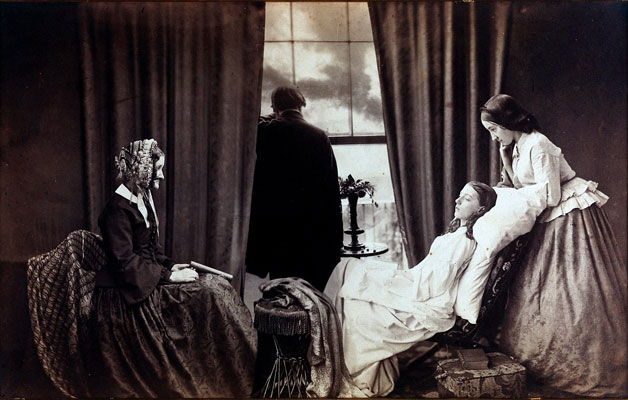
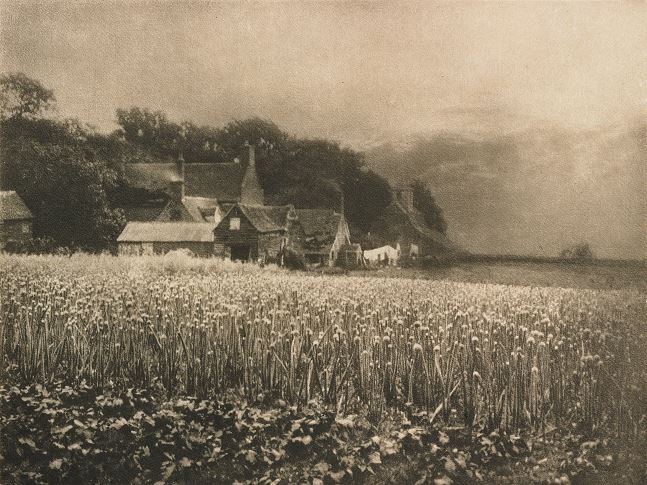
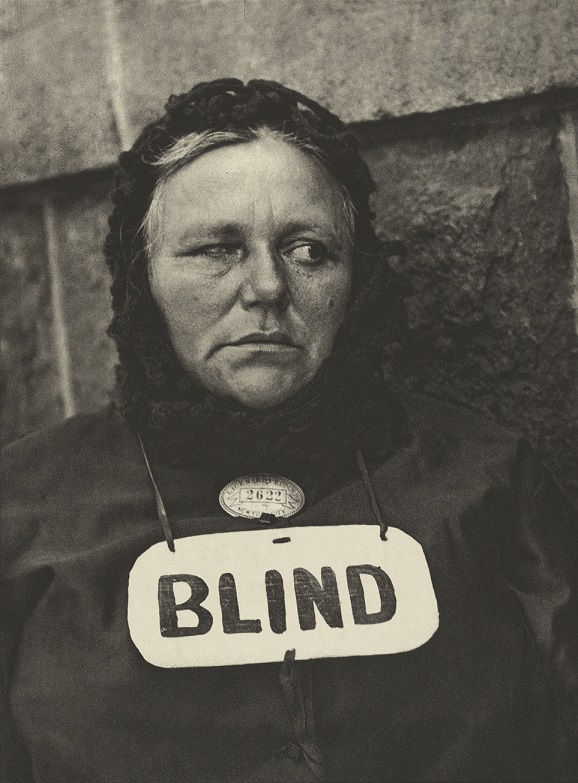
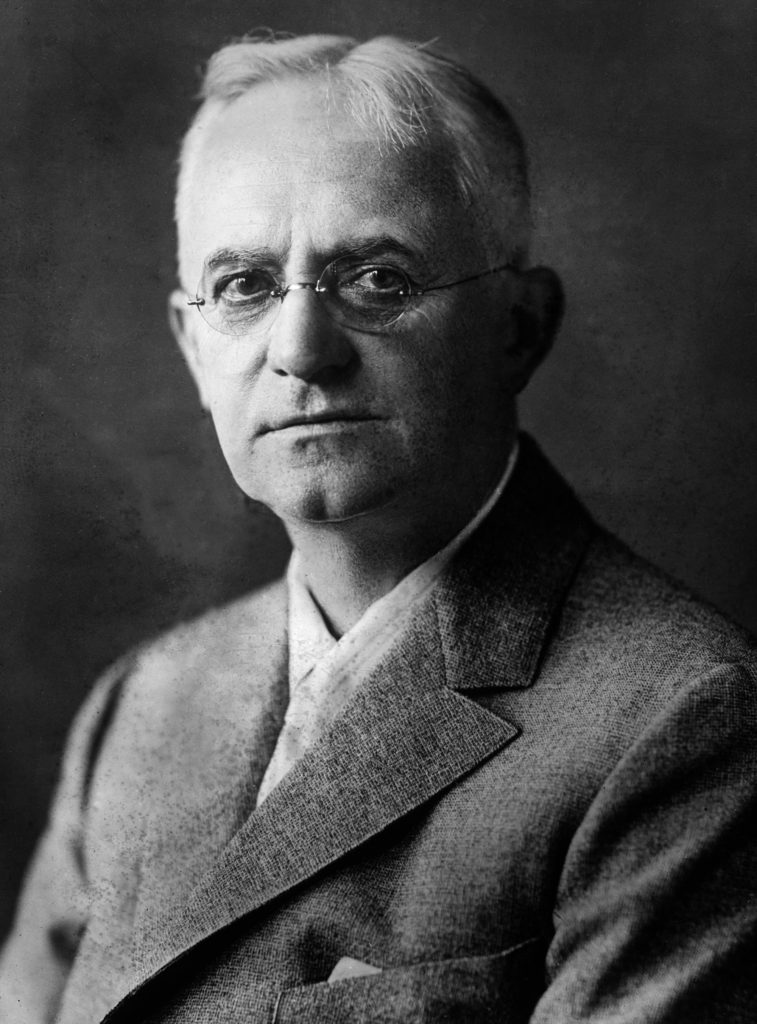Pictorialism
Time Period : 1880-1920
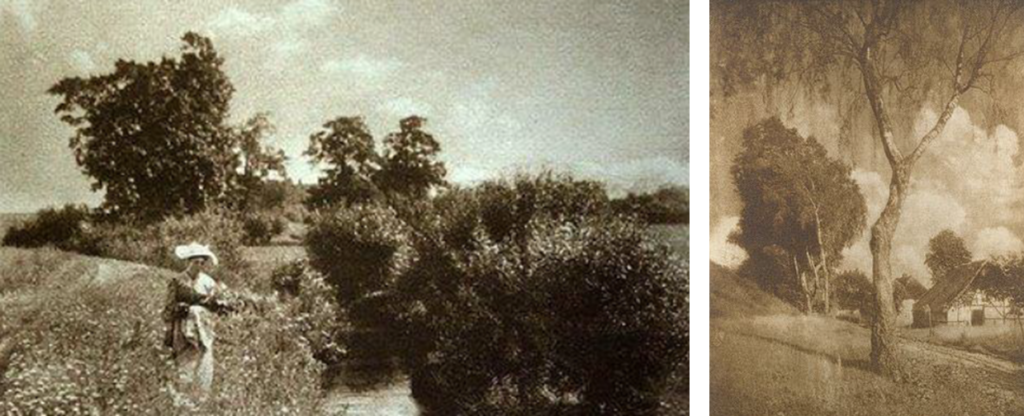
Key Characteristics: The make it look like art, look handmade. It reacted against mechanization and industrialisation. They abhorred the
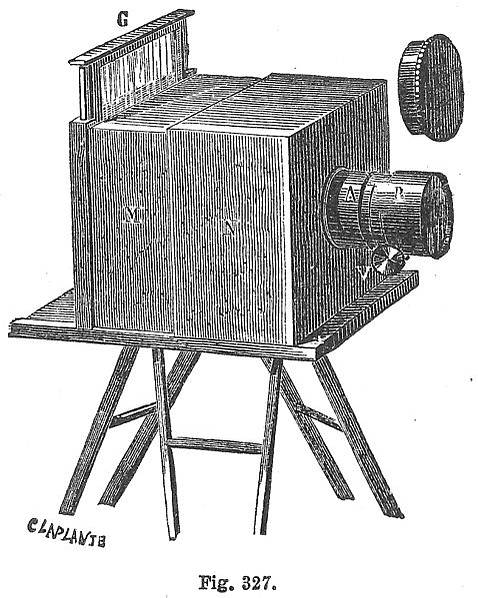
Methods/Techniques/Processes: Rub Vaseline on the camera lens to blur parts of the picture. Scratch the negative, and use chemicals to create an interesting print.
Artist Associated:
Alfred Stieglitz. He was an American photographer and modern art promoter who was instrumental over his 50-year career in making photography an accepted art form. In addition to his photography, Stieglitz was known for the New York art galleries that he ran in the early part of the 20th century, where he introduced many avant-garde European artists to the U.S. He was married to painter Georgia O’Keeffe.

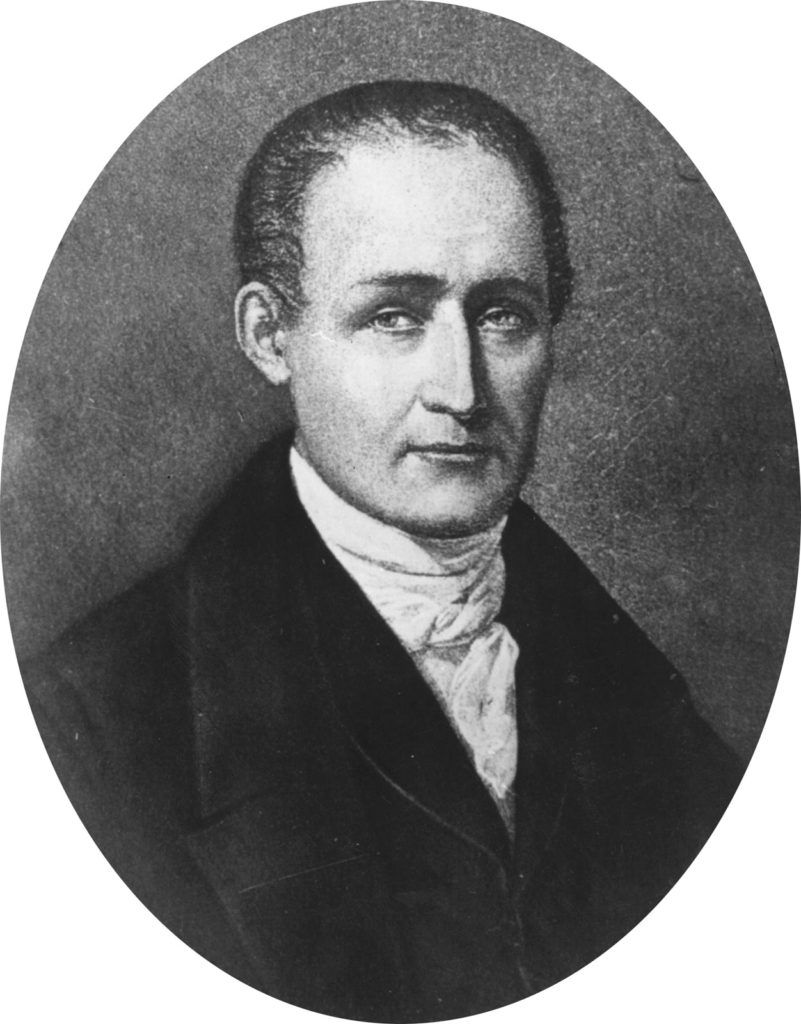
Hugo Henneberg. An amateur photographer originally trained in the sciences, Henneberg came to the medium from his study of physics, chemistry, astronomy, and mathematics. His knowledge of the technical aspects of photography served his aesthetic interests particularly well, as he created gum bichromate prints that involved multiple stages of development.

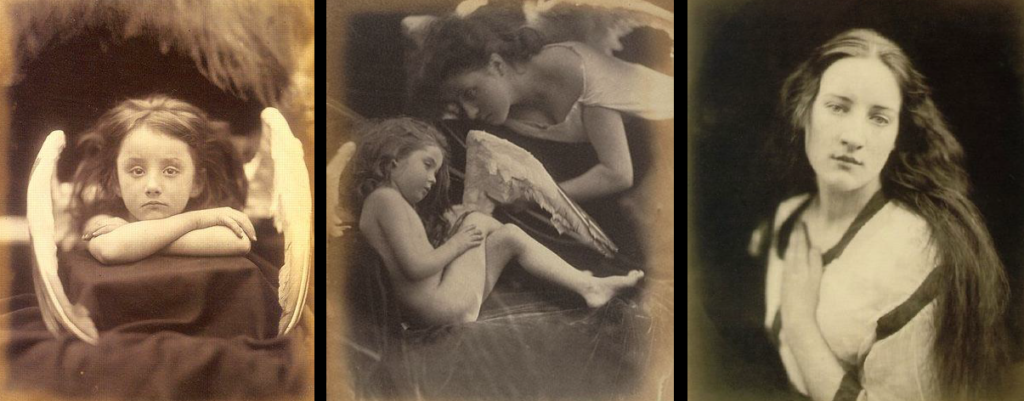
Julia Margret Cameron. The bulk of Cameron’s photographs fit into two categories closely framed portraits and illustrative allegories based on religious and literary works.

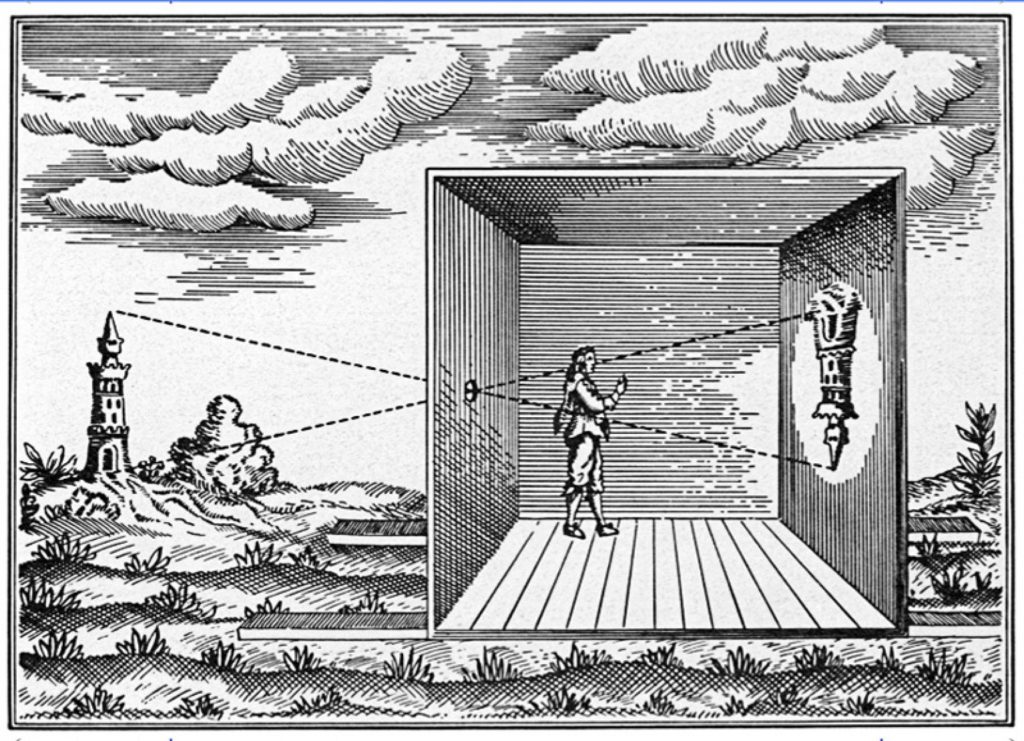
Realism / Straight Photography
Time Period : 1915
Key Characteristics: Politics, Revolutions, Cubism. Straight photographers were photographers who believed in the intrinsic qualities of the photographic medium and its ability to provide accurate and descriptive records of the visual world. These photographers. Realism photography grew up with claims of having a special relationship to reality, and its premise, that the camera’s ability to record objectively the actual world as it appears in front of the lens was unquestioned. A belief in the trustworthiness of the photograph is also fostered by the news media who rely on photographs to show the truth of what took place.
Methods/Techniques/Processes: Sharp Focus, Shape, Form, To face reality. “The camera is an instrument of a new kind of vision.”
Artist Associated:
Paul Strand. He was an American photographer and filmmaker who, along with fellow modernist photographers like Alfred Stieglitz and Edward Weston, helped establish photography as an art form in the 20th century.

Walker Evans. Often considered to the leading American documentary photographer of the 20th century. He rejected Pictorialism and wanted to establish a new photographic art based on a detached and disinterested look. He most celebrated work is his pictures of three Sharecropper families in the American South during the 1930s Depression.
Modernism
Time Period : early 1900s through to the 1960s.
Key Characteristics: characterised intellectually by a belief that science could save the world and that, through reason, a foundation of universal truths could be established. The common trend was to seek answers to fundamental questions about the nature of art and human experience. Modernity imbue all aspects of society and are apparent in its cultural forms including fiction, architecture, painting, popular culture, photography.
Methods/Techniques/Processes:
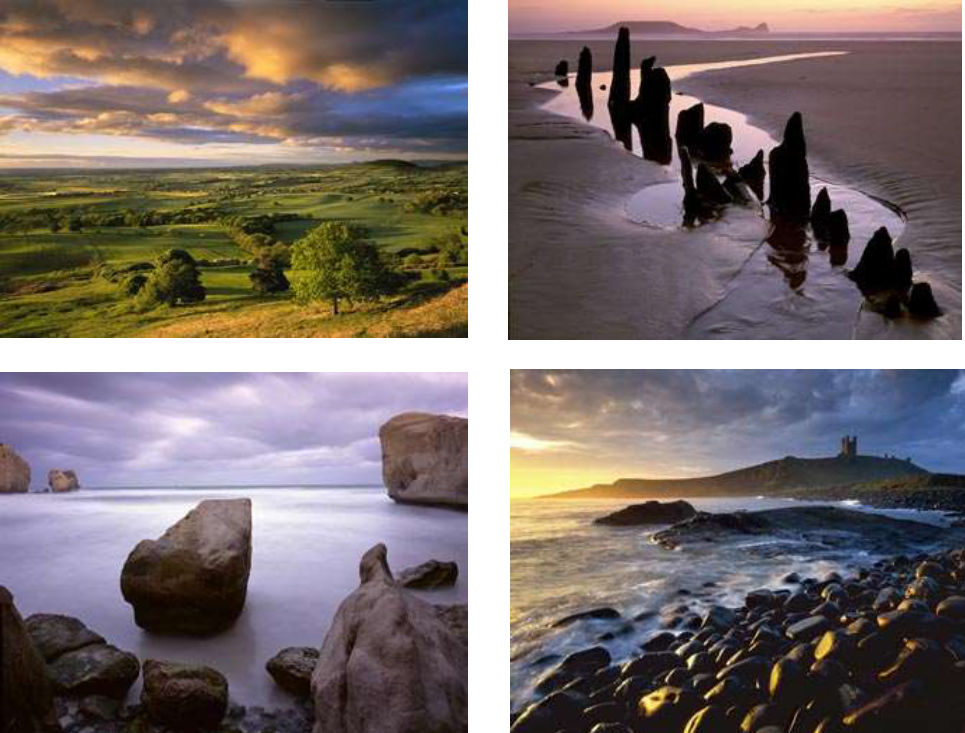
Artist Associated: Joe Cornish. He is a British photographer noted for his large format landscapes. Born in Exeter, Devon, England in 1958, he graduated with a degree in Fine Art from University of Reading in 1980 and then went to America to train as a photographer’s assistant.

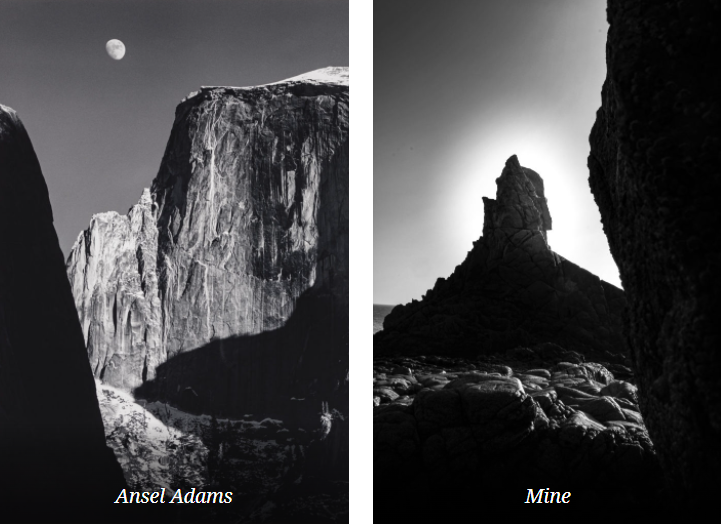
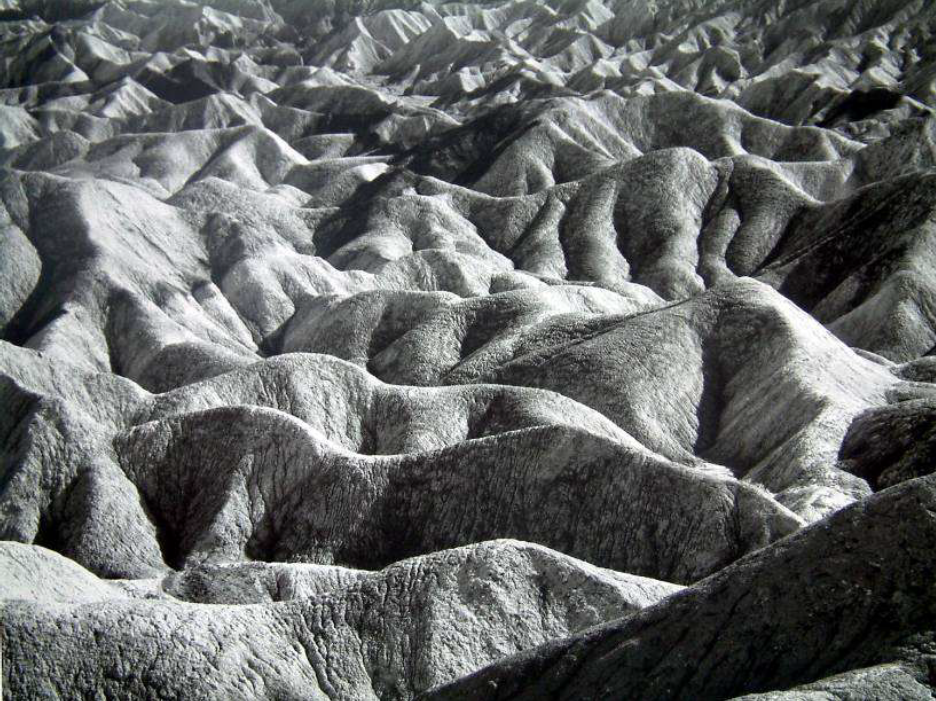
Ansel Adams. He was an American landscape photographer and environmentalist known for his black-and-white images of the American West. He helped found Group f/64, an association of photographers advocating “pure” photography which favoured sharp focus and the use of the full tonal range of a photograph.

Edward Weston. He was a 20th-century American photographer. He has been called “one of the most innovative and influential American photographers…” and “one of the masters of 20th century photography.”

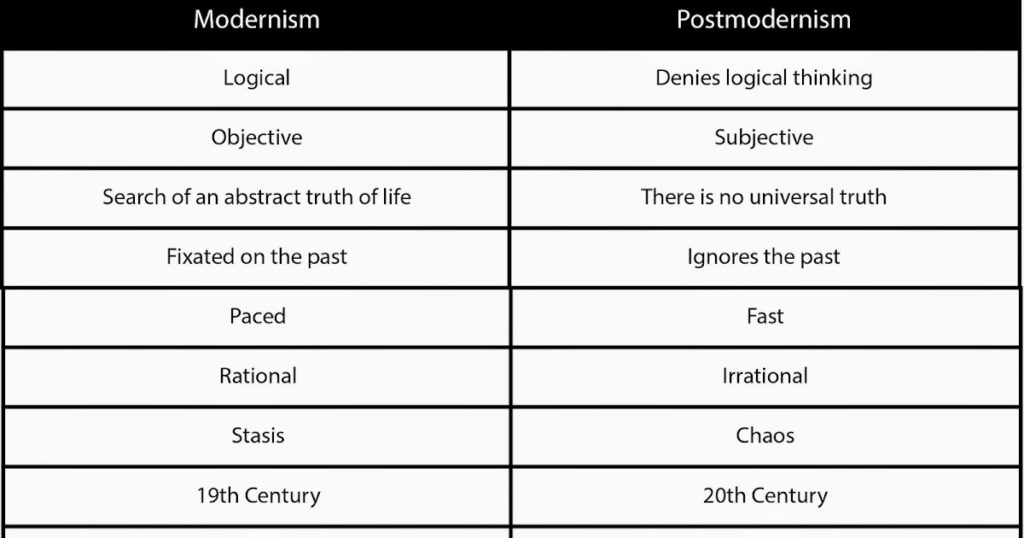
Post-Modernism
Time Period : second half of the 20th century
Key Characteristics: Postmodernism is relativism – the belief that no society or culture is more important than any other. It explores power and the way economic and social forces exert that power by shaping the identities of individuals and entire cultures.
Methods/Techniques/Processes:
Artist Associated: Anna Gaskell. She is an American art photographer and artist from Des Moines, Iowa. She is best known for her photographic series that she calls “elliptical narratives”
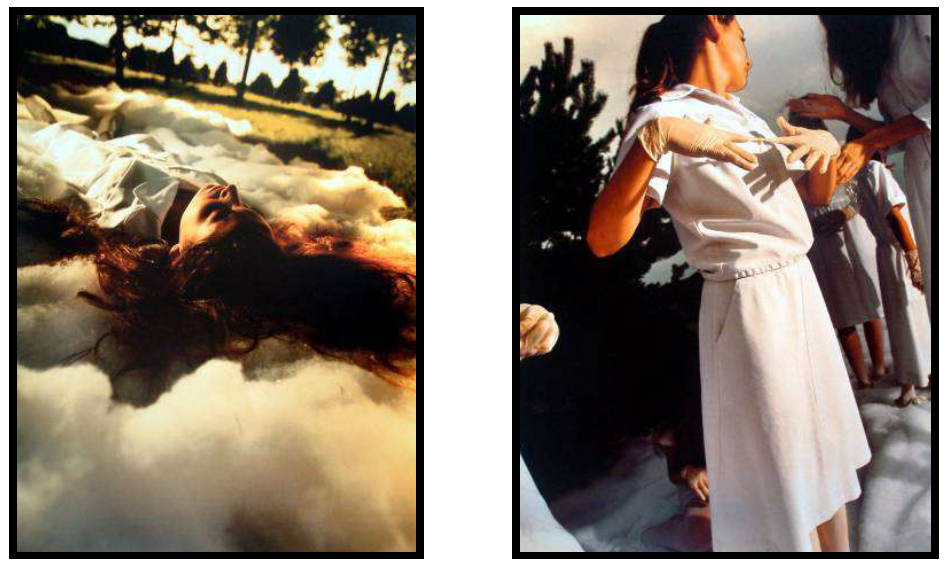

David LaChapelle. Is a famous American pop photographer, moviemaker and video artist that made his name by shooting celebrities like Lady Gaga, Kanye West, Michael Jackson, etc. But unlike most “celebrity photographers” he expands his portfolio with other kinds of work and creates beautiful exhibitions. His photography often references art history and sometimes conveys social messages.