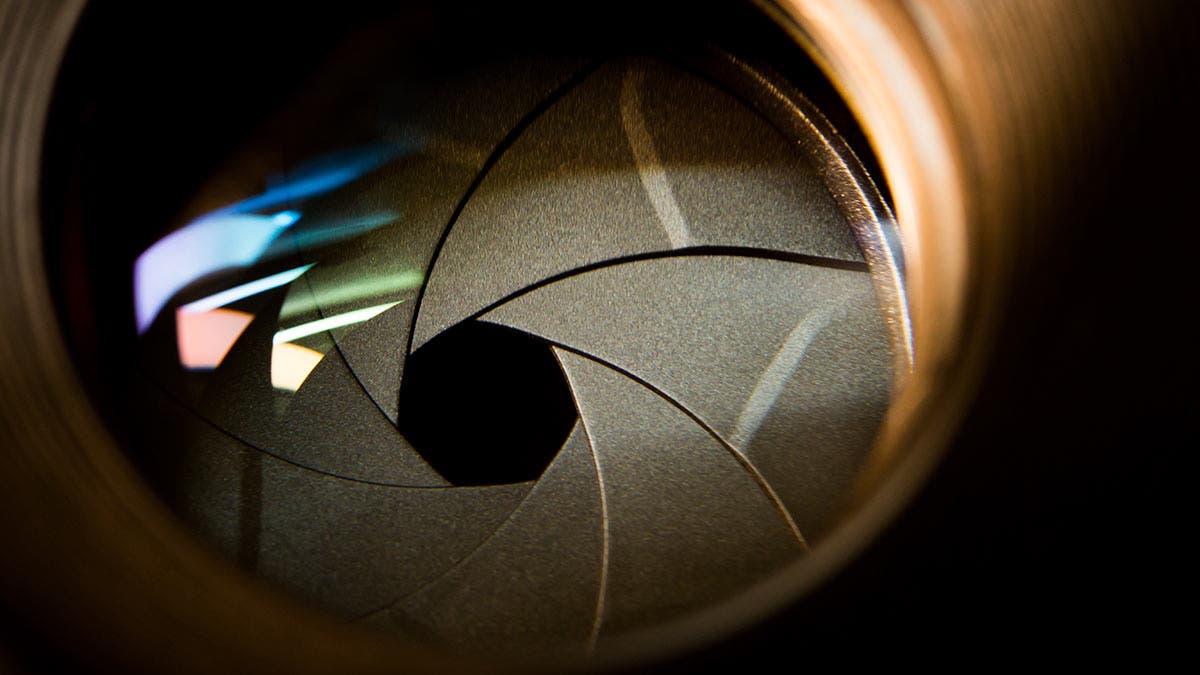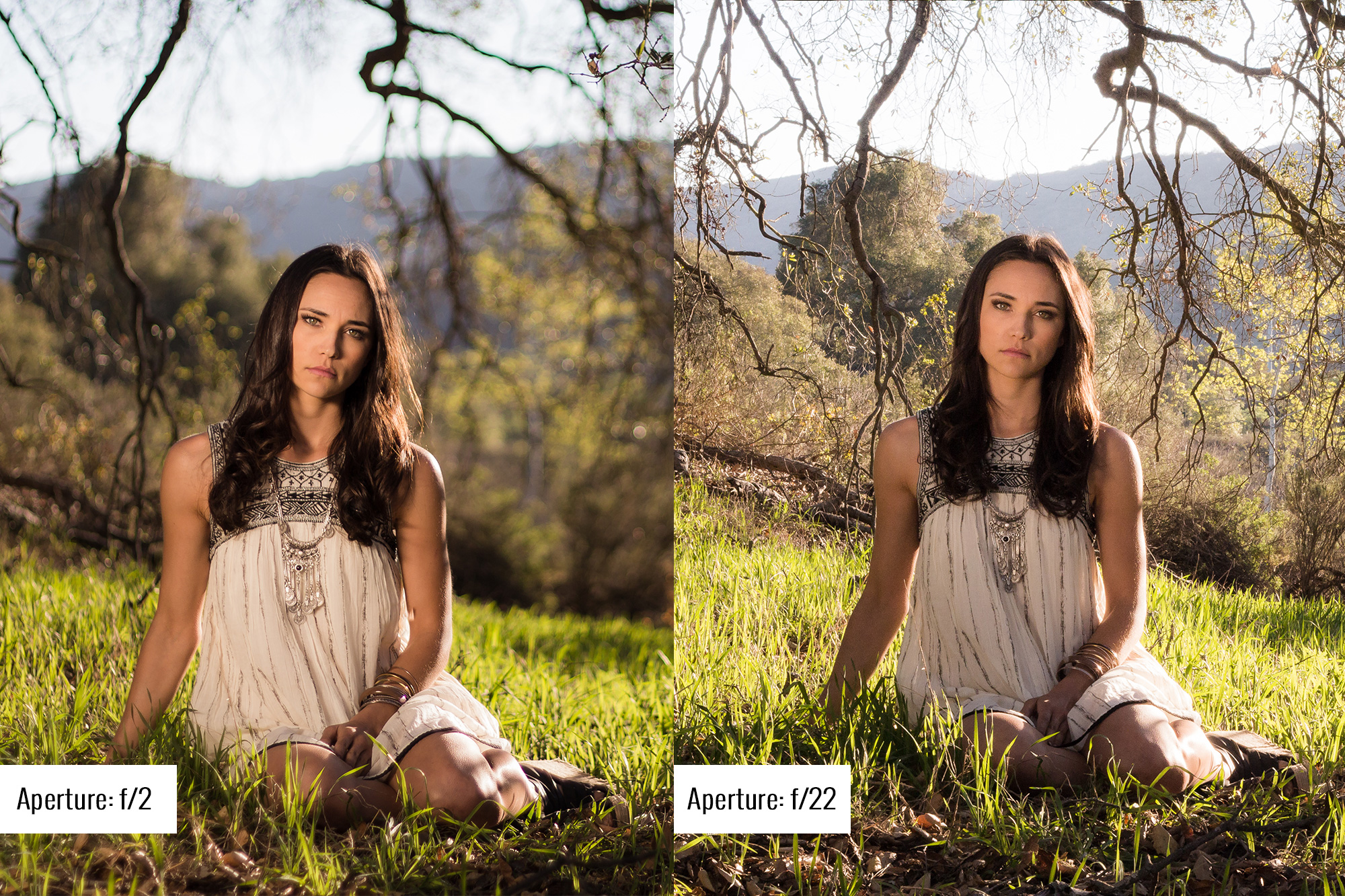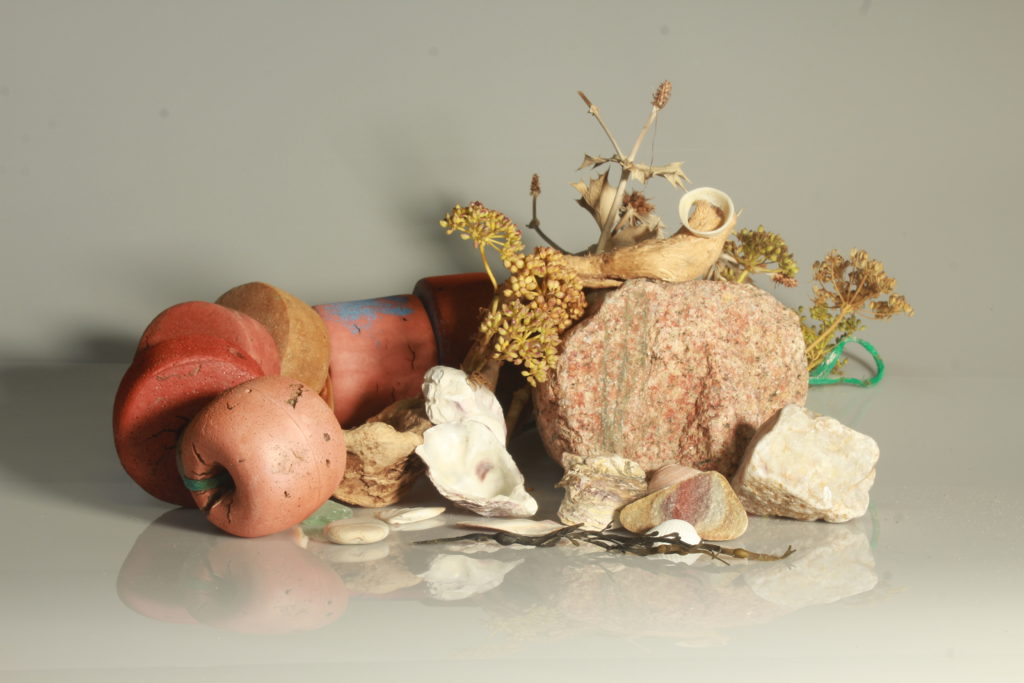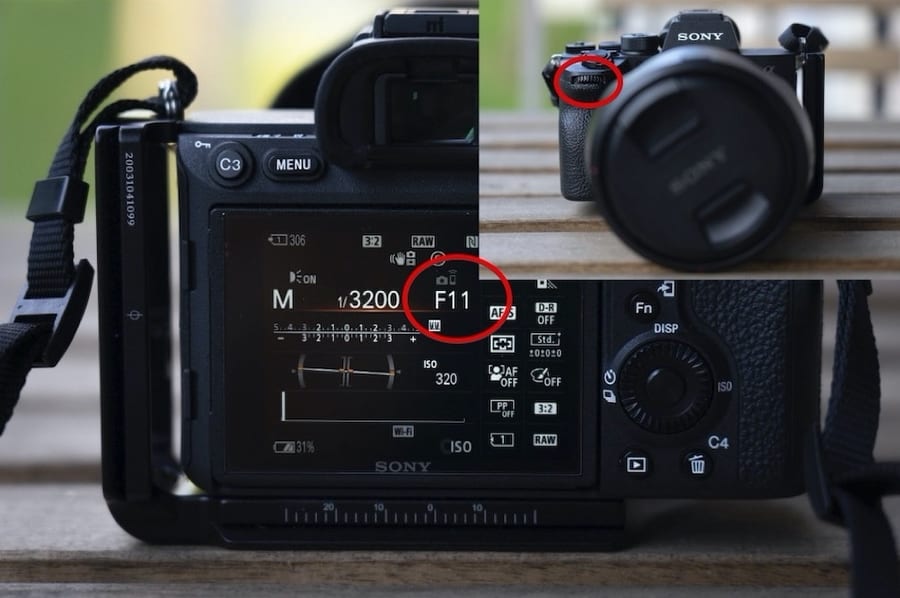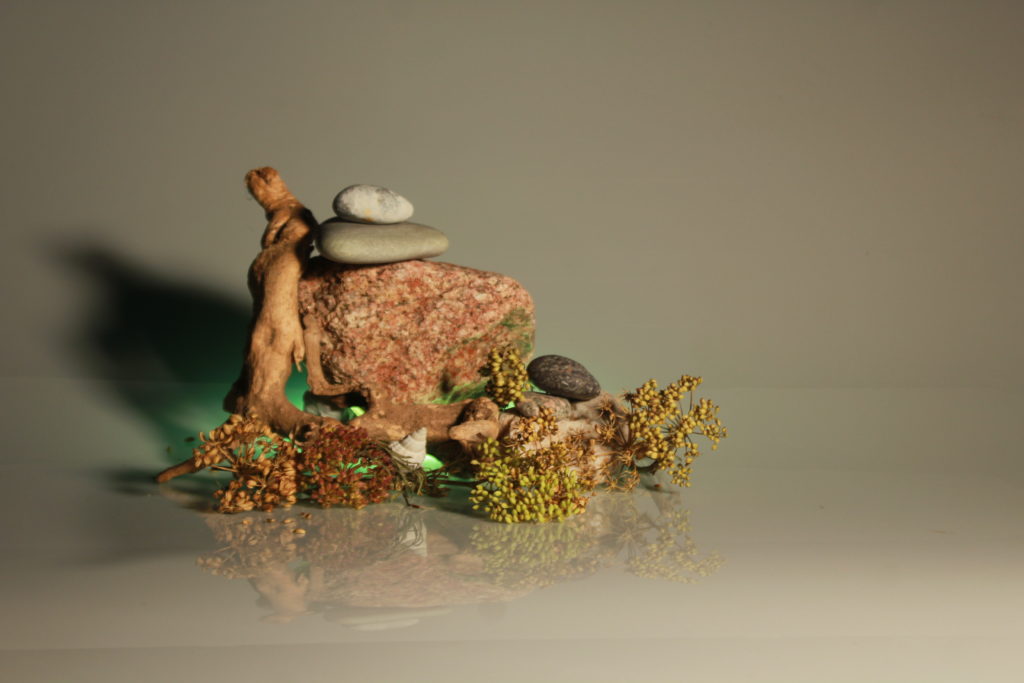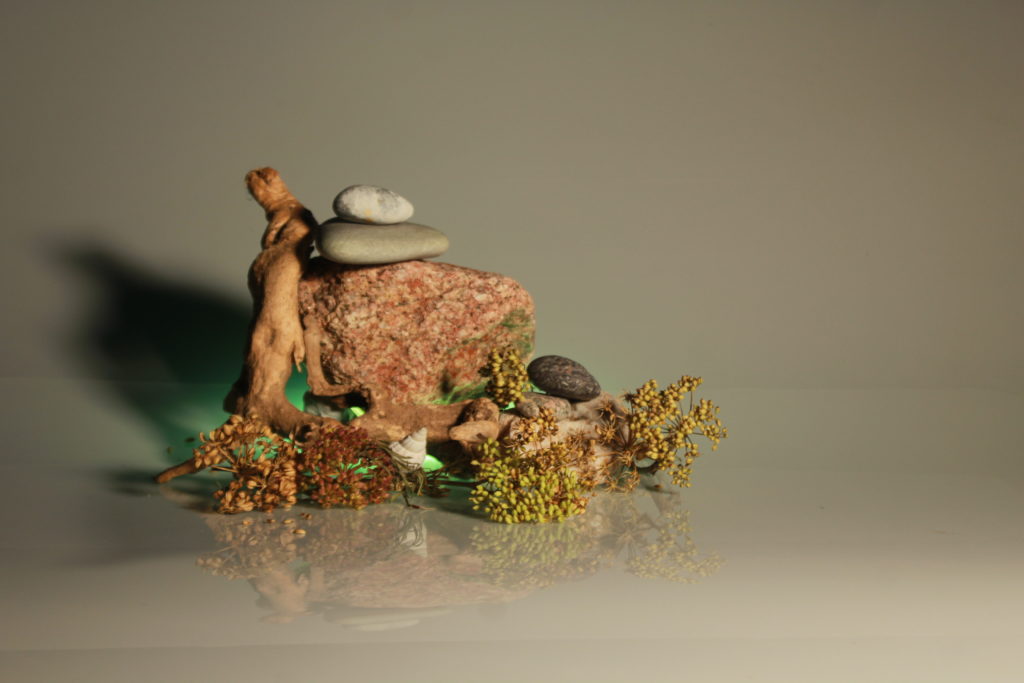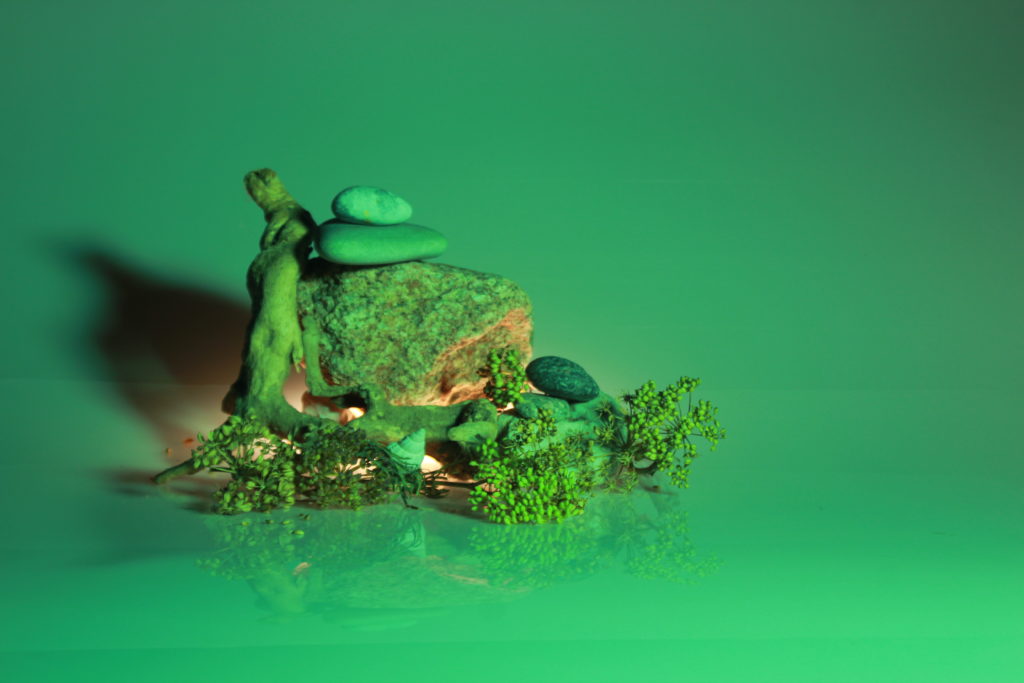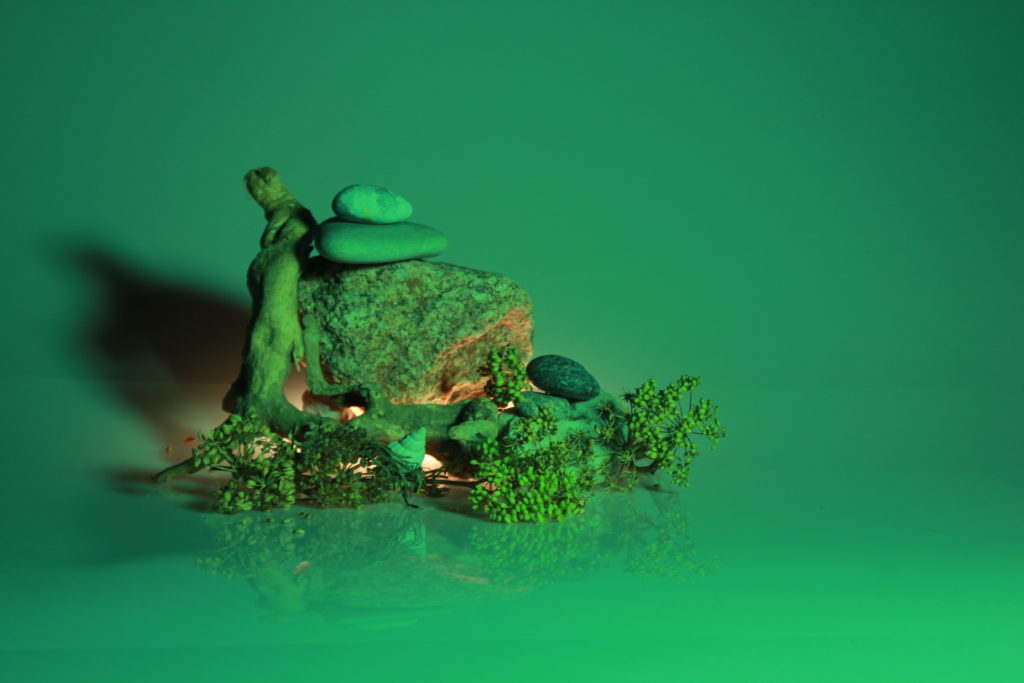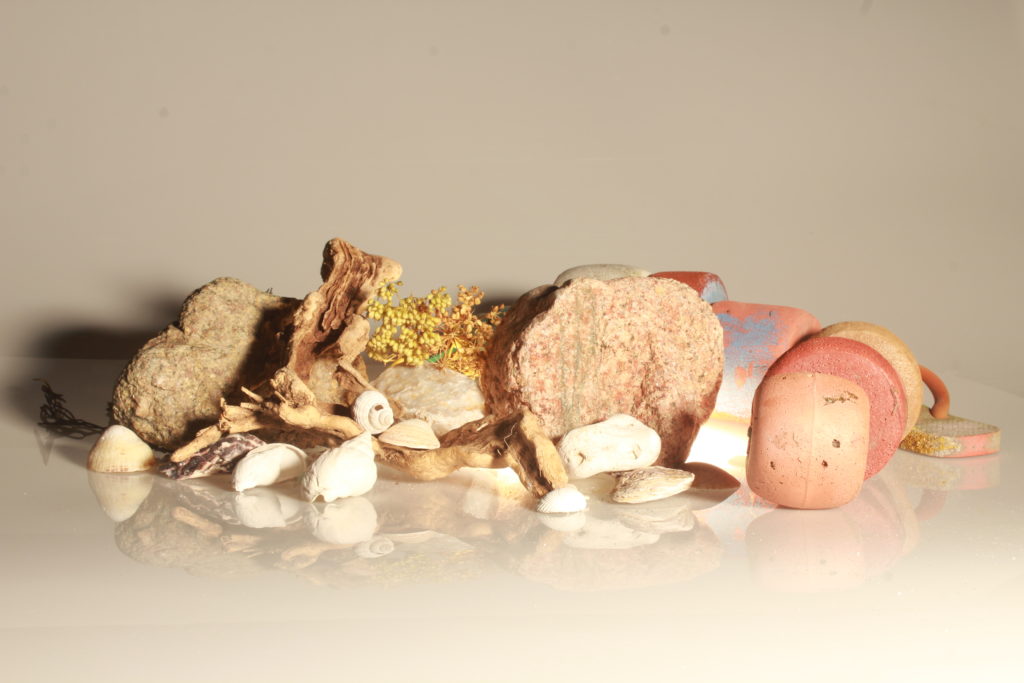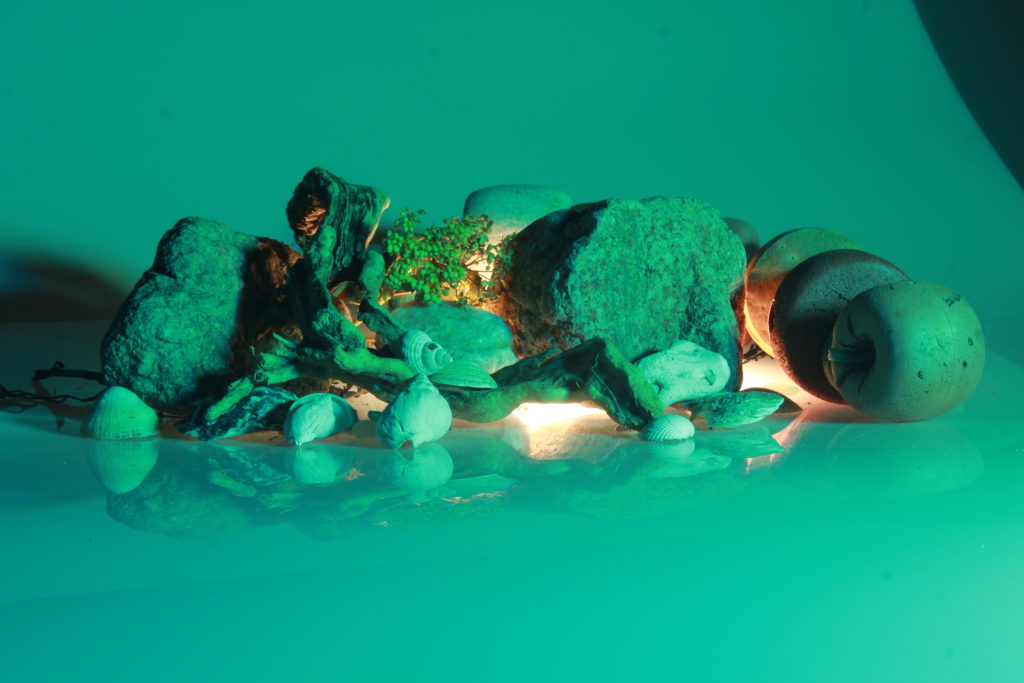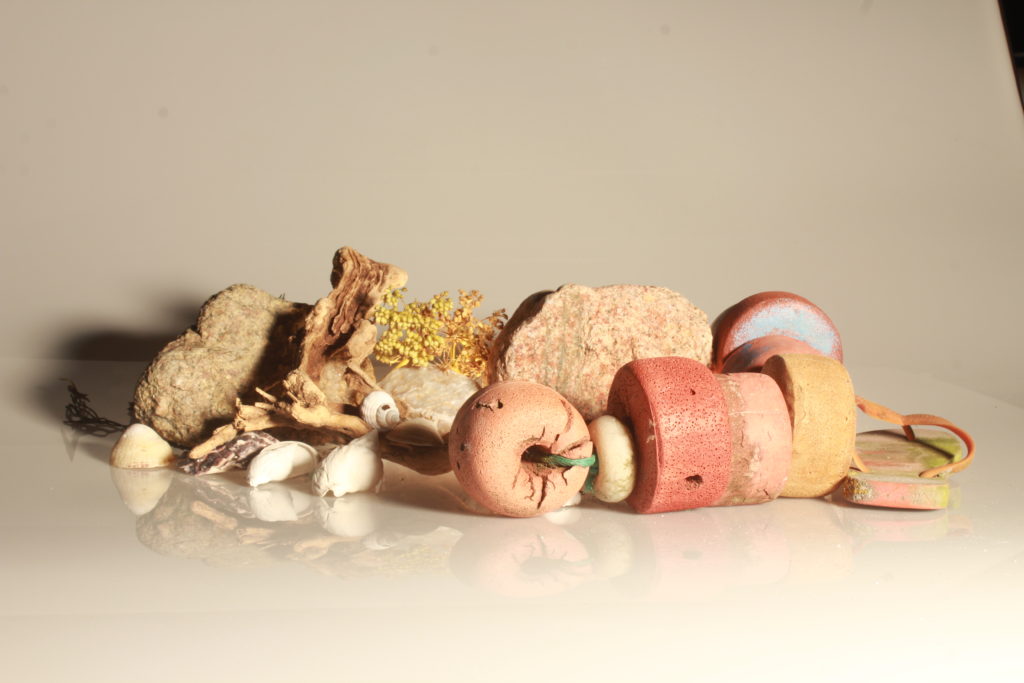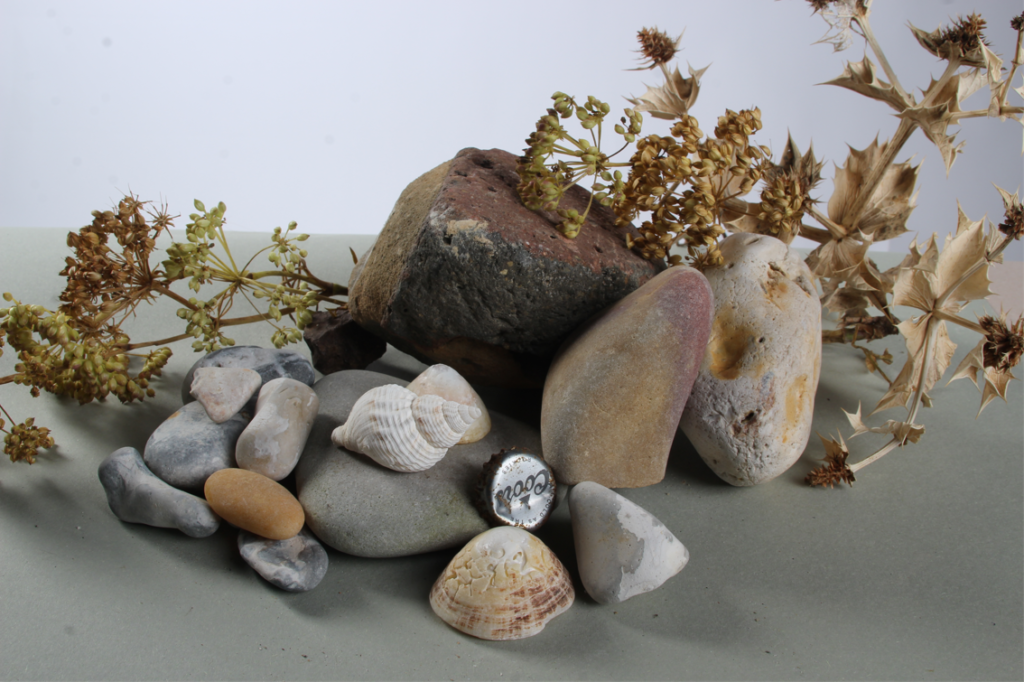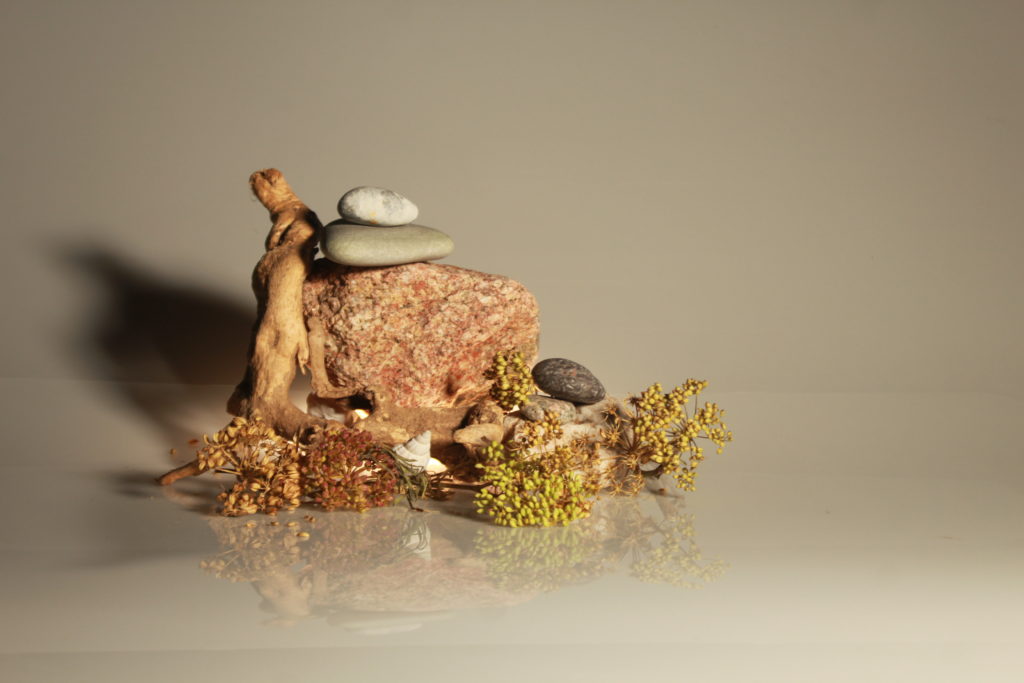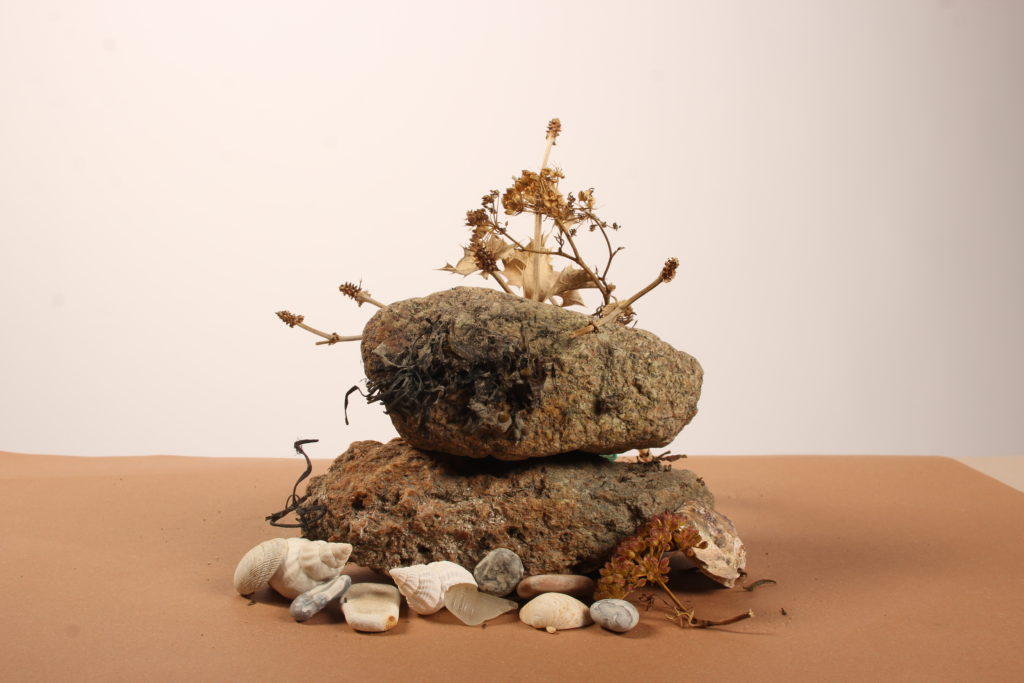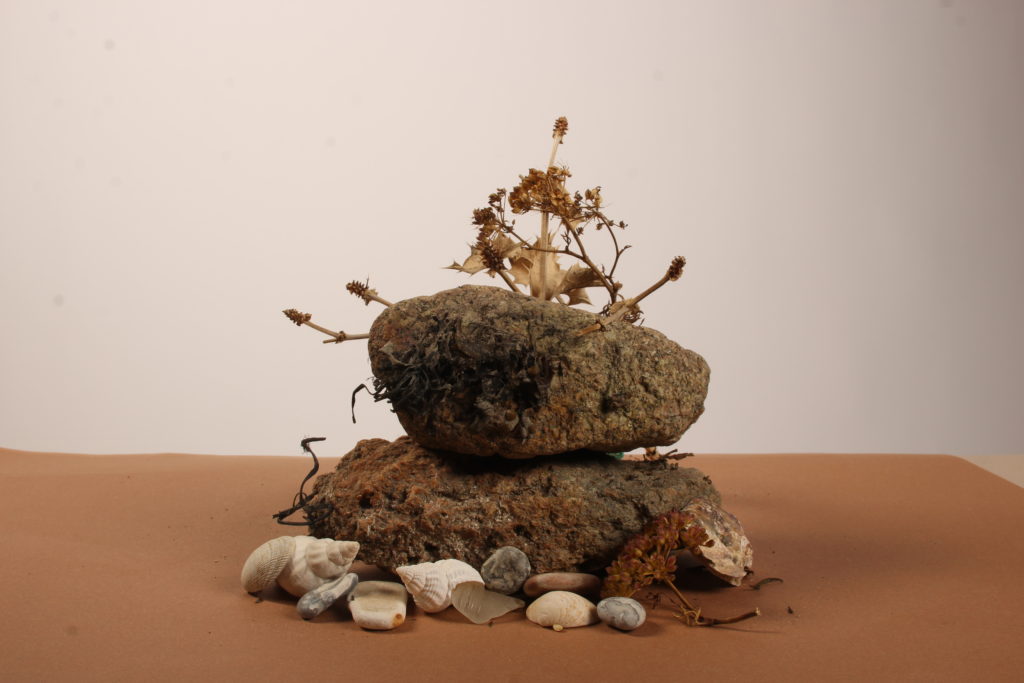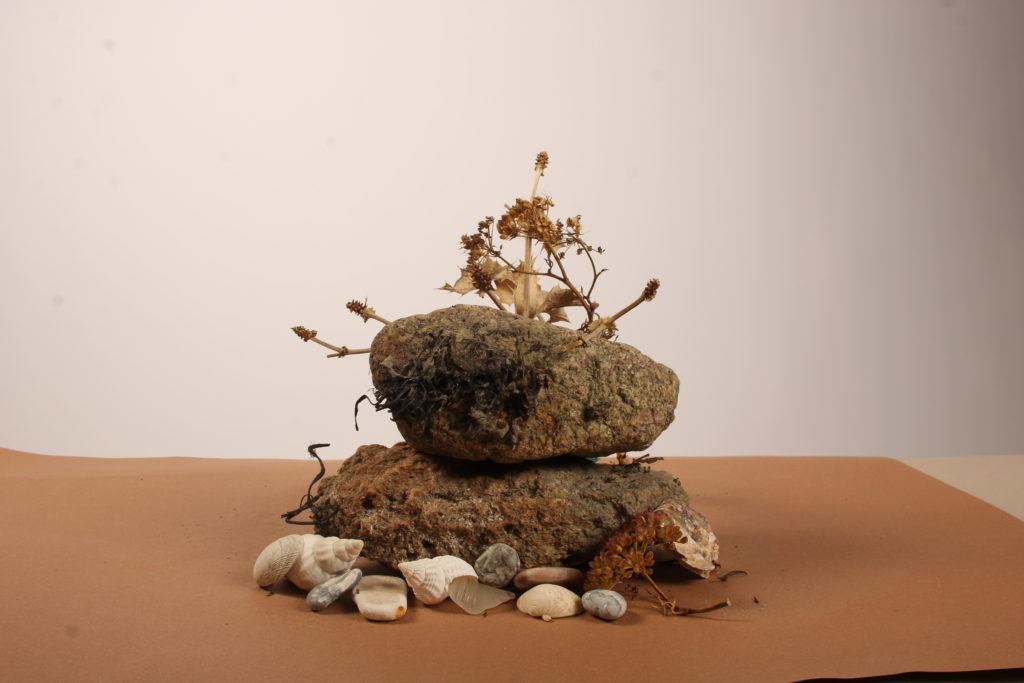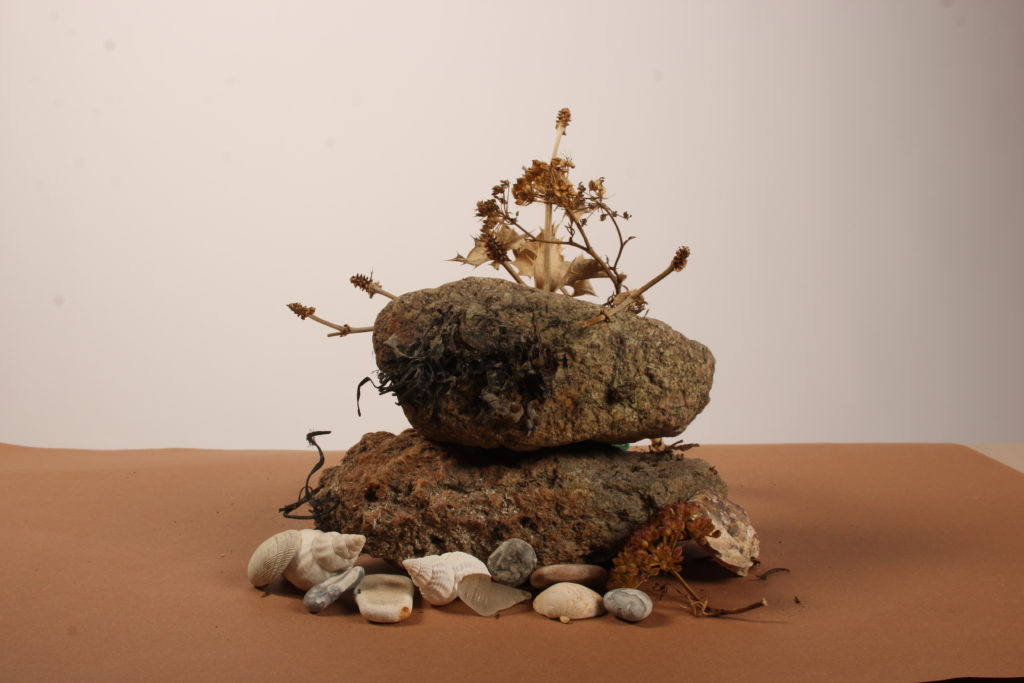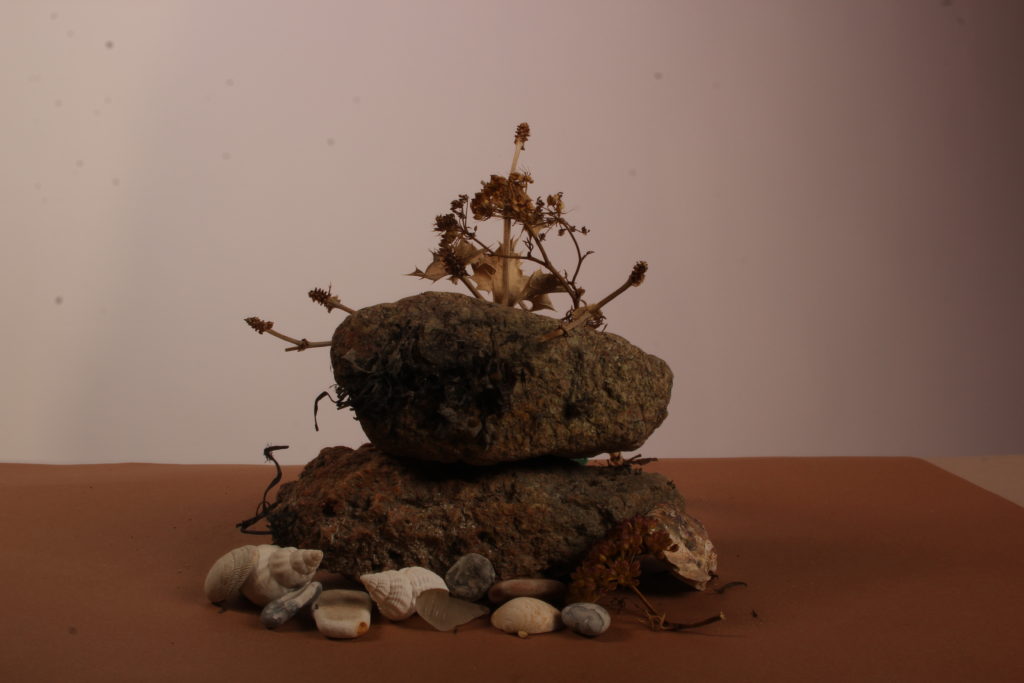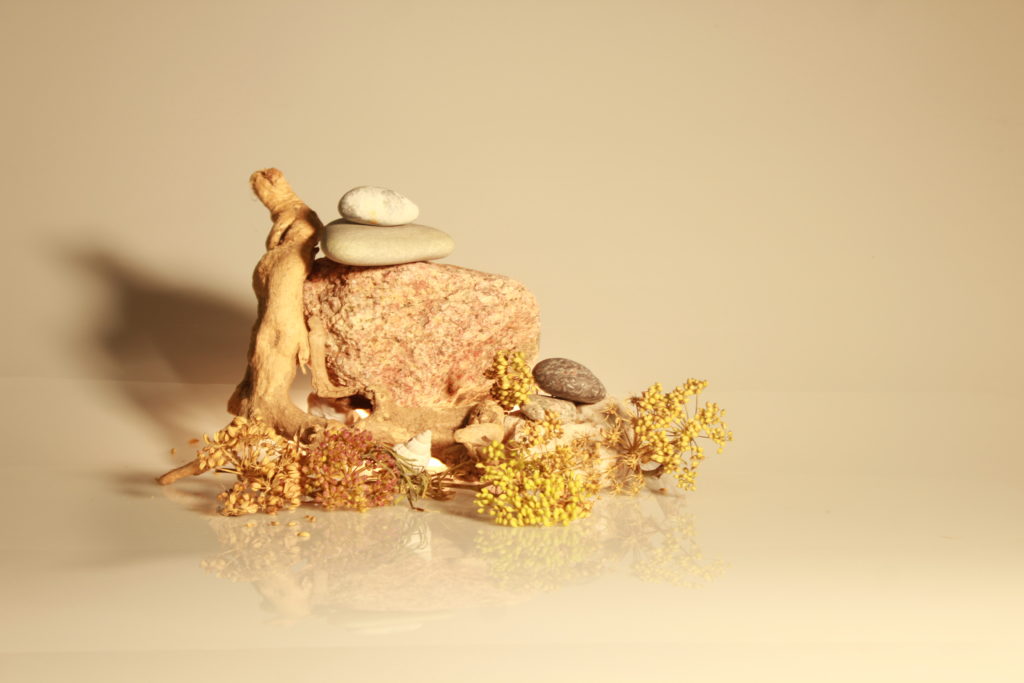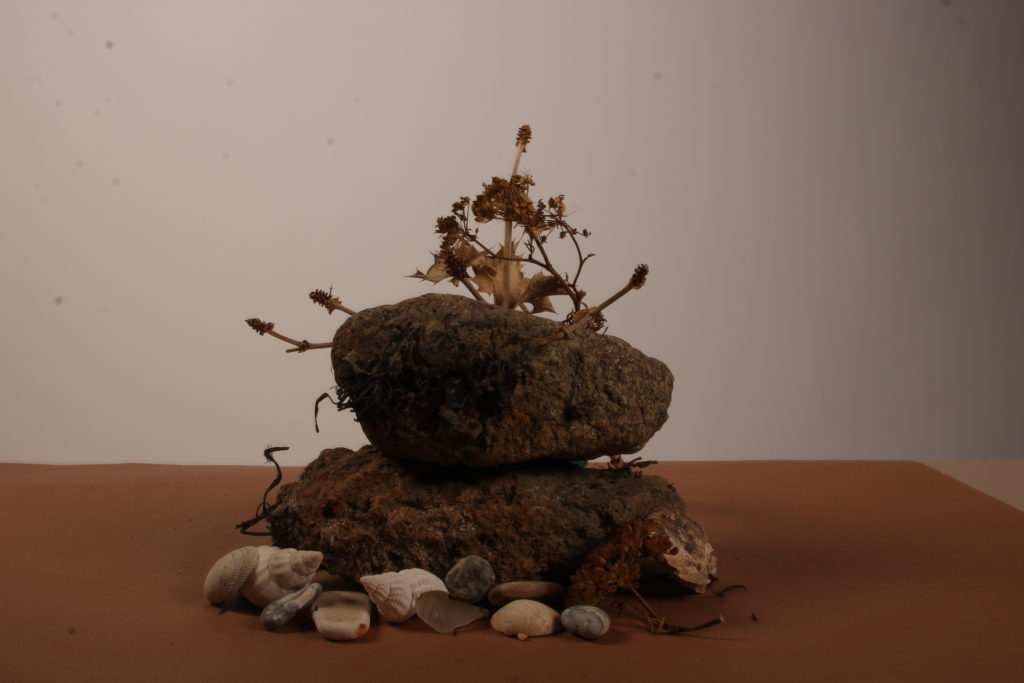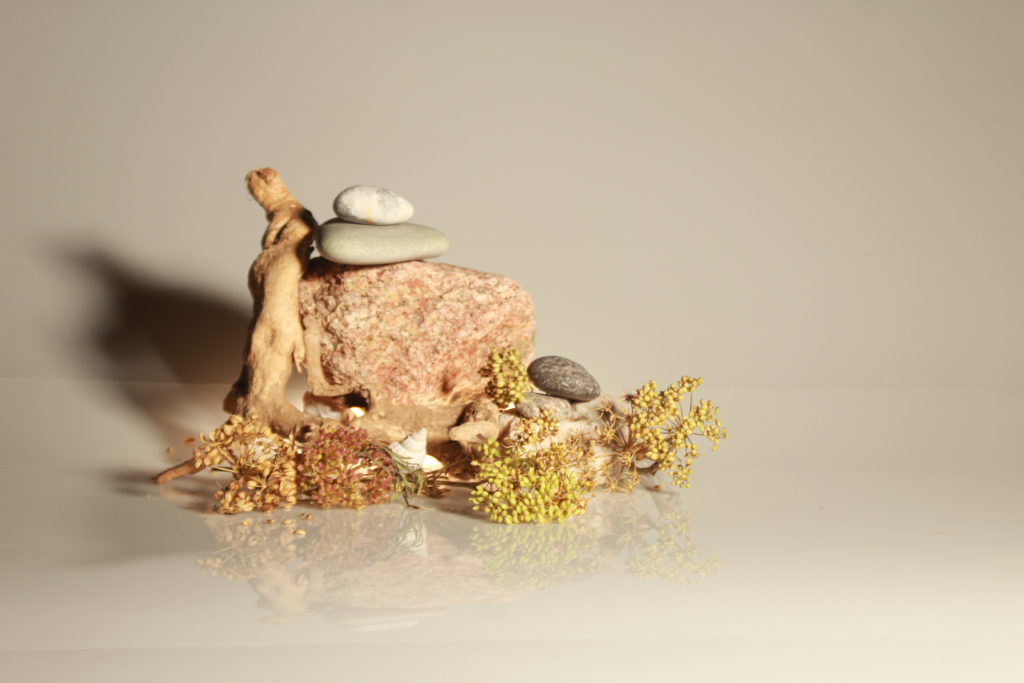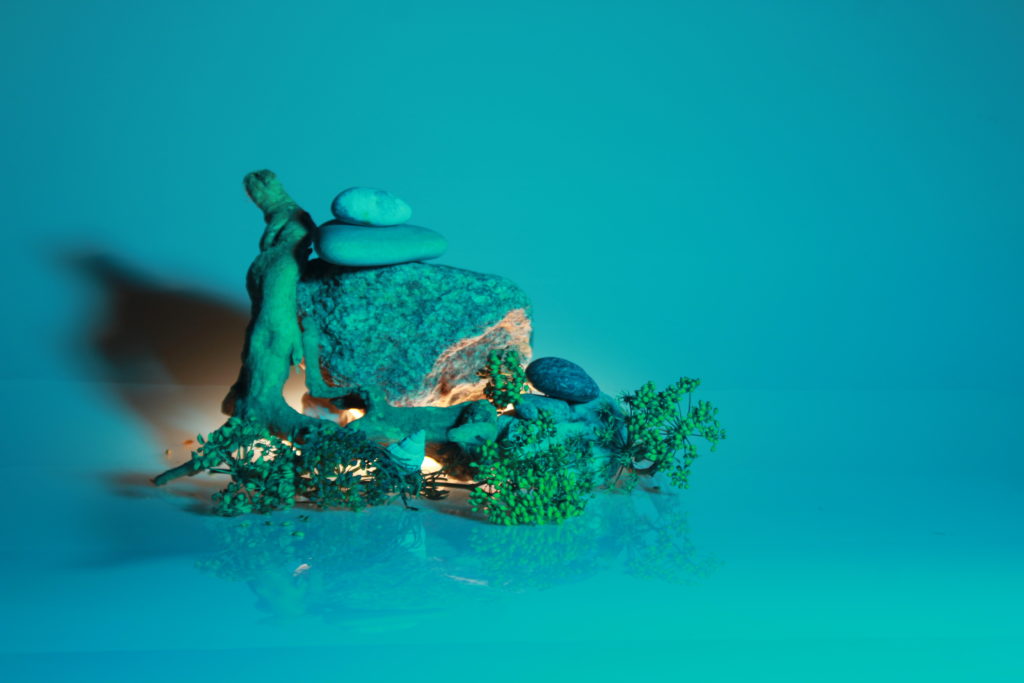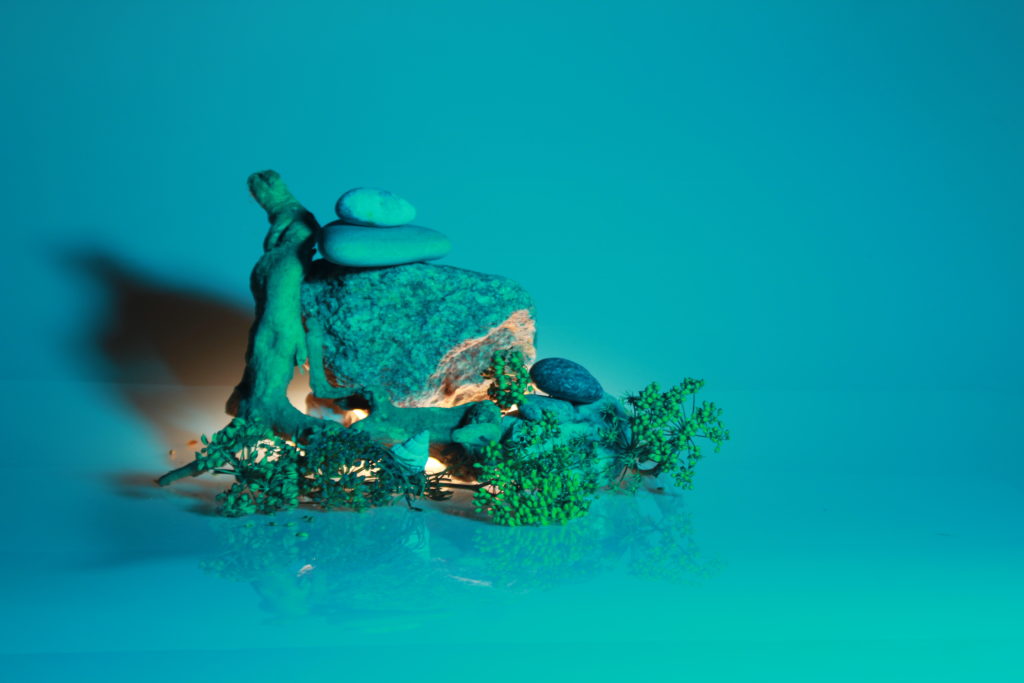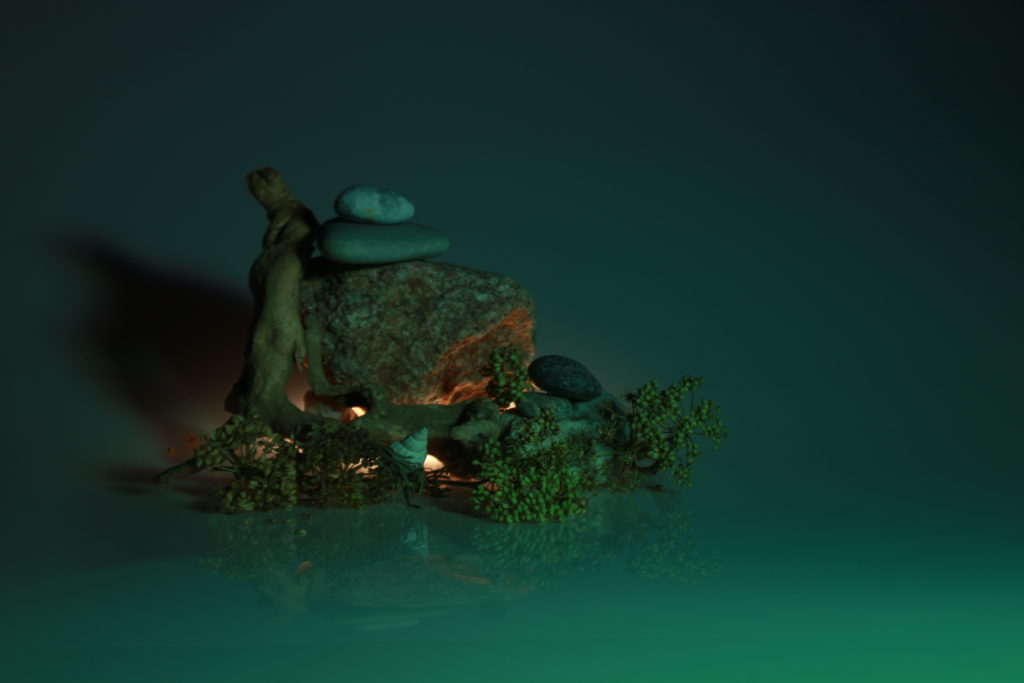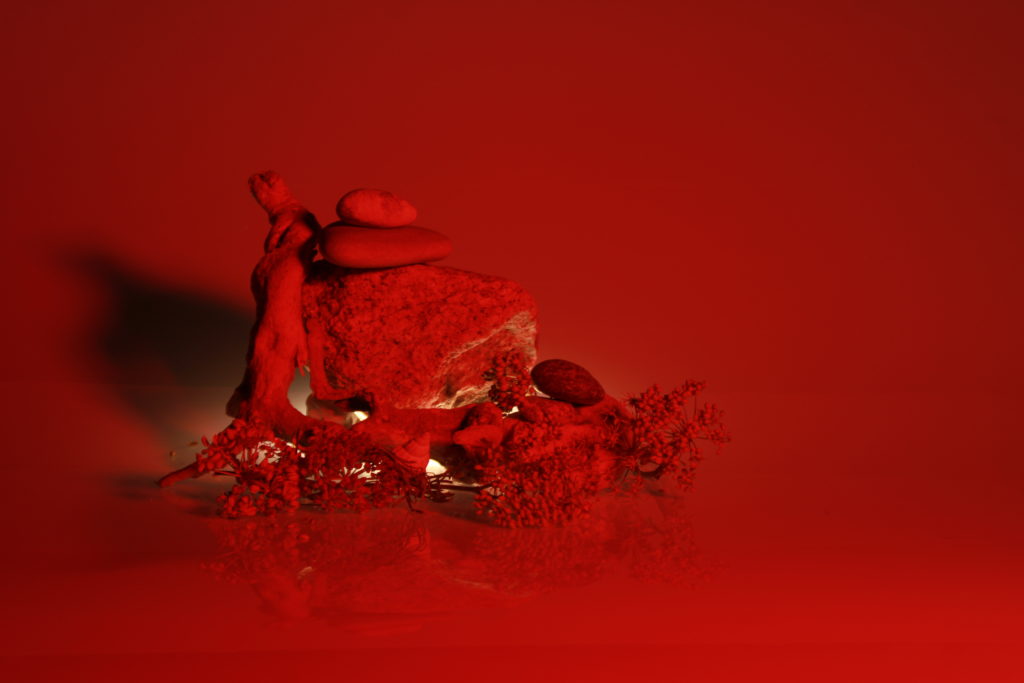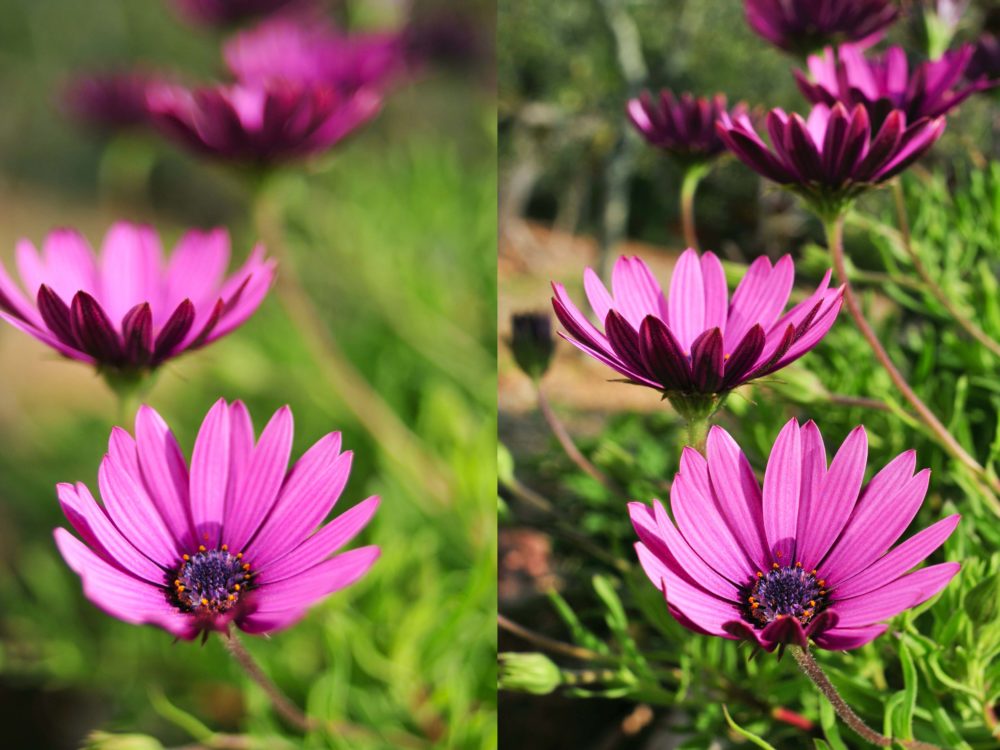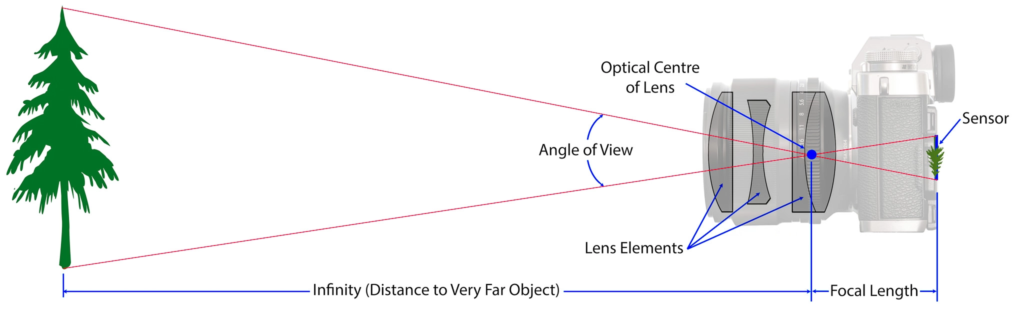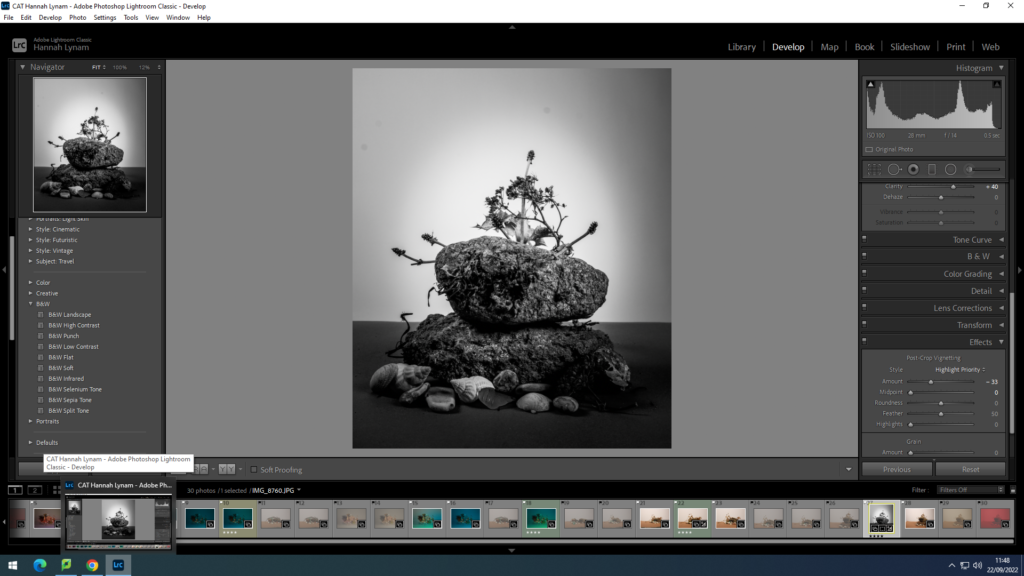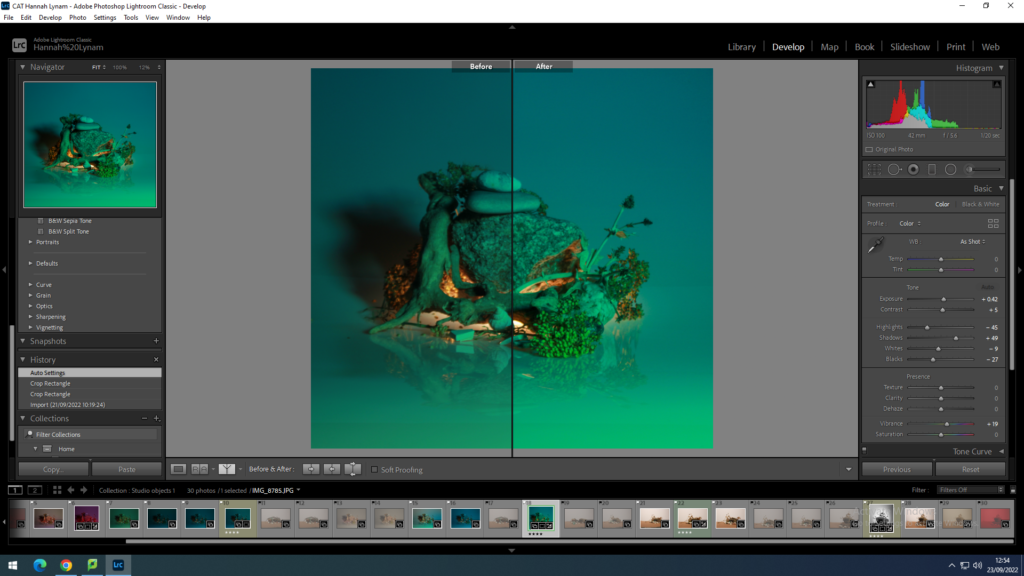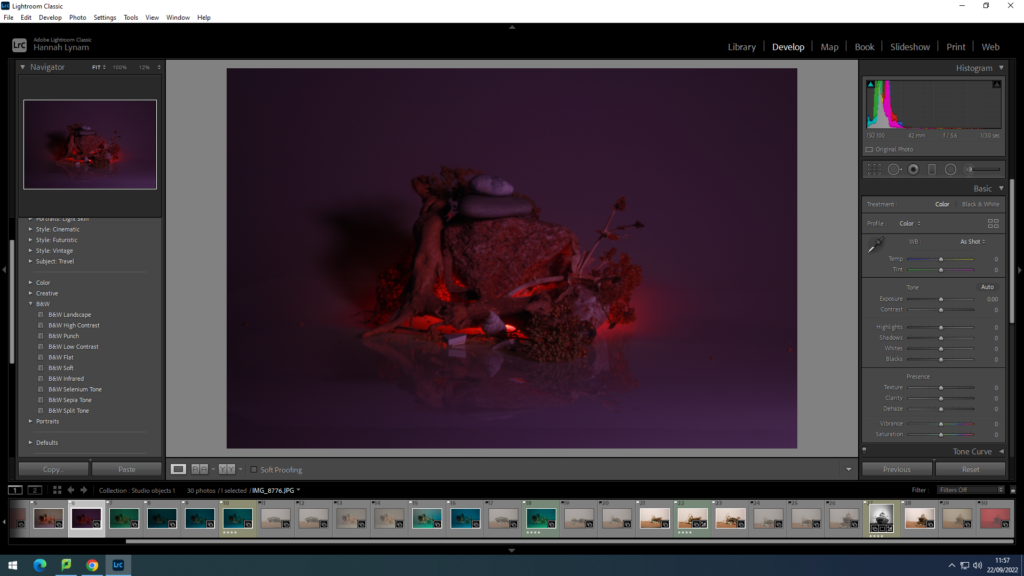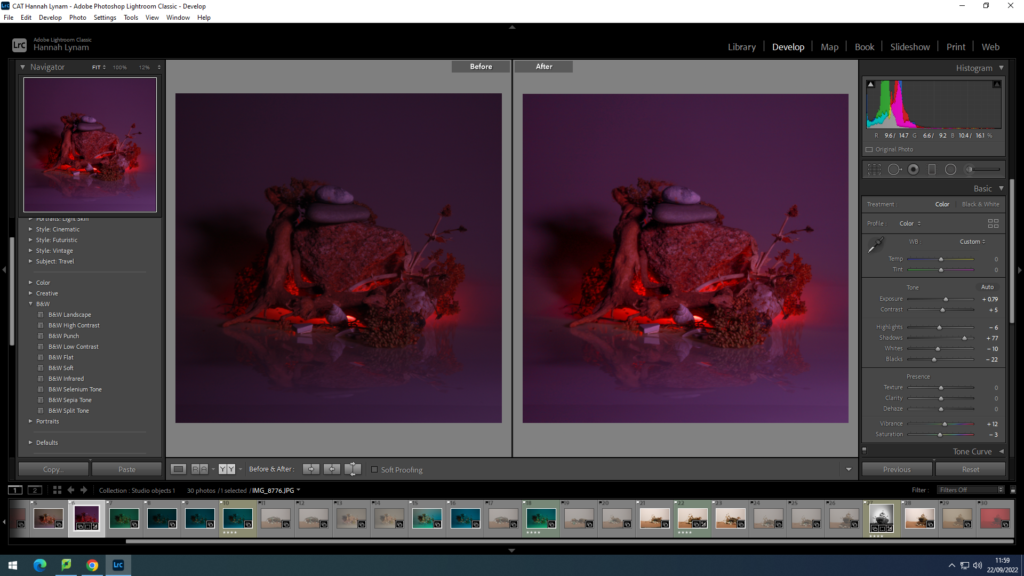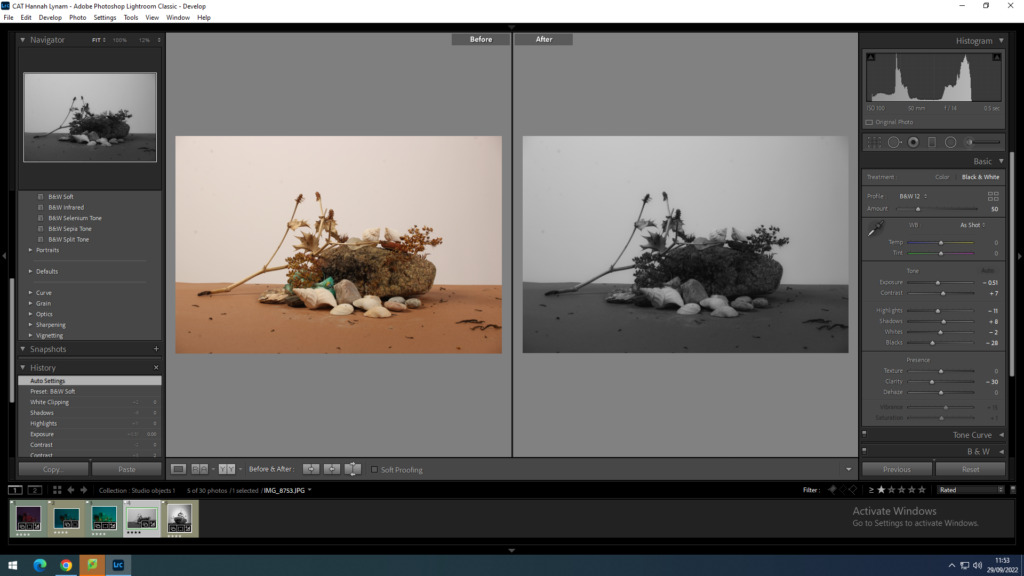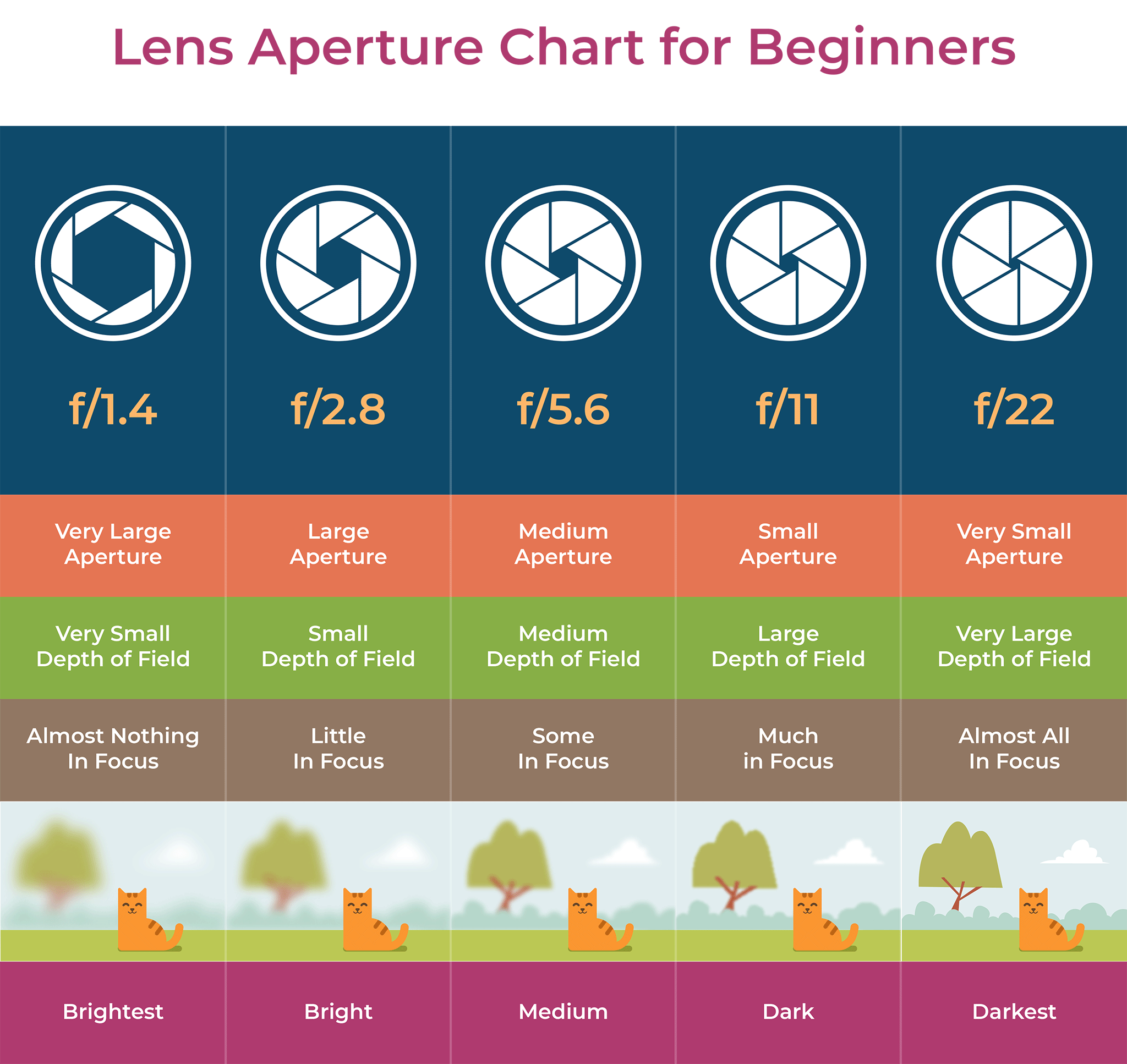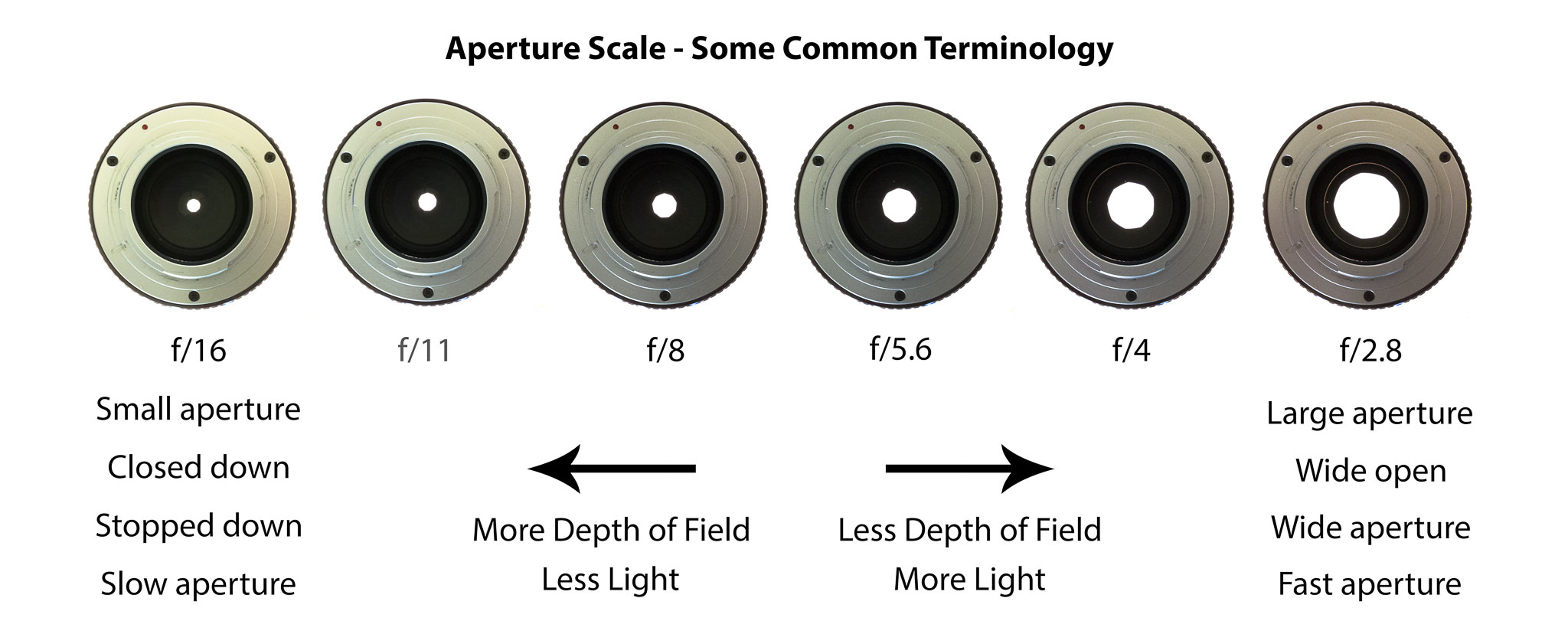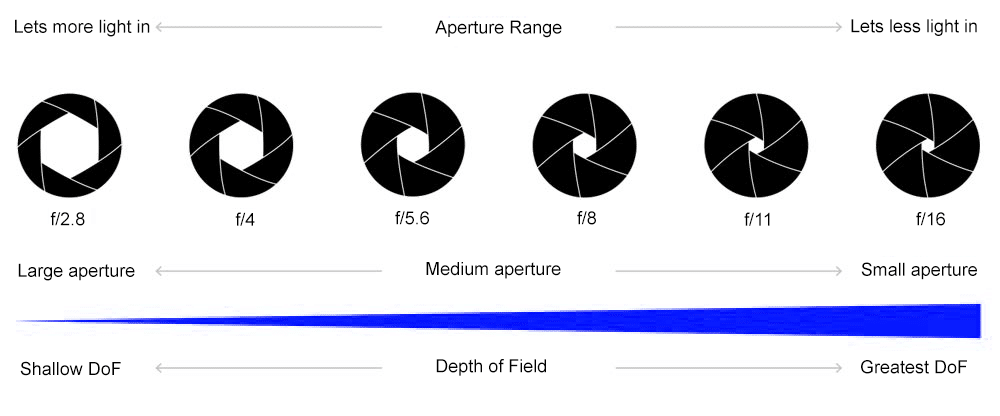
In photography, depth of field refers to the range of distance within an image that appears to be in focus. This effect is created by adjusting the aperture of the camera’s lens, which controls the amount of light that hits the camera’s sensor. Wider apertures – such as f/1.8 – will result in shallower depths of field, whereas a narrow aperture – such as f/16 – will leave the final image with a deeper depth of field.
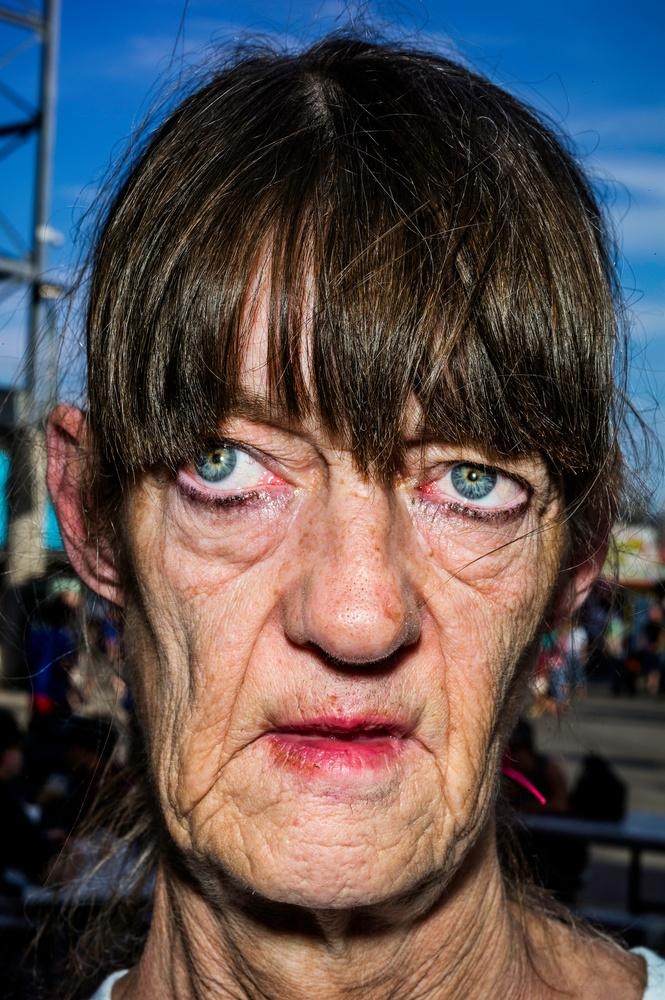

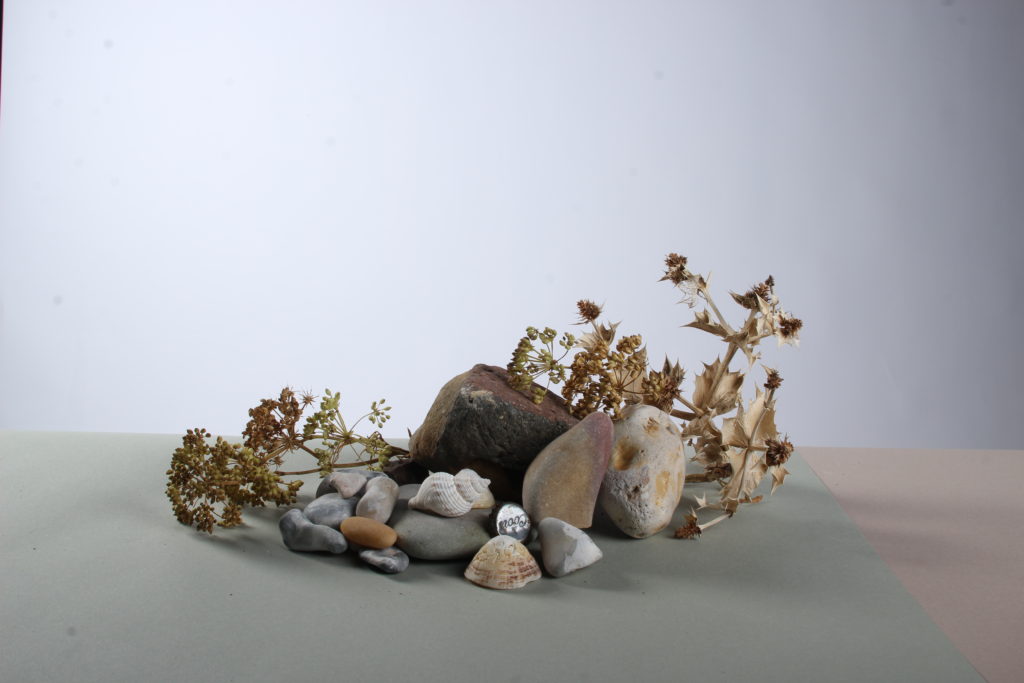
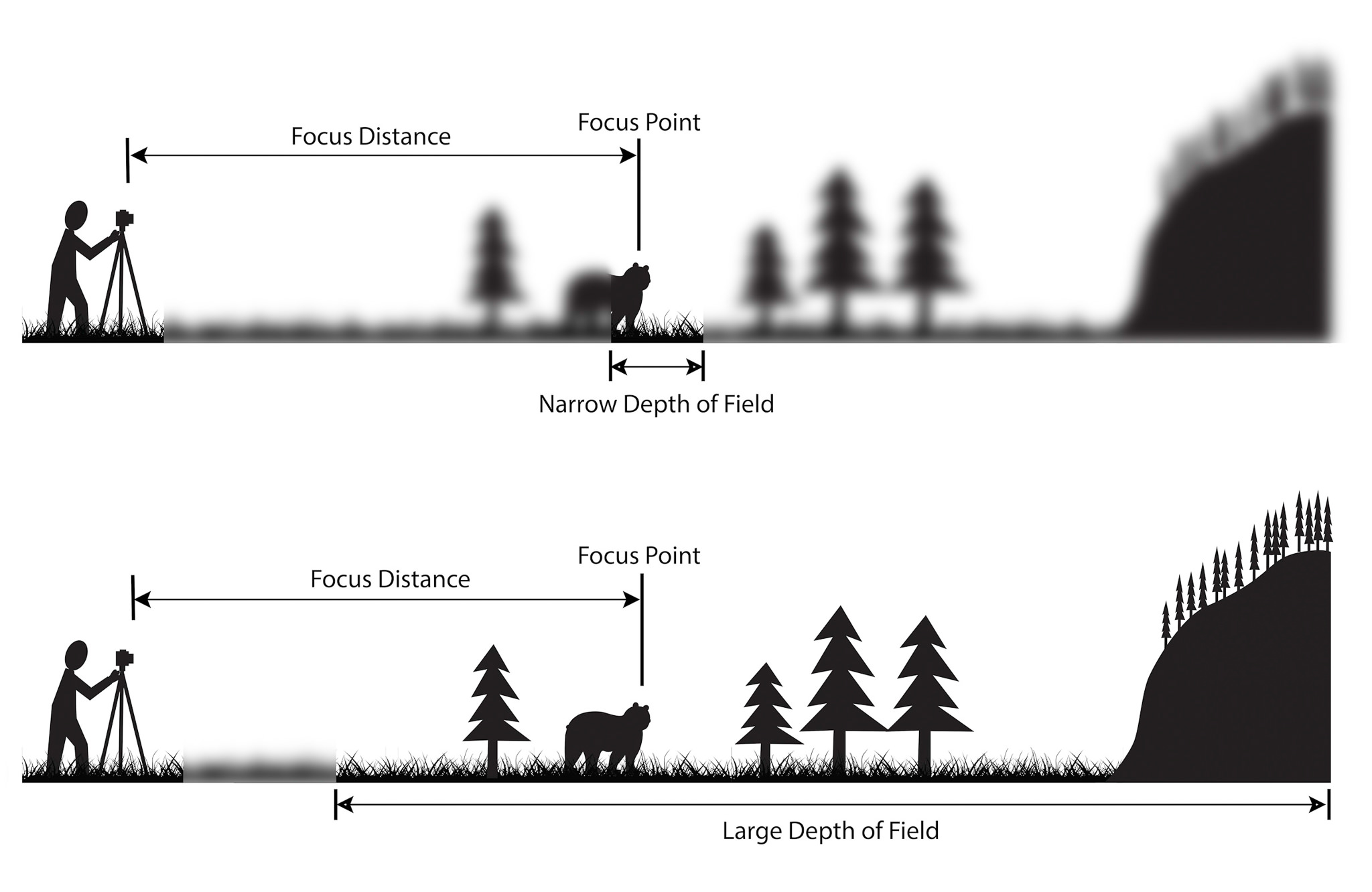
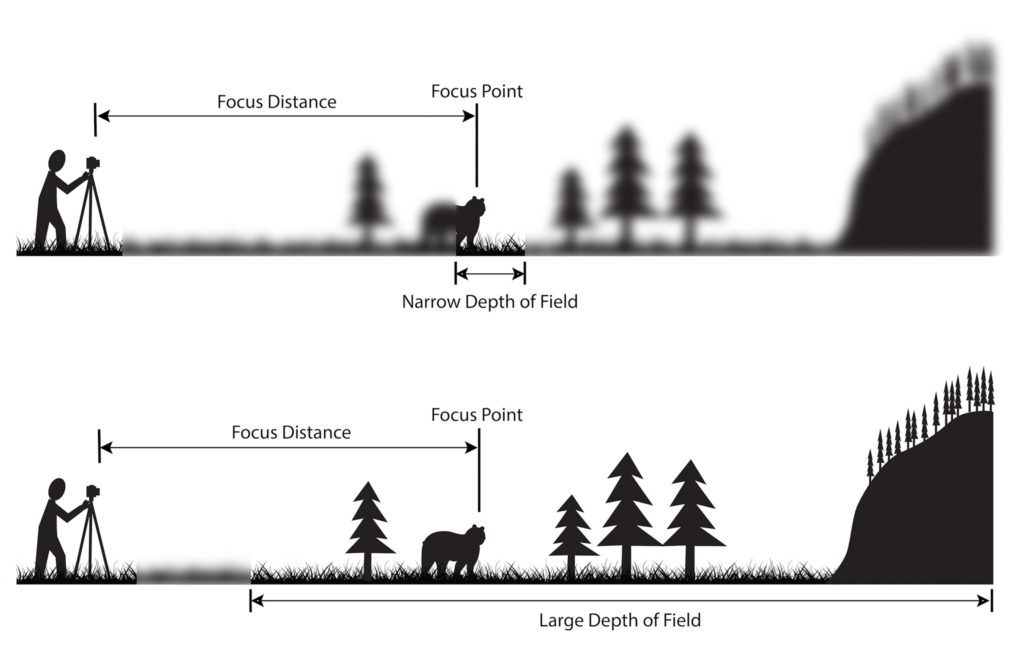
When the depth of field is shallow, the subject in the foreground will be in sharp focus, while the background should appear out of focus. This can often be used to draw attention to the subject and create a stronger sense of depth in the image – commonly used in portrait photography.
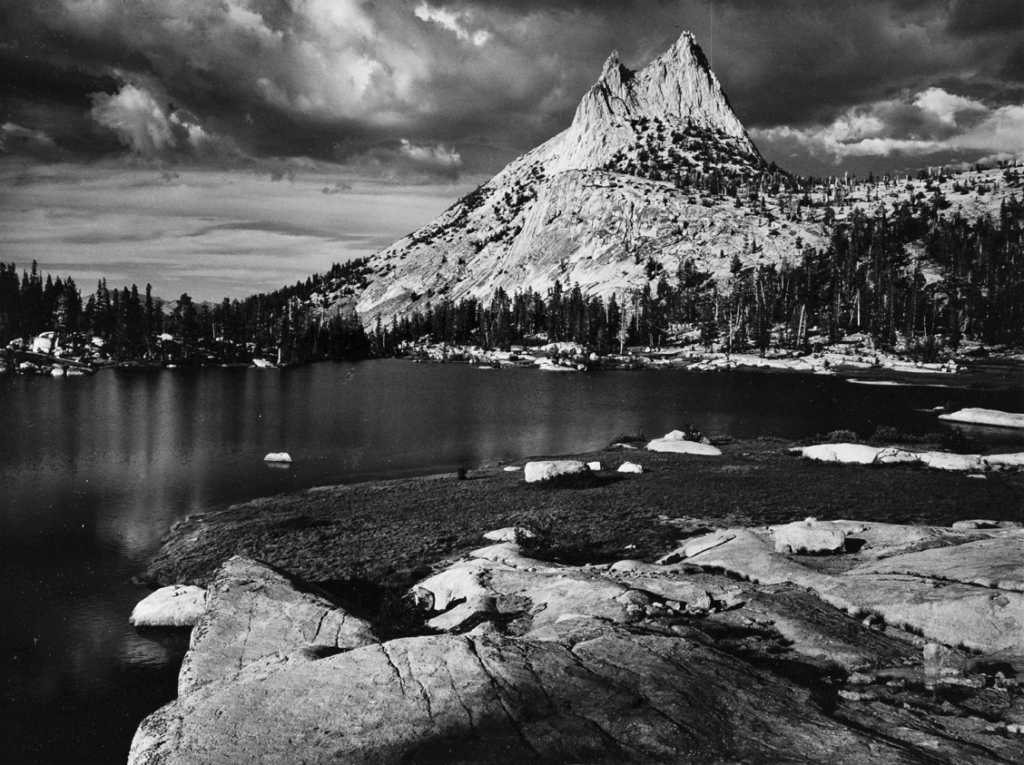

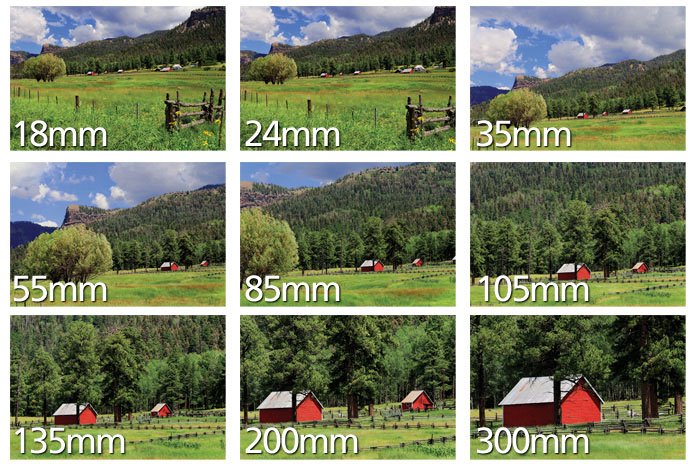
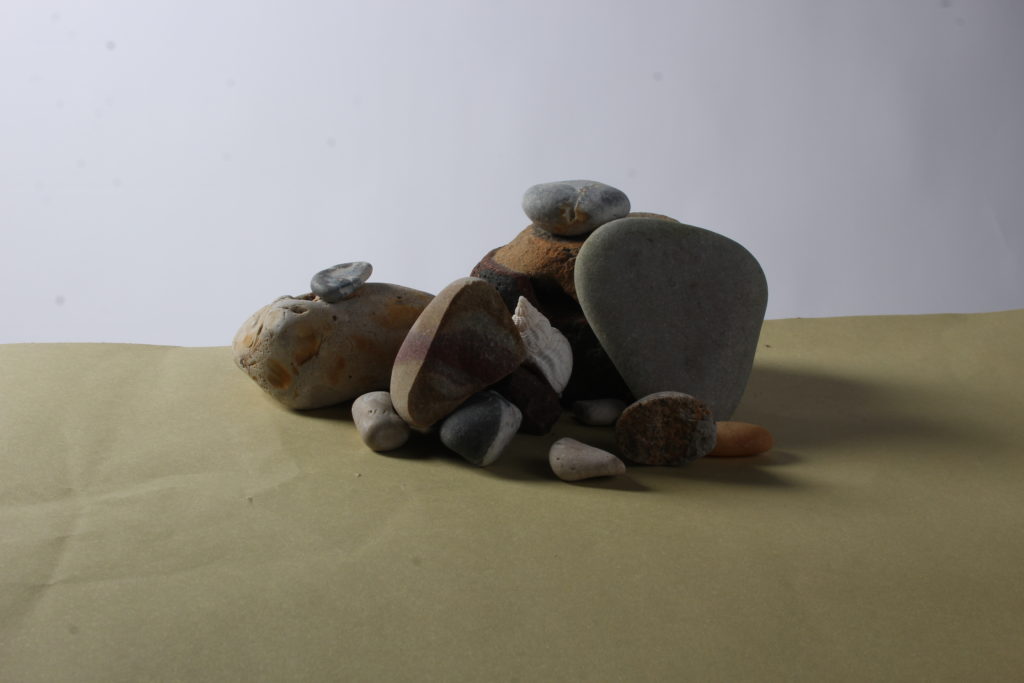
On the other hand, when the depth of field is deeper, more of the scene will appear in focus – which is typically present in landscape photography to capture more detail within the scenery. Either way, depth of field is essential when it comes to developing a more visually appealing photograph.
Depth of field is also controlled by the distance between the camera, subject and foreground, the closer the subject is, the shallower the depth of field is, and vice versa.