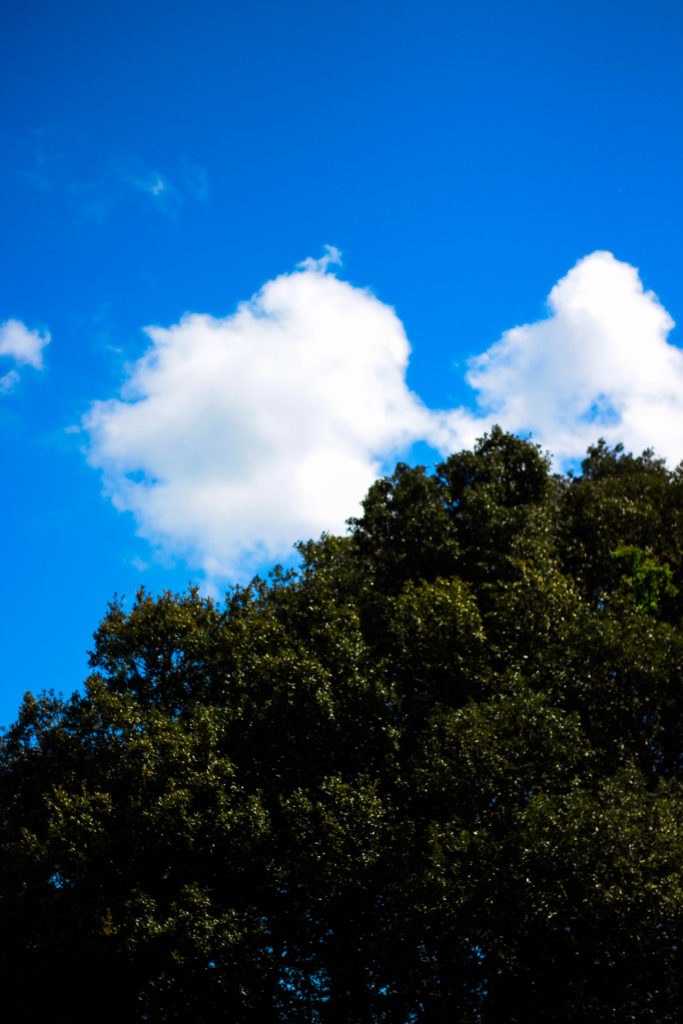
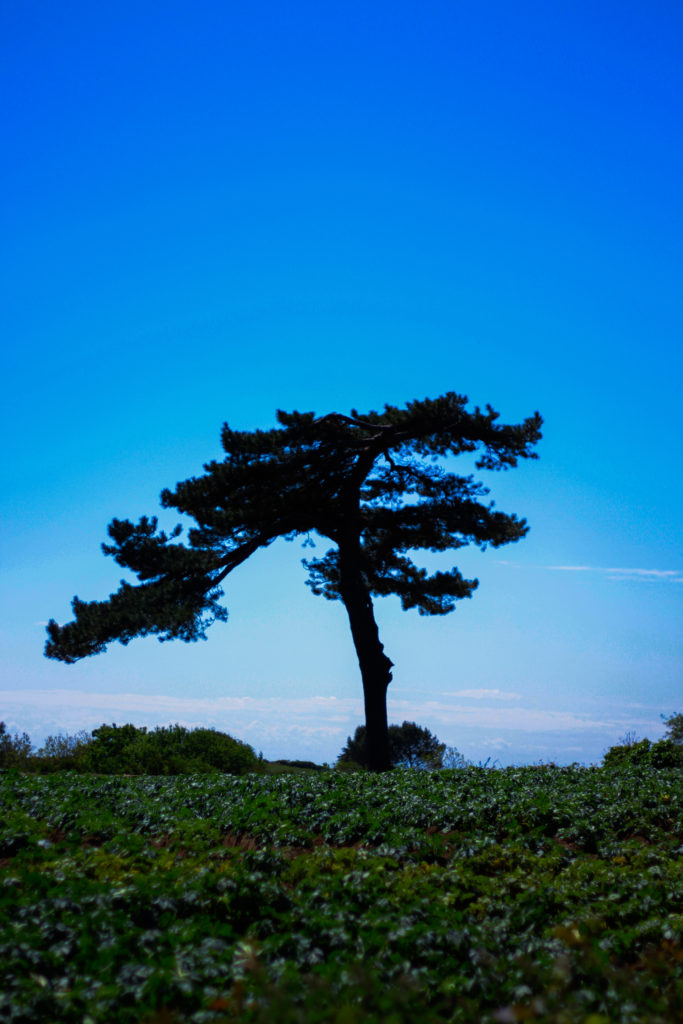
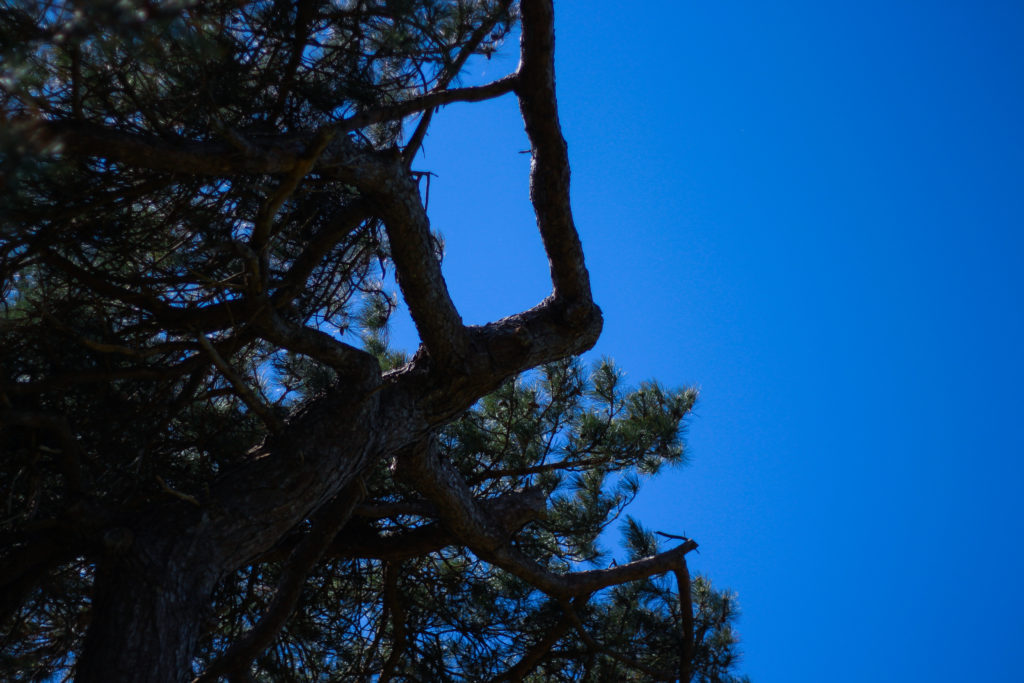
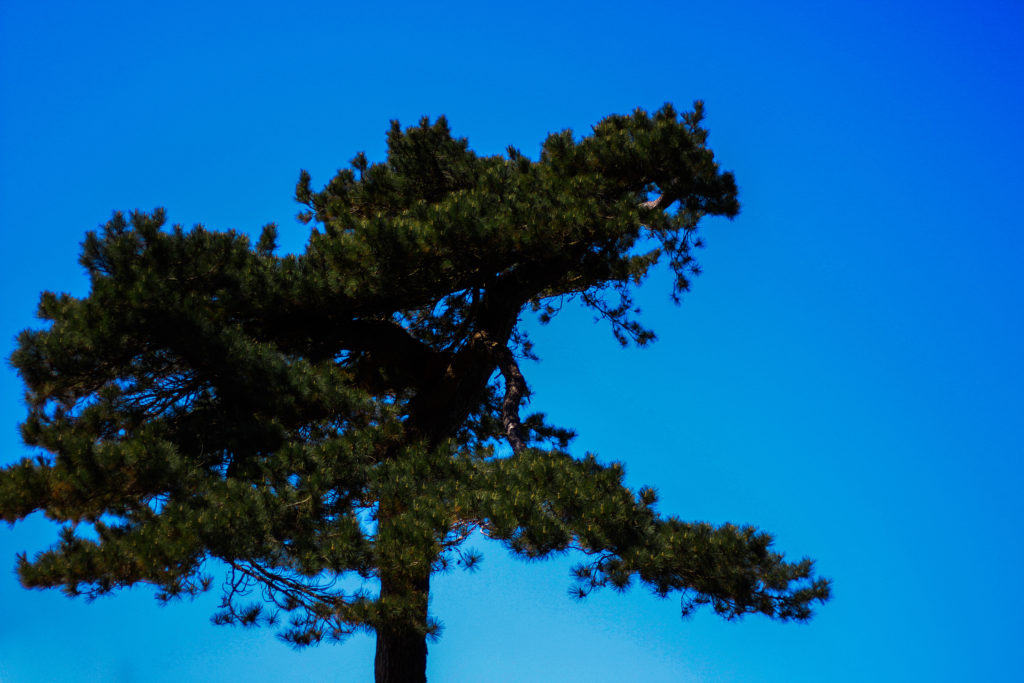
Photoshoot Plan
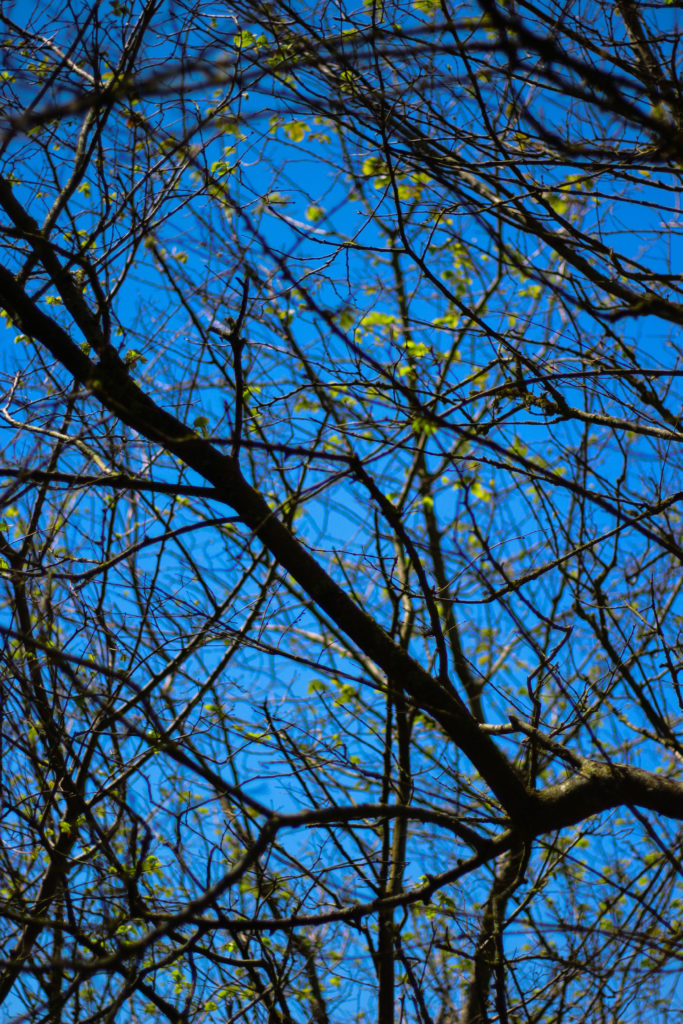
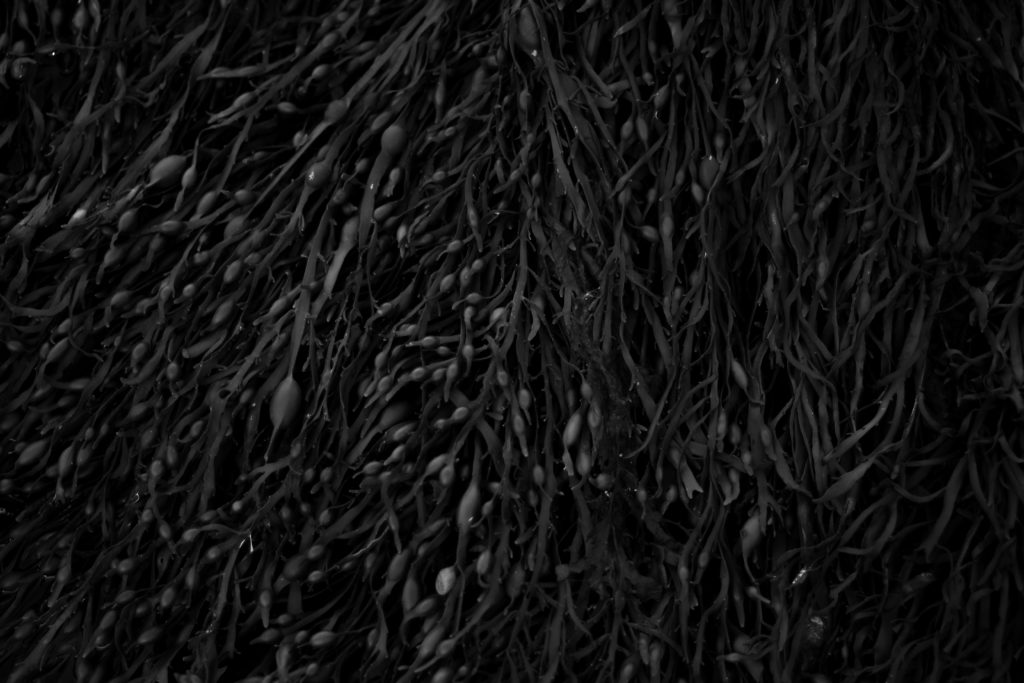
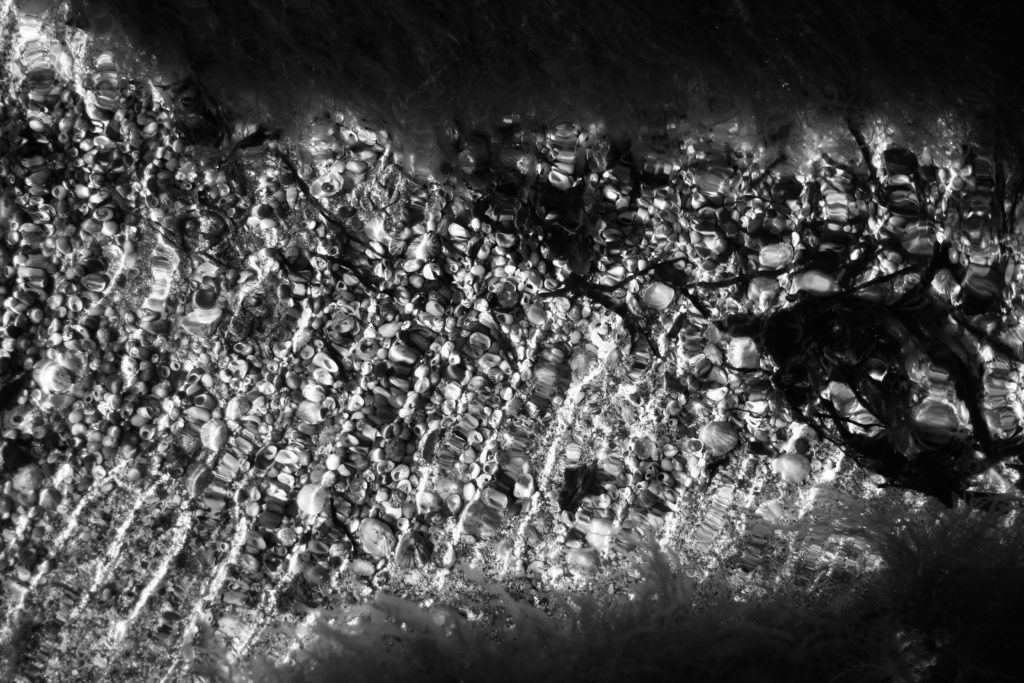
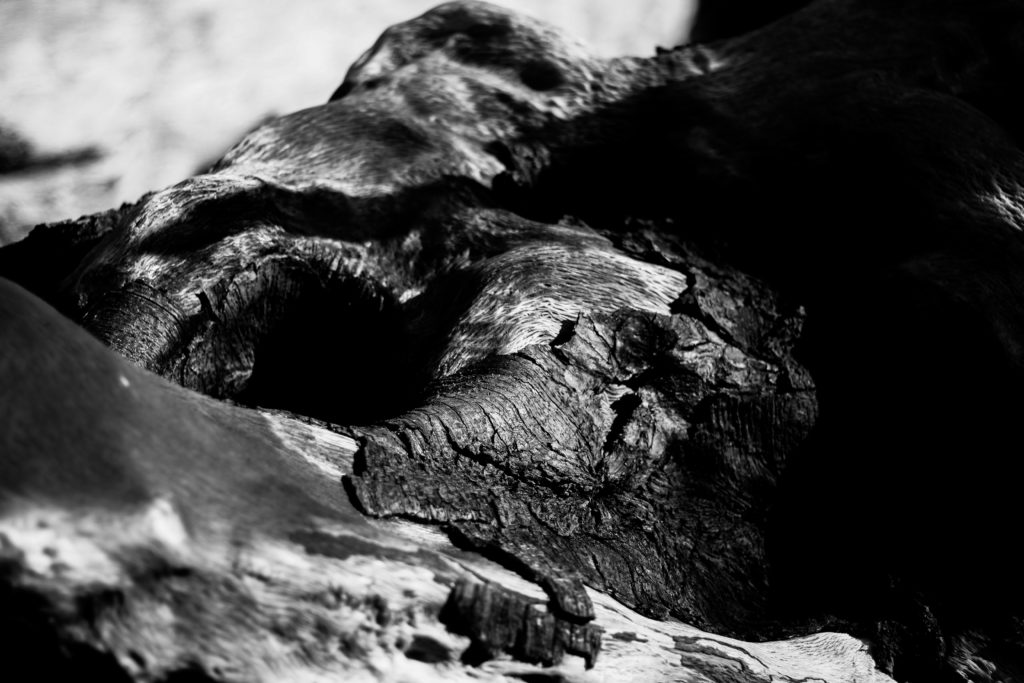
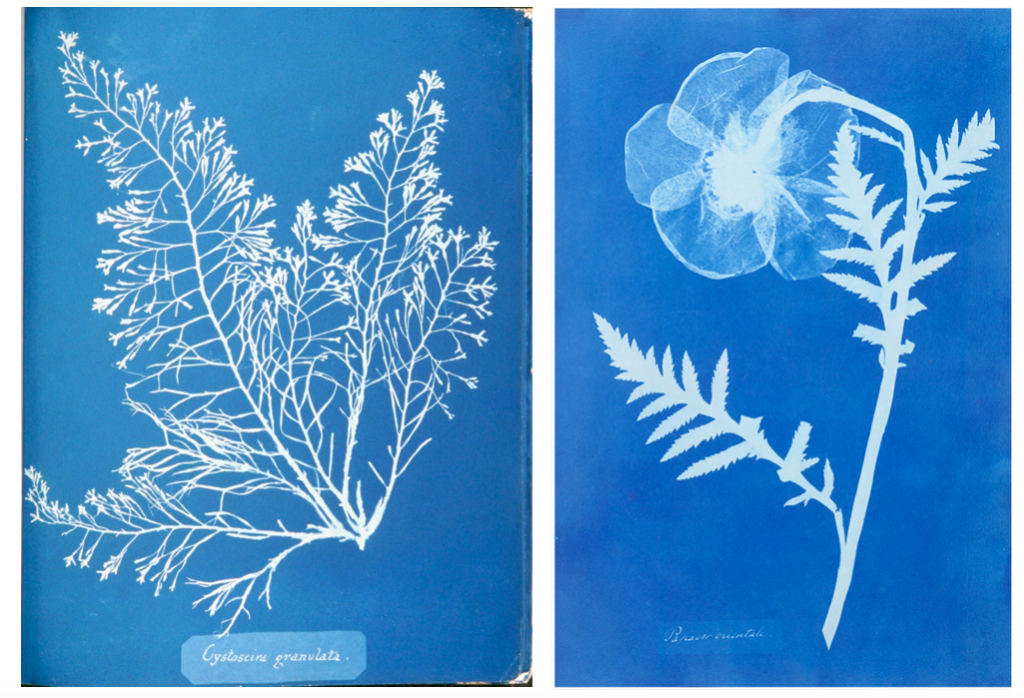
For this shoot I plan to experiment by creating images, like Anna Atkins, by using light sensitive paper and placing natural objects on top to create a print. I wanted to take inspiration from Anna Atkins as I think her images have a spiritual quality to them and I think by producing similar image, it will give my project a different type of photos, other than the landscape images, that will take my project further. I plan to see the outcomes of this experimentation and decide if i want to use them in my final outcome. If the outcomes aren’t as effective as I thought they would be, I plan to produce similar looking images from natural objects by editing, that have the same appearance of Anna Atkins images. I also think these images will reflect the work of Susan Derges as she also used light sensitive paper to create her images of the natural aspect water. I plan to take inspiration from both these photographer in my photoshoot.
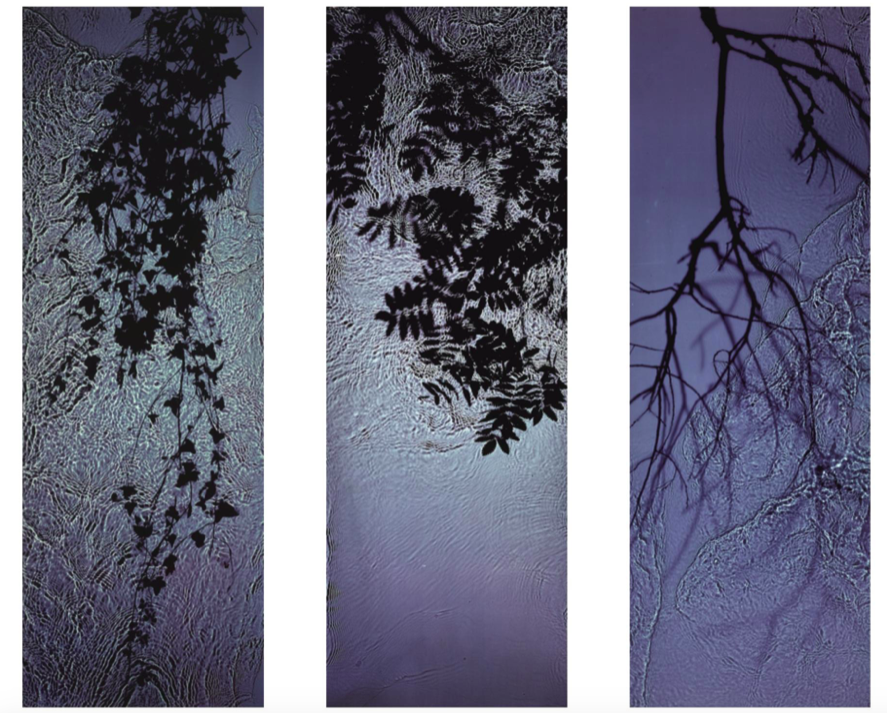


Light Sensitive Paper Experimentation
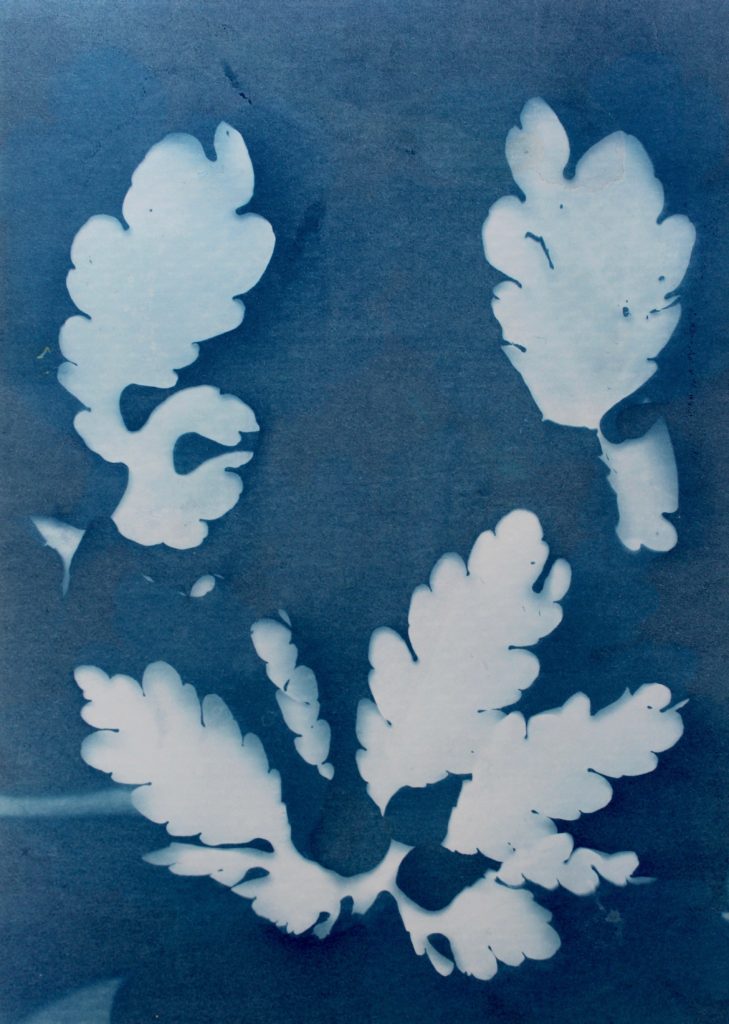




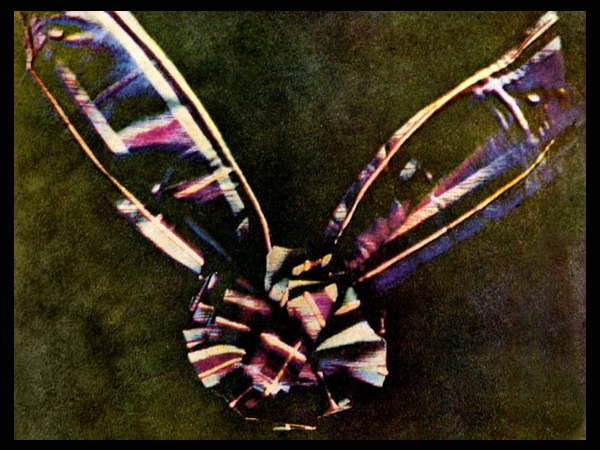
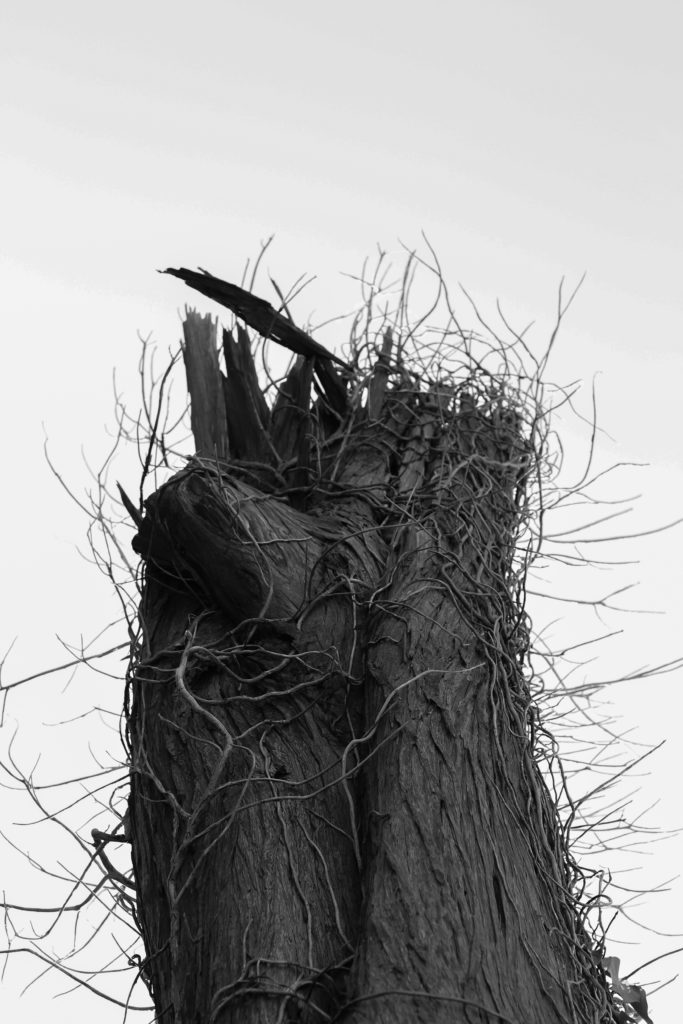
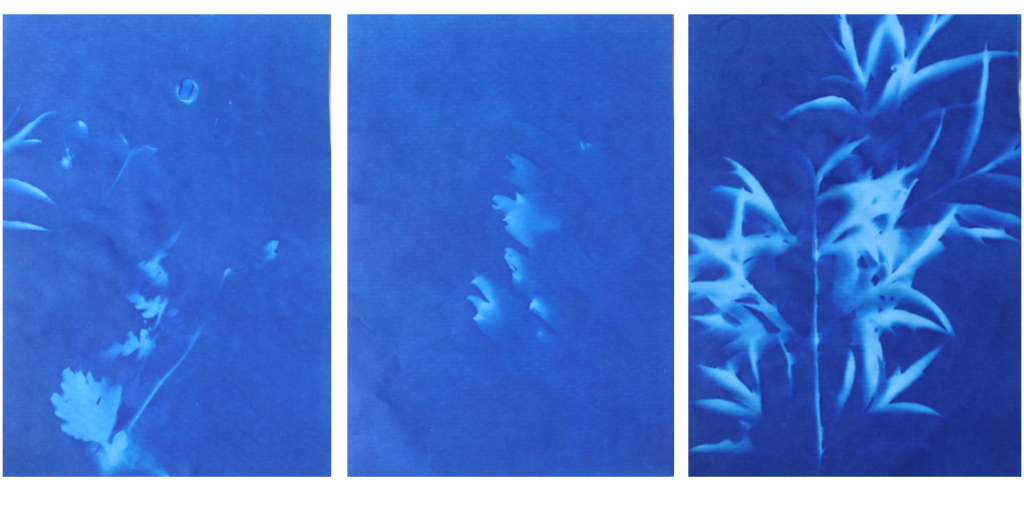
I think that these three photograms were the most effective in this shoot as they are the most clear and defined compared to others. I think this is specifically in the first image were I think that the shadows that were created by the plant on the paper were printed, making the outsides of objects on the paper darker, emphasising the brightness against the dark background. I like this as it makes the objects seem more 3D like they are coming out of the page. Other images in this shoot didn’t have this but were still effective. I also like how the specific rounded shapes of the leaves are precisely shown and noticeable against the blue background because i left it out in the sun for a long period so that the light sensitive paper had a long time to to change colour. I experimented in this shoot by leaving light sensitive paper out in the sun for different amounts of time and found that when I didn’t leave them for long, the outline of the object on the paper wasn’t as noticeable and as emphasised against the blue background. I think that both of these effects are successful as the blurred create a different look in comparison to the precise ones where I left them out in the sun for longer. I decided for some of the photograms, like the first one, to place multiple natural objects on the paper as I thought that this would create a more interesting composition when they printed. I also experimented with only one object and found that I preferred multiple.
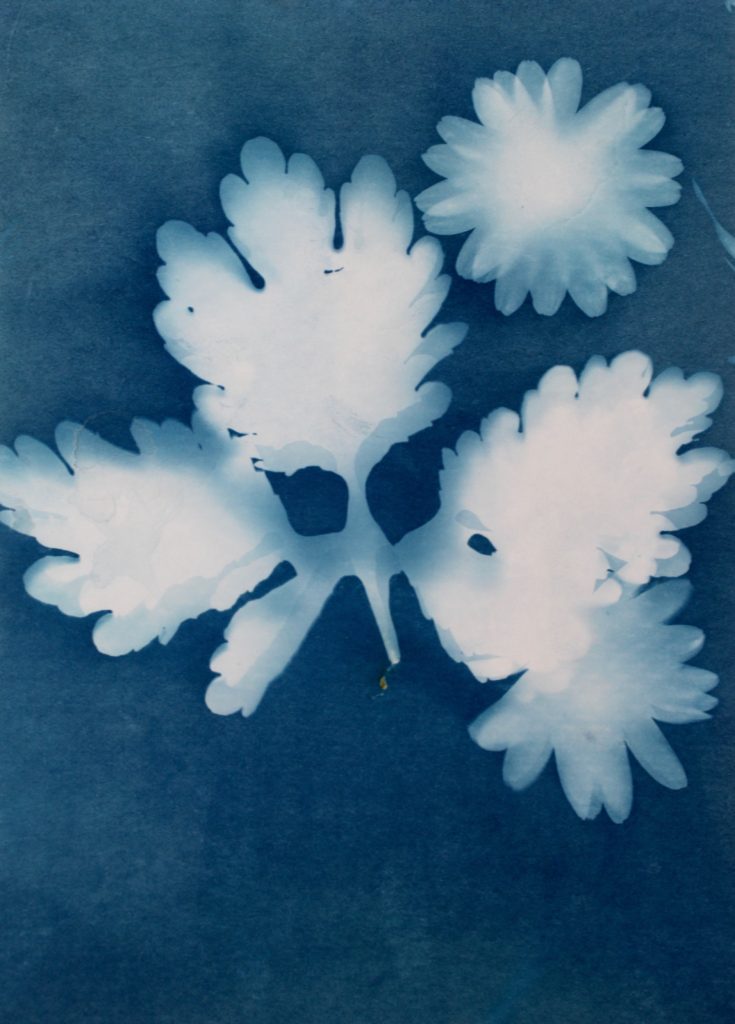
In the second image the natural objects had moved because of the wind but because of this the plants have two different outlines, one being more faint than the other. I think that this was effective, not being as precise as the first one, as it adds different ranges of blue tones on the plants. It also creates a blurred effect making it look as though the plants are moving. I also like how in this photogram that some of the plants overlap each other, I did this to create a more interesting composition.
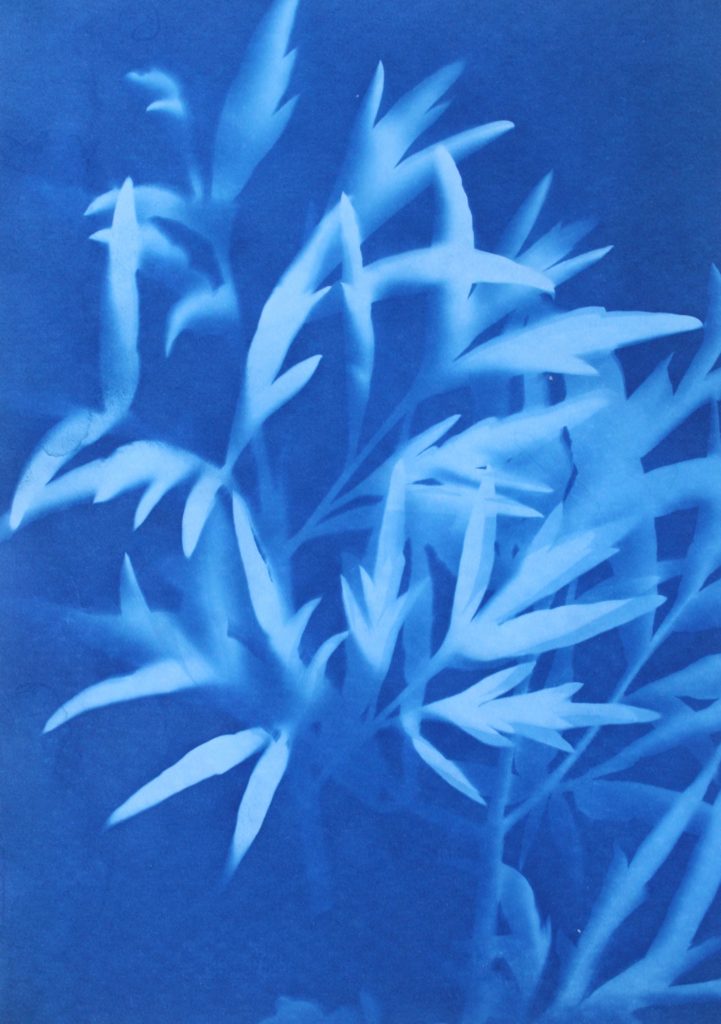

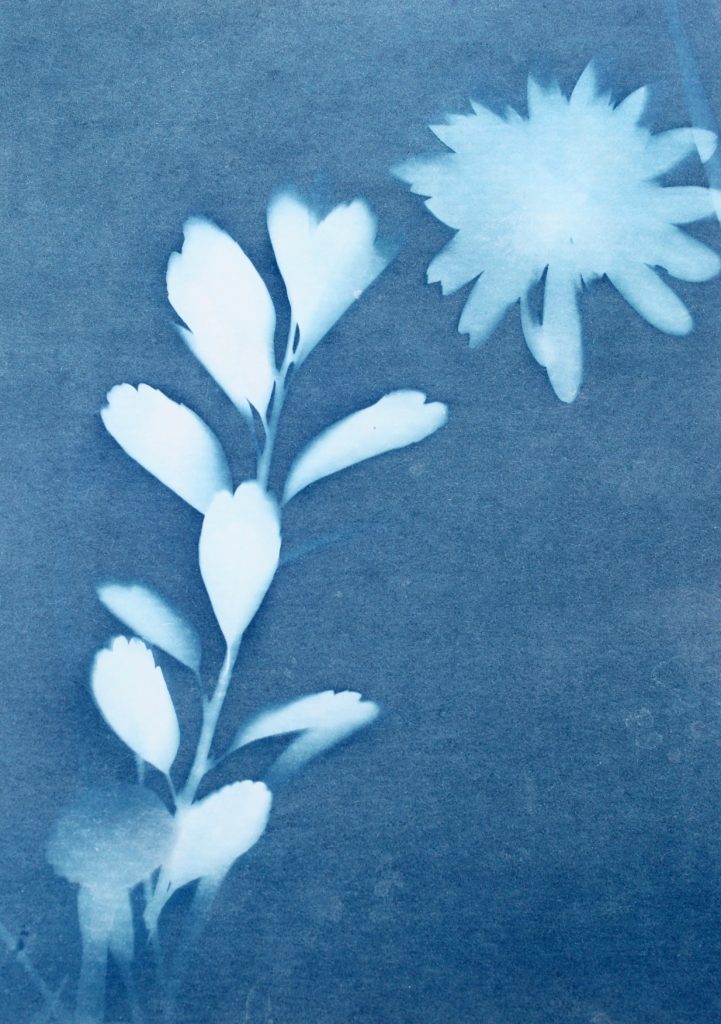
I also like this photograms as it has more shapes than any of the other ones because I used multiple of the same plant placed over each other, creating an interesting patterns against the blue background. By having the solid colours of the leaves more noticeable, it makes what the photogram is of more apparent. I like the smaller leaves that are coming from the stems as you can noticeably identify that they are leaves, linking to nature. The plants towards the top of the photograms are less clear than the ones in the middle, becoming more blurred as the edges. I think this is because the edges of the plant had started coming off the paper as it was left in the sun, but i think it’s effective as it focuses the audiences attention to the centre of the photogram. I think this is also emphasised by how it becomes darker towards the edges of the paper, highlighting the white colours in the middle. Another aspect I like is how the plant goes off the edges of the paper, as I think it contrasts nicely to the other photograms that are placed precisely in the middle or around each other. This is like Anna Atkins where she doesn’t let the plants she places on the light sensitive paper go over the edges. I thought that by doing this I would be creating my own interpretation of her work, but not directly copying the way she displays plants.
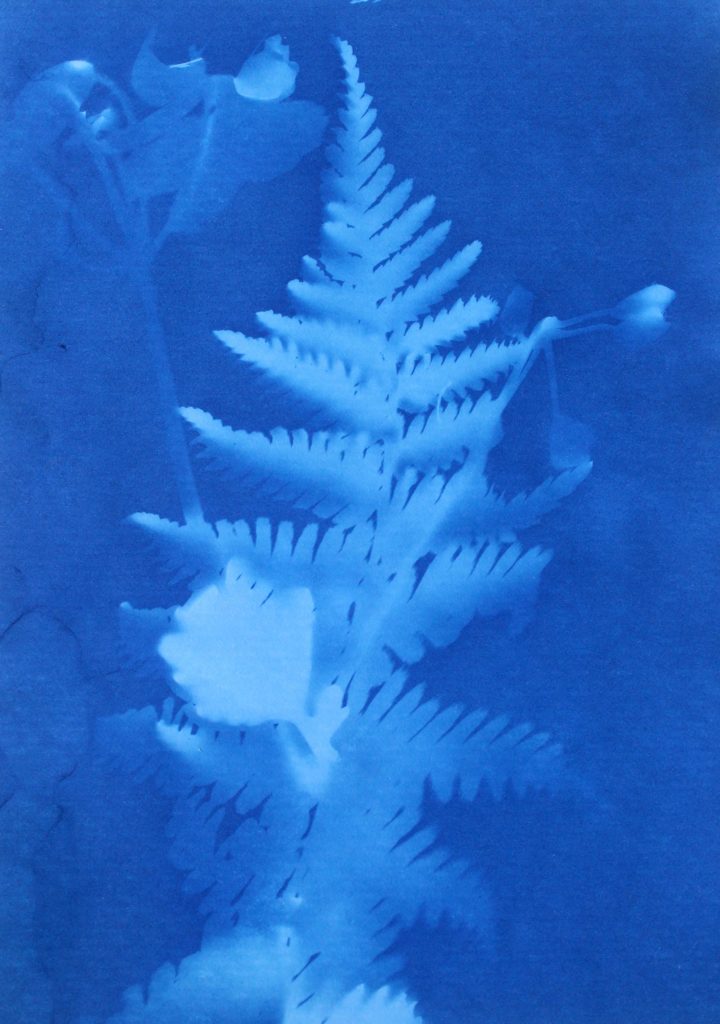
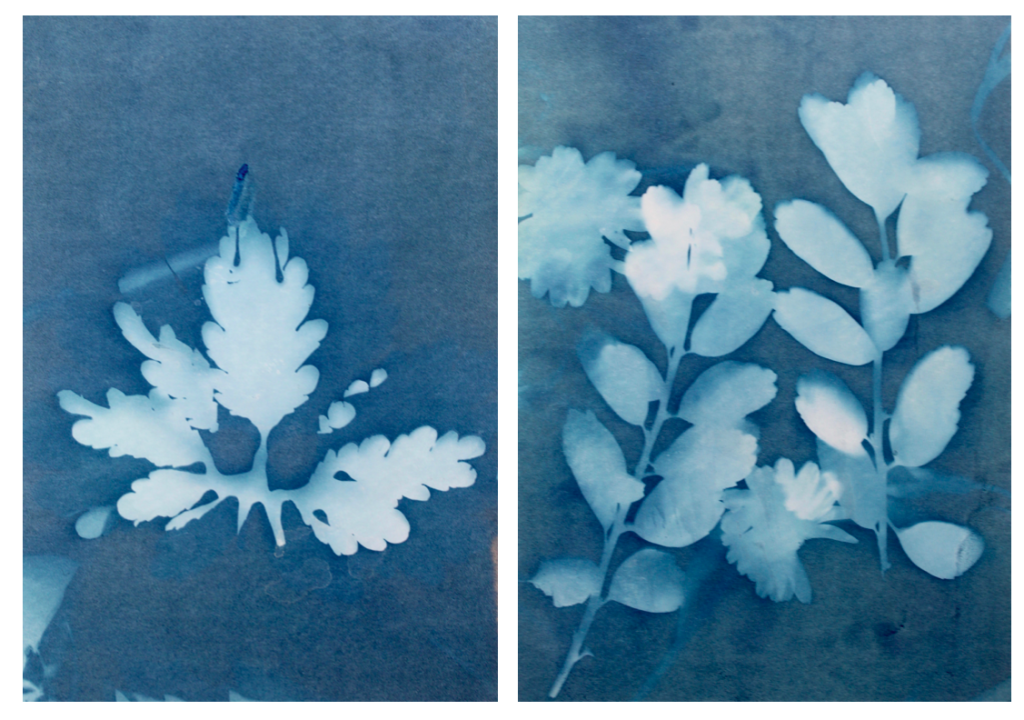


I tried to use a variety of different plants on the paper to create a range of different appearances and compositions. I tried to find plants that had interesting leaves and details so I could see the effect this created on the paper. I think this was effective as it means i could display all the photograms together and they will all be separate and contrast from one another. Also like in some photograms, like the first one displayed above, there are two plants on the paper, where one has printed clearly and the other hasn’t, creating a blurred effective in the background. I think this creates an interesting juxtaposition.
I also think that this experimentation looks at photograms in a different way to what people in the 1900s did where they were used in a scientific, analytical way. In my opinion those photograms in the 1900s still have a spiritual quality to them through the delicate lines and shapes. This is what I tried to interpret when creating my own by selecting plants with interesting shapes to highlight the intricate and delicate appearance even more.
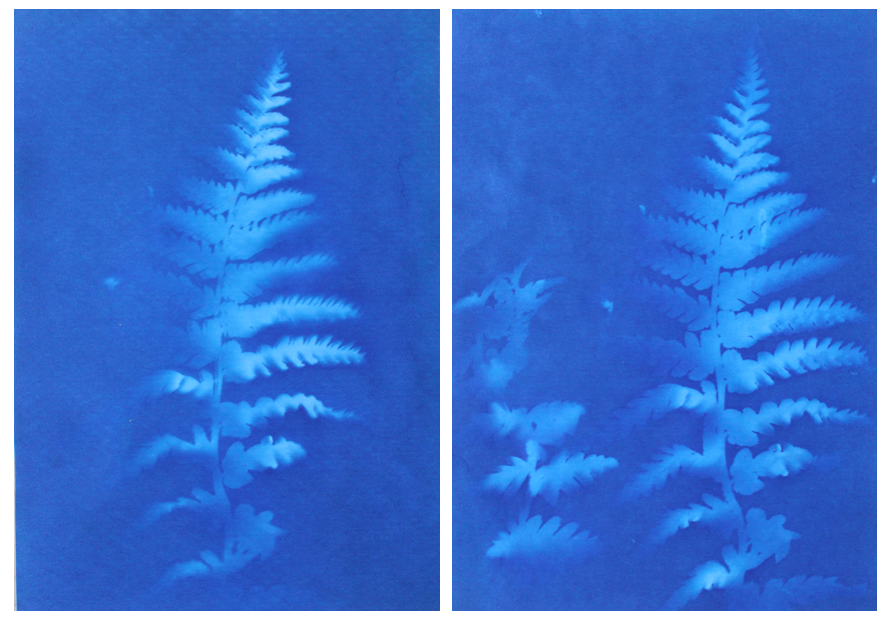

Evaluation
Overall I think that I successfully interpreted the work of Anna Akins by experimenting with the same the technique to produce camera-less images that she did. I think that I will use some of these photograms as some of my final outcomes as I think they add another level to my work, contrasting to the landscape and close up images I have taken in nature with a camera. By including some of these in my final pints and photobook, I can emphasise nature with a different technique, still following the same theme as the other images. I will experiment by seeing how these photograms look alongside my camera images, and what they loo like separately to decide how I am going to display them.