










Camera obscura and pinhole photography
Pinhole photography is when you use a camera without its lens and with a tiny aperture. It uses the lightproof box with a small whole on one side which is what camera obscura is.
Camera obscura is a darkened box with a convex lens or aperture for projecting the image of an external object onto a screen inside. The earliest known written about camera obscura was in 400BC by a Chinese philosopher called Mo-Tzu. He wrote that light from an illuminated object that passed through a pinhole into a dark room would invert the image.

Nicephore Niepce

Niepce was a French inventor who was most commonly linked to the invention of photography. He developed Heliography which was a technique he used to create the world’s oldest and first surviving product of a photographic process. In 1826/27 he used a primitive camera to produce the oldest surviving picture of a real world scene.
Heliography
Heliography is an early photographic process producing a photoengraving on a metal plate coated with an asphalt preparation. Heliography was developed using two distinct methods. The first consisted of “fixing the views” in the camera obscura, while the other copied existing methods to “reproduce them by printing using known methods of engraving.”

Louis Daguerre

Daguerre was a French artist and photographer who was known for his invention of the Daguerreotype process of photography. After this he became known as one of the fathers of photography. He developed the Daguerreotype process in 1839. Daguerre partnered with Nicephore Niepce in 1829. Niepce died in 1833 but Daguerre continued to experiment and evolved the process which would be known as the Daguerreotype process.
Daguerreotype process
The Daguerreotype process consisted of treating silver-plated copper sheets with iodine to make them sensitive to light, then exposing them in a camera and ‘developing’ the images with warm mercury vapor. Daguerre’s images made using the Daguerreotype process were praised and the news of this process then spread quickly around the world. The French Government then bought the rights to Daguerre’s invention in return for him having lifetime pensions. In 1839 the French Government presented the invention as something for the world to use and published working instructions on how to create images using the Daguerreotype process.

Henry Fox Talbot
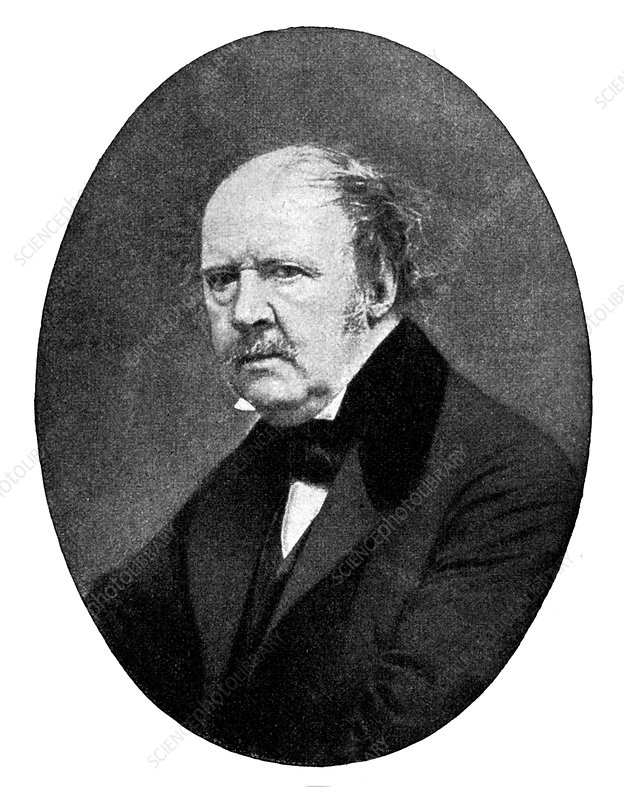

Talbot was an English photographer, scientist and also an inventor who invented the salted paper and Calotype method. His first successful camera photographs were made in 1835. He used paper which was sensitised with silver chloride which would darken when it was exposed to a light source. In the 1840’s he worked on something called photomechanical reproduction, (a reproduced photographic image that is printed in ink and usually on paper) which then led to his creation of the phytoglyphic engraving process which is a gelatine and bichromate mixture which was then coated over a metal plate and then placed in the light. When the light reaches the plate the gelatine hardened and the image area can be washed away. Talbot created the photographic process know as Calotype. The Calotype process is an early photographic process which was done using paper which was coated with silver iodine. Paper texture effects in calotype photography limit the ability of this early process to record low contrast details and textures.

Robert Cornelius

Robert Cornelius was an American photographer who designed the photographic plate for the first photograph taken in the US, which was an image of a Central High School taken by Joseph Saxton.
Cornelius took the first ever selfie. He did this by setting up his camera at the back his family store in Philadelphia. He took the selfie by removing the lens cap and then running into frame where he sat for a minute before covering the lens again.
Julia Margeret Cameron

Julia Margeret Cameron was a British photographer who is considered as one of the most important portraitists of the 20th century. She is mostly known for her close-ups of famous Victorian men and women.
After showing an interest in photography for many years, Cameron started photography as a profession after her daughter gave her a camera as a present. After this she started to capture men, women and children who would visit her studio which was at Freshwater. Her images of some respected men like Charles Darwin and Henry Taylor have been described as ‘extraordinarily powerful’ and she has been credited with producing the first close-ups in history.
Pictorialism
The movement known as Pictorialism represented a photographic aesthetic and a set of principles about photography’s role as art. This movement dominated photography during the late 19th and early 20th century. Pictorialism started in England but then expanded to New York which is where it centred around Alfred Stieglitz, which is who started Pictorialism.
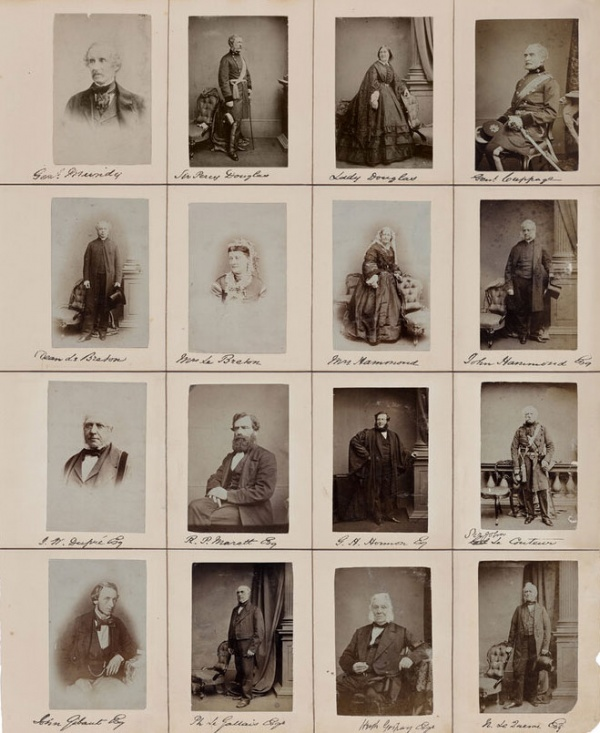
Henry Mullins

Henry Mullins Moved to Jersey in 1948 and set up a studio which was known as the royal saloon. At first Mullins was in a partnership with someone called Mr Millward who he only worked with for around a year. After that Mullins worked by himself and continued to for another 26 years.
When Mullins came to Jersey he started photographing the locals and managed to photograph almost 10000 people who lived in Jersey at the time.
Mullins was popular with officers of Jersey which were very popular to have their portraits taken. Their wives and children were also popular for having their portraits taken. The portraits of these officers show the fashion of their time with the long hair and beards and it is hard to tell the difference with some officers who were of the same rank.

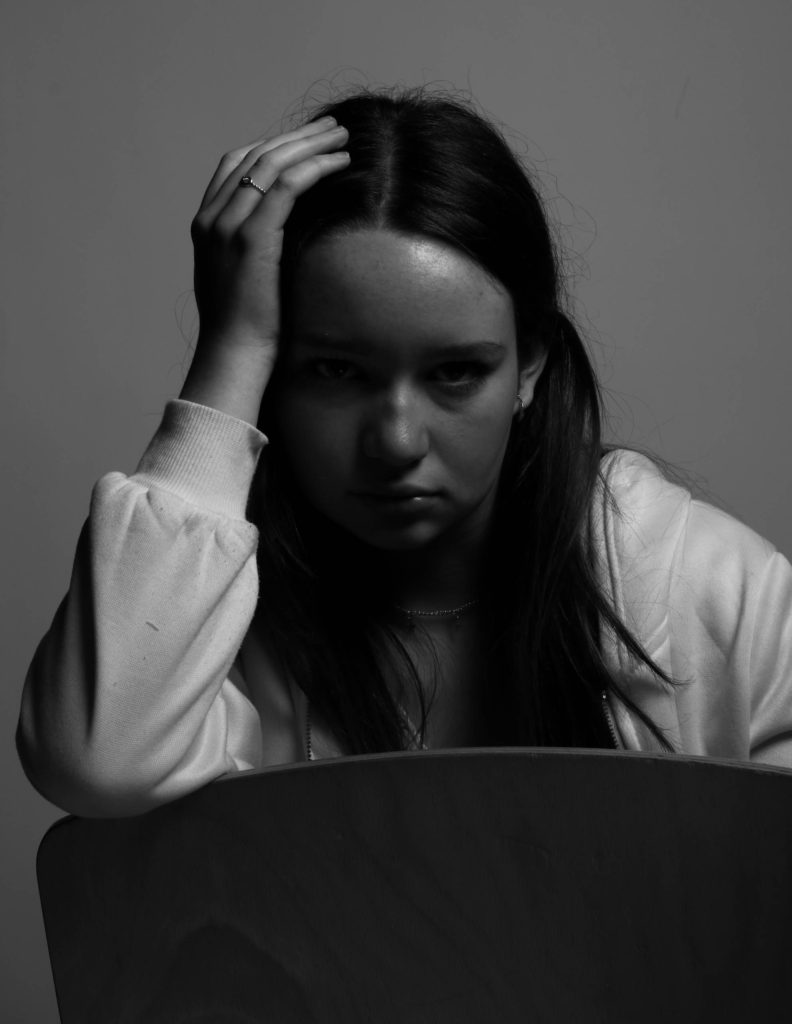
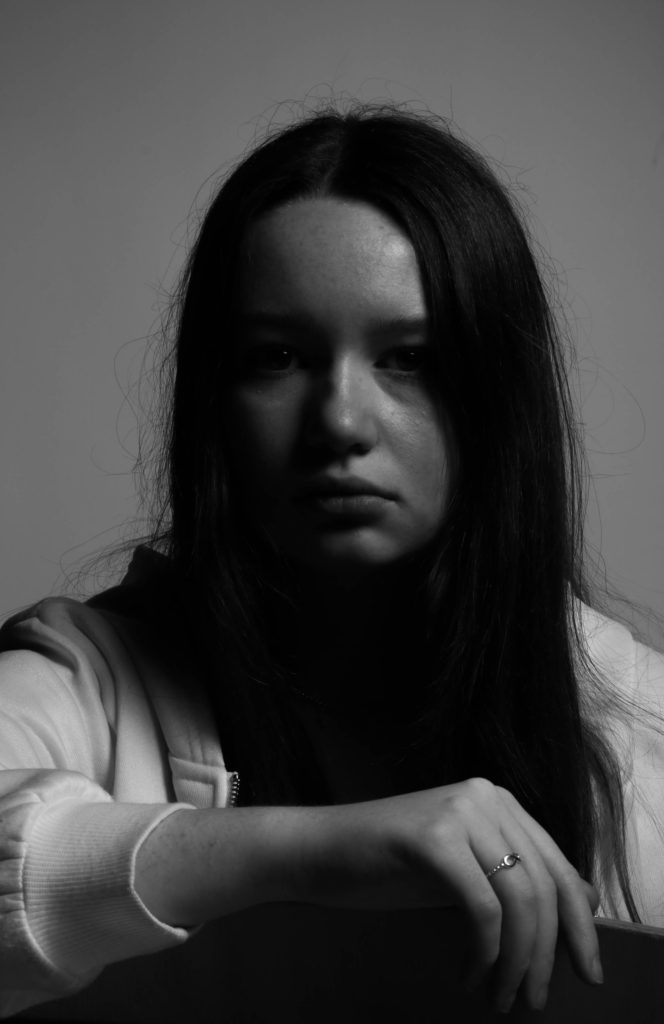
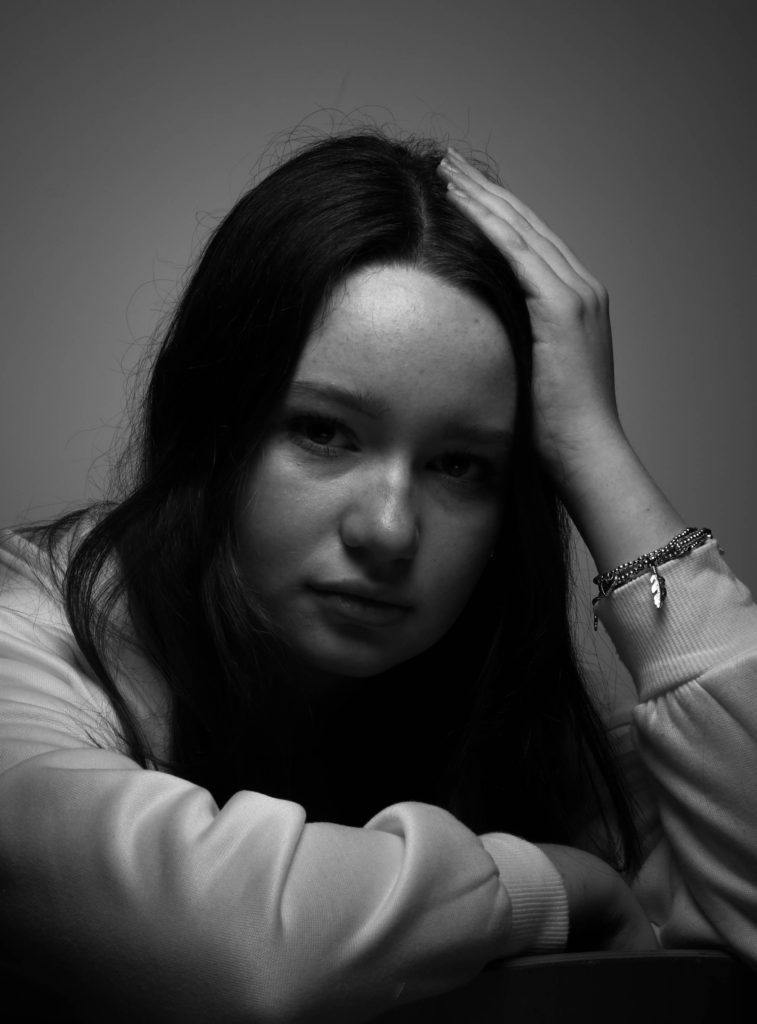
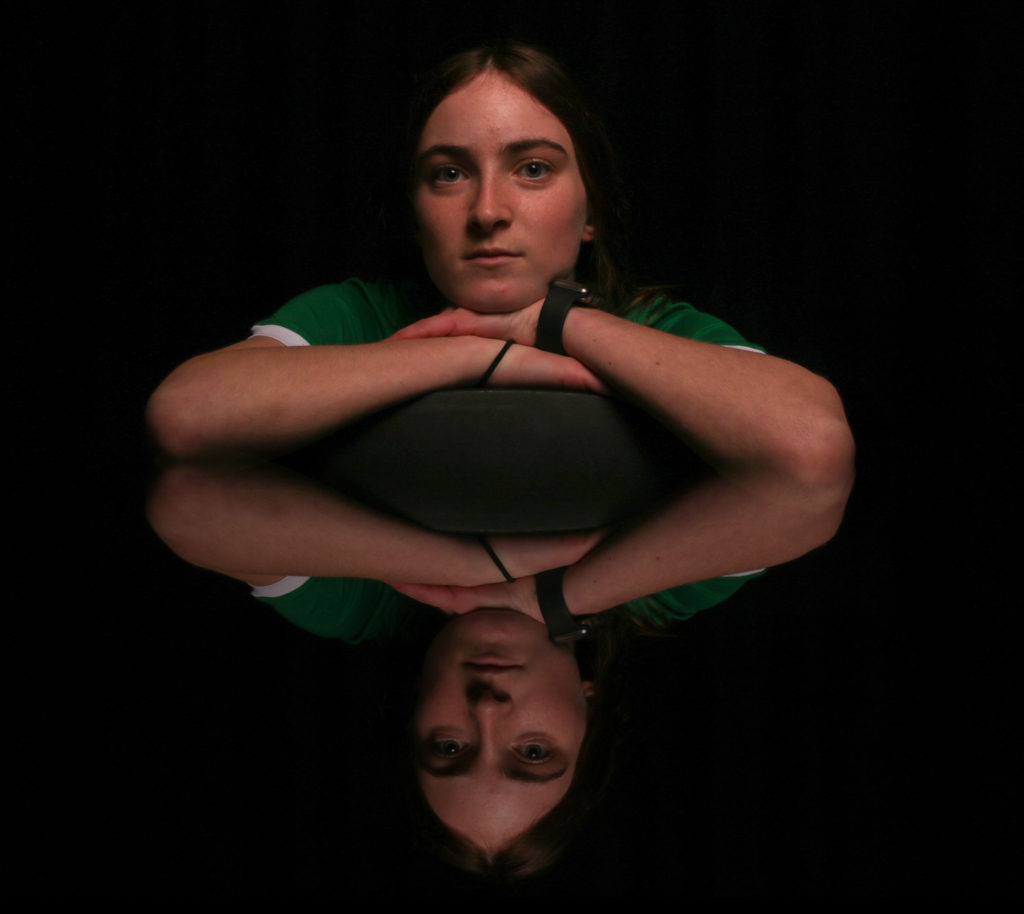
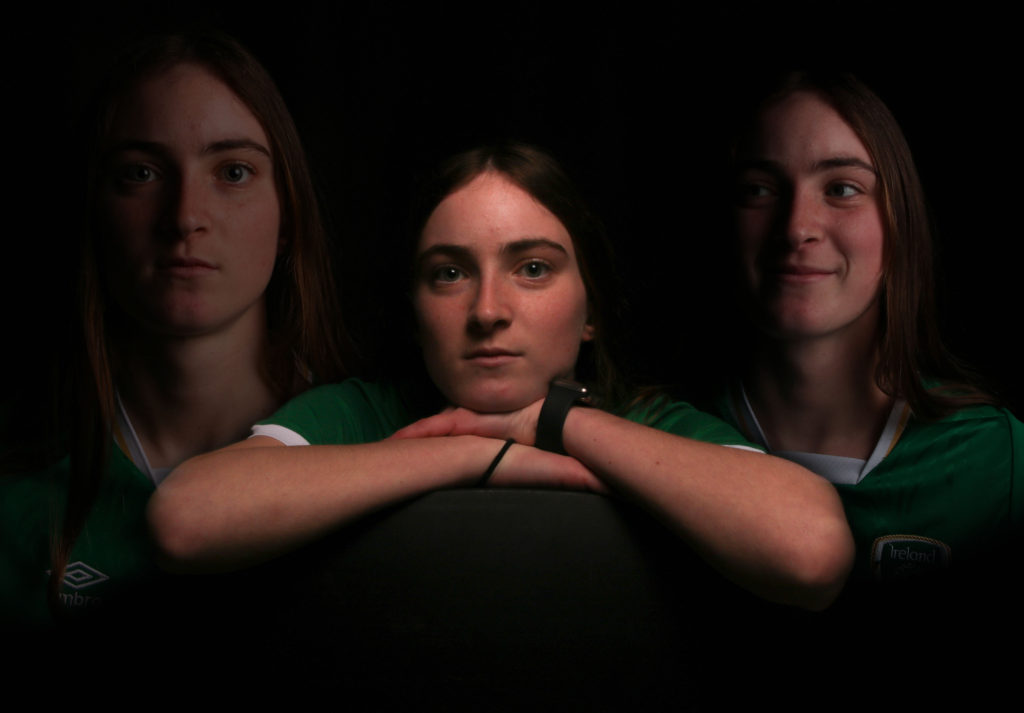
I wanted to experiment further with double exposures in photoshop. For this I took two or more images from the shoot and lowered the opacity, then erased parts that overlapped till I was happy with the outcome.
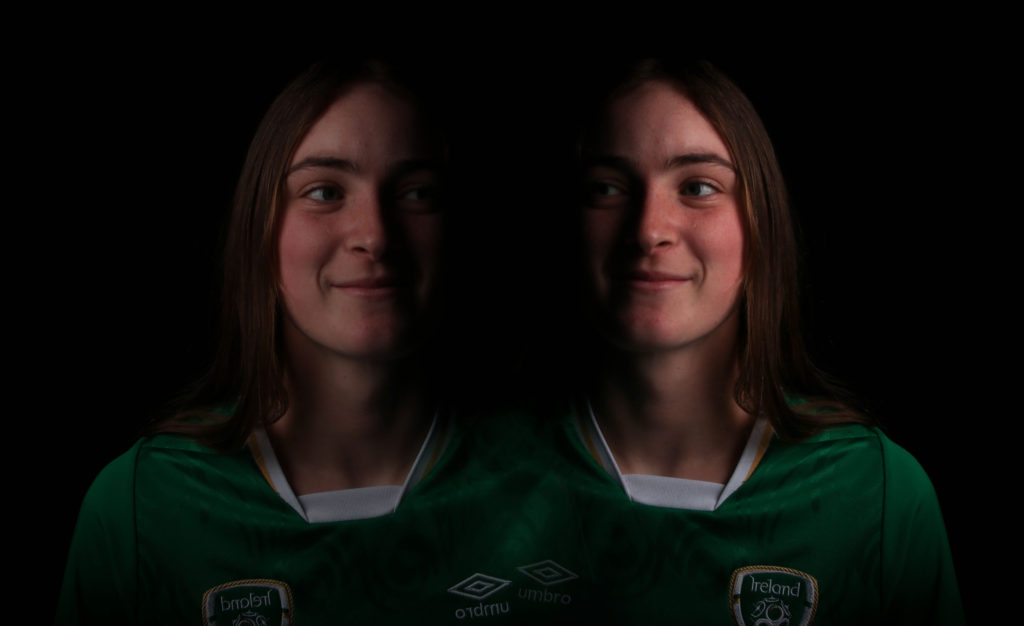


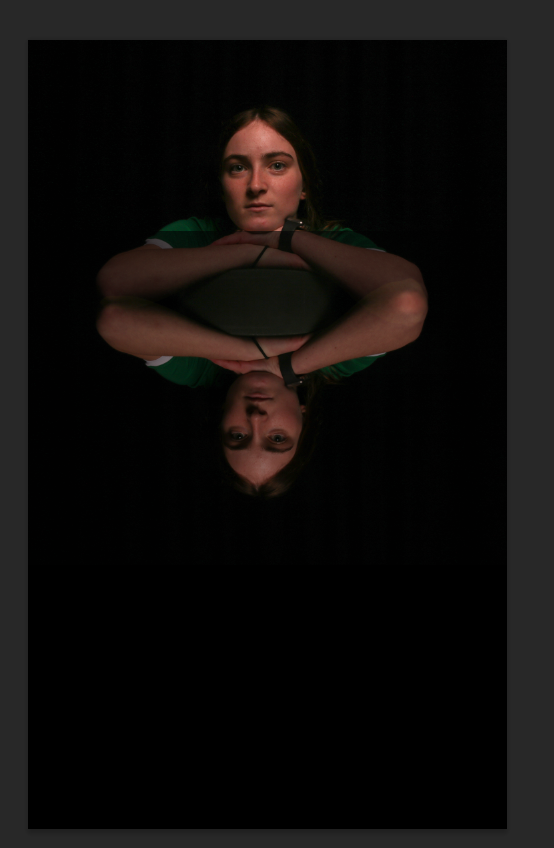
Mirror affect