
Mine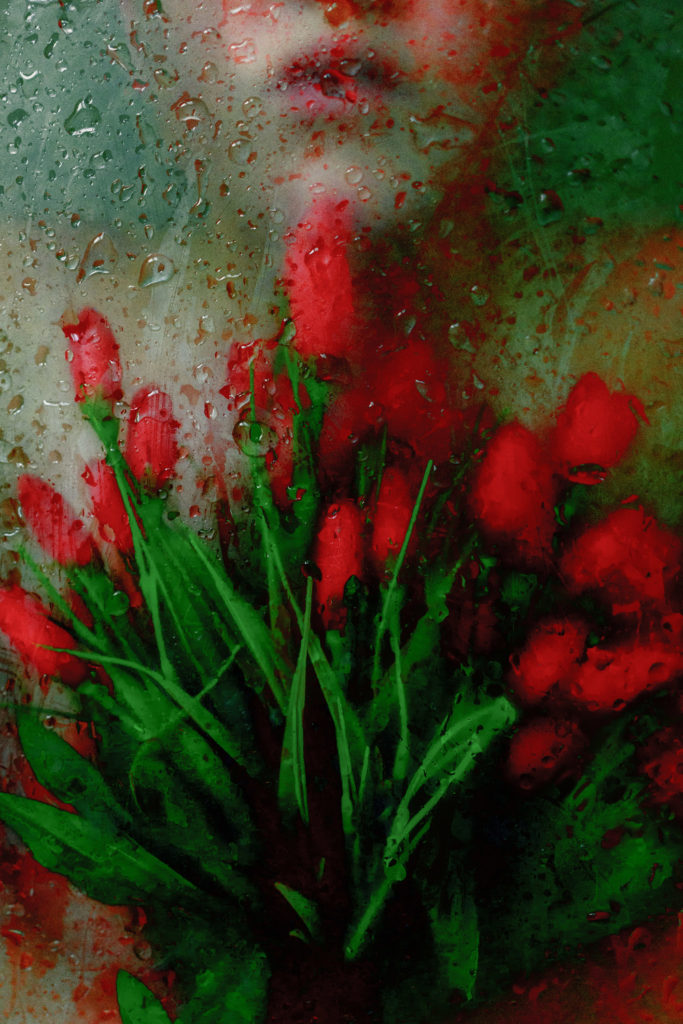 
Lara Gilks
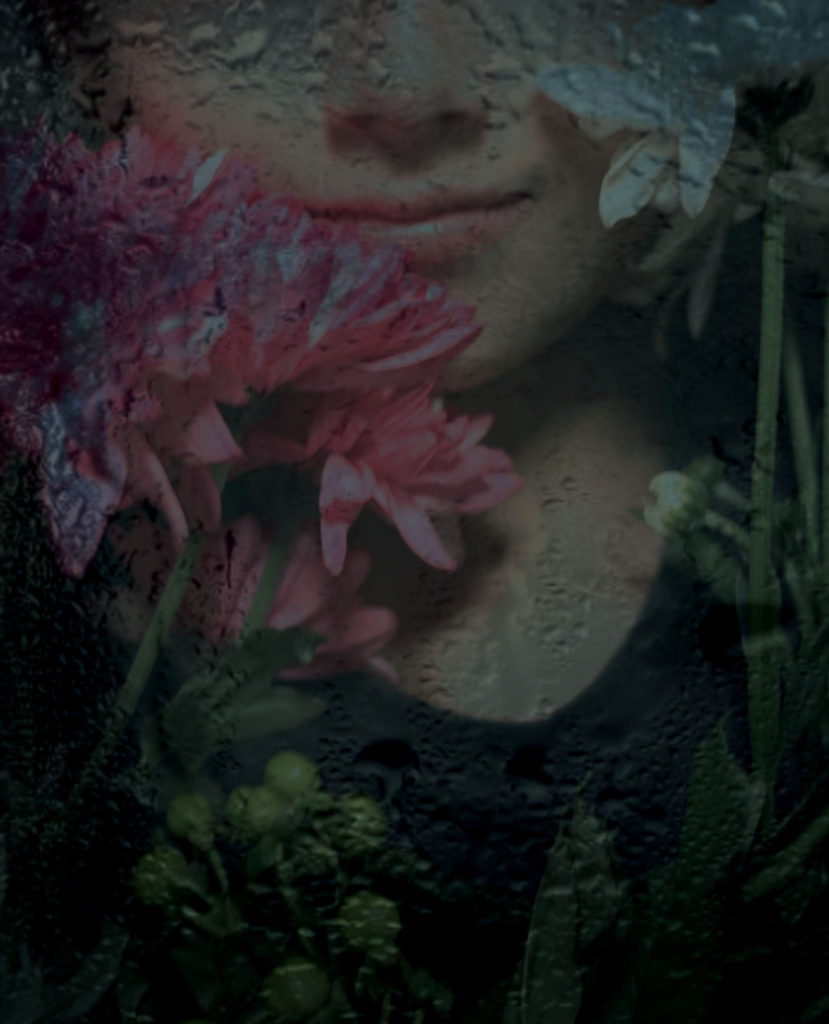
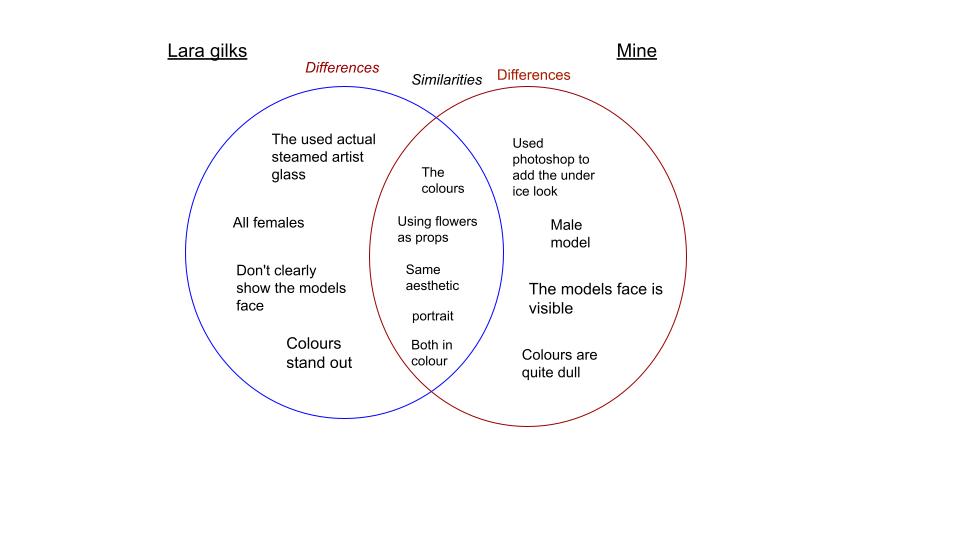
In both images the props are flowers but different colours and Lara gilks photo is more saturated than mine making the colours stand out



In both images the props are flowers but different colours and Lara gilks photo is more saturated than mine making the colours stand out
Juxtaposition refers to the side-by-side placement of two or more contrasting things. As with colour, shape, and cropping, juxtaposition can become a key component of photographic compositions, helping to tell a story and emphasize differences or similarities between objects or people.
EXAMPLES OF JUXTAPOSITION

Juxtaposition in street photography is hugely influenced by individuals emotions – some may volunteer to be photographed whilst some shots are candid. This photo shows two people, perhaps lovers, standing in front of a painting of two individuals kissing. The two in front are looking away from each other and away from the camera, this could symbolize conflict between the two. The woman is holding her arm as an act of defiance. The painting behind them juxtaposes the couples emotions.
MY PHOTOS
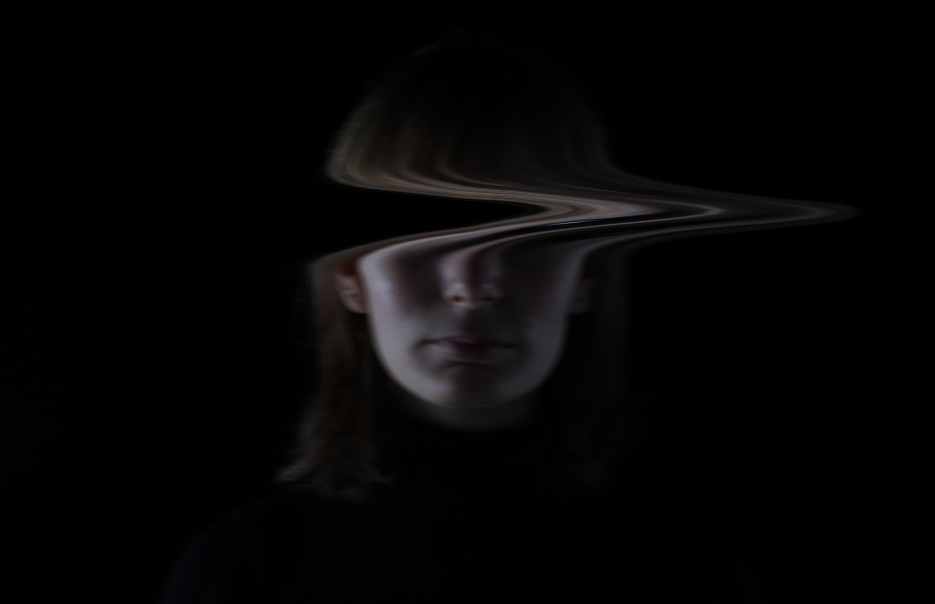
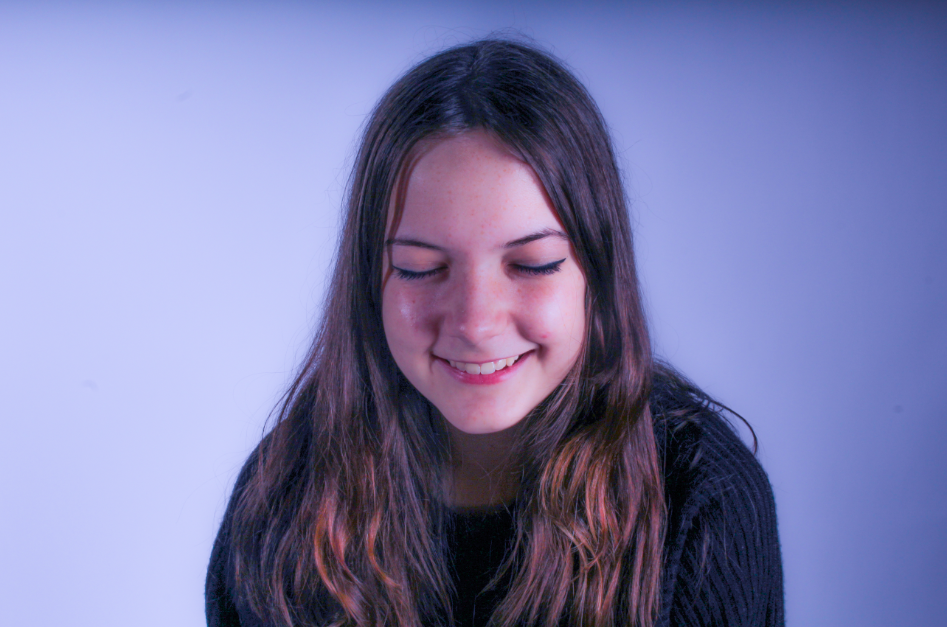


I edited these photos on Lightroom and Photoshop. For the first one i used the warp tool and motion blur to convey emotion, for the second one i increased the saturation and clarity to give the photo a soft blur and more vibrant background.
The juxtaposition between my photos is reliant on emotion. The first photo suggests a sadder more chaotic atmosphere, with the lack of eye contact due to the eyes blurred out to make it more mysterious. The black background makes the individual in the photo stand out more so she is the main focus. The second photo is the opposite – i am smiling in the photo to show a happier atmosphere, the brighter colours and light background furthermore suggest this.
Portrait photography has had a long and varied history since Louis Daguerre introduced the photographic process in 1839. In that same year, Robert Cornelius produced what’s considered the first photographic self-portrait. Photography has served many purposes, mainly to commemorate occasions and periods in history.

If you were a wealthy individual in the early 1800s, you might have been able to commission an artist to paint a portrait of you. This was not likely to have been a pain-free process, however, even if it meant that you got a framed likeness of yourself at the end. Think multiple sessions of sitting still and trying to keep your features frozen in a dignified smile. And if you didn’t quite like how the portrait turned out, there wasn’t much you could do about it.
Luckily, the invention of photography transformed portrait making into something less time consuming and with more reliable results. Early portraits were daguerrotypes. They were named after the French inventor, Louis Daguerre, who came up with this technique of imprinting images on an iodine-sensitized silver plate using mercury vapor. Daguerrotypes were produced for around twenty years starting in 1839 before they were edged out by other photographic techniques. Since they had a pretty short run overall, daguerrotypes that survive today (such as the two below) are valuable collectibles.
Photography. An art form invented in 1830s, becoming publicly recognised ten years later.
Today, photography is the largest growing hobby in the world, with the hardware alone creating a multi-billion dollar industry. Not everyone knows what camera obscura or even shutter speed is, nor have many heard of Henri Cartier-Bresson or even Annie Leibovitz.
In this article, we take a step back and take a look at how this fascinating technique was created and developed.
Before photography was created, people had figured out the basic principles of lenses and the camera. They could project the image on the wall or piece of paper, however no printing was possible at the time: recording light turned out to be a lot harder than projecting it. The instrument that people used for processing pictures was called the Camera Obscura (which is Latin for the dark room) and it was around for a few centuries before photography came along.
It is believed that Camera Obscura was invented around 13-14th centuries, however there is a manuscript by an Arabian scholar Hassan ibn Hassan dated 10th century that describes the principles on which camera obscura works and on which analogue photography is based today.

Camera Obscura is essentially a dark, closed space in the shape of a box with a hole on one side of it. The hole has to be small enough in proportion to the box to make the camera obscura work properly. Light coming in through a tiny hole transforms and creates an image on the surface that it meets, like the wall of the box. The image is flipped and upside down, however, which is why modern analogue cameras have made use of mirrors.
In the mid 16th century, Giovanni Battista della Porta, an Italian scholar, wrote an essay on how to use camera obscura to make the drawing process easier. He projected the image of people outside the camera obscura on the canvas inside of it (camera obscura was a rather big room in this case) and then drew over the image or tried to copy it.

The process of using camera obscura looked very strange and frightening for the people at those times. Giovanni Battista had to drop the idea after he was arrested and prosecuted on a charge of sorcery.
Even though only few of the Renaissance artists admitted they used camera obscura as an aid in drawing, it is believed most of them did. The reason for not openly admitting it was the fear of being charged of association with occultism or simply not wanting to admit something many artists called cheating.
Today we can state that camera obscura was a prototype of the modern photo camera. Many people still find it amusing and use it for artistic reasons or simply for fun.
Installing film and permanently capturing an image was a logical progression.
The first photo picture—as we know it—was taken in 1825 by a French inventor Joseph Nicéphore Niépce. It records a view from the window at Le Gras.

The exposure had to last for eight hours, so the sun in the picture had time to move from east to west appearing to shine on both sides of the building in the picture.
Niepce came up with the idea of using a petroleum derivative called “Bitumen of Judea” to record the camera’s projection. Bitumen hardens with exposure to light, and the unhardened material could then be washed away. The metal plate, which was used by Niepce, was then polished, rendering a negative image that could be coated with ink to produce a print. One of the problems with this method was that the metal plate was heavy, expensive to produce, and took a lot of time to polish.
