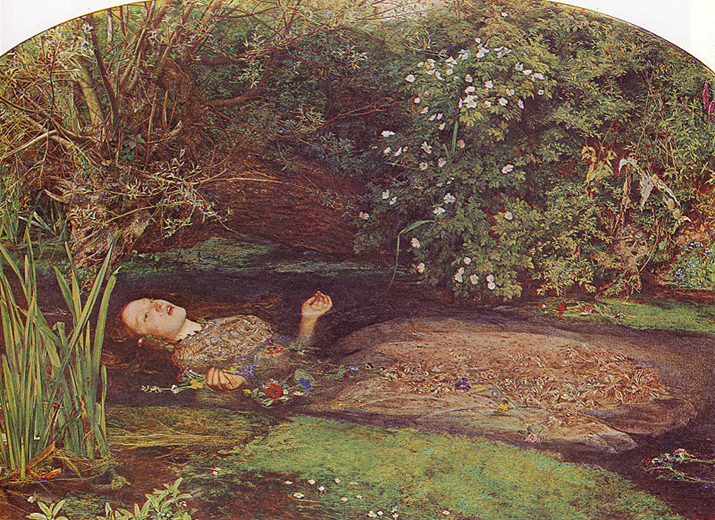
PICTORIALISM
Time period: 1880s – 1920s
Key characteristics/conventions: To make photography an accepted art form. People saw photography as being too easy because all you did was click a button, which was so much different that going to school for years and learning how to be a “real” artist.
Influences: Their ideas came from the history of painting, more specifically: allegorical painting. Peter Henry Emerson’s naturalistic photography. Julia Margaret Cameron used her family and created spiritual images.






Artists associated: Alfred Stieglitz – Heinrich Kuhn –
Key works:
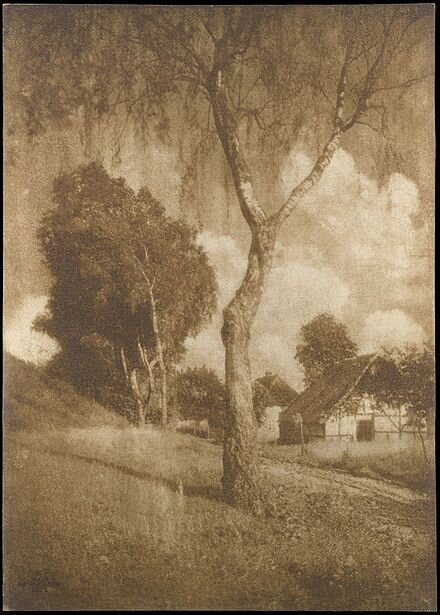
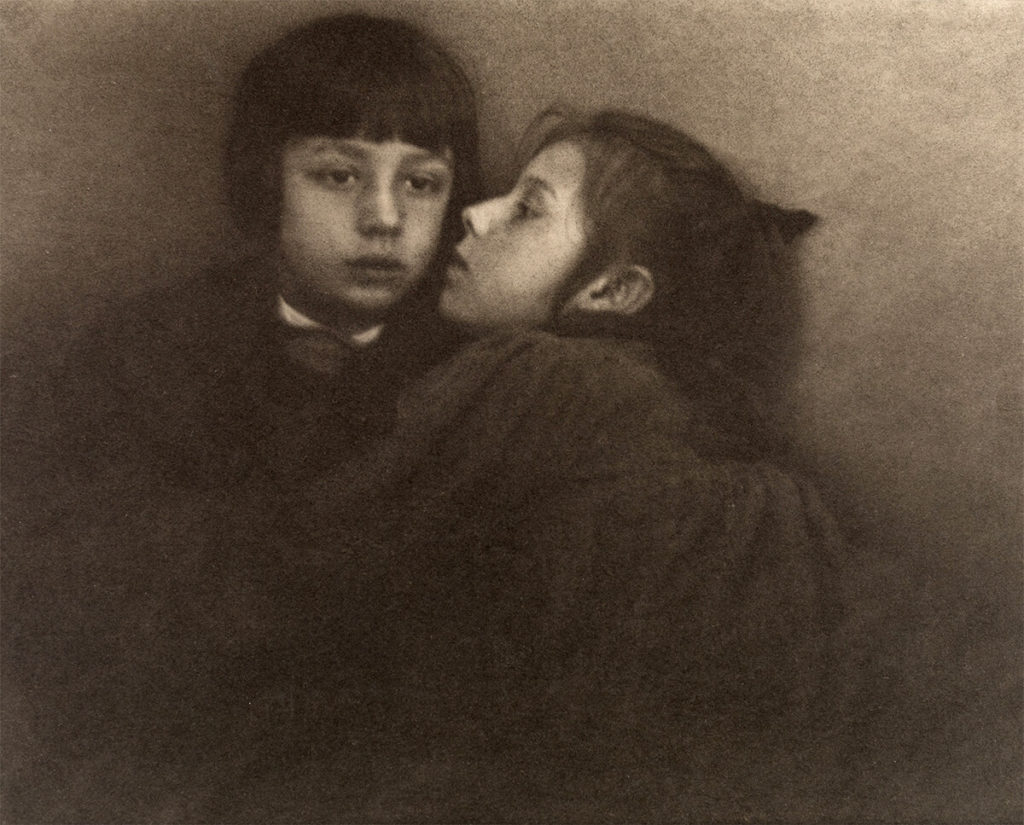



Alfred Baron Liebig, 1891
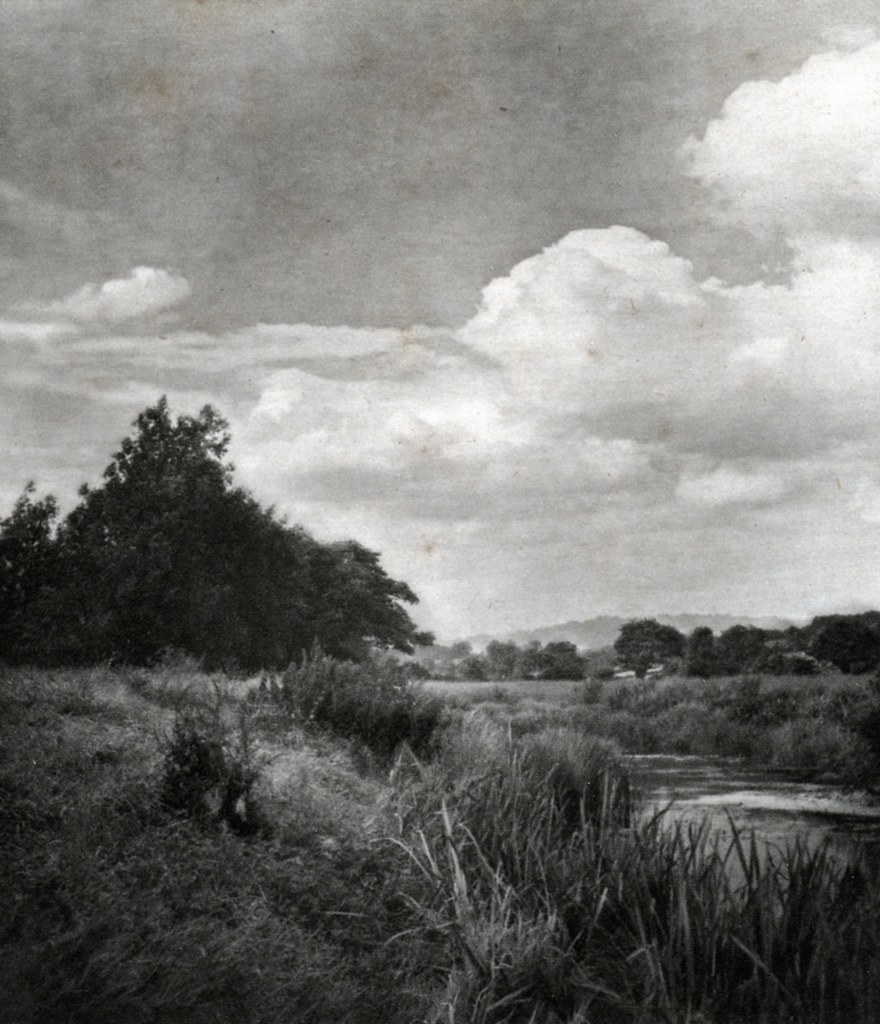



Methods/ techniques/ processes: They would use vaseline on the lenses to make the photographs blurry and painting like. Scratching the negatives. They used chemicals in the printing process to manipulate he colour of the photographs.
REALISM / STRAIGHT PHOTOGRAPHY
Time period: 1920s
Key characteristics/ conventions: To capture things as they were without any manipulation. To emphasise the quality of photography. The photographs differed depending on the photographer’s eyes. Abstraction as a genre was born in this period.
Influences: Inspired by the pictorialisms and cubism (Picasso and Braque).


Artists associated: Ansel Adams – Edward Weston – Alfred Stieglitz – Paul Strand – Walker Evans
Key works:
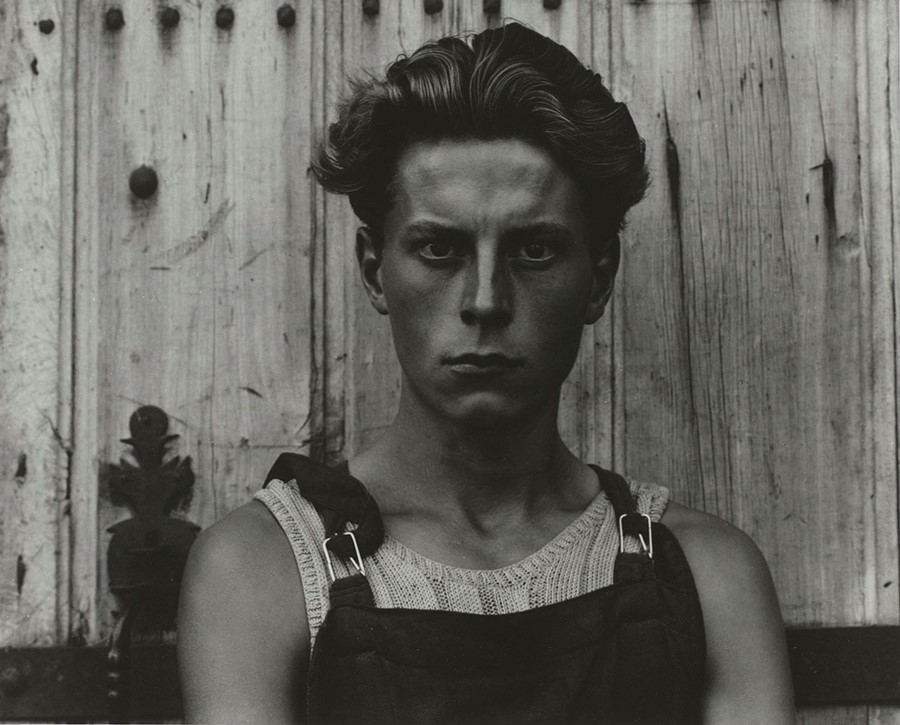
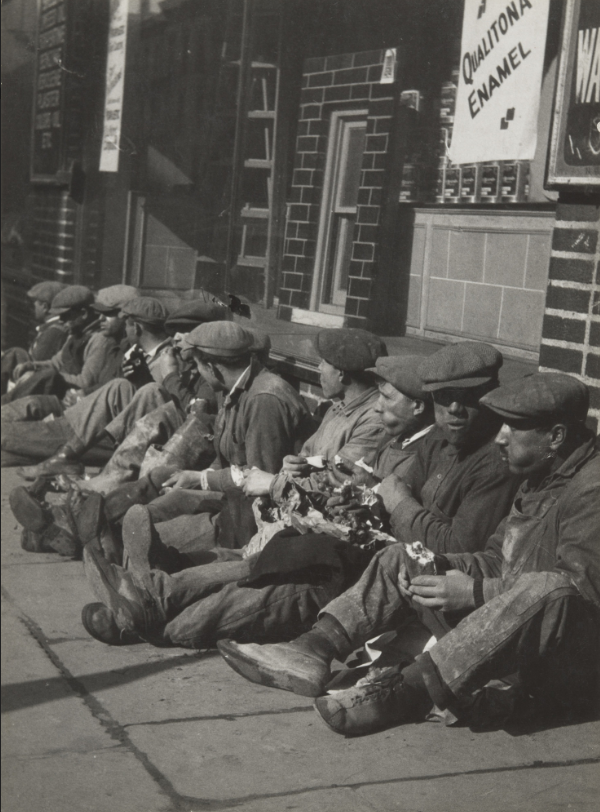
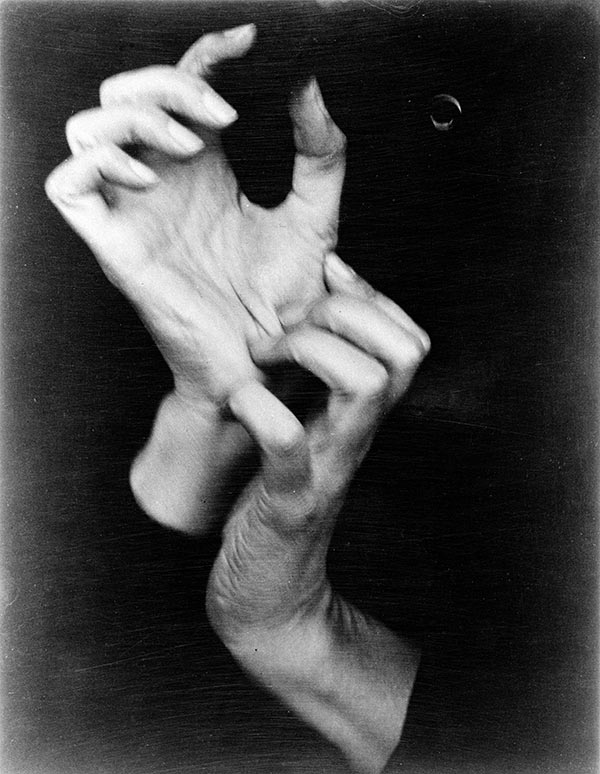



Methods/ techniques/ processes: To produce sharply focused mages without any manipulation and relay on the camera to record things as they are.
MODERNISM
Time period: 1900s – 1940s
Key characteristics/ conventions: Photojournalism, emphasised the truth/materiality of a work of art, believed meaning was embedded in work/created by the artist themselves (not interested in context), tried to produce timeless pieces that did not link to history/tradition, rejected older concepts + movements,
Influences: Against the enlightenment (pro science and technology), Dadaism (Hannah Hoch), expressionism, surrealism
Artists associated: Margaret Bourke-White, Ansel Adams
Key works:
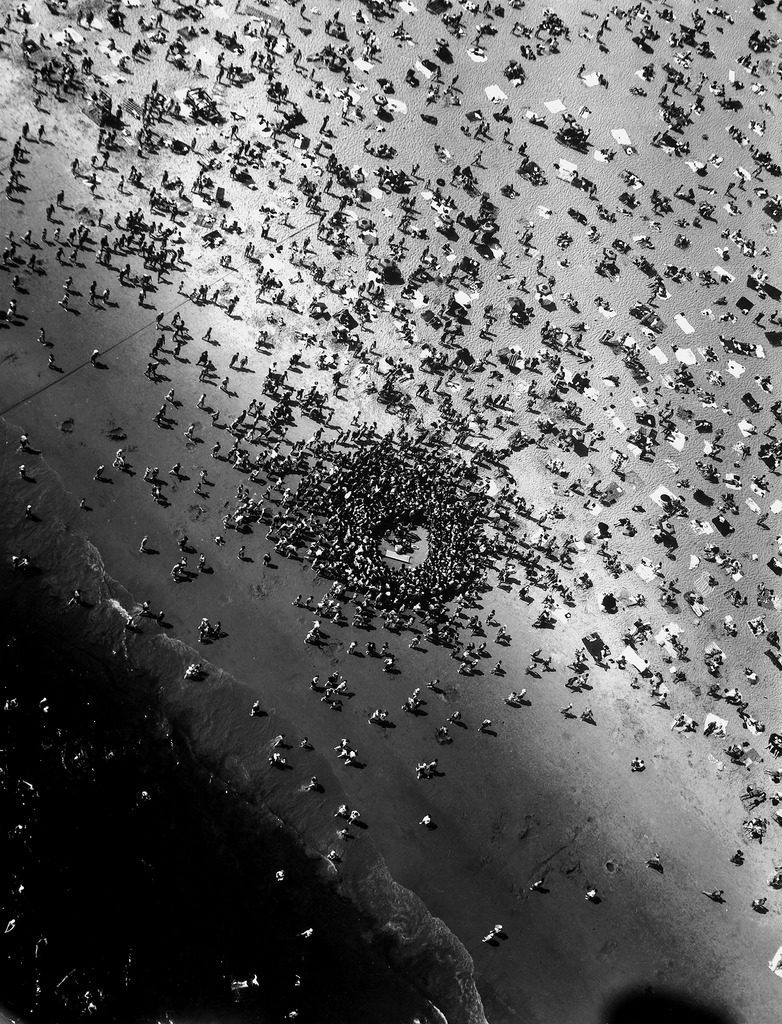
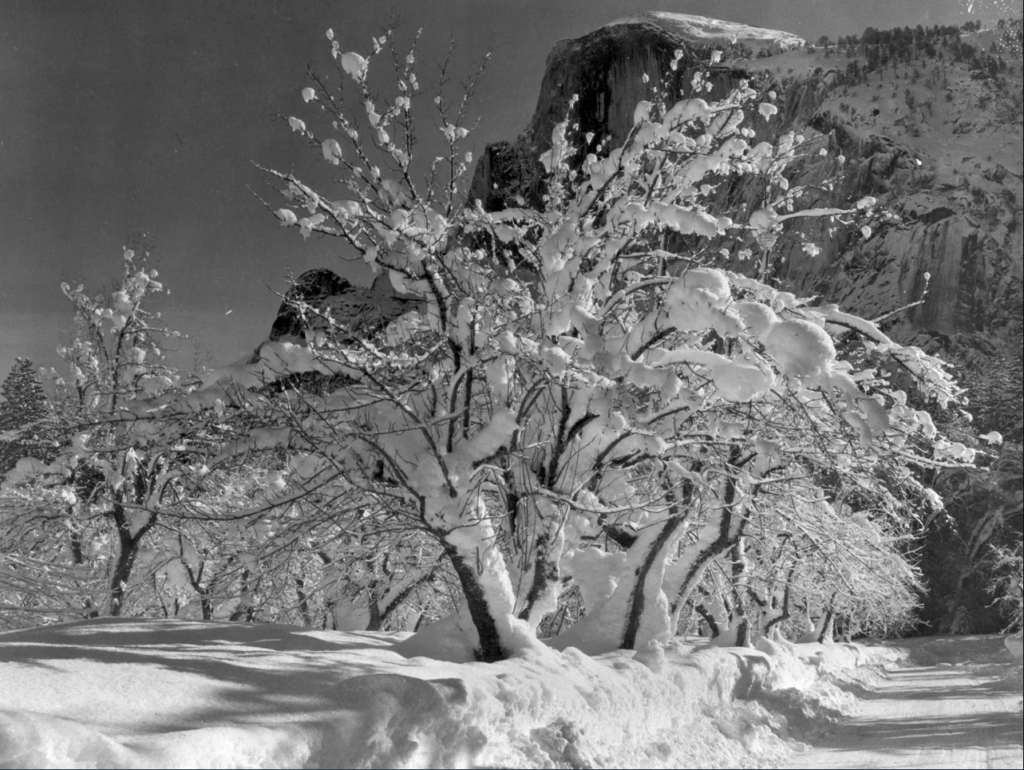
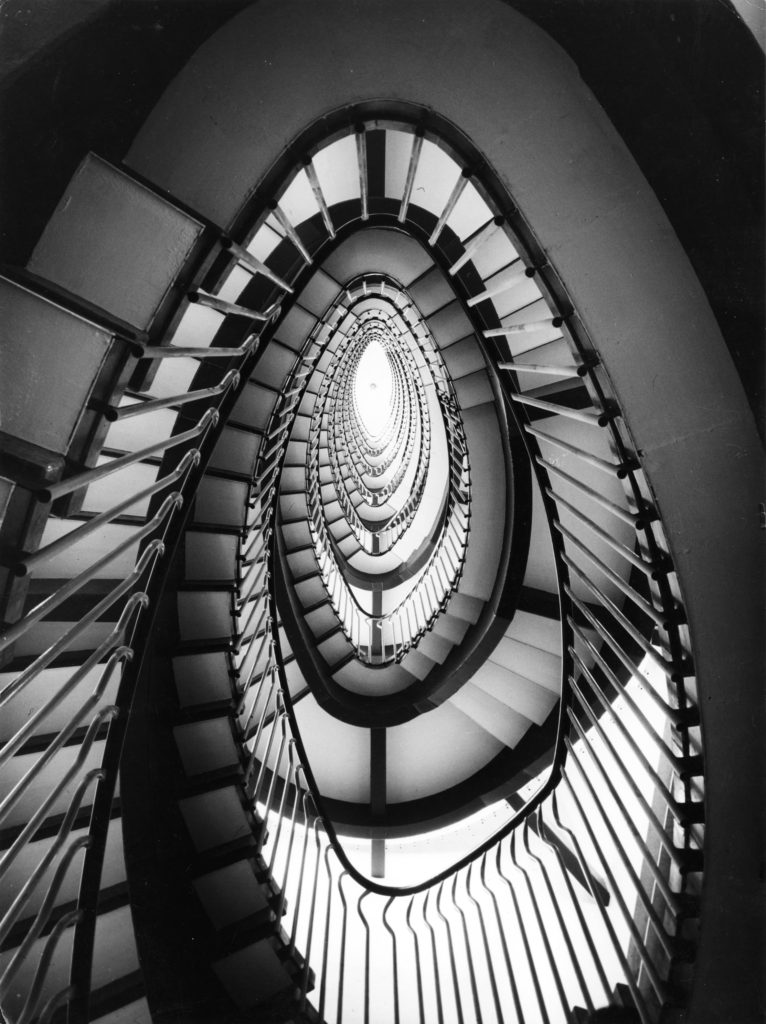



Methods/ techniques/ processes: Form, composition, focuses on object rather than content
POST-MODERNISM
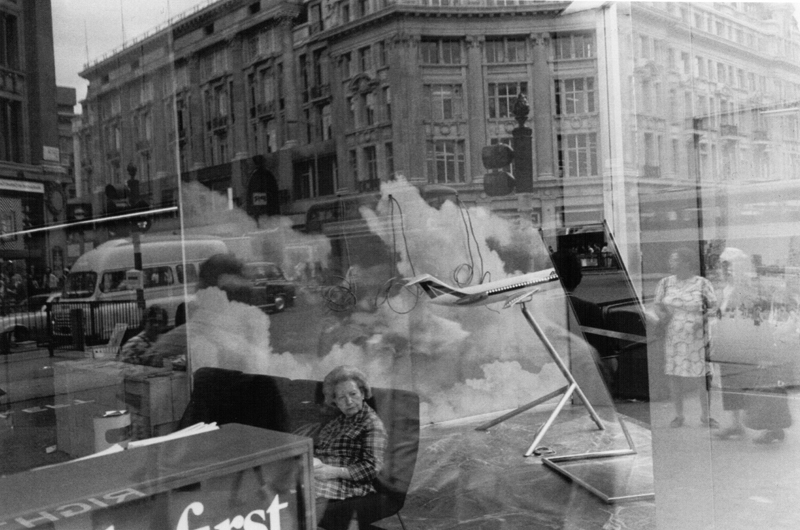
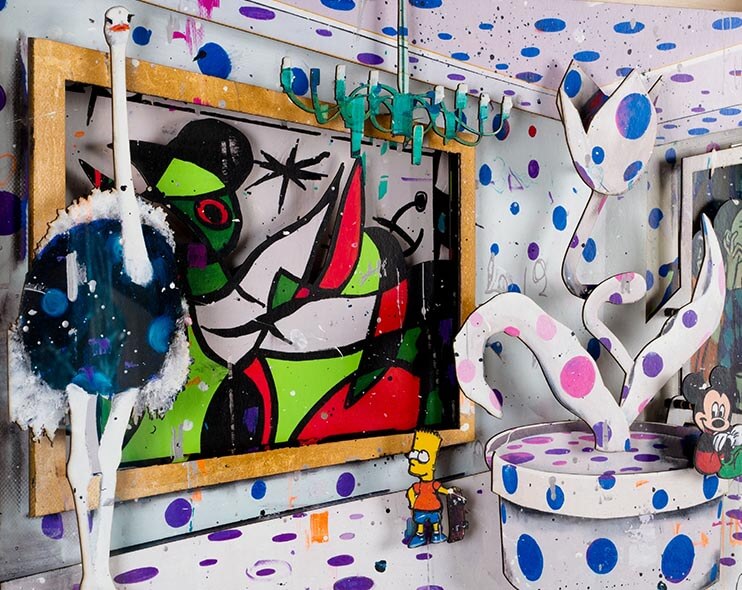
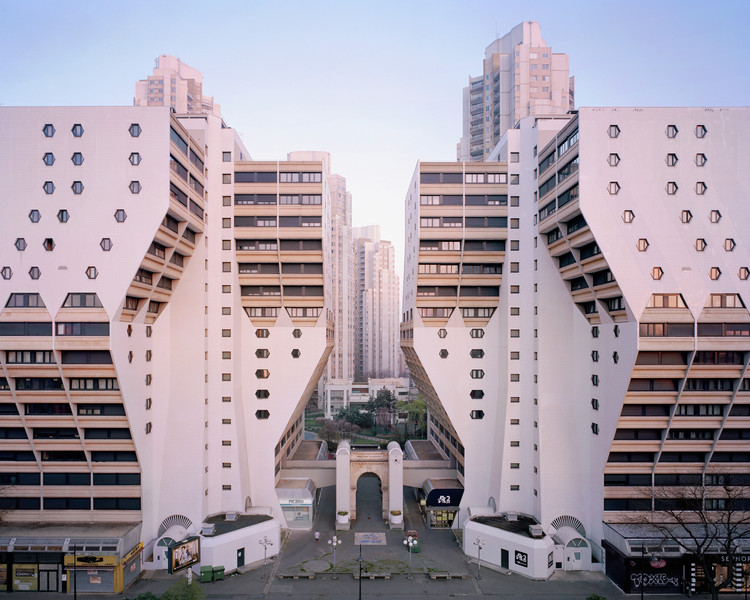
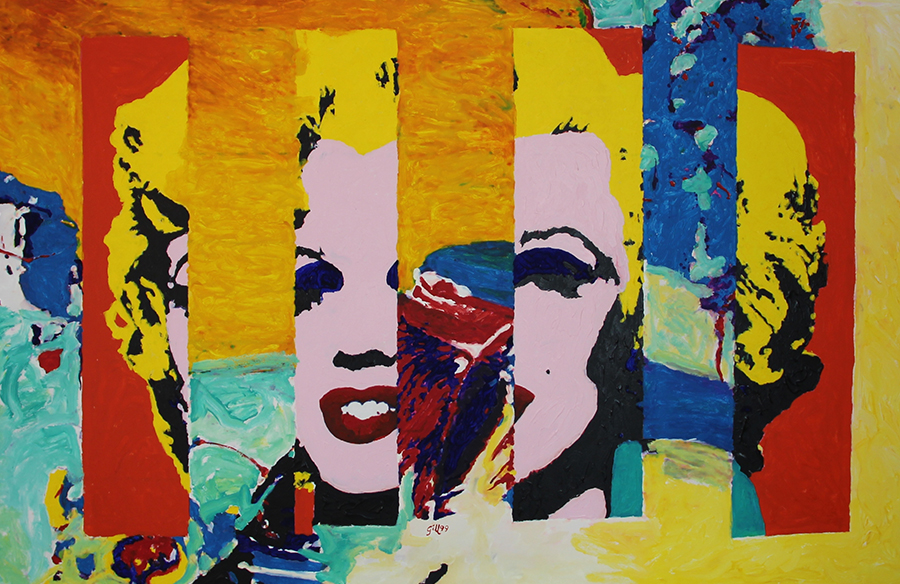








Time period: 1970 – current
Key characteristics/ conventions: It explores power and the way economic and social forces exert that power by shaping the identities of individuals and entire cultures. It has a sceptical and political approach to the world. It has no rules or manifesto. This type of photography also often features surrealism, expressionism or other similar themes.
Influences: Themes and ideas came from the modernism period (to reject it). Technology also had an impact.
Artists associated: Lee Friedlander, William Eggleston, Jeff Wall, Andreas Gursky and Cindy Sherman.
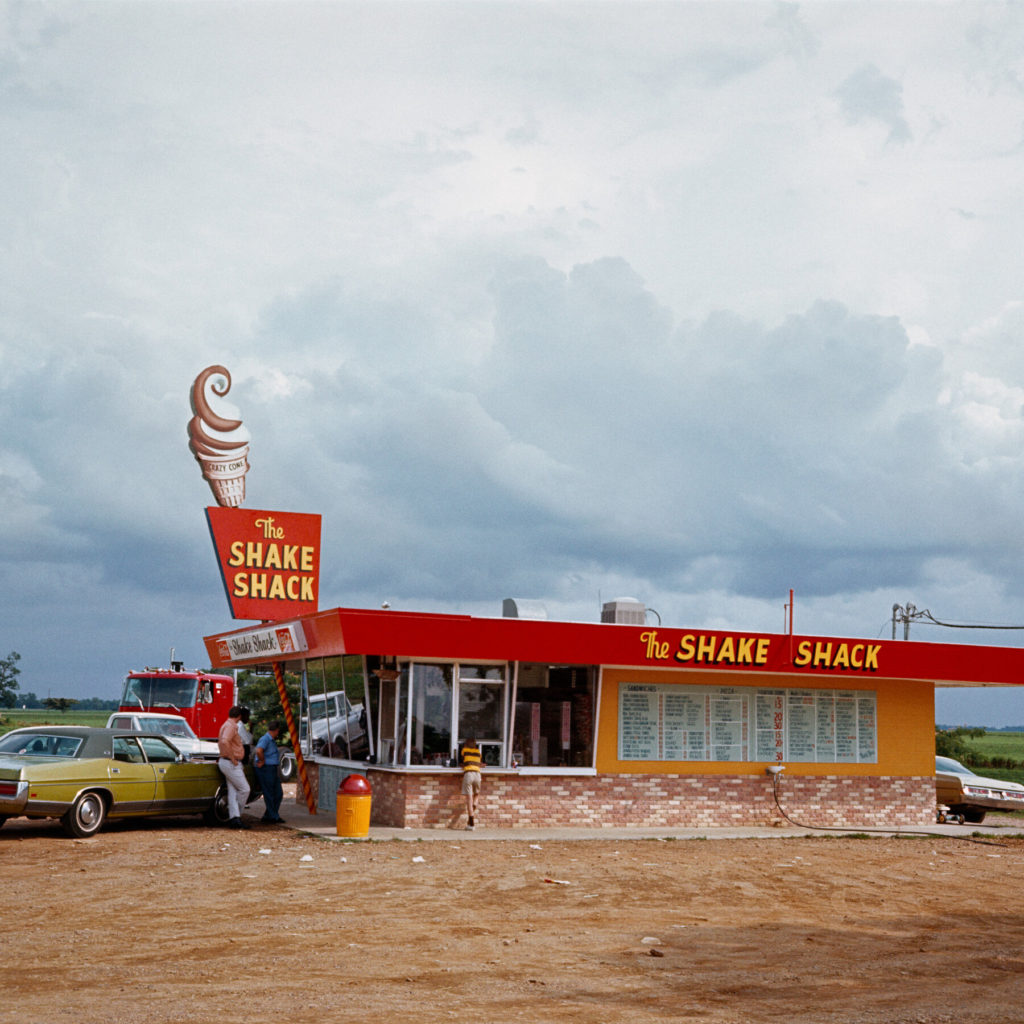
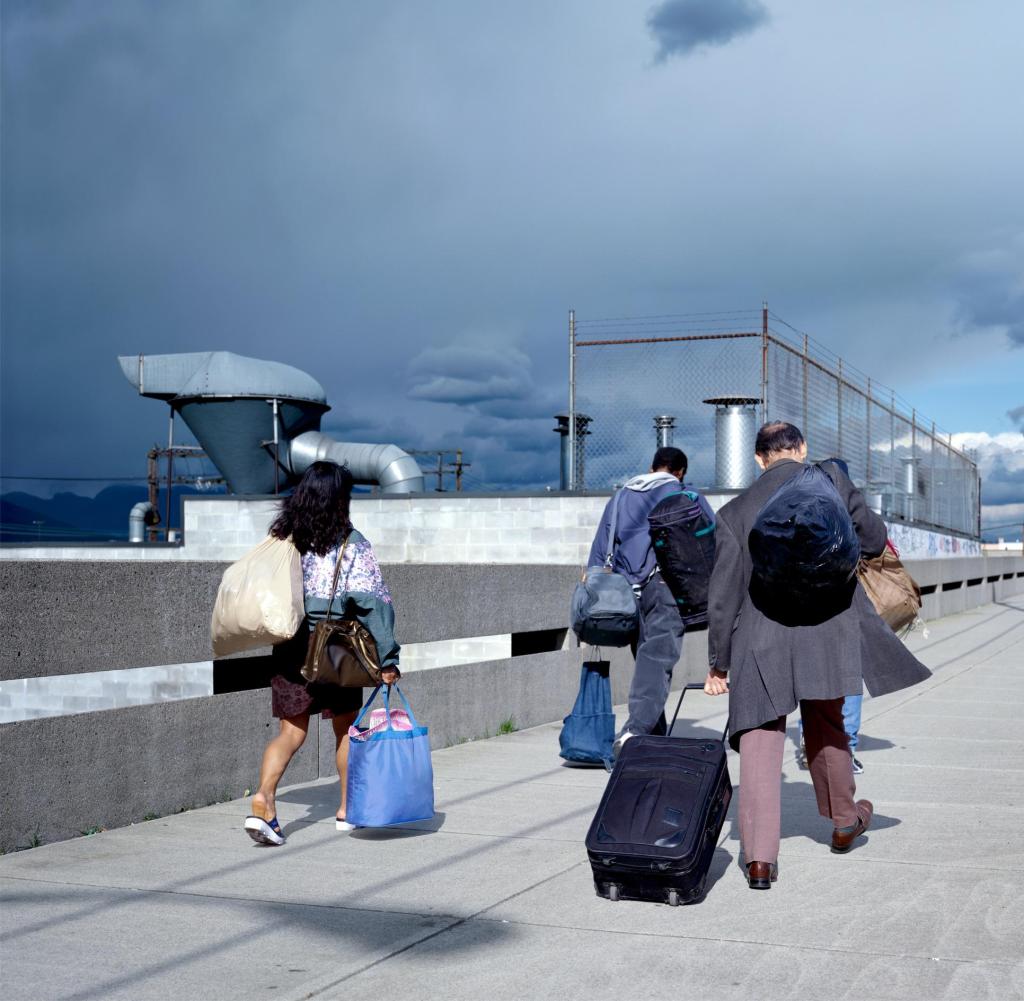



Key works:
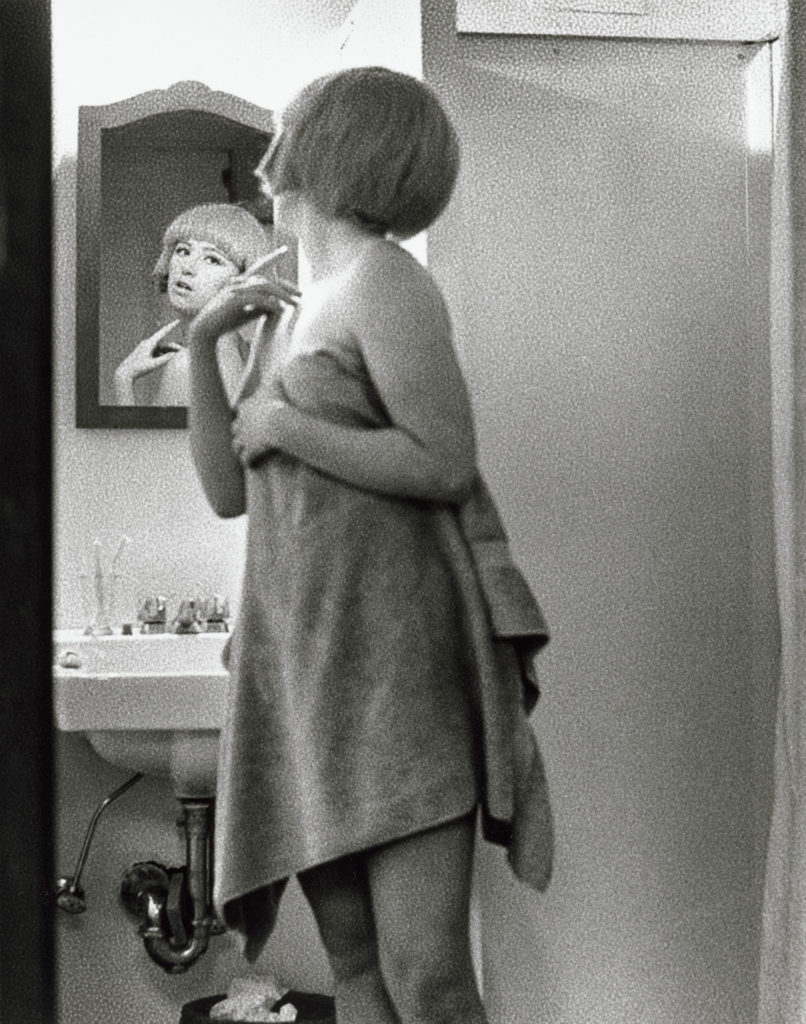
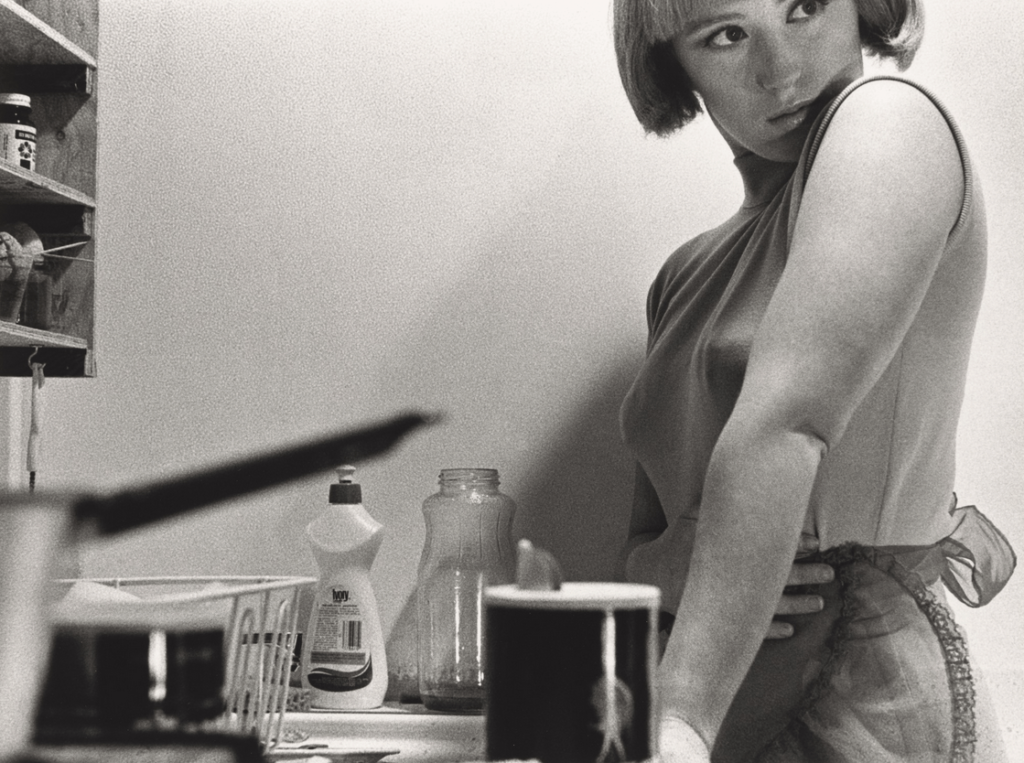
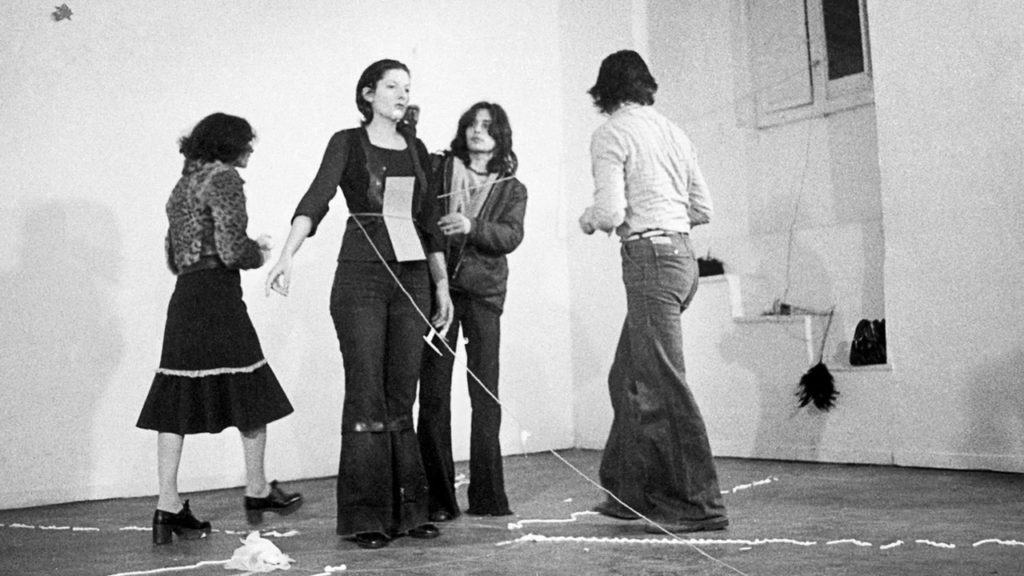





Methods/ techniques/ processes:
- Eclecticism – mixing art forms, mixing cultures, mixing styles
- No Value to the worth of Art – mixing high art with pop culture
- Intertextuality – Including the work of others, the “quoting” of others work
- Collaboration – Creating work with others
- Pastiche – copying an original
- Parody – imitating in order to ridicule, ironically comment on, or poke some fun at
- Recycling – re-using the same material more than once
- Refiguration – re-structuring of an original
- Bricolage – deconstructing and then restructuring existing materials in a new, exciting and inventive way

Yasmin,
Make a post with images you have researched in the photo-archive and comment on how it relates to your project. Include a few behind-the-scenes images of you working at the archive too.
Hi Yasmin, have you begun to write your essay introduction and paragraph 1? It would be good for you to publish what you have written so far as draft, so we as teachers can read it and give you some feedback on how to develop/ improve it etc.
Also, how are you getting in with some of the texts that I’ve given you on anthropology and photography?