complicating but it all comes down to the identity that you give yourself.
Identity

Identity is a big mix of things now compared to many years ago, and has changed drastically in the last 20 years. Identity is the fact of being who or what you are, and can come in many ideal ways especially now. Identity is formed through many things, one of them being your upbringing, and who you where surrounded by as a child, which is when your first identity starts to form. Child influences are a baseline ingrained into their identity for example looking up to a certain person, which would inspire them to be like them.
The identity is then challenged as a teenager which is when you are a person starts to form, and who/what you really want to be, It is especially grown through friends and pier groups, with some people wanting to be accepted into being something/someone, so a persona is put on to fit in or to get along with people in general, which then after time becomes this persons identity, as least temporarily. Other influences like where you where born, for example a tribe, where you where taught how to hunt and had rituals, which would create an identity to that tribe, and a feel of belonging. This concept links with being born in a certain country and even area, especially in jersey where it is a small area people identify as being from jersey.
Some forms of identity is formed negatively though, for example through a persons loss of a family member, especially a mother or father if they where at a young age, which would cause them to have an altered identity because of the lack of both sides which is normally needed. Another way is through a trauma, identity can be caused and altered though a bad experience which is held on by them and is never really let go, which causes them to have their identity changed through it, as if you where to learn a bad lesson and never do it again or learn form it.
One other form of identity is through gender, which especially now is very flexible. People can be identified as inanimate things, or without either gender towards them, as they identify as neither male or female.