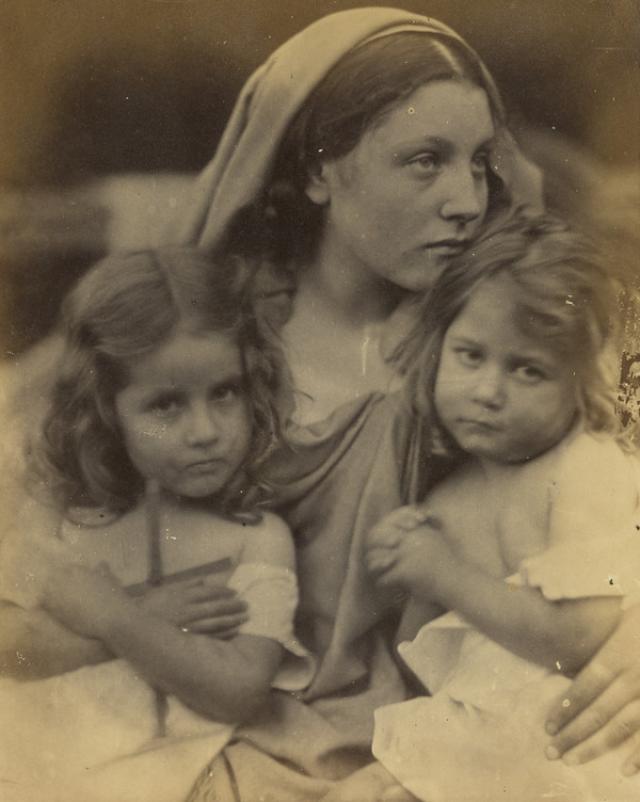Pictorialism
Pictorialism is an international style and aesthetic movement that dominated photography during the later 19th and early 20th centuries. It was an approach to photography which emphasized beauty of subject matter, tonality, and composition rather than the documentation of reality and was an imitate of art.
Time period:
1880 – 1920
Key Characteristics:
From the 1880s and onwards photographers strived for photography to be art and resemble hand made art by trying to make pictures that resembled paintings e.g. manipulating images in the darkroom, scratching and marking their prints to imitate the texture of canvas, using soft focus, blurred and fuzzy imagery and using Vaseline on their lenses.
Artists associated –
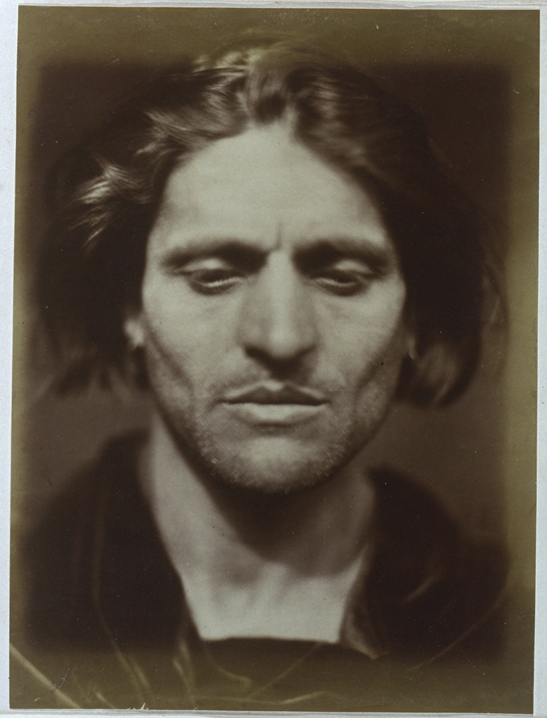
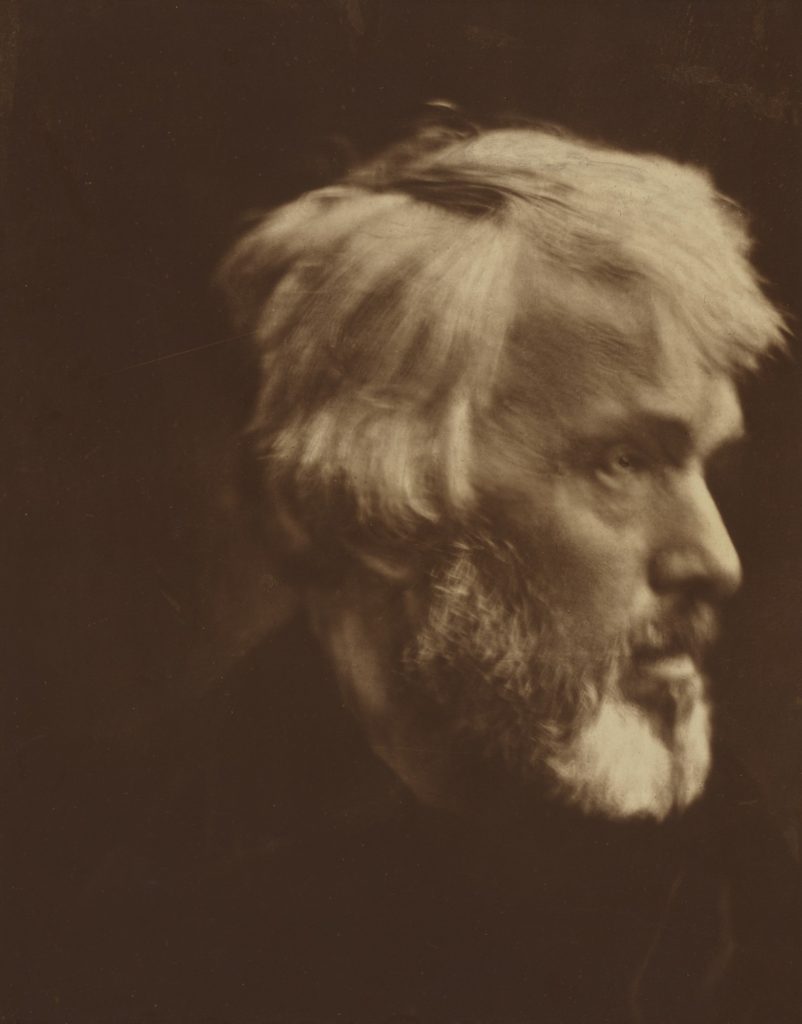
Julia Margaret Cameron
Julia Margaret Cameron was a British photographer who is considered one of the most important portraitists of the 19th century. She is known for her soft-focus close-ups of famous Victorian men and for illustrative images depicting characters from mythology, Christianity, and literature. In her works in particular, her artistic influence was Pre Raphaelite, with far away looks, limp poses and soft lighting. Cameron’s photographs were unusual in their intimacy and she had a visual habit of created blur through both long exposures, where the subject moved and by leaving the lens intentionally out of focus.
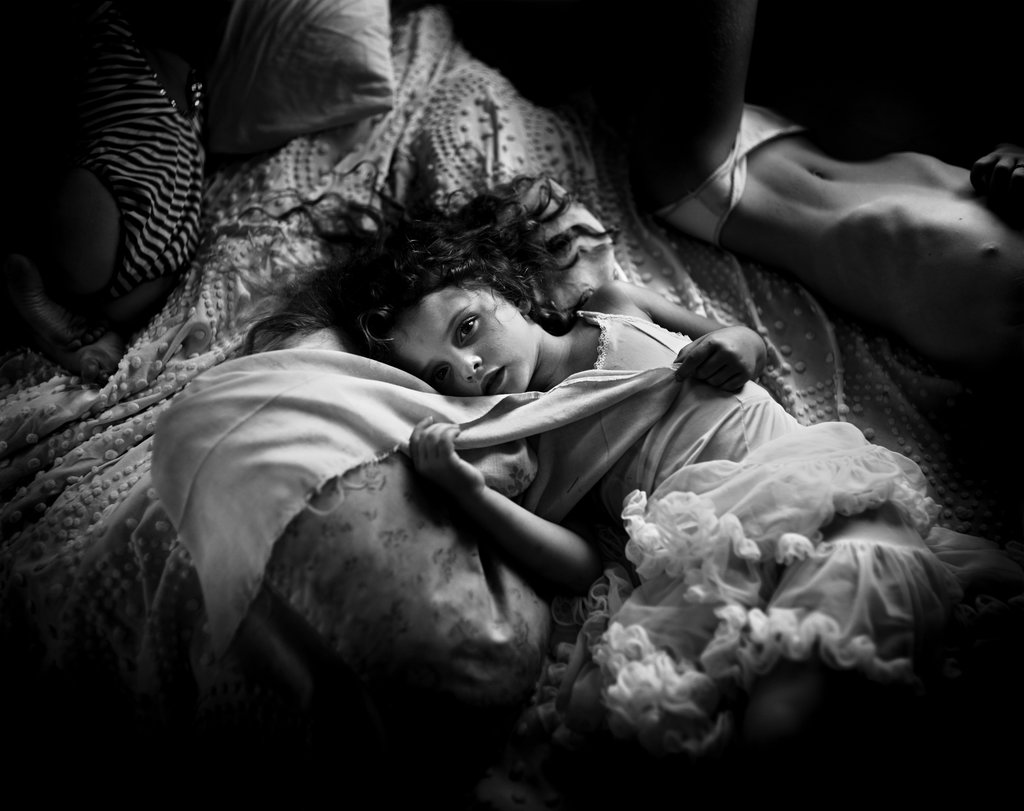
Sally Mann
Sally Mann is an American photographer, widely known for her large-format, black-and-white photographs, at first of her young children, then later of landscapes suggesting decay and death. Mann created a haunting series of photographs that tells a story about the one subject that affects us all, the loss of life. She created a project called ‘What Remains’ which was created in 2004 is a five part meditation on mortality and explores the ineffable divide between body and soul, life and death, spirit and
earth. In ‘What remains’ Munn reflects on her own personal feelings towards death as she examines the boundaries o contempary photography.
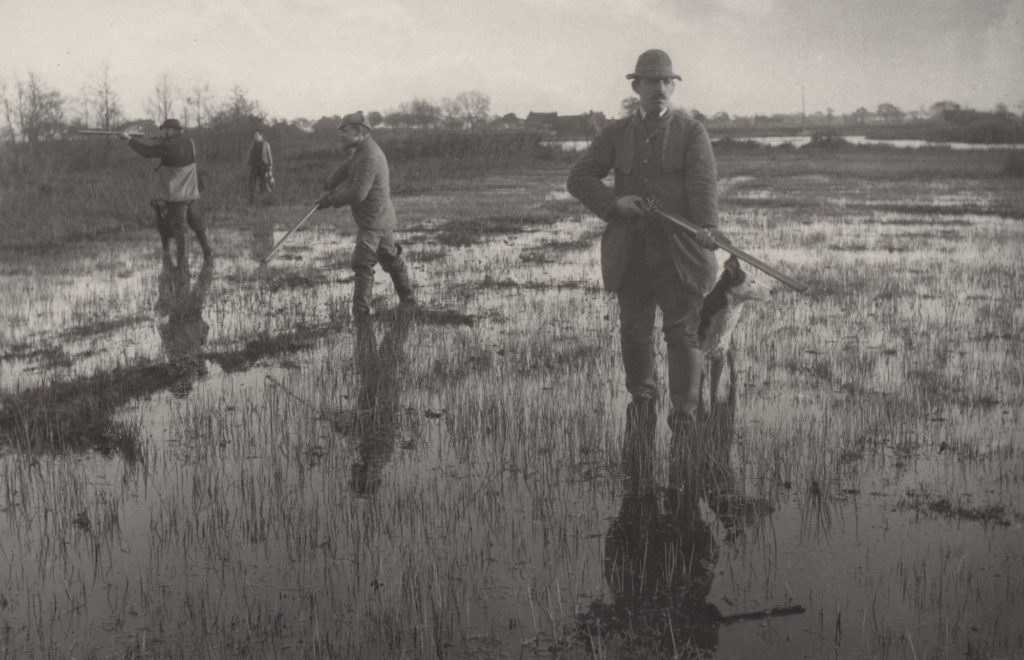
Peter Henry Emerson
Peter Henry Emerson was born 13th May 1856 and died 12th May 1936, he was a British writer and photographer. His photographs are early examples of promoting straight photography in an art form. Emerson is known for taking photographs which displayed rural settings and for his disputes with the photographic establishment about the purpose and meaning of photography. Initially he was influenced by naturalistic French painting, he argued for “naturalistic” photography and took photographs in sharp focus to capture country life as clearly as possible. His first photo album was published in 1886 and was titled ‘Life and Landscape on the Norfolk Broads‘ and it consisted of 40 platinum prints that were inspired by these ideas. However after a while he became dissatisfied with rendering everything in sharp focus, as he didn’t like that the undiscriminating emphasis it gave to all objects was unlike the way the human eye saw the world. He then started experimenting with soft focus, but was unhappy with the result of this aswell. He was experiencing difficulty with accurately recreating the depth and atmosphere which he saw as necessary to capture nature with precision. Although he was getting frustrated with his photography he carried on to take many photographs of landscapes and rural life in the East Anglian fenlands and went onto publish seven further books of his photography through the next ten years.
Modernism
Modernism was a broad movement surrounding all the innovative isms of the first half of the 20th century. Although different modern-isms were often incompatible they all rejected the dominance of older movements such as Classicism and Naturalism in favour of new experimental ways of producing art.
Time period:
Early 1900s and continued until the early 1940s.
Key Characteristics:
It was a broad movement encompassing all the avant-garde isms of the first half of the 20th century. Early modernity is characterised by a belief that science could save the world and that a foundation of universal truths could be established.
During the modernism photographers began to embrace its social, political and aesthetic potential by experimenting with light, perspective and developing, as well as new subjects and abstraction.
Surrealism
Surrealism was founded in Paris in 1924 by the poet ‘Andre Breton’ and continued Dadaism’ exploration of everything irrational and subversive in art. Surrealism was more explicitly preoccupied with spiritualism, Freudian psychoanalysis and Marxism. It aimed to create art which was ‘automatic’ which meant that it had emerged directly from the unconscious without being shaped by reason, morality or aesthetic judgements. The Surrealist also explored dream imagery an they were an important art movement within Modernism involving anything from paintings, sculpture, poetry, performance, film and photography.
Artists associated:
Rene Magritte
René François Ghislain Magritte was born on the 21st November 1898 and died on the 15th August 1967. In the 1920s, he began to paint in the surrealist style and became known for his witty images and his use of simple graphics and everyday objects, giving new meanings to familiar things. Often his images were depicting ordinary objects in an unusual context, his work is known for challenging observers’ preconditioned perceptions of reality. His imagery has influenced pop art, minimalist art, and conceptual art. Magrittes earliest paintings date back to 1915 which then sparked his career in surrealism. With his art becoming more and more popular he was able to pursue his art full-time and was celebrated in several international exhibitions.
Post Modernism

Post modernism was a reaction to modernism and was influenced by disenchantment brought on by the second world war. Postmodernism was the collective name given to the shattering of modernism. In photography this was the direct challenge to the ideal of fine art photography whose values were established on an anti-commercial stance.
Time Period:
Late 20th century
Key Characteristics:
Postmodernism makes references to things outside the art work, e.g. political, cultural, social, historical,psychological issues.
Postmodern work are aware of and make reference to the previously hidden agendas of the art market and its relation to art museums, dealers and critics.
Postmodern work often uses different approaches in the construction of the work such as collaboration, parody, recycling and reconfiguration.
Postmodernism favours the context of a work including examining subject and the reception of the work by its audience.
Artist associated:
Jeff Wall
Jeff Wall was born in 1946 in Vancouver, Canada, where he still lives. Wall is a leading contemporary photographer whose work is concerned with ideas about the nature of images, representation, and memory. He has been producing carefully staged photos since the end of the 1970s.