- Roland Barthes – was a French literal theorist, philosopher, critic and semiotician. He explored social theory, semiotics, the science of symbols
- C. S. Pierce – was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician and scientist who is sometimes referred to as “the father of pragmatism”.
- C. S. Pierce – was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician and scientist who is sometimes referred to as “the father of pragmatism”.
- Ferdinand de Saussure – was a Swiss linguist and semiotician. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiology in the 20th century.
- Semiotics – the study of signs and symbols and their use and interpretation.
- Sign – an object, gesture or action that is used to convey information or an instruction.
- Signifier – a signs physical form.
- Signified – the meaning or idea expressed by a sign, as distinct from the physical form in which it is expressed.
- an iconic sign – which has a direct connection to its’ object
- an indexical sign – which has an indirect link to its’ object
- a symbolic sign – which has a random or arbitrary link based on a shared knowledge or an agreement
- Code – a system of words, letters, figures or symbols used to represent other things.
- Dominant Signifier – most accepted meaning of a sign. (the main sign/communicator)
- Anchorage – directs the viewer to a chosen meaning.
- Ideology – a system of ideas and ideals, especially one which forms the basis of economic or political theory and policy.
- Paradigm – a group or collection of similar things
- Syntagm – is the relationship is one where signs occur in sequence or parallel and operate together to create meaning. Signs working together
- Signifcation – the representation or conveying of meaning.
- Denotation – What the audience can visually see on a page.
- Connotation – is the second level of analysis, being what the denotation represents
- Myth – in media analysis refers to how words and images are systematically used to communicate cultural and political meanings
- Radical- It challenges our ideas
- Reaction-Supports our ideas
Category Archives: Uncategorized
Filters
Media Definitions
Barthes- An influential French philosopher and literary critic, who explored social theory, anthropology and semiotics, the science of symbols, and studied their impact on society
Pierce- American philosopher, logician, mathematician, and scientist
Saussure- A Swiss linguist and semiotician
Semiotics- The study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation
Sign- Something that signifies something else
Signifier- A sign’s physical form (such as a sound, printed word, or image) as distinct from its meaning (Saussure)
Signified- The meaning or idea expressed by a sign
Icon- Person or thing regarded as a representative symbol
Index- A sign that has a link to its object
Symbol- Thing that represents or stands for something else
Code- A system of words, letters, figures, or symbols used to represent others
Dominant Signifier- Main accepted meaning of sign
Anchorage- Words “pin down” the meaning of an image
Ideology- Set of opinions or beliefs by an individual or group
Syntagm- A set of linguistic forms that are in a relationship to one another
Paradigm– A typical example or pattern of something; a pattern or model
Signification- The representation or conveying of meaning
Denotation- The literal or primary meaning of a word (Barthes)
Connotation- An idea or feeling which a word invokes for a person in addition to its literal or primary meaning
Myth- A widely held but false belief or idea
A Radical test– Text that challenges dominant ideology
A Reactionary test– Text that supports the dominant ideology
Definitions
- Barthes- he was a French literary theorist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician and he studied signs.
- Pierce- he created the idea of signs being iconic, indexical and symbolic. He was an American philosopher, mathematician, and scientist.
- Saussure- he was a Swiss linguist and semiotician. He theorized in language and the connections between their meanings associated with the language.
- Semiotics- the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation.
- Sign- an object, gesture or action that is used to convey information or an instruction.
- Signifier- a sign’s physical form (such as a sound, printed word, or image) as distinct from its meaning.
- Signified- the meaning expressed by a sign.
- Icon- a person or thing regarded as a representative symbol
- Index- a sign or measure of something
- Symbol- a sign that represents or is associated with something
- Code- a system of words or figures or symbols that is used to represent something
- Dominant Signifier- dominant meaning of a sign.
- Anchorage- some signs hold down and fix meaning.
- Ideology- set of ideas or beliefs that people have regarding different. kinds of technologies.
- Paradigm- a typical example of something.
- Syntagm- when a sign appears in a sequence, that creates a different meaning.
- Signifcation- making meaning.
- Denotation- the object.
- Connotation- an idea or feeling or meaning of the object.
- Myth- a story that has been made up that isn’t 100% true.
- A radical text- a text that challenges a dominant ideology .
- A reactionary text. – a text that supports dominant ideology.
Definitions
- Roland Barthes – was a French literal theorist, philosopher, critic and semiotician.
- C. S. Pierce – was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician and scientist who is sometimes referred to as “the father of pragmatism”.
- Ferdinand de Saussure – was a Swiss linguist and semiotician. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiology in the 20th century.
- Semiotics – the study of signs and symbols and their use and interpretation.
- Sign – an object, gesture or action that is used to convey information or an instruction.
- Signifier – a signs physical form. (saussure)
- Signified – the meaning or idea expressed by a sign, as distinct from the physical form in which it is expressed. (saussure)
- an iconic sign – which has a direct connection to its’ object
- an indexical sign – which has an indirect link to its’ object
- a symbolic sign – which has a random or arbitrary link based on a shared knowledge or an agreement
- Code – a system of words, letters, figures or symbols used to represent other things.
- Dominant Signifier – most accepted meaning of a sign.
- Anchorage – directs the viewer to a chosen meaning.
- Ideology – a system of ideas and ideals, especially one which forms the basis of economic or political theory and policy.
- Paradigm – a group or collection of simialr things
- Syntagm – is the relationship is one where signs occur in sequence or parallel and operate together to create meaning.
- Signifcation – the representation or conveying of meaning.
- Denotation – What the audience can visually see on a page. (barthes)
- Connotation – is the second level of analysis, being what the denotation represents. (barthes)
- Myth – in media analysis refers to how words and images are systematically used to communicate cultural and political meanings.
- Radical – Challenges our ideas and society.
- Reactionary – Supports our ideas.
Media forms
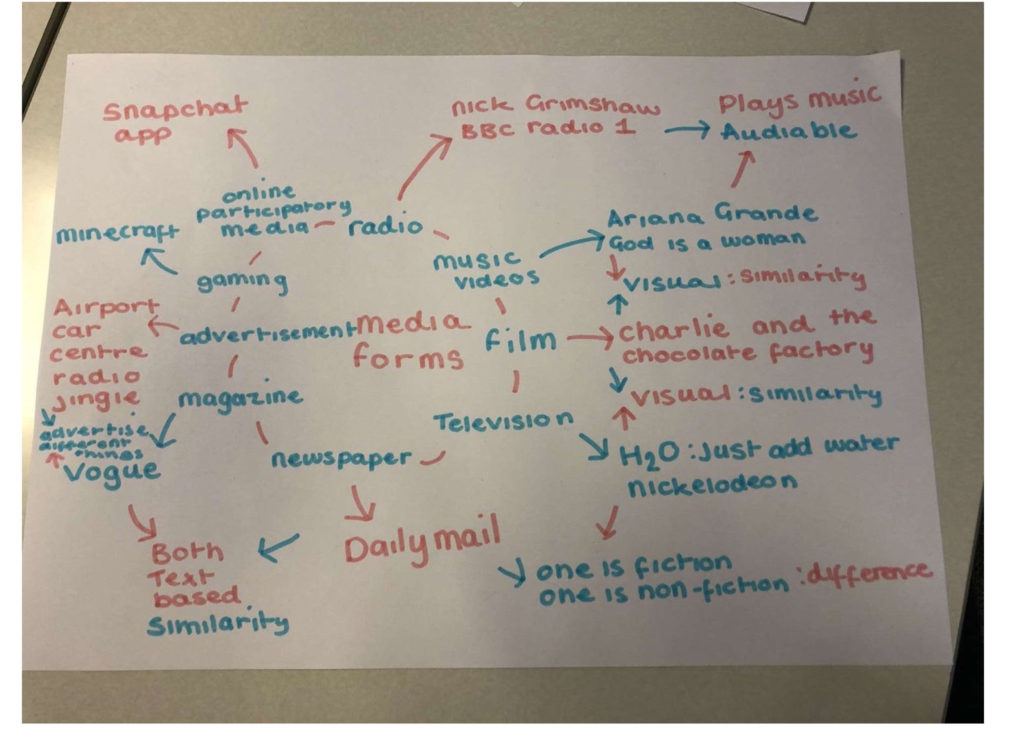
Summer task
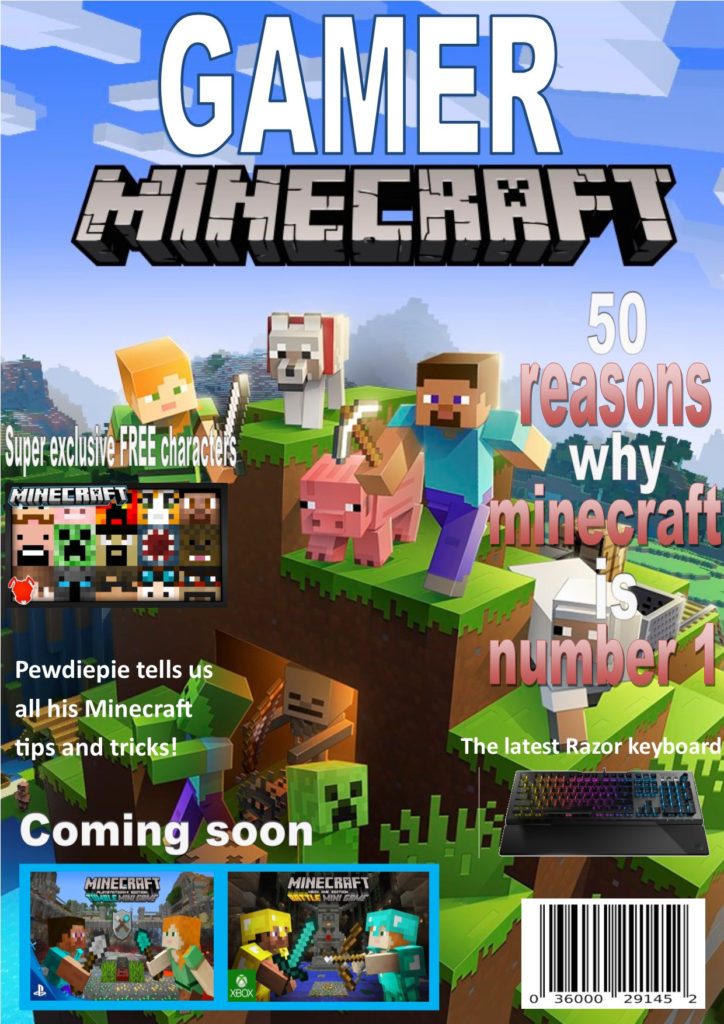
For my gaming magazine I have decided to use a currently popular game for the main image because it is relevant and will interest lots if people since a lot of people are currently playing that game therefore they will be interested to find out what the magazine is about and they will be more likely to buy it.
I then decided to make a really big and bold colorful title to catch the attention of the gamers, the big bright title will catch their eye and if the title is interesting then the buyers are more likely to notice this specific magazine and that makes them more prone to reading the title and becoming more interested in actually purchasing the magazine. I also decided to use complementary colours because that makes the writing and the writing stand out even more.
I also decided to use words like ‘you’ and ‘we’ to make the reader feel like this specific magazine was directed towards them and make them feel included in what this magazine is talking about and like they belong which I believe will make them want to buy the magazine more.
I then added a few different smaller images of different games around to add more of a variety because the reader may not be specifically interested in the main game I have put on the front; however they may be interested in one of the other games and this broadens the variety of readers and creates a bigger possibility of a reader finding something they are interested in and in general increases potential number of magazines sold.
I also made sure that the secondary pictures were in different sizes as I have made the currently more relevant games larger and the less relevant games smaller. I decided to do this because the larger the image the higher the potential of someone noticing it and if the game is more popular then theres a higher chance of the reader being interested.
I have also put words like ‘free’ and ‘super exclusive’ because these words catch the readers eye and help sell the product because it makes them believe that they are gaining something more from buying this magazine and everyone loves free gifts and this may make their parents more likely to buy it because they’re getting a lot from this magazine. Also the word ‘exclusive’ makes them feel special and like they’re being let in on a very important and unknown new piece of information.
I have added a few smaller subtitles with a few intriguing headings so that once the reader does hopefully pick up the magazine they have other things that they can look at and hopefully become interested in enough to actually buy the magazine. Also these subheadings give sneak peeks of whats in the magazine so they can determine wether they want to buy it.
I also put some advertisement on the magazine because if they buy the magazine and they see this they will know what to expect in future magazines and make them want to buy more and get excited for new things coming out.
- Iconic signs– looks like its object (e.g : camera work, sets and props)
- sonic is the actual character
- the yellow character
- Indexical– a sign that links to its object (e.g : sounds, props)
- ‘Boom’ is onomatopoeia and sounds like explosion
- ‘new’ sticker
- Symbolic– a sign that has a random link to its object (e.g : numbers, letters and colors)
- the writing
- the letters
- the colors
- the ‘£’
- green eyes show he’s a good person
- gold ring shapes= money
Definitions
Roland Barthes – was a French literal theorist, philosopher, critic and semiotician.
C.S Pierce – was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician and scientist who is sometimes referred to as “the father of pragmatism”.
Ferdinand de Saussure – was a Swiss linguist and semiotician. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiology in the 20th century.
Semiotics – the study of signs and symbols and their use and interpretation.
Sign – an object, gesture or action that is used to convey information or an instruction.
Signifier – a signs physical form. (Saussure)
Signified – the meaning expressed by a sign.
Iconic signs – a sign that is directly connected to something.
Indexical signs – something that is indirectly connected to a sign .
symbol – a symbol has no resemblance between the signifier and the signified.
Code – a system of words, letters, figures or symbols used to represent other things.
Dominant Signifier – most accepted meaning of a sign. The main sign.
Anchorage – directs the viewer to a chosen meaning.
Ideology – set of ideas or beliefs.
Paradigm – a typical example or pattern of similar signs.
Syntagm – when signs occur in a series and operate together to create a meaning.
Signification – a representation or conveying a message.
Denotation – the literal meaning of a word. (Barthes)
Connotation – the abstract meaning of a term.
Myth – a false belief or idea.
Radical text – Something that challenges society and ideology.
Reactionary text – Something that supports ideas.
Header

Definitions
- Roland Barthes – he was a French literary theorist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician and the study of sign
- C. S. Pierce – created the idea of signs being iconic, indexical and symbolic. He was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician, and scientist who is sometimes known as “the father of pragmatism”
- Ferdinand de Saussure – he was a Swiss linguist and semiotician. He theorised in language and the connections between their meanings associated with the language
- Semiotics – the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation
- Sign – an object, gesture or action that is used to convey information or an instruction
- Signifier – A signs physical form (Saussure)
- Signified – The meaning expressed by a sign
- an iconic sign – A person or thing represented as a symbol for a deeper meaning
- an indexical sign – A sign of something
- a symbolic sign – Is a sign that is represents/ is associated with something
- Code – a system of words/ figures or symbols that is used to represent others
- Dominant Signifier – main accepted meaning of a sign
- Anchorage – directs the viewer to a chosen meaning.
- Ideology – a set of ideas or beliefs that people have regarding different kinds of technologies
- Paradigm – a grouped/typical example of something similar
- Syntagm – when a sign appears in a sequence, that creates a different meaning
- Signification – A representation or conveying of a message, a sequence to create meaning
- Denotation – The literal meaning of words in contrast to what the word suggests (Barthes)
- Connotation – an idea or feeling that is abstract to the meaning of intentions
- Myth – A false belief or idea
- Radical text – A text that goes against the dominant ideology.
- A Reactionary text – A text that conforms to the dominant ideology.
Definitions
Roland Barthes (his ideas of dominant signs / dominant ideology)
was a French literary theorist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician.
C. S. Pierce (and his categories of sign)
Peirce was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician, and scientist who is sometimes known as “the father of pragmatism”.
Ferdinand de Saussure (the separation of object and meaning)
was a Swiss linguist and semiotician
Semiotics: the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation.
Sign: an object, gesture or action that is used to convey information or an instruction
Signifier: A signs physical form
Signified: The meaning expressed by a sign
an iconic sign: signs where the signifier resembles the signified
an indexical sign: signs where the signifier is caused by the signified
a symbolic sign: signs where the relation between signifier and signified is purely conventional and culturally specific
Code:
a system of words, letters, figures, or symbols used to represent others, especially for the purposes of secrecy.
Dominant Signifier: most important sign in a product
Anchorage: signs that fix meanings
Ideology:
is a world view, a system of values, attitudes and beliefs which an individual, group or society holds to be true or important
Paradigm:a grouped/typical example of something similar
Syntagm:
when a sign appears in a sequence, that creates a different meaning
Signifcation:
A representation or conveying of a message, a sequence to create meaning
Denotation:
The literal meaning of words in contrast to what the word suggests (Barthes)
Connotation:
an idea or feeling that is abstract to the meaning of intentions
Myth:
A false belief or idea
Dominant ideology: a dominant attitude values or beliefs in society
Radical: Challenges the dominant ideology
Reactionary: Meaning of something
