
In 1204 King John lost the Battle of Rouen against the French King Philippe-Auguste. The defeat signalled the loss of continental Normandy, united with the English Crown since the invasion of England by William the Conqueror in 1066. The Channel Islands, part of the Duchy of Normandy for more than a hundred years at that point, might have been expected to align themselves with the French King in 1204 but they were persuaded by a combination of carrot and stick to side with King John instead.
Among the privileges which the King granted Islanders was the right to be governed by their own laws and he instructed them to select their 12 best men as Jurats who, sitting with the Bailiff, became the Island’s Royal Court. A warden, later to become governor, was appointed by the King to organise the defence of the Island.
The Crown Dependencies are three island territories in the British Islands that are self-governing possessions of the British Crown: the Bailiwick of Guernsey, the Bailiwick of Jersey, and the Isle of Man. They are not part of the United Kingdom (UK) nor are they British Overseas Territories. They have the status of “territories for which the United Kingdom is responsible”, rather than sovereign states. As a result, they are not member states of the Commonwealth of Nations. However, they do have relationships with the Commonwealth and other international organisations, and are members of the British–Irish Council. They have their own teams in the Commonwealth Games.
Each island’s political development has been largely independent from, though often parallel with, that of the UK, and they are akin to ‘miniature states with wide powers of self-government’.
As the Crown Dependencies are not sovereign states, the power to pass legislation affecting the islands ultimately rests with the King-in-Council (though this power is rarely exercised without the consent of the dependencies, and the right to do so is disputed). However, they each have their own legislative assembly, with the power to legislate on many local matters with the assent of the Crown (Privy Council, or in the case of the Isle of Man in certain circumstances the lieutenant-governor). In Jersey and the Isle of Man, the head of government is called the chief minister. In Guernsey, the head representative of the committee-based government is the President of the Policy and Resources Committee.
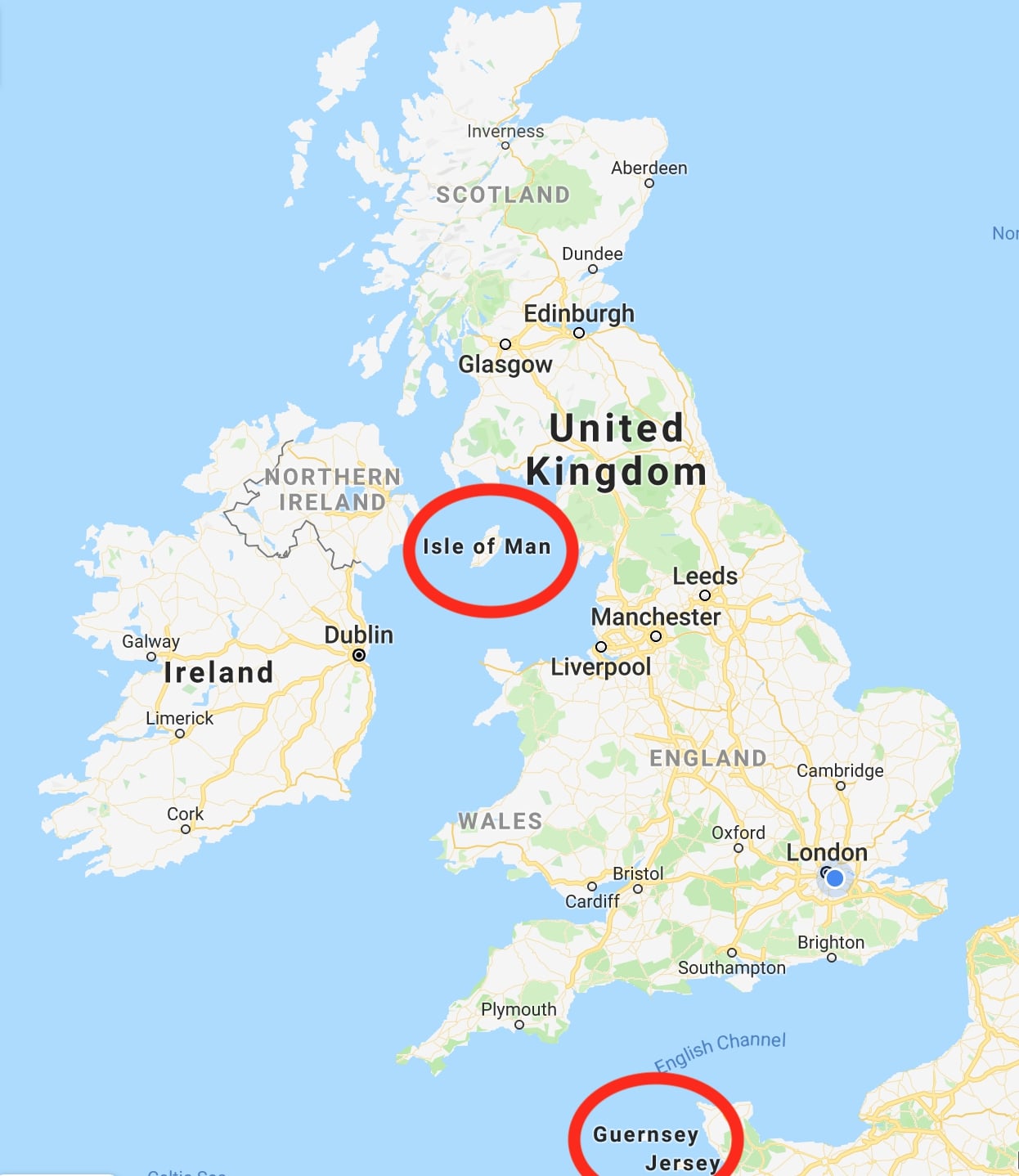
“The Crown” is defined differently in each Crown Dependency. In Jersey, statements in the 21st century of the constitutional position by the Law Officers of the Crown define it as the “Crown in right of Jersey”, with all Crown land in the Bailiwick of Jersey belonging to the Crown in right of Jersey and not to the Crown Estate of the United Kingdom. Legislation of the Isle of Man defines the “Crown in right of the Isle of Man” as being separate from the “Crown in right of the United Kingdom”. In Guernsey, legislation refers to the “Crown in right of the Bailiwick”, and the Law Officers of the Crown of Guernsey submitted that “The Crown in this context ordinarily means the Crown in right of the république of the Bailiwick of Guernsey” and that this comprises “the collective governmental and civic institutions, established by and under the authority of the Monarch, for the governance of these Islands, including the States of Guernsey and legislatures in the other Islands, the Royal Court and other courts, the Lieutenant Governor, Parish authorities, and the Crown acting in and through the Privy Council.” This constitutional concept is also worded as the “Crown in right of the Bailiwick of Guernsey”.

The Bailiwick of Jersey consists of the island of Jersey and a number of surrounding uninhabited islands.
The parliament is the States Assembly, the first known mention of which is in a document of 1497. The States of Jersey Law 2005 introduced the post of Chief Minister of Jersey, abolished the Bailiff’s power of dissent to a resolution of the States and the Lieutenant Governor’s power of veto over a resolution of the States, and established that any Order in Council or Act of the United Kingdom proposed to apply to Jersey must be referred to the States so that the States can express their views on it. There are a few political parties, as candidates generally stand for election as independents.
