Camera Skills
Auto Focus
Auto focus is the best time saver of the camera and is found in most cameras. Initially the auto focus helps clear up the quality of the images we take. It often uses a computers to run miniature motor that focuses the lens for you. Focusing is the lens means moving in and out until the sharpness of photo is at the highest level possible. Depending on the distance of the object you are trying to focus on, will affect the distance in the lens from the film to present a clear photograph.
Manual focus
As well as having an auto focus setting on your camera you have a manual setting for focusing images. On the side of your lens there will me a switch labelled ‘’AF-MF’’ short for Auto focus and Manual focus. When you wish to use manual focus switch to manual on the camera. The main advantage over auto focus is the speed of the manual focus . All manual focus lenses have a gauge depicting the DOF at small aperture and the on the focus ring, the focal distance is depicted in metres

White Balance
White balance (WB) is the process of removing unrealistic color casts, so that objects which appear white in person are rendered white in your photo. Proper camera white balance has to take into account the “color temperature” of a light source, which refers to the relative warmth or coolness of white light. Our eyes are very good at judging what is white under different light sources, but digital cameras often have great difficulty with auto white balance

Shutter speed
Shutter speed is the length of time your camera shutter is open, exposing light onto the camera sensor. Essentially, it’s how long your camera spends taking a photo. This has a few important effects in how your images will appear. When you use a long shutter speed, you end up exposing your sensor for a significant period of time. The first big effect of shutter speed is motion blur. If your shutter speed is long, moving subjects in your photo will appear blurred along the direction of motion. Shutter speeds are typically measured in fractions of a second, when they are under a second. For example 1/4 means a quarter of a second, while 1/250 means one two-hundred-and-fiftieth of a second (or four milliseconds).

Using Focus-points
Focus points are often shown as small squares when you look through the camera and is seen on the viewing screen. When you got to take a photo and lightly press down on the shutter button to focus on your image, the focus pint you are using will light up. A focus point can be virtually anything ranging from a person, to a building etc. other way in which will help with focusing on your image is also considering blurs, size colour, shape.

IOS
ISO stands for International Organization for Standardization. The IOS controls the expose by using software in the camera to make it extra sensitive to light. A high ISO such as ISO 1,600 will produce a brighter picture than a lower ISO such as ISO 100. The drawback to increasing the ISO is that it makes the picture noisier. Digital noise is apparent when a photo looks grainy.

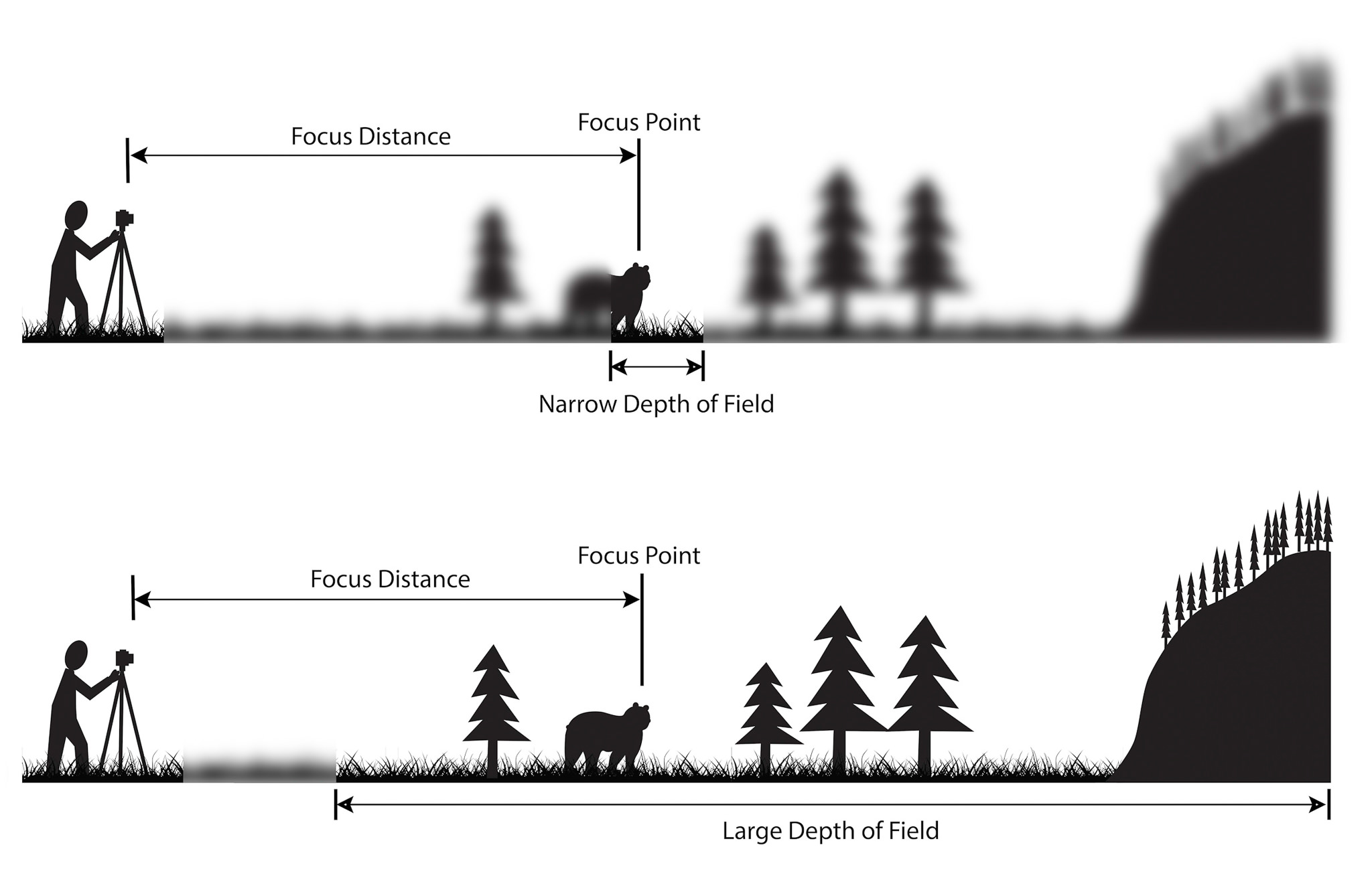
Depth of field
A camera can only focus its lens at a single point, but there will be an area that stretches in front of and behind this focus point that still appears sharp. This zone is known as the depth of field. It’s not a fixed distance, it changes in size and can be described as either ‘shallow’ (where only a narrow zone appears sharp) or deep (where more of the picture appears sharp) Because depth of field has an impact on both the aesthetic and technical quality of a picture. Sometimes you’ll want to use an extensive depth of field in order to keep everything sharp. A classic example is when you’re photographing a landscape, where generally the most desirable outcome is to capture detail from the foreground to the horizon.
Aperture
‘The opening of the lens’ The aperture is a small set of blades in the lens that controls how much light will enter the camera. The blades create a octagonal shape that can be widened or closed down to a small hole. If you shoot with the aperture wide open, then more light is allowed into the camera than if the aperture is closed down to only allow a tiny hole of light to enter the camera
![]()
