Pictorialism
Time Period
1880 to 1920
Key Characteristics/conventions
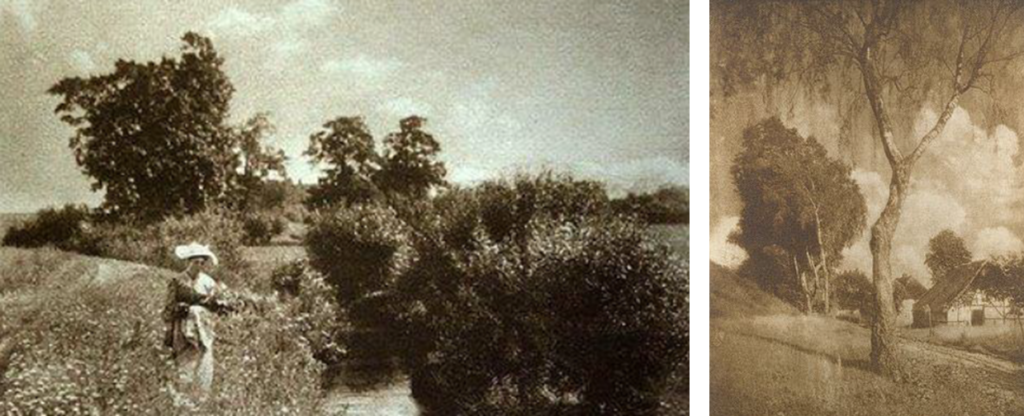
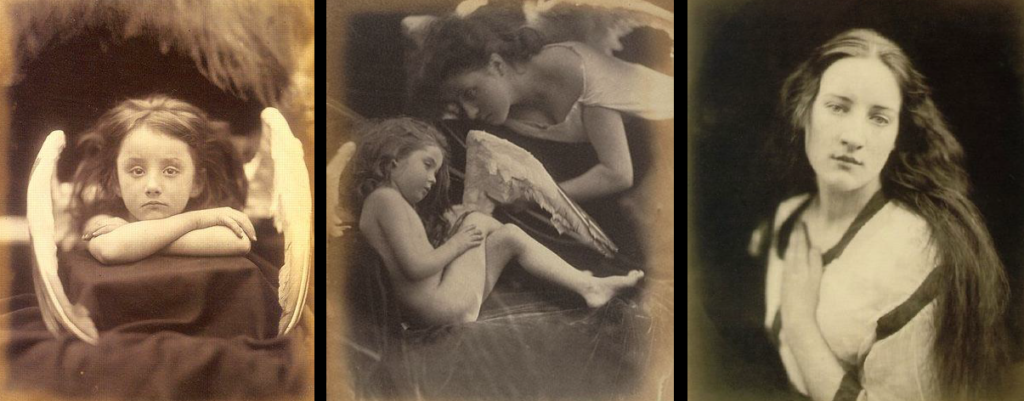
Photographs that resemble art, making photography handmade, break away from commercialism.
Artist Associated
Alfred Stieglitz, Julia Margret Cameron, Peter Emmerson, Alvin Langdon Coburn, Photo-succession, Brotherhood of the linked ring, Vienna camera club.
Key Works
Alfred Stieglitz – Equivalent (cloud studies)
John Everett Millais – Ophelia (inspiration)
George Davidson – Reflections
Methods
Vaseline on lense
Scratching the negative
Brushing prints with chemicals
Realism
Time Period
1915
Key Characteristics/Conventions
Break away from pictorialism, focus on sharp focus, shape and form.
Artists Assosiated
Paul Strand, Edward Western, Walker Evans, Cunningham
Key Works
Paul Strand – Photograph, Blind woman
Dorothea Lange – Migrant Mother
Walker Evans – Alabama Tenant Farmer Wife
Methods
Picture looks like it does in the viewfinder, emphasis on framing, abstraction and sharp focus.
Modernism
Time Period
1900 – 1940
Key Characteristics/Conventions
Reaction to the enlightenment, examine impediments holding society back. New alignment with the experience and values of modern industrial life. New imagery, materials and techniques to create artworks that they felt better reflected the realities and hopes of modern societies.
Artists Associated
Picasso, Paul Strand, Alfred Stieglitz, Dora Maar, Edward Weston, Man Ray
Key Works
Edward Weston Nude 1936
Edward Steichen A Bee on a Sunflower 1920
Dora Maar Untitled (Hand-Shell) 1934
Herbert Bayer Humanly Impossible (Self-Portrait) 1932
Tina Modotti Bandelier, Corn and Sickle 1927
Man Ray Glass Tears 1932
Methods
False brass lens to the side of camera, abstraction and a highly defined clarity, photomontage, cropping and framing a single body part, distorting and accentuating its curves and angles, solarisation and using photograms (developing directly onto photographic paper rather than onto film)
Postmodernism
Time Period
1970 – 2000
Key Characteristics/Conventions
Reaction against the ideas and values of modernism, as well as a description of the period that followed modernism’s dominance in cultural theory and practice in the early and middle decades of the twentieth century. Scepticism, irony and philosophical critiques of the concepts of universal truths and objective reality.
Artists Associated
Cindy Sherman, Jeff Wall, Sherrie Levine, Jean Baudrillard, Edward Burtynsky, Jeff Koons
Key Works
Jeff Koons – Three Ball Total Equilibrium Tank (Two Dr J Silver Series, Spalding NBA Tip-Off) 1985
Marilyn Diptych by Andy Warhol, 1962
Cut Piece by Yoko Ono, 1964
Joseph Kosuth – One And Three Chairs (1965)
Methods
artists experimented with form, technique and processes rather than focusing on subjects
interpretation of our experience was more concrete than abstract principles