During the late 1950s and early 1960s in New York City, the dominant art movements were Abstract Expressionism, followed by Pop art, then Minimalism. In the mid-1960s, a far smaller movement of individual artists producing realistic paintings related to photography began to practice their craft, also in New York. This was labelled as Photorealism. Photorealism artists’ work depended heavily on photographs, which they often projected onto canvas allowing images to be replicated with precision and accuracy. The exactness was often aided further by the use of an airbrush, which was originally designed to retouch photographs. Photorealism complicates the notion of realism by successfully mixing together that which is real with that which is unreal. While the image on the canvas is recognizable and carefully outlined to suggest that it is accurate, the artist often based their work upon photographs rather than direct observation. Therefore, their canvases remain distanced from reality factually and metaphorically. Many Photorealists adamantly insist that their works are not communicative of social criticism or commentary.
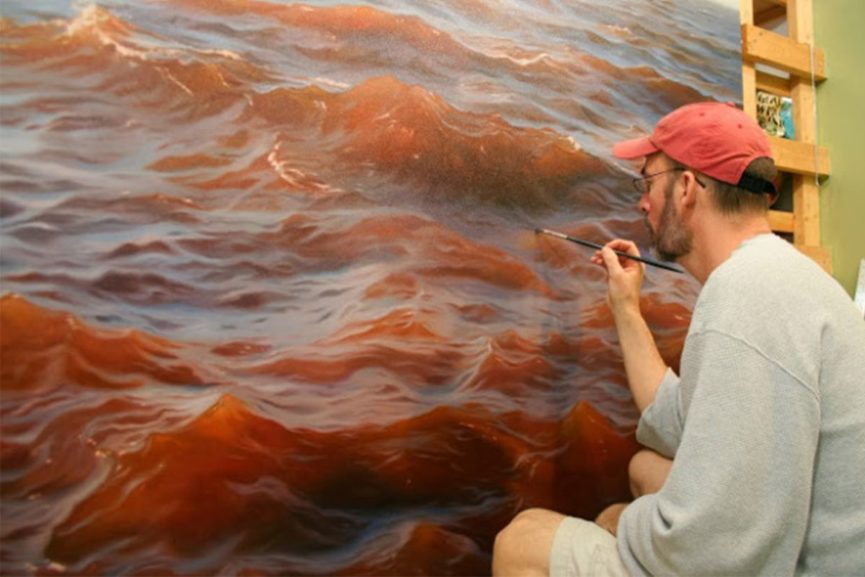

“SOMETIMES I REALLY WANT TO PAINT SOMEBODY AND I DON’T GET A PHOTOGRAPH THAT I WANT TO WORK FROM.”
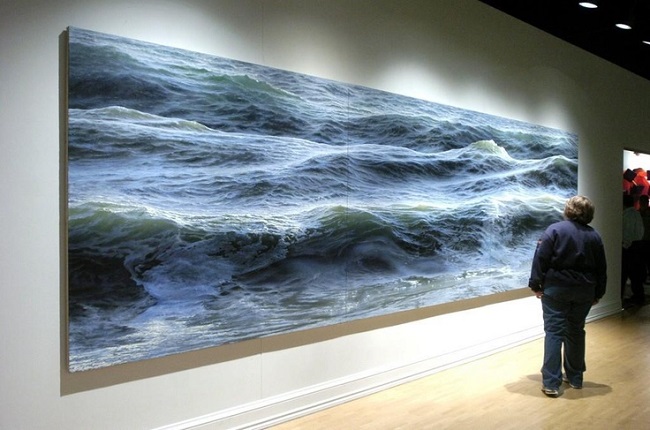

Since the origin of photography in the early-19th-century, artists have used the camera as a tool in picture making; however, artists would never reveal in paint their dependency on photographs as to do so was seen as “cheating”. In contrast, Photorealists acknowledge the modern world’s mass production and proliferation of photographs, and they do not deny their dependence on photographs. In fact, several artists attempt to replicate the effects of photography such as blurriness or multiple-viewpoints, because they favor the aesthetic and look. Therefore, while the resulting image is realistic, it is simultaneously one-stage away from reality by its dependence on the reproduced image. These works question traditional artistic methods, as well as the differences between reality and artificiality. The representation of light, as well as the interaction of light and color together has concerned artists throughout time. By using slide machines to project images onto bare canvas, Photorealism for the first time unites color and light together as one element. Furthermore, Photorealists, along with some practitioners of Pop art, reintroduced the importance of process and deliberate planning over that of improvisation and automatism, into the making of art, draftsmanship, and exacting brushwork.
