To embed your understanding of the origins of photography and its beginnings you’ll need to produce a blog post which outlines the major developments and practices. Some will have been covered in the documentary above but you also need to research and discover further information.
Your blog post must contain information about the following and keep it in its chronological order:
- Camera Obscura & Pinhole photography
- Nicephore Niepce & Heliography
- Louis Daguerre & Daguerreotype
- Henry Fox Talbot & Calotype
- Robert Cornelius & self-portraiture
- Julia Margeret Cameron & Pictorialism
- Henry Mullins & Carte-de-Visit
Each must contain dates, text and images relevant to each bullet point above. In total aim for about 1,000-2000 words.
Try and reference some of the sources that you have used either by incorporating direct quotes, paraphrasing or summarising of an idea, theory or concept, or historical fact.
Film notes
-1928, André Kertész’s meudon piece was an eye opener to photography.
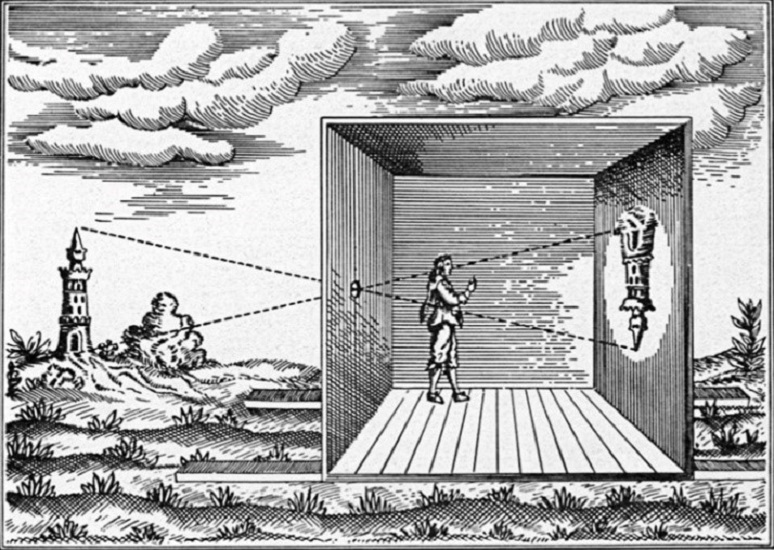
-Camera obscura or pinhole photography is a darkened room with a small hole or lens at one side through which an image is projected onto a wall or table opposite the hole. It is a natural method of creating unique and interesting pieces, in which the room becomes the camera. It is also the origin of photography
-It was well known that certain chemicals are reactive to light, e.g. silver salts. This was firstly used to try to capture images however the pictures would fade away shortly after appearing.
-Henry Fox Talbot was know as the inventor of the first photograph. In 1834 he discovered how to make and fix images through the action of light and chemistry on paper. These ‘negatives’ could be used to make multiple prints and this process revolutionised image making.
-De Geer’s photography style copies the subject onto metal plates, showing incredible detail and being one of the first methods of photography.
-Nicéphore Niépce was one of the most important figures in the invention of photography. He was born in France 1765, and was an amateur scientist, inventor and artist. In 1807, together with his brother, he invented the world’s first internal combustion engine, which they called the pyreolophore.
-Heliography is a photographic process that was invented by Nicéphore Niepce. In some cases – it is still used today (mainly for photo engraving). It was the process of Heliography that created the first and earliest known permanent photograph, taken from a nature scene.
-In February 2014 a daguerreotype self-portrait taken by the American photography pioneer Robert Cornelius of Philadelphia was considered the first American photographic portrait of a human ever produced, and since this was a self-portrait, it was also possibly the first selfie.
-Julia Margaret Cameron was a British photographer who is considered one of the most important portraitists of the 19th century. Pictorialism, an approach to photography that emphasizes beauty of subject matter, tonality, and composition rather than the documentation of reality.
Essay
The very first type of photography ever invented was the camera obscura or pinhole photography. This method was created by Alhazen or Ibn Al-Haytham, as well as the pinhole camera which is based on the same idea. He carried out experiments with candles and described how the image is formed by rays of light travelling in straight lines. In order to accomplish camera obscura is to use a darkened room with a small hole or lens at one side, through which an image is projected onto a wall or table opposite the hole. It is a natural method of creating unique and interesting pieces, in which the room becomes the camera. It is also the very first showcase of being able to copy scenery from one place to another.
Moving on to Heliography. It is a photographic process that was invented by Nicéphore Niepce. It was this process that created the first and earliest known permanent photograph, taken from a nature scene. It is still sometimes used today, although mainly for photo engraving. In order to create a heliograph, traces of solar energy are burnt into the film material using self-constructed devices and lenses with a diameter of up to one meter. Afterwards, the shots are then enlarged and printed on either; paper, the film sheets are directly shown in lightboxes, or the film slides themselves are projected onto hangar-sized walls.

Next in the timeline is Louis Daguerre and his Daguerreotype of photography. Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre was a French artist and photographer who invented a new process to photography. The daguerreotype was the first commercially successful photographic process from 1839 to 1860 made it possible to capture the image seen inside a camera obscura and preserve it as an object. This meant it was the first practical photographic process, and it ushered in a new age of pictorial possibility. In order to make a daguerreotype the silver-plated copper plate had first to be cleaned and polished until the surface looked like a mirror and was to be handled with great care. The plate, held in a lightproof holder, was then transferred to the camera. After exposure to light, the plate was developed over hot mercury until an image appeared. To fix the image, the plate was immersed in a solution of sodium thiosulfate or salt and then toned with gold chloride. While being an impressive discovery and process, it was incredibly toxic to humans due to the number of dangerous chemicals involved, including mercury, cyanide, and sulfuric acid.
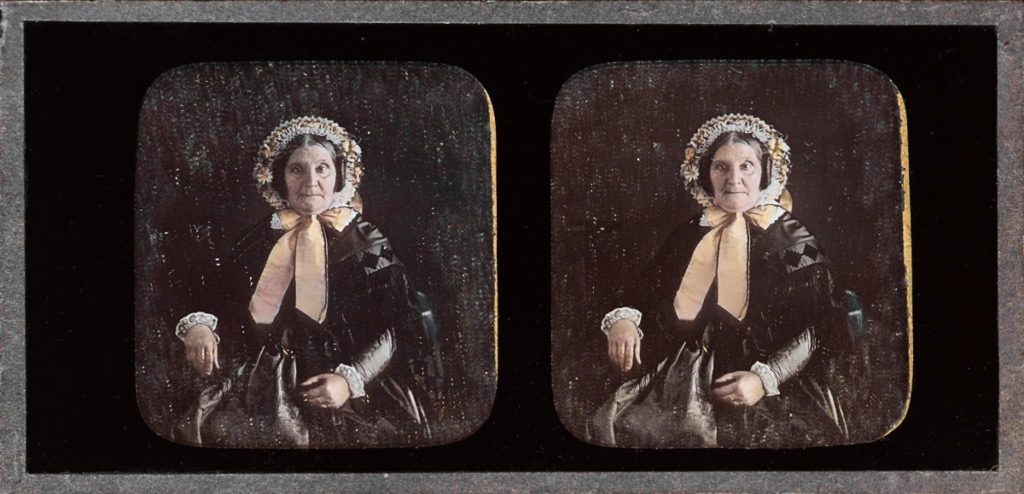

After Daguerre, Henry Fox Talbot created a new method of photography called the Calotype. William Henry Fox Talbot was an English scientist, inventor, and photography pioneer who invented the salted paper and calotype processes, precursors to photographic processes of the later 19th and 20th centuries. He was born on February 11, 1800, and died 77 years later on September 17, 1877. Calotype or talbotype is an early photographic process introduced in 1841 using paper coated with silver iodide. Paper texture effects in calotype photography limits the ability of this early process to record low contrast details and textures. To produce a calotype, Talbot created a light-sensitive surface by coating a sheet of paper, usually writing paper, with a solution of silver nitrate. He dried the paper to some degree and coated it with potassium iodide to produce silver iodide. Compared to the daguerreotype, many people saw the calotypes differences as flaws. The process was slower, and chemicals weren’t regulated and often impure which led to inconsistent results. Also, the fixing of an image was still a problem, as prints often faded over time.

Robert Cornelius was an American photographer and pioneer in the history of photography. He designed the photographic plate for the first photograph taken in the United States, which was an image of Central High School taken by Joseph Saxton in 1839. Cornelius shot the first successful portrait, a self-portrait to be exact, using the venerable daguerreotype as well as his own makeshift camera with the lense being made out of opera glass. He took advantage of the light outdoors to get a faster exposure but still had to stand motionless for around 15 to 20 mins. He became the first ever self-portrait photographer.

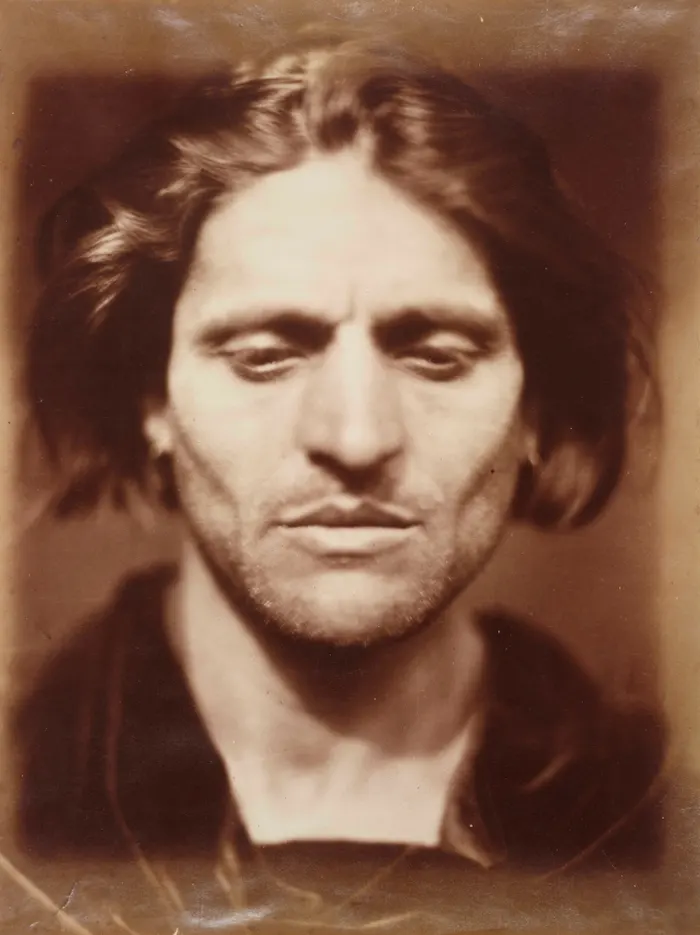
Julia Margaret Cameron was a British photographer who is considered one of the most important portraitists of the 19th century. She was an ambitious and devoted pioneer of photography who was best known for her powerful portraits often using the style of pictorialism. Born on June 11th, 1815, in India she would later pass on January 26rh 1879. Pictorialism, an approach to photography that emphasizes beauty of subject matter, tonality, and composition rather than the documentation of reality. Cameron and her pictorialist contemporaries pursued painterly compositions, subjects, and qualities, hoping to elevate photography to a high art, a representation of a person or thing in a work of art. She revolutionised photography and immortalised the age of the eminent Victorian through her monumental photographs with her use of muzzy focus and dramatic lighting (including both sunshine and moonlight) against voluminous dark, her portraits were extremely famous in their day and have never gone out of style.

Henry Mullins was the first professional photographer to come to Jersey and establish a portraiture business in the very early days of photography. He is best known for his cartes de visite which were small photographic portraits of a person that were mounted on a piece of card. They were very popular as well as being very inexpensive. In 1864, the cost for these photos were between 25 cents and 50 cents in addition to the 3 cents tax. The cost would be equal to £3.17 to £6.30 today. While he mainly worked on portrait photographs, he would also take some family photos too.

